Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PMT 30104
Uploaded by
Yousef Adel HassanenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PMT 30104
Uploaded by
Yousef Adel HassanenCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Encyclopedia
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Controlling Project Costs
Note: The source of the technical material in this volume is the Professional
Engineering Development Program (PEDP) of Engineering Services.
Warning: The material contained in this document was developed for Saudi
Aramco and is intended for the exclusive use of Saudi Aramco’s employees.
Any material contained in this document which is not already in the public
domain may not be copied, reproduced, sold, given, or disclosed to third
parties, or otherwise used in whole, or in part, without the written permission
of the Vice President, Engineering Services, Saudi Aramco.
Chapter : Project Management For additional information on this subject, contact
File Reference: PMT30104 Rod Kuan on 873-9701
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
Content Page
VARIOUS ESTIMATES PREPARED DURING THE PROJECT LIFE CYCLE................. 1
Budget/Conceptual Estimates.................................................................................... 1
Expenditure Request (ER) Estimates......................................................................... 1
Steps in Development of ER Estimate ........................................................... 2
ER Estimate Minimum Criteria...................................................................... 2
ER Estimate Package..................................................................................... 3
ER Estimate Accuracy ................................................................................... 4
Company Estimates................................................................................................... 4
Types of Project Funds.............................................................................................. 5
Type Code 68 Funds...................................................................................... 5
Prior Approval Expenditure Request Funds ................................................... 5
Type Code 60 Funds...................................................................................... 6
Type Code 67 Funds...................................................................................... 6
Estimating Guidelines ............................................................................................... 6
CONTROL PROJECT COSTS USING THE ER ESTIMATE AND ER SUPPORT
DOCUMENTATION AS CONTROL TOOLS..................................................................... 7
Preparation of Expenditure Request Estimate ............................................................ 7
Role of Project Support and Controls Department ..................................................... 9
DIVIDE THE EXPENDITURE REQUEST INTO JOB ORDERS AND
AUTHORIZATION FOR EXPENDITURE TO FACILITATE CONTROL ........................10
Job Orders................................................................................................................10
Authorization For Expenditure (AFE) ......................................................................11
Cash Flow and Expenditures versus Commitments .......................................12
FORECAST AGAINST THE PROJECT COST BASELINE ..............................................13
Saudi Aramco Project Forecast ................................................................................13
Parts of the Project Forecast .....................................................................................13
Simplified Method of Calculating Forecasted Cost .......................................14
GLOSSARY........................................................................................................................15
ADDENDUM......................................................................................................................16
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
VARIOUS ESTIMATES PREPARED DURING THE PROJECT LIFE CYCLE
Capital budgeting is an integral part of the overall Saudi Aramco Financial Planning process. All
projects must go through a financial justification and approval process before the required
funding is authorized. The purpose of the justification and approval process is to ensure that
Saudi Aramco's capital investments result in the most cost-efficient use of the Kingdom’s
resources.
To qualify for project funds, the cost of each project must be estimated. During the life cycle of
a project, various levels of estimates are developed based on available project information. The
accuracy of the estimate will vary depending upon the project definition at that time and the
quality of project information. This section discusses the various estimates that are developed
for a Saudi Aramco capital project during its project life cycle.
Budget/Conceptual Estimates
Budget/conceptual estimates, which are produced in the earliest stages of project development,
are normally based only on the facility type, capacity, and probable site location. Consequently,
their accuracy may be as low as +/-40% of the actual total project cost.
Budget/conceptual estimates are produced as a basis for preliminary feasibility, process
selection, site location, and layout studies. They may be prepared by the Project Support and
Controls Department (PS&CD) estimating functions or by contractors that operate under the
direction of a SAPMT.
The estimates are used to develop the budget briefs, summary statements of purpose, and the
financial considerations that are involved. Historical data from previously constructed similar
facilities in Saudi Arabia, updated to represent probable costs at the planned construction date,
are the ideal information source for these estimates.
Expenditure Request (ER) Estimates
An Expenditure Request (ER) estimate is a definitive estimate that is prepared in support of a
request for Budget Item (BI) funding and it is used as the basis of project cost control baseline.
The Project Manager has overall responsibility for the estimate. The SAPMT may utilize the
services of a contractor to develop parts of the estimate. In such cases, the contractor works
under the direction of the SAPMT with the assistance of the appropriate Project Support and
Control Department (PS&CD) Estimating Unit.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 1
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
Steps in Development of ER Estimate
PS&CD has primary responsibility to ensure that the ER estimate satisfies all standards of format
and quality. PS&CD/ESD presents the ER preparation requirements and other basic information
to the contractor at a "kick off" meeting early in the estimate preparation phase. At the kick off
meeting, an ER preparation guideline package is presented and discussed with the Saudi Aramco
Project Management Team (SAPMT) and the Project Proposal Contractor's cost control and
estimating personnel. At least one week prior to the kick off meeting, copies of the ER
Preparation Guideline Package are distributed to the participants of the kick off meeting.
ER estimate progress milestones are established during the kickoff meeting and progress is
monitored to judge PS&CD's participation, timing and special-support requirements. A team of
PS&CD estimators conducts at least one detailed analysis and progress review before the final
review and endorsement of the ER estimate.
After the kick off meeting, a supplement package is developed by the PS&CD for the SAPMT
and the Project Proposal Contractor. The supplement package documents customized
adjustments and project-specific information to accommodate any special strengths or
weaknesses in the relations between PS&CD, SAPMT, and the contractor. The intent is to
document and communicate all Saudi Aramco requirements to the Project Proposal Contractor
and to open a constructive dialogue early enough to take advantage of any contractor special
expertise, state-of-the-art methods and procedures, or adjust to a specific contractor weakness.
