Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Igneous Rock
Uploaded by
Venice Edaño0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesOriginal Title
IGNEOUS ROCK
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesIgneous Rock
Uploaded by
Venice EdañoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
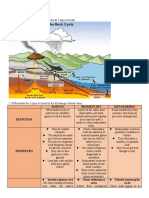
IGNEOUS ROCK - defined as types of rocks that when a gas-rich froth of glassy lava solidifies
are formed when molten rock (rock liquefied by rapidly.
intense heat and pressure) cools to a solid state. It
forms about 15% of the Earth's current land SEDIMENTARY ROCK - are display grains that are
surface. cemented together, often with visible layers, fossils,
or unique features like mud cracks or ripple marks.
A. Intrusive igneous rocks - also
They often appear as layered deposits forming a
called plutonic rocks, this surface is known as strata or bed structures.
a phaneritic texture. They have large crystals
that are usually visible without a microscope. Types of sedimentary rocks:
2 examples of intrusive rocks
Granite also called as plutonic rock, it is a coarse- A. Organic sedimentary rock – type of
grained rock found in plutons, sedimentary rock that contains significant
which are large, deep-seated amounts of organic carbon. this forms from the
bodies of rock that slowly cooled accumulation and lithification of organic debris,
from the molten state.it is made up such as leaves, roots, and other plant or animal
of clearly visible crystals of material.
various minerals. 2 examples of organic sedimentary rock:
Diorite is a grey to dark-grey intermediate Coal An organic sedimentary rock composed
intrusive igneous rock predominantly of carbon that is
composed principally of readily combustible. Coal is
plagioclase feldspar, biotite, formed when dead plant
hornblende, and pyroxene. It is matter decays into peat and is
visibly crystalline and usually converted into coal by the heat
has a granular texture and pressure of deep burial
(composed of roughly equally sized crystals) over millions of years.
although the appearance may vary widely. Fossiliferous limestone
B. Extrusive igneous rock - Extrusive igneous a type of limestone, made
rocks are rocks that erupt onto the surface mostly of calcium carbonate
resulting in small crystals as the cooling takes (CaCO3) in the form of the
place quickly. These are the rocks that form at mineral’s calcite or
erupting volcanoes and oozing fissures. aragonite, that
2 examples of extrusive rocks: contains abundance of fossils
Basalt is an aphanitic or fossil traces. They are usually marine
(fine-grained) extrusive invertebrates such as brachiopods, crinoids,
igneous rock formed from mollusks, gastropods, and coral.
the rapid cooling of low B. Clastic sedimentary rocks - composed of
viscosity lava rich in fragments, or clasts, of pre-
magnesium and iron (mafic existing minerals and rock. Is a fragment
lava). Basalt is one of the main rocks that are of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains
prevalent in the oceanic crust, it is rich in iron of rock broken off other rocks by physical
and serves as an ingredient in concrete. weathering.
Pumice a very light and 2 examples of clastic
porous igneous volcanic sedimentary rocks:
rock that forms during Sandstone is a clastic
explosive volcanic sedimentary rock composed
eruptions. It is formed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625
to 2 mm) silicate grains. It is
composed of sediment materials that are formed foliated metamorphic rocks tend to be simpler than
from other processes such as weathering & erosion foliated rocks.
of other rocks.
Shale is a fine-grained sedimentary rock that forms 2 examples of non-foliated rock:
from the compaction of silt and Marble Is a metamorphic rock composed of
clay-size mineral particles that recrystallized carbonate
we commonly call "mud." It is minerals, most commonly
the most common sedimentary calcite or dolomite. It
rock, which accounts for about forms when limestone is
70 percent of the Earth’s crust. subjected to the heat and
C. Chemical sedimentary rocks - This type of rock pressure of metamorphism.
is created when minerals that are present in
rock forms undergo a chemical reaction that Quartzite
causes them to cool as precipitates over time is a non-foliated
before changing back to rock form. It is formed metamorphic rock composed
by precipitation of minerals from water. almost entirely of quartz. It
2 examples of chemical sedimentary rock: forms when a quartz-rich
Rock salt is a chemical sedimentary rock that sandstone is altered by the
heat, pressure, and chemical
isometric crystals are formed
activity of metamorphism.
from. It forms where large
volumes of sea water or salty
lake water evaporate from
Foliated rocks - are a type of metamorphic rock
an arid-climate basin --
that has a characteristic banded (or striped)
where there is a replenishing
pattern. Foliated rocks are produced by exposure to
flow of salt water and a
heat and directed pressure.
restricted input of other water.
