Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SuggestedAnswers 08 E
Uploaded by
RaiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SuggestedAnswers 08 E
Uploaded by
RaiCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2 Microscopic World I Mastering Chemistry
Suggested answers to in-text activities and unit-end exercises
Topic 2 Unit 8
Practice
P8.1 (page 113)
1 a) 2,7
b) A diatomic molecule is a molecule made up of two atoms bond together.
c) Two fluorine atoms share a pair of electrons in their outermost shells to make a fluorine
molecule.
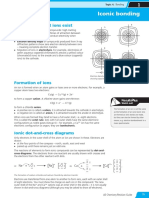
2 a) A covalent bond is the electrostatic forces of attraction between the positively charged
nuclei of the two bonded atoms and the negatively charged shared electrons.
b) An ionic bond is the strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged
ions.
P8.2 (page 118)
1
2 a)
b) CS2
P8.3 (page 119)
a) HBr
b) NCl3
c) SiS2
P8.4 (page 120)
1 a) Nitrogen trifluoride
b) Dichlorine monoxide
©2019 Jing Kung Educational Press All Rights Reserved
Topic 2 Microscopic World I Mastering Chemistry
2 a) N2O3
b) SF6
P8.5 (page 124)
1
Does it have
Compound covalent bonding? Explanation
(yes / no)
Both hydrogen and iodine are nonmetals.
Hydrogen iodide yes A hydrogen atom shares electrons with an
iodine atom to make a molecule.
Magnesium is a metal while nitrogen is a
non-metal.
Magnesium nitride no When magnesium and nitrogen combine,
magnesium atoms lose electrons while
nitrogen atoms gain electrons.
Silver is a metal while chlorine is a
nonmetal.
Silver chloride no When silver and chlorine combine, silver
atoms lose electrons while chlorine atoms
gain electrons.
Both sulphur and oxygen are non-metals.
Sulphur dioxide yes A sulphur atom shares electrons with two
oxygen atoms to make a molecule
©2019 Jing Kung Educational Press All Rights Reserved
Topic 2 Microscopic World I Mastering Chemistry
2 Compound P
a) Covalent
b)
c) Hydrogen sulphide
Compound Q
a) Ionic
b)
c) Potassium sulphide
P8.6 (page 126)
P8.7 (page 128)
1 a) 14.0 + 3 1.0 = 17.0
b) 2 35.5 = 71.0
c) 2 16.0 = 32.0
d) 2 1.0 + 16.0 = 18.0
2 a) 2 14.0 + 8 1.0 + 12.0 + 3 16.0 = 96.0
b) 3 40.1 + 2 31.0 + 8 16.0 = 310.3
c) 2 39.1 + 32.1 = 110.3
©2019 Jing Kung Educational Press All Rights Reserved
Topic 2 Microscopic World I Mastering Chemistry
Unit Exercise (pages 134-141)
1 a) (i) metallic
(ii) positive metal ions and a ‘sea’ of delocalised electrons
(iii) covalent
(iv) molecules
(v) a network of covalent bonds linking atoms
(vi) discrete atoms
b) (i) ionic
(ii) oppositely charged ions
(iii) covalent
(iv) molecules
(v) a network of covalent bonds linking atoms
2 B
3 D An atom of Y shares a pair of electrons with each of four atoms of X to make a molecule
of molecular formula YX4.
4 D A phosphorus atom has an electronic arrangement of 2,8,5 while a chlorine atom has an
electronic arrangement of 2,8,7. A phosphorus atom shares a pair of electrons with each of
three chlorine atoms so that all the atoms get the electronic arrangements of atoms of
noble gases.
5 A Carbon and sulphur are both nonmetals. They combine to form a covalent compound.
A carbon atom has an electronic arrangement of 2,4 while a sulphur atom has an
electronic arrangement of 2,8,6.
A carbon atom shares two pairs of electrons with each of two sulphur atoms to make a
CS2 molecule.
