Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Part II 2019 Updated QB
Uploaded by
teresa tsoiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Part II 2019 Updated QB
Uploaded by
teresa tsoiCopyright:
Available Formats
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part II Microscopic world I
Part II Microscopic world I
Q1
Rhenium, which has the relative atomic mass of 186.2, has two naturally occurring
isotopes, 185Re and 187Re. What is the ratio of 185Re to 187Re in natural rhenium?
A. 1 : 2
B. 2 : 1
C. 2 : 3
D. 3 : 2
##C Let the relative abundance of 185Re be x%.
185 × x% + 187 × (1 x%) = 186.2
x = 40
Ratio of 185Re : 187Re = 40% : 60% = 2 : 3##
Q2
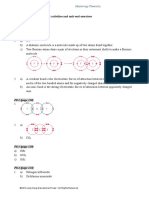
Consider the following set-up:
a drop of CrCl3(aq)
filter paper soaked
with NaNO3(aq)
electrode X electrode Y
12 V d.c. supply
When the circuit is closed for some time, a coloured spot moves towards electrode X.
Which of the following statements about the experiment are correct?
(1) The filter paper is soaked with NaNO3(aq) to increase the electrical conductivity
of the filter paper.
(2) The coloured spot is green in colour.
(3) Electrode X is the negative electrode.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
3+ 3+
##D Cr (aq) is green in colour. When the circuit is closed, Cr (aq) ions are attracted
to the negative electrode.##
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2019 Part II
7
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part II Microscopic world I
Q3
Which of the following substances has the strongest covalent bond?
A. Hydrogen
B. Carbon dioxide
C. Diamond
D. Sulphur
##B In H2, C(diamond) and S8, the atoms are held together by single covalent bonds.
In CO2, the C and O atoms are held together by double covalent bonds. Double
covalent bonds are stronger than single covalent bonds.##
Q4
The table below lists some information about two elements M and N:
Element Atomic number Relative atomic mass
M 17 35.5
N 20 40.1
What is the formula mass of the compound formed between M and N?
A. 75.6
B. 111.1
C. 115.7
D. 151.2
##B The electronic arrangements of M and N are 2, 8, 7 and 2, 8, 8, 2 respectively.
The formula of the compound formed between M and N is NM2. Its formula mass is
40.1 + 35.5 × 2 = 111.1.##
Q5
Which of the following combinations about the structures of substances is
INCORRECT?
Substance Structure
A. N2H4 Simple molecular structure
B. SiCl4 Giant covalent structure
C. Na/Hg Giant metallic structure
D. K3[Fe(CN)6] Giant ionic structure
##B N2H4 and SiCl4 exist as simple molecules. Sodium amalgam (Na/Hg) is an alloy
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2019 Part II
8
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part II Microscopic world I
of sodium and mercury. It has a giant metallic structure. K3[Fe(CN)6] consists of K+
ions and [Fe(CN)6]3 ions.##
Q6
Aluminium (Al) and gallium (Ga) are metals in Group III of the Periodic Table.
69
(a) Ga and 71Ga are the two naturally occurring isotopes of gallium.
(i) Explain why 69Ga and 71Ga have the same chemical properties. (1 mark)
(ii) Given that the relative atomic mass of Ga is 69.7. Calculate the relative
abundance of 71Ga. (2 marks)
(b) When chlorine passes over hot aluminium, they react to produce aluminium
chloride. Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved. (1 mark)
(c) Comment on the following statement:
‘Gallium also reacts with chlorine to give gallium(III) chloride.’ (1 mark)
##
(a) (i) They have the same number of outermost shell electrons. 1
(ii) Let the relative abundance of 71Ga be y%.
69.7 = 71 × y% + 69 × (1 y%) 1
y = 35 1
(b) 2Al(s) + 3Cl2(g) 2AlCl3(s) 1
(c) The statement is correct. Elements of the same group have similar
chemical properties. 1
___
5
##
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2019 Part II
9
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part II Microscopic world I
Q7
The following diagram shows the atomic structure of element G:
(a) Name subatomic particle X. (1 mark)
(b) State the mass number of G. (1 mark)
(c) Explain which period of the Periodic Table G belongs to. (1 mark)
(d) Explain whether G is found as a free element in nature. (2 marks)
(e) Draw the electron diagram of the compound formed by G and oxygen, showing
electrons in the outermost shells only. (1 mark)
##
(a) Proton 1
(b) 7 1
(c) As the atom of G has two occupied electron shells, it belongs to Period 2. 1
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2019 Part II
10
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part II Microscopic world I
(d) No. The atom of G does not have a stable electronic arrangement / the
outermost electron shell is not fully filled. 1
It forms compounds by losing its outermost shell electron to get the
electronic arrangement of a noble gas. 1
(e)
or 1
___
6
##
Q8
Silicon is a semi-metal. It forms silicon dioxide with oxygen.