The Project Proposal Contractor may use an in-house proprietary computer application program
or any commercial software package to prepare the estimate. During the PS&CD review,
PS&CD can confidentially recalculate the estimate with Saudi Aramco labor and equipment
rates. It is also important that the Project Proposal Contractor develop the estimate in Saudi
Aramco format and generate all the details that are required to prepare Form 56D. The
preparation of Form 56D should be done by the SAPMT with the assistance of PS&CD
estimators. PS&CD's role under different Project Management strategies is explained in the
following table:
ER Estimate Minimum Criteria
Project Execution Plan - An approved Project Execution Plan (PEP) for projects in excess of
$25 million.
Project Proposal - The ER estimate is based on an approved Project Proposal.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 2
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
ER Estimate Package
The ER estimate package must contain the following components:
• Project proposal document and approved minutes of the project proposal
meeting and technical review meeting
• Expenditure Request Form 56D
• Basis of estimate
• Detailed estimates
• Contractor's supplement
Expenditure Request Form, Saudi Aramco Form 56D reflects the total project cost as
determined through development of the ER estimate. After completion of the estimate, Form
56D is prepared by the SAPMT. There is one Form 56D for each job order phase listing; and one
Form 56D for each BI. It should be noted that the method and structure of control is SAPMT’s
responsibility. SAPMT’s method and structure has a significant influence on the approach to
the detailed estimating; therefore, they should be established early in the Project Proposal Phase.
Basis of estimate is intended as a management review tool and defines the various assumptions
that are made during the development of the ER estimate. The basis of estimate is the
responsibility of the concerned Estimating Unit in PS&CD, which works with the SAPMT. The
basis of estimate includes but is not limited to:
• Allowances for assumptions due to incomplete design detail material quotes, or
uncertain construction conditions
• Cost trends (escalation)
• Labor productivity adjustment factors
• Currencies and exchange rate
• Exceptions to ER Preparation Guidelines, including justification
• Explanation of major variations from previous estimates
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 3
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
Contractor's Supplement is prepared by the engineering contractor. Generally, it consists of
the costs that are associated with bulk material takeoffs, engineered equipment costs, labor
estimates by craft for construction, and contractor man-hours for detailed design.
Normally, PS&CD and PMT hold a kick off meeting with the contractor's office. At the kick off
meeting, the ER Preparation Guideline package is presented to the contractor's project control
and estimating personnel. Prior to the kick off meeting, copies of the ER Estimate Preparation
Guidelines should be distributed to key SAPMT and Contractor personnel so that they may
familiarize themselves with the contents prior to the meeting. PS&CD estimators normally
execute at least one separate progress check visit to the contractor's office.
ER Estimate Accuracy
If all the above points have been satisfied and the estimate has been prepared in accordance with
these guidelines, there is a good probability that the project can be completed within ±10% of the
ER total cost estimate.
Company Estimates
Company estimates are used by Saudi Aramco to test the reasonableness of bidders' proposals
for contracts, amendments and change orders, i.e., "contract actions". Company estimates reflect
the price for which a given contract action would be awarded under competitive conditions in the
current market environment.
All proposed contract actions that have a financial impact, whether competitively bid or
negotiated, require a company estimate unless they fall under one of the exceptions listed in
Procedure 9 of the Contracting Manual. All company estimates are confidential and the
information that is contained within them is provided only on a need-to-know basis to SAPMT's
Program Management Contractor's Personnel.
The contract proponent department (e.g., SAPMT for major projects) prepares the company
estimate if the price of such contract action is expected to be SR300,000 or less. The contract
proponent keeps the estimator adequately informed regarding the scope of work and maintains
confidentiality.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 4
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
For all contract actions where Engineering & Project Management (E&PM) is the contract
proponent and the price is expected to exceed SR300,000, E&PM may direct the Project
Management Contractor (PMC) to:
• Prepare the Company estimate for verification by the PS&CD Estimating
• Request that PS&CD Estimating prepare the Company estimate
The estimator uses the best available pricing information including the most up-to-date Saudi
Aramco cost data and information from any reliable source outside Saudi Aramco that is also
available to bidders. The bidding patterns and economic circumstances of all contractors are also
considered.
Types of Project Funds
As stated earlier, the project uses various estimates to accomplish different purposes at different
phases of the project life cycle. The project also uses various types of project fundings during
the project life cycle.
Type Code 68 Funds
Type Code 68 (T/C 68) funds are used by the project during the Preliminary Engineering Phase.
T/C 68 funds are used to fund those activities that occur during the Preliminary Engineering
phase. T/C 68 funds are requested as soon as the PMT receives the approved DBSP from FPD.
The funds may be used for work until the ER is approved. Typically, this work includes the
preliminary engineering contractor costs and the PMT costs. No materials are allowed to be
purchased for the project. At that time, the T/C 68 expenditures are incorporated into the ER
funds and the T/C 68 funding is closed.
Prior Approval Expenditure Request Funds
Prior Approval Expenditure Request (PAER) funds are sometimes requested when there are
long-lead materials that must be purchased prior to the ER funding. PAER funds are the same as
T/C 68 funds except that materials that affect the ERC may be purchased prior to ERA. PAER
funding may be approved for projects that have an accelerated schedule. The purpose of PAER
funding is to:
• Purchase critical long-lead material items
• Commence definitive engineering/design
• Begin construction
Such prior approval does not constitute a commitment to full funding approval. T/C 68 funds are
transferred to T/C 60 on prior or full funding approval.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 5
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
Type Code 60 Funds
Type code 60 (T/C 60) funds are used by the project during the Detailed Engineering ,
Procurement and Construction phases. In other words, these funds cover the project from ERA
to ERC.