Chert is composed of remains of siliceous ooze, 2 examples of foliated rocks:
the sediment which covers Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous
the major portion of the metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-
deep ocean floor. It type sedimentary rock
commonly occurs in the composed of clay or
form of nodules, layered volcanic ash through low-
deposits and grade regional
concretionary masses. metamorphism. Slate is
formed when a
METAMORPHUC ROCKS -. Metamorphic rocks sedimentary rock (shale,
are formed when rock changes over a period of mudstone, or basalt) is compressed.
time due to a lot of physical changes like pressure,
heat and different chemical activity. It is classified Phyllite is a foliated
as either foliated or non-foliated depending on their metamorphic rock that has
mineral structure and pattern. been subjected to low levels
Types of metamorphic rock: of heat, pressure and
chemical activity. It is
Non-foliated - are formed around igneous composed mainly of flake-
intrusions where the temperatures are high but the shaped mica minerals in
pressures are relatively low and equal in all parallel alignment.
directions. It is composed of minerals that do not
elongate or align during metamorphosis, non-
You might also like
- Introductory Petrography of FossilsDocument313 pagesIntroductory Petrography of FossilsLuisMauricioValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- C568Document2 pagesC568Yaser Al Shabasy100% (2)
- Carbonate Environments and Sequences of Caicos PlatformDocument81 pagesCarbonate Environments and Sequences of Caicos PlatformAlana SéguierNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Classification of Rocks: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesLesson 4: Classification of Rocks: ObjectivesArabella Balasanos MorfeNo ratings yet
- Earthsci Lesson (Rocks&minerals)Document3 pagesEarthsci Lesson (Rocks&minerals)Ara MaglangitNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials and ResourcesDocument5 pagesEarth Materials and Resourceshezekiah minNo ratings yet
- PetrologyDocument5 pagesPetrologyMar PalmaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Lesson 4 RocksDocument66 pagesEarth and Life Lesson 4 RocksMagdalena TagubaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 RocksDocument22 pagesModule 4 RocksAQUINO JAYSON KIERNo ratings yet
- Module 4 (Classification of Rocks)Document2 pagesModule 4 (Classification of Rocks)AkiNo ratings yet
- CE2B - Group 3 - Classification-of-RocksDocument14 pagesCE2B - Group 3 - Classification-of-RocksMarvin CarcidoNo ratings yet
- The Rock Cycle: Formation of Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic RocksDocument7 pagesThe Rock Cycle: Formation of Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic RocksGLENMAR VINEGASNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Classification of RocksDocument4 pagesLesson 4 - Classification of RocksRowela Mariel MorongNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals HandoutDocument6 pagesRocks and Minerals Handoutrosana f.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Rock Classification GuideDocument132 pagesRock Classification GuideDELOS SANTOS GERALDNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle ProjectDocument28 pagesRock Cycle Projectamaeamee ameaimeNo ratings yet
- ROCKSDocument40 pagesROCKSAngelica Mae PartosaNo ratings yet
- Igneous Sedimentary MetamorphicDocument3 pagesIgneous Sedimentary MetamorphicKezel AtangenNo ratings yet
- LESSON-5-ROCKSDocument36 pagesLESSON-5-ROCKSmizpehman12No ratings yet
- Petrology Wps OfficeDocument4 pagesPetrology Wps OfficeDante PazNo ratings yet
- L4 RocksDocument33 pagesL4 RocksFARHA NAAZNo ratings yet
- RocksDocument5 pagesRocksangelic dailyNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Types of Rocks: Activity 1: Classifying Rocks Rock Characteristics Type of Rock Describe How It Is FormedDocument3 pagesEarth Science Types of Rocks: Activity 1: Classifying Rocks Rock Characteristics Type of Rock Describe How It Is FormedRaven CortezaNo ratings yet
- You Rock! Well at Least The Earth Rocks!Document12 pagesYou Rock! Well at Least The Earth Rocks!Lance AmoresNo ratings yet