6 B is lithium atom. Lithium is a metal. It does NOT form a covalent bond.
7 A Ammonia contains hydrogen and nitrogen. Both hydrogen and nitrogen are non-metals.
Their atoms share electrons to form a covalent compound.
©2019 Jing Kung Educational Press All Rights Reserved
Topic 2 Microscopic World I Mastering Chemistry
8 B X is fluorine (a non-metal) while Y is calcium (a metal). They combine to form an ionic
compound.
When calcium atoms combine with fluorine atoms, two electrons from each calcium atom
are transferred to two fluorine atoms, one for each. The chemical formula of the
compound formed is CaF2, i.e. YX2.
9 C
10 A Both oxygen and fluorine are non-metals. Their atoms share electrons to form a covalent
compound.
11 B NH4+ ion is formed when NH3 molecule combines with H+ ion via dative covalent
bonding. Ionic bonding exists between NH4+ ion and Cl– ion.
12 A The chemical formula of the compound is Al2X3. One aluminium ion carries three
positive charges. The compound has no overall charges. In the compound, two Al3+ ions
are needed for three ions of X to make the total charge zero. Thus, the ion of X should
carry two negative charges. X is sulphur. A carbon atom has an electronic arrangement of
2,4 while a sulphur atom has an electronic arrangement of 2,8,6.
A carbon atom shares two pairs of electrons with each of two sulphur atoms to make a
CS2 molecule.
13 C
14 A The electron diagram of an ammonia molecule is shown below.
(2) The number of bonding electrons contributed by the nitrogen atom in the molecule is
3.
(3) The total number of electrons in the molecule is 10.
15 A (1) Hydrogen chloride is a covalent compound.
16 B X is carbon while Y is oxygen.
A carbon atom shares two pairs of electrons with each of two oxygen atoms to make a
CO2 molecule.
©2019 Jing Kung Educational Press All Rights Reserved
Topic 2 Microscopic World I Mastering Chemistry
17 C (1) An atom of X gains one electron so as to obtain a stable outermost shell of 8
electrons.
18 a) (1)
b) (1)
c) (1)
d) (1)
e) (1)
©2019 Jing Kung Educational Press All Rights Reserved
Topic 2 Microscopic World I Mastering Chemistry
f) (1)
19 a) The two hydrogen atoms in a hydrogen molecule are held together by the strong
electrostatic forces of attraction between their positively charged nuclei and the
negatively charged shared electrons. (1)
b) i)
(1)
ii) (1)
iii) (1)
©2019 Jing Kung Educational Press All Rights Reserved
Topic 2 Microscopic World I Mastering Chemistry
iv) (1)
20 a) Nitrogen dioxide (1)
b) Silicon tetrafluoride (1)
c) Diphosphorus trisulphide (1)
21 a) Any three of the following:
․ Helium (1)
․ Neon (1)
․ Argon (1)
․ Krypton (1)
․ Xenon (1)
․ Radon (1)
b) i) Discrete atom (1)
ii) Each atom of noble gases has a full outermost electron shell. An outermost shell
of 8 electrons (or 2 electrons for helium) is extremely stable. (1)
Thus, each of these atoms has little tendency to combine with other atoms.
22 a) Group V (1)
Period 4 (1)
b) 33 (1)
c) i)
(1)
ii) 74.9 + 3 x 35.5 = 181.4 (1)
©2019 Jing Kung Educational Press All Rights Reserved
Topic 2 Microscopic World I Mastering Chemistry
23
Ionic / Chemical
Elements combined Covalent formula of Name of compound
compound compound
Carbon and sulphur covalent CS2 carbon disulphide (3)
Lithium and bromine ionic LiBr lithium bromide (3)
Magnesium and nitrogen ionic Mg3N2 magnesium nitride (3)
Phosphorus and fluorine covalent PF3 phosphorus trifluoride (3)
24
Compound Ionic / covalent Chemical formula
Ammonia covalent NH3 (2)
Copper(II) sulphate ionic CuSO4 (2)
Hydrogen iodide covalent HI (2)
Sulphur trioxide covalent SO3 (2)
Silver nitrate ionic AgNO3 (2)
25 a) i) An ionic bond is the strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely
charged ions. (1)
ii) (1)
iii) Aluminium fluoride (1)
AlF3 (1)
b) i) A covalent bond is the electrostatic forces of attraction between the positively
charged nuclei of the two bonded atoms and the negatively charged shared electrons.