Type Code 67 Funds
It may be advantageous to close an ER before the punch list items are completed. In order to
take this action, Saudi Aramco has established Type Code 67 (T/C 67) funds. These funds are
also called Special Project Account (SP) funds. Like other funds they cover a specific scope of
work. SP funds are requested by the project when the punch list items are considered to require
and extra ordinary long time to complete. SP funds help the Project Engineer limit the remaining
work to the current punch list items.
Expense items may also be completed by the SAPMT. Work that is not classified as capital will
be classified as expense. The details of work that is classified as expense can be obtained from
Fixed Assets and Work in Progress Accounting.
Estimating Guidelines
All requests for budget/conceptual estimates, including requests for re-estimates after schedule or
scope changes, are processed through the Project Support and Control Department (PS&CD).
Saudi Aramco Form 5759, Request for Estimating Services, is prepared and included with the
DBSP. In varying degrees, the development of the DBSP and budget/conceptual estimate
involves the proponent, the Facilities Planning Department (FPD), PS&CD, and SAPMT.
All estimates that precede the ER estimates are considered budgetary estimates. Budgetary
estimates are prepared by the PS&CD based on the DBSP. Their accuracy range is assumed to
be ± 20 to ± 40% of final cost but they are still considered acceptable for their purpose. The
degree of accuracy depends on the extent of project definition and other available information.
They are used to develop the budget briefs, summary statements of purpose of projects and the
financial considerations that are involved.
An ER estimate is a definitive estimate based on an approved Project Proposal. The accuracy of
an ER estimate is expected to be +/-10% of the final project cost.
NOTE: To support expenditure forecasting/estimating, Saudi Aramco maintains historical data
and develops cost models and graphical formats of spending patterns. This data can be obtained
by contacting the PS&CD Estimating Methods & Procedures Unit (EM&PU).
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 6
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
CONTROL PROJECT COSTS USING THE ER ESTIMATE AND ER SUPPORT
DOCUMENTATION AS CONTROL TOOLS
Preparation of Expenditure Request Estimate
An Expenditure Request (ER) estimate, which is prepared on Saudi Aramco Form 56D, is a
definitive estimate that supports a request for the approval of funds for a specific Budget Item
(BI). The control budget for each Job Order (JO) in a BI is based on an ER estimate detail (see
Addendum 4). When an ER amount is approved by the Board of Directors, funds are officially
allocated for expenditure. Funds can be released only through an Authorization for Expenditure
(AFE). The AFE provides authorization for a Saudi Aramco Project Management Team
(SAPMT) to incur expenditures and to make commitments for the detailed engineering, material
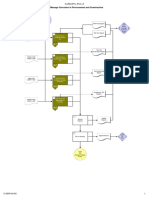
procurement, and construction contracts. The ER development process is shown on the
flowchart in Addendum 1.
The ER estimate is normally prepared after the Project Proposal is approved but, if required by
the schedule, it may be prepared simultaneously. For a Prior Approval Expenditure Request
(PAER), the ER estimate is normally prepared concurrently with the Project Proposal. In all
cases, the minimum criteria must be met to support the required accuracy of ± 10%.
Along with Saudi Aramco Form 56D, SAPMT submits an ER expenditure forecast in BI
summary format to the Project Support and Control Department (PS&CD). Each ER estimate,
along with the expenditure forecast, is reviewed and agreed to by the Project Manager and the
General Supervisor of Estimating Services Division or the Manager of PS&CD. Afterwards, the
ER estimate is transmitted to the Budget Director and presented to the Board of Directors for
approval. The Project Manager that endorses the Form 56D has the overall responsibility for that
ER estimate.
The Project Engineer plays an important role in the development of an ER estimate. He is the
principal coordinator in the ER development and approval process. The Project Engineer
ensures that the ER estimate is developed according to the ER development guidelines and the
specific project requirements. The Project Engineer works closely with the PS&CD and/or the
contractor in the development of the ER estimate.
At the time the ER cost estimate is prepared, the Project Engineer should assure that the ER is
broken into parts that can be controlled all the way through the project, i.e., until commissioning
completion.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 7
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
In order to determine which definition of parts will be most controllable, the Project Engineer
must be able to visualize the project through each of its life cycle phases. In order to implement
and enforce the best control, the Project Engineer determines the best way to divide the ER into
parts based on the following factors:
• Geographical locations
• Plot limits
• Process distinctions
• Capital size of parts
• Technical distinctions
• Split of responsibilities between different Saudi Aramco departments
If the project is composed of work in various countries, it is important for the manager in each
location to be responsible for his respective part and to know his responsible costs. It may be
appropriate for different process units to be the responsibility of different managers or engineers;
therefore, the costs should be split accordingly. When the project crosses various technical skill
groups such as communications, process, and inspection, each group should be able to control
their respective parts.
In subsequent phases of the project life cycle, the elements of control become increasingly
complex. At the time that the project is in the Preliminary Engineering phase, the only concern
of the Project Engineer is preparation of the Project Proposal and ER estimate. The funding
restriction, although it is tightly controlled, is not under the same constraints as the ER approval.