(a) State ONE natural source of silicon dioxide. (1 mark)
(b) State ONE industrial use of silicon dioxide. (1 mark)
(c) Silicon can be extracted from silicon dioxide. When silicon dioxide is heated
with coke (a form of carbon), silicon and compound X are produced.
(i) Given that X does not turn limewater milky, suggest what X is. (1 mark)
(ii) Hence, write a chemical equation for the reaction of silicon dioxide with
coke. (1 mark)
(d) Explain why silicon dioxide has a high melting point. (2 marks)
##
(a) Sand / silica / quartz 1
(b) To make glass / cement / ceramics / chemicals such as SiCl4 and Si 1
(c) (i) Carbon monoxide 1
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2019 Part II
11
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part II Microscopic world I
(ii) SiO2(s) + 2C(s) Si(s) + 2CO(g) 1
(d) Silicon dioxide has a giant covalent structure. 1
In melting silicon dioxide, a lot of heat energy is required to break the
strong covalent bonds between the atoms. 1
___
6
##
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2019 Part II
12
You might also like
- Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument26 pagesIntermolecular Forces of AttractionEsaïe GreñaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 1A 1B 2 - New QuestionDocument58 pagesQuestion Bank 1A 1B 2 - New Questionteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Bonding Exam RevisionDocument19 pagesBonding Exam RevisionVaida MatulevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- Seperation Techniques PDFDocument232 pagesSeperation Techniques PDFAmitranjan KarNo ratings yet
- AISI Steel Grading SystemDocument7 pagesAISI Steel Grading Systemechobot1No ratings yet
- DPP-Chemical Bonding - CombinedDocument67 pagesDPP-Chemical Bonding - CombinedKeerthana Reddy DomaNo ratings yet
- Laundry - An Housekeeper PerspectiveDocument24 pagesLaundry - An Housekeeper Perspectivegrgnolis100% (1)
- MolarityDocument12 pagesMolarityDemelza MulciberNo ratings yet
- Mil STD 286cDocument407 pagesMil STD 286cGabriela Paes100% (1)
- ANSWERS - Yr 10 Chem Practice Test QuestionsDocument8 pagesANSWERS - Yr 10 Chem Practice Test QuestionsJerryNo ratings yet
- Carbonate Acidizing AHDocument79 pagesCarbonate Acidizing AHMarrry Florencia100% (1)
- IB Chemistry HL Periodicity Review 1.: (Total 1 Mark)Document5 pagesIB Chemistry HL Periodicity Review 1.: (Total 1 Mark)y. k.No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Structured QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter 8 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Ch8 SQDocument16 pagesCh8 SQhihiNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 2 Microscopic World I - LQ - PDFDocument22 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 2 Microscopic World I - LQ - PDFSiu Hon ChengNo ratings yet
- Final SSC-I Chemistry Model PaperDocument8 pagesFinal SSC-I Chemistry Model Papershamsuddin816191No ratings yet
- SMK Dato Jaafar, JohorDocument8 pagesSMK Dato Jaafar, JohorJun Hao ChongNo ratings yet
- Set2 Chem Ms MidTerm 1 2021 Teacher - Co .Ke F3 ExamDocument10 pagesSet2 Chem Ms MidTerm 1 2021 Teacher - Co .Ke F3 Exambiztim69No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Test 2 300920Document11 pagesUnit 1 Test 2 300920ibrahim ahmedNo ratings yet
- TN 11th Chemistry Model Question Paper 2018 WWW - Governmentexams.co - inDocument9 pagesTN 11th Chemistry Model Question Paper 2018 WWW - Governmentexams.co - inJohn alexanderNo ratings yet
- Chem S3 Hy QPDocument8 pagesChem S3 Hy QPyu yi xiNo ratings yet
- Grade11-UT 2-Chemistry-QPDocument4 pagesGrade11-UT 2-Chemistry-QPKrishna NayakNo ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument112 pagesAnimal NutritionJames TongNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 11C GOC (Mechanism)Document7 pagesWORKSHEET 11C GOC (Mechanism)Hardik Chhabra100% (1)
- 2IIT1920 (IIT Camp) (Main) CWS01 (Atomic Structure, Periodic Properties and Chemical Bonding) (SAG Mam) PDFDocument3 pages2IIT1920 (IIT Camp) (Main) CWS01 (Atomic Structure, Periodic Properties and Chemical Bonding) (SAG Mam) PDFvidhit dlNo ratings yet
- GT Group of Institutions CHEMISTRY-Revision Worksheet Class 11 Chemistry Worksheet 12/02/2021Document6 pagesGT Group of Institutions CHEMISTRY-Revision Worksheet Class 11 Chemistry Worksheet 12/02/2021jayashree krishnaNo ratings yet