(1)
©2019 Jing Kung Educational Press All Rights Reserved
Topic 2 Microscopic World I Mastering Chemistry
ii) (1)
iii) Silicon tetrafluoride (1)
SiF4 (1)
26 a) i) The boiling point of chlorine is below room temperature. (1)
ii) The melting point of bromine is below room temperature but its boiling point is
above room temperature. (1)
b) Two fluorine atoms share a pair of electrons in their outermost shells to make a fluorine
molecule, F2. (1)
c) 79.9 + 3 19.0 = 136.9 (1)
d)
(1)
(1)
27 a) (1)
b) A magnesium atom loses two electrons to form a magnesium ion. (1)
An astatine atom gains one electron to form an astatide ion. (1)
©2019 Jing Kung Educational Press All Rights Reserved
Topic 2 Microscopic World I Mastering Chemistry
28 Answers for the HKDSE question are not provided.
29 a) A dative covalent bond is a type of covalent bond in which both electrons come from the
same atom. (1)
b) (1)
30 a) 8 (1)
b) Fractional distillation of liquid air (1)
c) A fluorine atom gains one electron to form a fluoride ion. (1)
d) i) Covalent bonding (1)
Both carbon and hydrogen are non-metals. They combine to form a covalent
compound. (1)
ii) Ionic bonding (1)
Calcium is a metal while chlorine is a non-metal. They combine to form ionic
compound. (1)
31 A sulphur atom has an electronic arrangement of 2,8,6 while a hydrogen atom has an electronic
arrangement of 1.
A sulphur atom shares a pair of electrons with each of two hydrogen atoms to make a hydrogen
sulphide molecule (H2S). Now, all the atoms get the electronic arrangements of atoms of noble
gases. (1)
A potassium atom has an electronic arrangement of 2,8,8,1.
When potassium and sulphur react to form potassium sulphide (K2S), one electron from each
of two potassium atoms is transferred to one sulphur atom. (1)
Communication mark (1)
©2019 Jing Kung Educational Press All Rights Reserved
Topic 2 Microscopic World I Mastering Chemistry
32 a) i) E (1)
ii) C (1)
iii) A (1)
iv) C (1)
b) i) Both elements B and D are non-metals. They combine to form a covalent compound.
(1)
ii)
(1)
c) i) Element D is a non-metal while element F is a metal. They combine to form an ionic
compound. (1)
ii)
(1)
33 a) 40.1 + 2 35.5 + 8 16.0 = 239.1 (1)
b) 4 12.0 + 10 1.0 = 58.0 (1)
©2019 Jing Kung Educational Press All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- Chemical Bonding X ICSE CHEMISTRYDocument34 pagesChemical Bonding X ICSE CHEMISTRYjoycepeter100% (1)
- 2 2TextAnswersDocument4 pages2 2TextAnswerssherfudadNo ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers 07 E PDFDocument9 pagesSuggestedAnswers 07 E PDFCelemusicNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 7 QPDocument9 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 7 QPaliayanraza5No ratings yet
- Soalan 10Document2 pagesSoalan 10rudi_zNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For S2Document7 pagesChemistry For S2ngirisinicholasNo ratings yet
- Keira Resalsingh - Metallic and Ionic Bonding Worksheet Week 1 April 20th-24thDocument3 pagesKeira Resalsingh - Metallic and Ionic Bonding Worksheet Week 1 April 20th-24thSideka ResalsinghNo ratings yet
- Unit Exercise (Pages 125-131)Document6 pagesUnit Exercise (Pages 125-131)LeeBruceNo ratings yet
- PS G10 Chemistry Exemplar (June)Document6 pagesPS G10 Chemistry Exemplar (June)Dean WillemseNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Structure and Properties of Materials, Ionic Bonding, Covalent Bonding AnswersDocument12 pagesTopic 4 Structure and Properties of Materials, Ionic Bonding, Covalent Bonding AnswersKaixin HuangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument2 pagesChapter 6 Ionic and Covalent BondingsliversniperNo ratings yet
- Print Level I Chemical BondingDocument14 pagesPrint Level I Chemical Bondingudayshirsat1708No ratings yet