After the ER is approved, the Project Engineer has other elements to control (i.e., detailed
engineering, procurement and construction). The materials procurement process is an important
part of the cost control process. Depending on the type of project, materials generally represent
from 35% to 65% of the total ER value. Thus, material cost control is absolutely essential to
keep the ER within the 10% limits that are required for ER approval. When the ER is approved,
the pricing for the major equipment items that must be engineered should have been verified by
quotes from the vendors. If this verification has occurred, the uncertainty within the materials
part of the ER estimate/budget can be reduced. The uncertainty in meeting the ER estimate is
also reduced as more materials are verified by actual prices from vendors or as bulk materials are
verified when definitive material take-offs are prepared from the detailed drawings. Of course,
this process continues until the uncertainty (and the contingency in the ER) is reduced to the
point where the Project Engineer is confident that he will complete within the ER estimate.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 8
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
When the design contractor prepares the construction part of the ER estimate, he can improve the
estimate by preparing defined quantities for the work that is required in construction. These
quantities, or units, can be priced by the contractor or Saudi Aramco to define the construction
costs. The cost of construction will not become more firm until the construction bids are
received and compared to the ER estimate. The more definition in detailed design at the time of
bidding the construction contract, the better the confidence of the Project Engineer that the ER
funds will cover the construction.
The Project Engineer may be responsible for a refinery project today and a chemical plant
project tomorrow. He may not be experienced in all areas that he may be asked to manage. The
design contractor, who is contracted to do the detailed design, must have specific knowledge of
the type of project. The contractor may have recently designed the same type of plant for
another client and this expertise should be utilized by the Project Engineer. If the Project
Engineer has implemented a good partnering relationship with the contractor, his ability to
maximize the contractor’s expertise should be easy.
Role of Project Support and Controls Department
The PS&CD can help the Project Engineer with areas of concern about the cost estimating and
control processes. The Project Engineer should consider the PS&CD as one of his resources of
expertise that is available to help complete the project.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 9
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
DIVIDE THE EXPENDITURE REQUEST INTO JOB ORDERS AND
AUTHORIZATION FOR EXPENDITURE TO FACILITATE CONTROL
As stated in the last section, the Expenditure Request (ER) is divided into distinct parts to
facilitate control. The ER cost is defined on the Form 56D. The Form 56D, or ER estimate, is
broken into parts called Job Orders (JOs). Each JO is further broken into Authorizations for
Expenditure (AFEs).
Job Orders
Form 56D (Addendum 2) is a part of the ER approval package that is assembled by the Budget
Director of the Facilities Planning Department (FPD). Each JO in a BI is estimated separately
and summarized on Form 56D with phase-level detail. Afterwards, a Summary Form 56D is
prepared to show all of the JO subtotals and the total ER estimate amount. The number of JOs is
dependent on the established project execution method and structure of cost control. The
number of JOs is decided by the SAPMT in consultation with PS&CD.
A typical ER estimate reflects the basic Saudi Aramco cost structure, with three major cost
elements:
• Engineering
• Material
• Construction
The contingency amounts are added to the cost-category subtotals. The amounts shown for cost
trends are not additive. As noted on the form, those amounts, if any, will have already been
included and are for information only.
Contingency, which is included in the ER estimate for unforeseeable costs, would normally be
10% or less. Contingency covers the following:
• Productivity variances
• Unknown conditions
• Change orders
• Changes to assumed rates for items such as air freight, catering, and
accommodation and prorates
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 10
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
Contingency is not intended to cover the following:
• Scope changes
• Natural disasters
• Contractor non-performance
• Claims
The SAPMT completes a cash-flow expenditure forecast by quarters/years in terms of capital
and expense.
An approved ER is the authority to commit and expend the Company's resources for the
purchase or construction of assets that are necessary to meet the Company's stated goals and
project objectives. While an ER is used primarily for funding capital projects, it is also used as
the authority to fund non-capital projects that serve the Company's interest. Examples of non-
capital BIs are Saudi-Aramco-built government schools, home ownership, community
development and major roads. Project Management budgets and accounts for capital and non-
capital expenditures.
Authorization For Expenditure (AFE)
An Authorization For Expenditure (AFE), Addendum 3, authorizes the SAPMT to expend funds.
An approved ERA authorizes the SAPMT to commit funds, but an AFE is required to authorize
the SAPMT to spend funds. AFEs are required for most BIs including master appropriation BIs.
AFE revisions are required for ER supplements, redefinitions, and partial cancellations. The cost
engineer prepares an AFE. AFEs are organized by JO number. For each JO, the following cost
elements are identified:
• Engineering
• Material
• Construction
• Contingency
AFE preparation must follow specific guidelines as defined in the Cost Manual for:
• AFE Development
• AFE Revisions
• Master Appropriation AFE
• AFE Closing
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 11
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
Cash Flow and Expenditures versus Commitments
The Project Engineer is not directly involved in the actual flow of cash from the company. The
Project Engineer may sign the contractor’s invoice as approved, but the actual process of writing
the check comes from the accounting process. The Project Engineer is, however, in complete
control of the commitment of project funds and this is the point of control that he needs to
understand. When the Project Engineer makes a commitment of project funds, it should be
communicated to the project’s Cost Engineer and debited from the project’s available funds.
The Project Engineer can control the expenditure of project funds by being aware and exercising
control over the payment terms that were agreed to by the vendor or contractor. The control of
expenditures is an extremely important process in most companies. At the time that the
expenditure occurs, the cash flows from the company. Note that there is never a cash flow (or
expenditure) without a commitment. Conversely, there is never a cash flow without a prior
commitment.