- Classification of RocksDocument18 pagesClassification of RocksStrng PndNo ratings yet
- 03 Handout Sedimentary RocksDocument4 pages03 Handout Sedimentary RocksEricson CecNo ratings yet
- SSC Petrology: Classification of Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic RocksDocument11 pagesSSC Petrology: Classification of Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic RocksArianne Mae De Vera GallonNo ratings yet
- Understanding Petrology: The Study of RocksDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Petrology: The Study of RocksKangNo ratings yet
- Classification of RocksDocument11 pagesClassification of RocksAkshay EverNo ratings yet
- RocksrockDocument52 pagesRocksrockCheret LengNo ratings yet
- Act 2Document4 pagesAct 2Mark Anthony FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Types of Rocks PDFDocument61 pagesTypes of Rocks PDFziyannn0408No ratings yet
- Rock types and propertiesDocument30 pagesRock types and propertiesrhaine100% (1)
- Minerals and Rocks: Lesson 7Document35 pagesMinerals and Rocks: Lesson 7Cristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Geology M2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesGeology M2 ReviewerDenjay CatalanNo ratings yet
- Classification of RocksDocument33 pagesClassification of RocksBel Esguerra CabillonNo ratings yet
- 2 Minerals and RocksDocument35 pages2 Minerals and RocksJessica May DimeNo ratings yet
- EARTH SCIENCE RocksDocument26 pagesEARTH SCIENCE RocksDAKSINo ratings yet
- Answer To Module 2 (Earth and Life Science)Document9 pagesAnswer To Module 2 (Earth and Life Science)Angel MarieNo ratings yet
- Geo Reports Hand OutDocument1 pageGeo Reports Hand OutDiburah Ponsica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Rocks EditedDocument103 pagesRocks Editedivyshane827No ratings yet
- PETROLOGYDocument24 pagesPETROLOGYsaifalsahab80No ratings yet
- Rock Types: Igneous, Sedimentary, and MetamorphicDocument6 pagesRock Types: Igneous, Sedimentary, and MetamorphicDenjay CatalanNo ratings yet
- Earth and Earth SystemsDocument11 pagesEarth and Earth SystemsKimberly LopezNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Assessment: Kimberly Wealth M. Magnaye Bsce Iv-1Document3 pagesModule 1 - Assessment: Kimberly Wealth M. Magnaye Bsce Iv-1Kimberly Wealth Meonada MagnayeNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - Week 4 Module 4Document2 pagesEarth and Life Science - Week 4 Module 4Aya CatanghalNo ratings yet
- Rocks and minerals guideDocument5 pagesRocks and minerals guideGURU BEN PIANO STUDIO PRODUCTIONNo ratings yet
- 1ST Mid QTR - Earth Sci - RocksDocument3 pages1ST Mid QTR - Earth Sci - RocksjarNo ratings yet
- Activity SheetDocument1 pageActivity SheetJARYL PILLAZARNo ratings yet
- The Rock Cycle: Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rock FormationDocument112 pagesThe Rock Cycle: Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rock Formationallen2912100% (1)
- The Classification of RocksDocument21 pagesThe Classification of RocksEric Sylvan D. SalinasNo ratings yet
- Rock FormationDocument5 pagesRock FormationGerwin SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Rocks (Contd.) : Note 6 Class 9 Sedimentary RocksDocument3 pagesRocks (Contd.) : Note 6 Class 9 Sedimentary RockssubhaseduNo ratings yet
- The Rock CycleDocument2 pagesThe Rock CycleAletta Gregg CataloniaNo ratings yet
- PETROLOGYDocument4 pagesPETROLOGYJeffer BontesNo ratings yet
- RocksDocument14 pagesRocksNovrei YucsonNo ratings yet
- GLY-Chapter 4 PDFDocument15 pagesGLY-Chapter 4 PDFBrendon GovaNo ratings yet
- Minerals and RocksDocument8 pagesMinerals and RocksSensoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Rocks Rocks Are Grouped Into Three Types, Namely Igneous, Metamorphic and SedimentaryDocument13 pagesLecture 2-Rocks Rocks Are Grouped Into Three Types, Namely Igneous, Metamorphic and Sedimentaryeng20072007100% (1)
- Types of RocksDocument5 pagesTypes of RocksADRIEL JAN BRUNONo ratings yet
- Rocks and minerals guideDocument21 pagesRocks and minerals guideRockers ArulNo ratings yet
- Rock Heat Pressure 'Morph': Igneous RocksDocument2 pagesRock Heat Pressure 'Morph': Igneous RocksannilynNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Learning CompetenciesDocument54 pagesDerivatives Learning CompetenciesVenice EdañoNo ratings yet