- ACFrOgDx1bVYvYs4ZSOHncy Lxwh252QwZ3fFL9jXIkG3a3C1VLDY Vr37kfXVajSVfx5aaqhaxlzrLaHGCZJqMVo6sl xJ6PpIbb 9PdW2nmPH61nrs58pY8k6KWgfbxmkEfVWkqRByaPp7m4RDocument9 pagesACFrOgDx1bVYvYs4ZSOHncy Lxwh252QwZ3fFL9jXIkG3a3C1VLDY Vr37kfXVajSVfx5aaqhaxlzrLaHGCZJqMVo6sl xJ6PpIbb 9PdW2nmPH61nrs58pY8k6KWgfbxmkEfVWkqRByaPp7m4RDr. Fatima IhsanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table 3 QPDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure & The Periodic Table 3 QPMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- 172 Bonding and Electronegativity - Van Arkel TrianglesDocument4 pages172 Bonding and Electronegativity - Van Arkel TrianglesM DiNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Paper 1Document2 pagesElectrolysis Paper 1Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Concise Chemistry Chemical Bonding SolutionsDocument30 pagesClass 10 Concise Chemistry Chemical Bonding SolutionsPIYUSH DikshitNo ratings yet
- Part II 2019 Updated QBDocument6 pagesPart II 2019 Updated QBteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 4 StudyDocument5 pagesChemistry Unit 4 StudycurtisNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS Ionic Bonding and Ionic Compounds Mutiple Choice 2 2012-07-05Document3 pagesANSWERS Ionic Bonding and Ionic Compounds Mutiple Choice 2 2012-07-05Raghoda AsimNo ratings yet
- Chem11 SM 1 RDocument8 pagesChem11 SM 1 RdudoocandrawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Structured QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter 7 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- WS4,5,6,7 WK 16-20 Aug Energy and Chemicals Class 10 ZoyaDocument18 pagesWS4,5,6,7 WK 16-20 Aug Energy and Chemicals Class 10 ZoyaUsman AsmatullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Chemical BondsDocument11 pagesChapter 4: Chemical BondsNahed YacoubNo ratings yet
- Bonding Exam RevisionDocument19 pagesBonding Exam RevisionVaida MatulevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument4 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionElsie VanpraetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document4 pagesChapter 3叶震森No ratings yet
- Chemist Chapter 3Document11 pagesChemist Chapter 3Emelia DeeNo ratings yet
- 04-Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFDocument43 pages04-Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFKumutha RavichandranNo ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers T02 EDocument10 pagesSuggestedAnswers T02 ERaiNo ratings yet
- Bonding Test Review TCDocument4 pagesBonding Test Review TCDessere SosasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Ionic Bonding - Occurs When Two or More Ions Combine To Form An Electrically-NeutralDocument28 pagesChemical Bonding: Ionic Bonding - Occurs When Two or More Ions Combine To Form An Electrically-NeutralananntsharmaNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL BONDING - NotesDocument30 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING - NotesP YNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Quick AssessmentDocument3 pagesIonic Bonding Quick AssessmentCodyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry EM IMPDocument53 pagesChemistry EM IMPdharmishthakaneriya4No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 02 Sept 2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 02 Sept 2023Negi DeepakNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 2 Microscopic World I - LQ - PDFDocument22 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 2 Microscopic World I - LQ - PDFSiu Hon ChengNo ratings yet
- CM TB Solutions C06Document3 pagesCM TB Solutions C06Nisha75% (8)