The time lag between the commitment and the expenditure varies for each commitment. It is
important for the Project Engineer to define this time lag. In the case of detailed engineering the
commitment may be one month’s notice plus appropriate demobilization. The commitment is
seldom the complete detailed engineering period, although it is often thought to be as a matter of
convenience. Most of the time, the commitment in materials is the full value because the
cancellation charges are generally not a very big discount of the total invoice price. This is
particularly true if the basic materials of fabrication have been procured. It is important for the
company departments that manage cash flow to have accurate cash flow forecasts from the
project management teams.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 12
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
FORECAST AGAINST THE PROJECT COST BASELINE
Saudi Aramco Project Forecast
After ER approval, commitments are made and the accumulation of actual “costs” begins. As
additional costs are committed, prediction of the total project costs becomes increasingly clear.
Obviously, management is not willing or able to wait until the last project cost has been
committed and/or expended to know what the final project costs will be. Management expects
the SAPMT to be able to predict what the final project costs will be at any time after ER
approval. This prediction is called a forecast. At ERA, the forecast will equal the ER value, and
at ERC, the forecast will equal the total installed cost. The predictions between the ERA and
ERC are sometimes hard to make.
Parts of the Project Forecast
It is important for the Cost Engineer and the Project Engineer to fully understand the details of
the ER baseline because this baseline will be used to define the actual commitments and to
forecast the remaining costs. At the time that the project is complete, the accountant can show:
every cost for the project in detail; each invoice; and the line item accounting that was charged
against the project. The Project Engineer has to break the JOs into pieces so that he can forecast
with similar detail. The Project Engineer will not have to define each predicted invoice, but the
larger invoices will be important to predict. The control process is divided into the three
categories of the ER:
• Engineering
• Materials
• Construction
In preparing the project forecast, the Project Engineer first takes the actual costs for the work that
is completed to date and then forecasts the costs for the work yet to be completed. The sum of
these two parts is the total project cost. When the project cost is totaled, it can be compared
against the ER value, or baseline, to evaluate the project. Individual differences can then be
identified and explained.
The Saudi Aramco report that helps to define the costs-to-date is the AFAG 60. This report
identifies all project charges up to the accounting cutoff date. The Project Engineer and the Cost
Engineer should assure themselves that the charges are accurate and that they belong to the
project.
The Project Engineer uses the project experience to-date, his own knowledge, and the knowledge
of the other SAPMT members and contractors to forecast the costs to complete the project
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 13
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
Simplified Method of Calculating Forecasted Cost
The SAPMT places special emphasis on cost forecasting based on the performance to-date. Cost
forecasting is not only based on manpower loading, but on other factors such as productivity.
For example:
Project Plan:
Budgeted Man-hours = 200,000
Budgeted Hourly Rate = $20 per hour
Budgeted Cost = Budgeted Man-hours X Budgeted Hourly Rate
= 200,000 X $20
= $4,000,000
Project Status:
Actual % Complete = 40%
Actual Man-hours = 100,000
Earned Man-hours = Budgeted Man-hours X Actual % Complete
= 200,000 X 40 %
= 80,000 Man-hours
Actual Productivity To-date = Earned Man-hours/Actual Man-hours
= 80,000/100,000
= 80%
Total Forecast Man-hours = Budgeted Man-hours/Actual Productivity To-date
= 200,000/80%
= 250,000 Man-hours
Total Forecast Cost = Total Forecast Man-hours X Budgeted Hourly Rate
= 250,000 X $20
= $5,000,000
Conclusion: If the reasons for lower than expected productivity are not resolved, then the project
will experience a cost overrun of $1,000,000 from the budgeted cost of $4,000,000.
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 14
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
GLOSSARY
AFE Authorization for Expenditure
BI Budget Item
DES Design Engineering Statistics Report
ER Estimate Definitive estimate based on an approved project proposal.
ERA Expenditure Request Approval
ERC Expenditure Request Completion Date
JO Job Order. A specific part of a budget item
LSTK Lump Sum Turn-Key Contract
MPU Monthly Progress Update
PCR Project Change Request
PES Proposal Engineering Statistics Report
PMC Program Management Contractor
PPU Project Proposal Update Report
PS&CD Project Support and Controls Department
SAPMT Saudi Aramco Project Management Team
TC-67 Special Project Account funds to capture project cost after ERC.
WBS Work Breakdown Structure
WER Work Element Release
WRT Work Element Review Team
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 15
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
ADDENDUM
1. Expenditure Request Development Process Flowchart
2. Expenditure Request Form 56D
3. Summary of Job Orders
4. Authorization for Expenditure, Form 6035A
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 16
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
ADDENDUM 1: ER Development Process Flowchart
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 17
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
ADDENDUM 2: Expenditure Request Form 56D
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 18
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
ADDENDUM 3: Summary of Job Orders
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 19
Engineering Encyclopedia Project Management
Controlling Project Costs