- Learn How to Calculate Derivatives Using the Delta MethodDocument45 pagesLearn How to Calculate Derivatives Using the Delta MethodVenice EdañoNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument4 pagesBusiness PlanVenice EdañoNo ratings yet
- Pointers For Long Quiz 2ND QuizDocument2 pagesPointers For Long Quiz 2ND QuizVenice EdañoNo ratings yet
- Explain The Rock Cycle in 5 SentencesDocument2 pagesExplain The Rock Cycle in 5 SentencesVenice EdañoNo ratings yet
- Makueni-Paul Ngei Mutwota Hydro-Report - 2Document50 pagesMakueni-Paul Ngei Mutwota Hydro-Report - 2pablo studiosNo ratings yet
- Advanced Concrete Technology - Manu SanthanamDocument1,066 pagesAdvanced Concrete Technology - Manu SanthanamGandhi Sagar100% (2)
- Applied Geology Lab ManualDocument22 pagesApplied Geology Lab ManualkoloshrabeaaNo ratings yet
- Unusual Properties of WaterDocument44 pagesUnusual Properties of WaterHanan ShehaNo ratings yet
- ASTM C1097 Standard Specification For Hydrated Lime For Use in Asphalt Cement or Bituminous Paving MixturesDocument2 pagesASTM C1097 Standard Specification For Hydrated Lime For Use in Asphalt Cement or Bituminous Paving MixturesRafael EstradaNo ratings yet
- Gallegos Stone CatalogDocument17 pagesGallegos Stone CatalogRamon AlonsoNo ratings yet
- 2 Reservoir LithologyDocument7 pages2 Reservoir Lithologyزين العابدين هيثم لفته جابرNo ratings yet
- Carbonate Sedimentation Controls and Sequence StratigraphyDocument42 pagesCarbonate Sedimentation Controls and Sequence StratigraphyMaria MawarNo ratings yet
- Geology of Malta and GozoDocument6 pagesGeology of Malta and GozoCarolina Pérez P.No ratings yet
- Partido State University: Camarines SurDocument7 pagesPartido State University: Camarines Suranabelle ramirezNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Mega Quarry Proposed by The Highland CompaniesDocument9 pagesOverview of The Mega Quarry Proposed by The Highland CompaniesSTOP THE QUARRYNo ratings yet
- 3 Applied Geomorphology AkshayDocument10 pages3 Applied Geomorphology Akshaygajendra100% (1)
- (2022) NwaniDocument11 pages(2022) NwaniPamela Rodrigues RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Rocks Minerals Notes Kean UniversityDocument38 pagesRocks Minerals Notes Kean Universityapi-323312952No ratings yet
- House's Building Materials AssignmentDocument24 pagesHouse's Building Materials AssignmentUhGuanHongNo ratings yet
- Secular Variation in Seawater Chemistry and The Origin of Calcium Chloride Basinal BrinesDocument5 pagesSecular Variation in Seawater Chemistry and The Origin of Calcium Chloride Basinal BrinesAnonymous PdzpkUNo ratings yet
- Karst Landform FeaturesDocument26 pagesKarst Landform FeaturesA S Verma100% (1)
- Hydrometallurgia A PresionDocument484 pagesHydrometallurgia A PresionJhon Barzola Palomino100% (2)
- OPSS - MUNI 1350 Nov17 PDFDocument19 pagesOPSS - MUNI 1350 Nov17 PDFAlireza DehghanNo ratings yet
- Characteristics, Classification and Uses of BricksDocument12 pagesCharacteristics, Classification and Uses of BricksKazi Almuqtadir100% (1)
- Applied Geochemistry: Charles A. Cravotta IIIDocument19 pagesApplied Geochemistry: Charles A. Cravotta IIIMatias VenegasNo ratings yet
- Huygens Institute - Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW)Document18 pagesHuygens Institute - Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW)BUMI ManilapaiNo ratings yet
- Dolomite Stability Assessment for an Area South of PretoriaDocument96 pagesDolomite Stability Assessment for an Area South of PretoriamatshonaNo ratings yet
- Geologi Dan Karakteristik Cebakan Skarn Pb-Zn-Cu-Ag Di Ruwai, Kabupaten Lamandau, Kalimantan TengahDocument11 pagesGeologi Dan Karakteristik Cebakan Skarn Pb-Zn-Cu-Ag Di Ruwai, Kabupaten Lamandau, Kalimantan TengahDen SuhendraNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Geology (Fieldtrip) of Cepu AreaDocument31 pagesPetroleum Geology (Fieldtrip) of Cepu AreaPradipta Gora KusumaNo ratings yet
- Report Writing ReportsDocument17 pagesReport Writing ReportsFarhan Husein MahriNo ratings yet
- Building TechDocument16 pagesBuilding TechKen AndreiNo ratings yet