- Ionic Bonding Quick AssessmentDocument3 pagesIonic Bonding Quick AssessmentCheezy NachosNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Chapter 2 - Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesChemistry: Chapter 2 - Chemical BondingSiri JambulaNo ratings yet
- MNBHJNKDocument70 pagesMNBHJNKvaibhav sharmaNo ratings yet
- AS Level Chemistry Notes: BondingDocument12 pagesAS Level Chemistry Notes: BondingAyesha Ahmed100% (1)
- Chemistry by Ashwani Ohri: Electronegativity and Miscl. QuestionsDocument3 pagesChemistry by Ashwani Ohri: Electronegativity and Miscl. QuestionsSavvy GuptaNo ratings yet
- ???? ?? ???????? ???????Document8 pages???? ?? ???????? ???????chopramanya34No ratings yet
- Second Quarter Summative TestDocument3 pagesSecond Quarter Summative TestSharon100% (3)
- Chemistry 9th Chapter 04Document1 pageChemistry 9th Chapter 04jahanzeb aliNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2Document62 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2Killer boy SidNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-01-31 at 19.23.33Document9 pagesScreenshot 2023-01-31 at 19.23.33deeznuts urmomNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Structured QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter 8 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Answers 15 09 2021 at 9 AmDocument61 pagesAtomic Structure Answers 15 09 2021 at 9 AmPevin De silvaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Structure and Properties of Materials, Ionic Bonding, Covalent BondingDocument33 pagesTopic 4 Structure and Properties of Materials, Ionic Bonding, Covalent BondingKaixin HuangNo ratings yet
- Covalent and Metallic Bonding: Test Yourself 7.1 (Page 114)Document2 pagesCovalent and Metallic Bonding: Test Yourself 7.1 (Page 114)khalil rehmanNo ratings yet
- Class X Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesClass X Chemical BondingvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Octet Rule and IonsDocument24 pages5.1 Octet Rule and IonsIvy Joyce BuanNo ratings yet
- D0679Sci-1-Ans 2Document5 pagesD0679Sci-1-Ans 2Shaikh KulsumNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Ionic Bonding WORKSHEETDocument6 pagesCH 7 Ionic Bonding WORKSHEETkashif mohammedNo ratings yet
- 02 Electrochemistry Ques. Final E PDFDocument21 pages02 Electrochemistry Ques. Final E PDFAri GamakiNo ratings yet
- Crystal Chemistry and Semiconduction in Transition Metal Binary CompoundsFrom EverandCrystal Chemistry and Semiconduction in Transition Metal Binary CompoundsNo ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers 11 EDocument9 pagesSuggestedAnswers 11 ERaiNo ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers 07 EDocument8 pagesSuggestedAnswers 07 ERaiNo ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers 09 EDocument15 pagesSuggestedAnswers 09 ERaiNo ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers 10 EDocument9 pagesSuggestedAnswers 10 ERaiNo ratings yet
- 12 Atoms: Level-IIDocument19 pages12 Atoms: Level-IIrithiram0No ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument19 pagesLiterature ReviewKaung KhantNo ratings yet
- Vegetation Patterns Along A Rainfall Gradient: Ehud Meron, Erez Gilad, Jost Von Hardenberg, Moshe Shachak, Yair ZarmiDocument10 pagesVegetation Patterns Along A Rainfall Gradient: Ehud Meron, Erez Gilad, Jost Von Hardenberg, Moshe Shachak, Yair ZarmiEmmanuel kpegloNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 1.Document3 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 1.Eduard Avila Meriño100% (1)
- Scott - 1982 - The Vibrational Structure of Davydov Solitons PDFDocument9 pagesScott - 1982 - The Vibrational Structure of Davydov Solitons PDFЮрий ЮрийNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Biological MacromoleculesDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Biological MacromoleculesAlejandra Gonzalez RuizNo ratings yet