ADDENDUM 4: Authorization for Expenditure, form 6035A
Saudi Aramco DeskTop Standards 20
You might also like
- PMT 10301Document23 pagesPMT 10301Yousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Contracting Process GuideDocument17 pagesSaudi Aramco Contracting Process GuideYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PMT 10505Document27 pagesPMT 10505cvg ertdNo ratings yet
- Saep 51Document39 pagesSaep 51Anonymous 4IpmN7OnNo ratings yet
- Controlling Project Schedules with PEPsDocument41 pagesControlling Project Schedules with PEPsYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- SAEP-14 Project ProposalDocument53 pagesSAEP-14 Project ProposalRaad AbwiniNo ratings yet
- Saep 72 PDFDocument11 pagesSaep 72 PDFRami ElloumiNo ratings yet
- Saep 26 PDFDocument31 pagesSaep 26 PDFSalik SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- PMT 30101Document37 pagesPMT 30101Yousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- Saep 14Document48 pagesSaep 14pookkoya thangalNo ratings yet
- Saep 26Document30 pagesSaep 26brecht1980No ratings yet
- Saep 25 PDFDocument84 pagesSaep 25 PDFBIPIN BALANNo ratings yet
- PMT 10507Document21 pagesPMT 10507cvg ertdNo ratings yet
- Saep 17Document31 pagesSaep 17OMER ELFADIL100% (1)
- Saep 26Document14 pagesSaep 26nadeem shaikhNo ratings yet
- Saep 140 PDFDocument28 pagesSaep 140 PDFAdnanAtifNo ratings yet
- Saep 25Document62 pagesSaep 25OMER ELFADILNo ratings yet
- Engineering ProcedureDocument34 pagesEngineering ProcedureAnthony YunNo ratings yet
- Project Controls in A Capital Project EnvironmentDocument30 pagesProject Controls in A Capital Project EnvironmentAbdulaziz IbrahimNo ratings yet
- MOT-04210005-PR-02 - AWP Engineering and ProcurementDocument52 pagesMOT-04210005-PR-02 - AWP Engineering and ProcurementpedroNo ratings yet
- Module Fabricator SOW Rev.0Document32 pagesModule Fabricator SOW Rev.0mohamedyosrymohamed100% (1)
- Petroleum Design Integrity ProcedureDocument9 pagesPetroleum Design Integrity ProcedurekattabommanNo ratings yet
- Saep 331Document82 pagesSaep 331zxbpxndrc6No ratings yet
- Saep 12Document39 pagesSaep 1269badbutchNo ratings yet
- S-000-5520-051 - 0 Project Quality PlanDocument34 pagesS-000-5520-051 - 0 Project Quality PlanMahadevan Mahalingam100% (1)
- Ara 1Document48 pagesAra 1Anonymous 4IpmN7On0% (1)
- PMR02 QMS Planning R01Document4 pagesPMR02 QMS Planning R01uday narayan singhNo ratings yet
- Pertmaster Risk RegisterDocument8 pagesPertmaster Risk RegisterDhanes PratitaNo ratings yet
- MD-451-0000-OM-CO-SPC-00007 Rev 0Document8 pagesMD-451-0000-OM-CO-SPC-00007 Rev 0Ruel BuntogNo ratings yet
- Saep 20 PDFDocument25 pagesSaep 20 PDFbrecht1980100% (1)
- SCH.Q - Contract No.6600044663 (IK)Document81 pagesSCH.Q - Contract No.6600044663 (IK)kamilNo ratings yet
- Sabp A 012Document92 pagesSabp A 012sethu1091No ratings yet
- Quality Policy of The CompanyDocument485 pagesQuality Policy of The Companyzainjotun406No ratings yet
- Integrity Management Review ProcessDocument16 pagesIntegrity Management Review Processpaul.eastwood9991No ratings yet
- Sabp A 033B PDFDocument11 pagesSabp A 033B PDFINSTECH ConsultingNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Epcprojectinterdepency and Work Flow 1pdfDocument103 pagesDokumen - Tips - Epcprojectinterdepency and Work Flow 1pdfAhmed AggourNo ratings yet
- 05-1 - EPC-GE-PTC-3-PR-00181 - Rev D2 Commissioning & Handover Execution PlanDocument55 pages05-1 - EPC-GE-PTC-3-PR-00181 - Rev D2 Commissioning & Handover Execution PlanHaianh PhamNo ratings yet
- Guide 05c - C and P Tactics DevelopmentDocument25 pagesGuide 05c - C and P Tactics Developmentodunze1No ratings yet
- Project Planning & Controls rEV. 2Document38 pagesProject Planning & Controls rEV. 2Vijay KambleNo ratings yet
- OPOIDocument56 pagesOPOIBIPIN BALANNo ratings yet
- Schedule B - Attachment IVDocument41 pagesSchedule B - Attachment IVwangruiNo ratings yet
- Engineering CVP RACI Feb 2013Document1 pageEngineering CVP RACI Feb 2013Taufik SantosoNo ratings yet
- Concept Definition Pre-FEED Oil Gas ConsultantsDocument3 pagesConcept Definition Pre-FEED Oil Gas Consultantsicq4joyNo ratings yet
- Comment - EEP Procurement Manual - Mgmt-Aa - RevisedDocument150 pagesComment - EEP Procurement Manual - Mgmt-Aa - RevisedBelay TadesseNo ratings yet
- Detailed Engineering Evaluation ProcedureDocument100 pagesDetailed Engineering Evaluation ProceduretomnubiNo ratings yet
- Section 8 - Quality Assurance/Quality Control PlanDocument3 pagesSection 8 - Quality Assurance/Quality Control PlanJoemon T JoyNo ratings yet
- FEL DeliverablesDocument12 pagesFEL DeliverablesParvezNo ratings yet
- Active Doc ListDocument360 pagesActive Doc ListLeo NunnikhovenNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management in Offshore Projects Uten Film 4Document40 pagesEngineering Management in Offshore Projects Uten Film 4limresNo ratings yet
- 00 Saip 13Document10 pages00 Saip 13Muhammad azeem AshrafNo ratings yet
- 1-Cover GCC Rev. 0Document27 pages1-Cover GCC Rev. 0Mohammed Mujeeb Ali FathaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Determine BudgetDocument26 pagesChapter 3 Determine BudgettewodrosNo ratings yet
- Guide To Cost PredictabilityDocument26 pagesGuide To Cost Predictabilityal-gazNo ratings yet
- Garun 4 XXX Qu XXX PR 004 00 Design Works Procedure As 20.11.2010Document23 pagesGarun 4 XXX Qu XXX PR 004 00 Design Works Procedure As 20.11.2010Mehmet Alper SahinNo ratings yet
- PT Borneo Mitra Sinergi: Project Close Out PlanDocument4 pagesPT Borneo Mitra Sinergi: Project Close Out PlanaswarNo ratings yet
- Job Description: Project EngineerDocument2 pagesJob Description: Project EngineerRichard GacitúaNo ratings yet
- PMT 20108Document52 pagesPMT 20108Yousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- Overview of EstimatingDocument59 pagesOverview of EstimatingChu le Van100% (3)
- Set-S-3 (Ipc) - 09 06 12Document2 pagesSet-S-3 (Ipc) - 09 06 12Yousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PT SEV - YE III +ûRNEK SORULAR - NG - L - ZCEDocument18 pagesPT SEV - YE III +ûRNEK SORULAR - NG - L - ZCEYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PTINDocument0 pagesPTINSihem BenNo ratings yet
- Set-Cr - Ipc - 07.07.12Document8 pagesSet-Cr - Ipc - 07.07.12Yousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- M/s. Smart Technocrats & Consultancy Services (I) PVT. LTDDocument7 pagesM/s. Smart Technocrats & Consultancy Services (I) PVT. LTDYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PT Sev - Ye Ii Deneme Test - NG - L - ZceDocument10 pagesPT Sev - Ye Ii Deneme Test - NG - L - ZceYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- msr3 5aprDocument3 pagesmsr3 5aprYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PT Theory FromDocument75 pagesPT Theory FromYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PT Theory FromDocument75 pagesPT Theory FromYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant Examination of Non-Porous Materials: 1. StatusDocument24 pagesLiquid Penetrant Examination of Non-Porous Materials: 1. StatusYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PT03 PDFDocument15 pagesPT03 PDFKhaled BouhlelNo ratings yet
- PT04 PDFDocument25 pagesPT04 PDFKhaled BouhlelNo ratings yet
- PT Level II Test PaperDocument7 pagesPT Level II Test PaperYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PT16Document19 pagesPT16Pradeep Kumar BowmarajuNo ratings yet
- PT2 Specific - MasterDocument4 pagesPT2 Specific - MasterYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Applications of Liquid Penetrant Testing: HapterDocument18 pagesElectric Power Applications of Liquid Penetrant Testing: HaptertariqNo ratings yet
- PT2 Specific - EsconDocument3 pagesPT2 Specific - EsconMangalraj MadasamyNo ratings yet
- PT General 2Document4 pagesPT General 2Yousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PT Specfic 2Document2 pagesPT Specfic 2Yousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PT2SDocument4 pagesPT2SYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PT2 Specific-Article 6Document3 pagesPT2 Specific-Article 6Yousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant Testing: Level-II GeneralDocument8 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testing: Level-II GeneralYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- CBIP Examination PTL1 GeneralDocument4 pagesCBIP Examination PTL1 GeneralHeather SullivanNo ratings yet
- PMT 30105Document29 pagesPMT 30105Yousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PMT 30108Document30 pagesPMT 30108Yousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PT Specfic 1Document2 pagesPT Specfic 1Mangalraj MadasamyNo ratings yet
- PMT 30106Document36 pagesPMT 30106Yousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- PMT 30101Document37 pagesPMT 30101Yousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma and SPIDocument8 pagesSix Sigma and SPIniningariati120876No ratings yet
- Management Control - Theories, Issues and PractiesDocument374 pagesManagement Control - Theories, Issues and PractiesThiago Ferreira MarquesNo ratings yet
- DIY IT Strategic Plan Less Than 40 CharactersDocument54 pagesDIY IT Strategic Plan Less Than 40 CharacterseryaryasaNo ratings yet
- 50 Journals Used in FT Research Rank - FTDocument4 pages50 Journals Used in FT Research Rank - FTGeorge Khris DebbarmaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Training and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesImportance of Training and DevelopmentAnnaIzzatNo ratings yet
- Organizational Culture and Job SatisfactionDocument18 pagesOrganizational Culture and Job SatisfactionryarezsaNo ratings yet
- MRO Material Master Data Cleansing Enrichment and ClassificationDocument7 pagesMRO Material Master Data Cleansing Enrichment and ClassificationindraNo ratings yet
- What Is Operations SchedulingDocument8 pagesWhat Is Operations SchedulingBishnu Ram GhimireNo ratings yet
- 02 Project SelectionDocument32 pages02 Project SelectionShamsul AlamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Summary: The Definition of ManagementDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Summary: The Definition of ManagementMahmood Mohammed TahaNo ratings yet
- CPM Network Analysis FinalDocument33 pagesCPM Network Analysis Finalsonali kambleNo ratings yet
- The Wells Fargo Cross-Selling ScandalDocument14 pagesThe Wells Fargo Cross-Selling ScandalStanford GSB Corporate Governance Research InitiativeNo ratings yet
- ISP Guide - Create a Comprehensive Information Security PolicyDocument2 pagesISP Guide - Create a Comprehensive Information Security PolicygydaNo ratings yet
- C T Case Study: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North CarolinaDocument5 pagesC T Case Study: Blue Cross and Blue Shield of North Carolinauser9216No ratings yet
- Literature Review on Strategy and Marketing StrategyDocument8 pagesLiterature Review on Strategy and Marketing StrategyBadhon Khan0% (1)
- Workshop 4 Inventory Management at PhilipsDocument5 pagesWorkshop 4 Inventory Management at PhilipsAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Certified Business Process Professional (CBPP®) Overview of Exam TopicsDocument15 pagesCertified Business Process Professional (CBPP®) Overview of Exam TopicsDuygu ErsolNo ratings yet
- 55787.-Full-Time MBA Brochure 2023Document21 pages55787.-Full-Time MBA Brochure 2023Backup PertamaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Operations Management: By: Raquel GrahamDocument15 pagesFundamentals of Operations Management: By: Raquel GrahamAHMEDNo ratings yet
- HP Deskjet Case Solution1 HP Deskjet Case Solution1Document7 pagesHP Deskjet Case Solution1 HP Deskjet Case Solution1Tun Thu LinNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nixon HodDocument12 pagesDr. Nixon HodreninrkNo ratings yet
- Call Centers: Organization Chart: Chief Operating OfficerDocument25 pagesCall Centers: Organization Chart: Chief Operating OfficerVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Principle of MarketingDocument58 pagesPrinciple of MarketingSamuel ChanNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Ihsan ResumeDocument4 pagesMuhammad Ihsan ResumeRifki ReinaldoNo ratings yet
- Point Method Job Evaluation ExampleDocument4 pagesPoint Method Job Evaluation ExampleAnum Seher100% (1)