- Pset 2Document13 pagesPset 2rishiko aquinoNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Tubes &Document45 pagesX-Ray Tubes &Aakash BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Practice Problems, Module 2: Engineering MechanicsDocument16 pagesSolutions To Practice Problems, Module 2: Engineering MechanicsShaun Patrick AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory I: 1. The Complete Equations of Classical ElectrodynamicsDocument13 pagesLecture 14 Notes, Electromagnetic Theory I: 1. The Complete Equations of Classical Electrodynamicssalsa bilaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - Semester End Project: The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument4 pagesPhysical Science - Semester End Project: The Electromagnetic SpectrumBreanna HartNo ratings yet
- Brake Calculations SheetDocument46 pagesBrake Calculations Sheetashish kumarNo ratings yet
- Defossez 2021Document13 pagesDefossez 2021Joe ChuNo ratings yet
- NTC ThermistorDocument3 pagesNTC ThermistorPablo AllosiaNo ratings yet
- Huygens' Principle, Maxwell's Displacement CurrentDocument7 pagesHuygens' Principle, Maxwell's Displacement CurrentGalleta Galleta MetralletaNo ratings yet
- Premium Gold Motor: TOSHIBA Top Runner MotorDocument17 pagesPremium Gold Motor: TOSHIBA Top Runner MotorMOTORES, MOTORREDUCTORES Y COMPONENTES GUADALAJARANo ratings yet
- DC 70D ManualDocument17 pagesDC 70D ManualAnonymous vqsuRyNo ratings yet
- Solved 2024 Specimen Paper ICSE Class 10 ChemistryDocument11 pagesSolved 2024 Specimen Paper ICSE Class 10 ChemistrymmroyalethegreatNo ratings yet
- 6 - Mass, Weight and C.GDocument17 pages6 - Mass, Weight and C.GRafayNo ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics MCQsDocument6 pagesGas Dynamics MCQsprawinlNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet For Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage-Motors SIMOTICS: Motor Type: 1CV3407B Simotics SD Pro - 400 - Im B3 - 4PDocument2 pagesData Sheet For Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage-Motors SIMOTICS: Motor Type: 1CV3407B Simotics SD Pro - 400 - Im B3 - 4Pnadia perezNo ratings yet
- Effect of Soil Plug Removal On The Load-Carrying Capacity of Symmetric and Non-Symmetric Pile GroupsDocument25 pagesEffect of Soil Plug Removal On The Load-Carrying Capacity of Symmetric and Non-Symmetric Pile GroupsChandra MouliNo ratings yet
- Detailed Design Study of North Java Corridor Flyover Project Balaraja Flyover Detailed Design SubstructureDocument228 pagesDetailed Design Study of North Java Corridor Flyover Project Balaraja Flyover Detailed Design SubstructureNetzoo FlixNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Board (Tantalum Less) : Solidworks Drawing: All Changes Must Be Done in Solidworks DatabaseDocument2 pagesPower Supply Board (Tantalum Less) : Solidworks Drawing: All Changes Must Be Done in Solidworks DatabasezizouhicheNo ratings yet
- CU-2022 B.sc. (Honours) Mathematics Semester-1 Paper-CC-1 QPDocument4 pagesCU-2022 B.sc. (Honours) Mathematics Semester-1 Paper-CC-1 QPMy MathNo ratings yet
- Pavement Engineering Notes 2012Document77 pagesPavement Engineering Notes 2012Mohamed Wehliye90% (10)
- Loss of Head Indicator - Capacitance TypeDocument2 pagesLoss of Head Indicator - Capacitance Typeaamer6789No ratings yet
- Structural Integrity Report PDFDocument9 pagesStructural Integrity Report PDFJoseph Mwangi WambuguNo ratings yet
- Overload Clutches For Index Drives (Type D-Sa, Adjustable) : Operating PrincipleDocument4 pagesOverload Clutches For Index Drives (Type D-Sa, Adjustable) : Operating PrincipleSuhas KODRENo ratings yet
- Sensors & Sensor Modules: YF-S201 Water Flow SensorDocument2 pagesSensors & Sensor Modules: YF-S201 Water Flow SensorPOOVENDHAN TNo ratings yet