- XDBS NotesDocument2 pagesXDBS Notesitsrohitpuri03No ratings yet
- Marketing Off-WhiteDocument12 pagesMarketing Off-Whitemariam bukiaNo ratings yet
- Hero Moto Corp - SWOT Analysis - Brand Guide - MBA Skool-Study - Learn.shareDocument3 pagesHero Moto Corp - SWOT Analysis - Brand Guide - MBA Skool-Study - Learn.shareTina Gupta0% (1)
- 8 - The Conversion Cycle WfaDocument70 pages8 - The Conversion Cycle WfaShandy MojicaNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of Serene AirlineDocument16 pagesSWOT Analysis of Serene AirlineShahid RasheedNo ratings yet
- The PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeFrom EverandThe PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (36)
- PMP Exam Prep: Master the Latest Techniques and Trends with this In-depth Project Management Professional Guide: Study Guide | Real-life PMP Questions and Detailed Explanation | 200+ Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP Exam Prep: Master the Latest Techniques and Trends with this In-depth Project Management Professional Guide: Study Guide | Real-life PMP Questions and Detailed Explanation | 200+ Questions and AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Change Management for Beginners: Understanding Change Processes and Actively Shaping ThemFrom EverandChange Management for Beginners: Understanding Change Processes and Actively Shaping ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Building a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialFrom EverandBuilding a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (238)
- The PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeFrom EverandThe PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Project Management All-in-One For DummiesFrom EverandProject Management All-in-One For DummiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Managing Time (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandManaging Time (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (47)
- Agile Product Management: Product Owner: 27 Tips to Manage Your Product and Work with Scrum TeamsFrom EverandAgile Product Management: Product Owner: 27 Tips to Manage Your Product and Work with Scrum TeamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Summary Guide: Blue Ocean Strategy: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make Competition Irrelevant: By W. Chan Kim & Renee Maurborgne | The Mindset Warrior Summary Guide: (Entrepreneurship, Innovation, Product Development, Value Proposition)From EverandSummary Guide: Blue Ocean Strategy: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make Competition Irrelevant: By W. Chan Kim & Renee Maurborgne | The Mindset Warrior Summary Guide: (Entrepreneurship, Innovation, Product Development, Value Proposition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Business Analysis for Practitioners: A Practice Guide - SECOND Edition: A Practice GuideFrom EverandBusiness Analysis for Practitioners: A Practice Guide - SECOND Edition: A Practice GuideNo ratings yet
- The Third Wave: An Entrepreneur's Vision of the FutureFrom EverandThe Third Wave: An Entrepreneur's Vision of the FutureRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (63)
- Come Up for Air: How Teams Can Leverage Systems and Tools to Stop Drowning in WorkFrom EverandCome Up for Air: How Teams Can Leverage Systems and Tools to Stop Drowning in WorkRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- 300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionFrom Everand300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionNo ratings yet
- Agile: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandAgile: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- High Velocity Innovation: How to Get Your Best Ideas to Market FasterFrom EverandHigh Velocity Innovation: How to Get Your Best Ideas to Market FasterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Project Management, Sixth EditionFrom EverandFundamentals of Project Management, Sixth EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Accidental Agile Project Manager: Zero to Hero in 7 IterationsFrom EverandAccidental Agile Project Manager: Zero to Hero in 7 IterationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Project Management: The Ultimate Guide for Managing Projects, Productivity, Profits of Enterprises, Startups and Planning with Lean, Scrum, Agile.From EverandProject Management: The Ultimate Guide for Managing Projects, Productivity, Profits of Enterprises, Startups and Planning with Lean, Scrum, Agile.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Unwritten Rules of Managing Up: Project Management Techniques from the TrenchesFrom EverandThe Unwritten Rules of Managing Up: Project Management Techniques from the TrenchesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- Agile: The Complete Overview of Agile Principles and PracticesFrom EverandAgile: The Complete Overview of Agile Principles and PracticesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Harvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsFrom EverandHarvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Building a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialFrom EverandBuilding a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (113)
- Prince2 for Beginners - Introduction to Prince2 Project Management ConceptsFrom EverandPrince2 for Beginners - Introduction to Prince2 Project Management ConceptsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideFrom EverandITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Complete Project Manager: Integrating People, Organizational, and Technical SkillsFrom EverandThe Complete Project Manager: Integrating People, Organizational, and Technical SkillsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Kaizen: The Step-by-Step Guide to Success. Adopt a Winning Mindset and Learn Effective Strategies to Productivity Improvement.From EverandKaizen: The Step-by-Step Guide to Success. Adopt a Winning Mindset and Learn Effective Strategies to Productivity Improvement.No ratings yet