- Past Papers and MCQs Class 9 - RemovedDocument22 pagesPast Papers and MCQs Class 9 - RemovedboundaryblastsNo ratings yet
- Exercise - I: (Conceptual Problems)Document3 pagesExercise - I: (Conceptual Problems)Siddharth RoyNo ratings yet
- CHM1102Document10 pagesCHM1102AliNo ratings yet
- CHMS3Y20E2Document13 pagesCHMS3Y20E2no nameNo ratings yet
- GIC TestDocument5 pagesGIC TestRishabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Structured QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter 7 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Society of Young Engineers Towards Achieving ExcellenceDocument4 pagesSociety of Young Engineers Towards Achieving ExcellenceAslagNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Xi Hy SQPDocument5 pagesChemistry Xi Hy SQPArchisha PradhanNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet Periodic Classification of Elements - 2022-23Document2 pagesRevision Worksheet Periodic Classification of Elements - 2022-23Malolan SriramNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties-03-Assignments (New)Document9 pagesPeriodic Properties-03-Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Topical SaveMyExamDocument14 pagesTopical SaveMyExamzainkolachieduNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Final Paper Class 8THDocument3 pagesChemistry Final Paper Class 8THimranyameen001No ratings yet
- WS Grade 9 IG Chemistry 22-23 - SA 1 Revision WorksheetDocument8 pagesWS Grade 9 IG Chemistry 22-23 - SA 1 Revision WorksheetSiyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry XII Practice Paper BOOK 1Document95 pagesChemistry XII Practice Paper BOOK 1hembrampriyanka07No ratings yet
- Class - XI CHEMISTRY ASSIGNMENT CH-3Document3 pagesClass - XI CHEMISTRY ASSIGNMENT CH-3divyanshgirivbpsNo ratings yet
- 09 Physics Chapter-21 (27-04-2021) (15TH Feb)Document3 pages09 Physics Chapter-21 (27-04-2021) (15TH Feb)komi jafarNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 To 11 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 11th JEEDocument22 pagesDPP - 01 To 11 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 11th JEEanichemindNo ratings yet
- CQ On Chap-3 (Chemistry 1 Paper)Document4 pagesCQ On Chap-3 (Chemistry 1 Paper)Mahin AzizNo ratings yet
- CH - 5-9 - Topic Revision Test 1Document23 pagesCH - 5-9 - Topic Revision Test 1Thomas LauNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Practice Paper ChemistryDocument9 pagesHalf Yearly Practice Paper ChemistrySOHAN DASNo ratings yet
- Chem F2 MS 1Document5 pagesChem F2 MS 1Selifa AbutiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - DPPsDocument12 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - DPPsRaxit PathakNo ratings yet
- Xi Chemistry QPDocument5 pagesXi Chemistry QPDamodar KasukurthiNo ratings yet
- CBSE 12 Chemistry Question Term2Document4 pagesCBSE 12 Chemistry Question Term2R roseNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (LDA) NMDocument19 pagesChemical Bonding (LDA) NMkaeshav manivannanNo ratings yet
- CH - 5-9 - HKCEE (1987-2011)Document63 pagesCH - 5-9 - HKCEE (1987-2011)HiiiNo ratings yet
- KimiaDocument7 pagesKimianoreza salleh hudinNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Assignment-4Document9 pagesPeriodic Table Assignment-4cpramkrishnaNo ratings yet
- BGIS-Y201920-HY Chemistry MM: 70 GRADE-11 (SCI) TIME: 3 HRDocument7 pagesBGIS-Y201920-HY Chemistry MM: 70 GRADE-11 (SCI) TIME: 3 HRGoutham SagarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Practice Sheet - JEE ChallengersDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding - Practice Sheet - JEE ChallengerssadatarbabedNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryChanaki PereraNo ratings yet
- CQ FundamentalsDocument7 pagesCQ Fundamentalsapi-3826629No ratings yet
- Chemistry Final QuestionDocument4 pagesChemistry Final QuestionSagar MannaNo ratings yet
- Goldengate Int'L College: First Terminal Examination-2080Document2 pagesGoldengate Int'L College: First Terminal Examination-2080sachin shahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 9647/03: Hwa Chong Institution C1 Block Test Higher 2Document6 pagesChemistry 9647/03: Hwa Chong Institution C1 Block Test Higher 220Y3G HONG JIN KAINo ratings yet
- (CC - 1) 22Document2 pages(CC - 1) 22Pralay MaitiNo ratings yet
- 25mints Pt7 Te eDocument14 pages25mints Pt7 Te eyyNo ratings yet
- Year 12 MidDocument15 pagesYear 12 MidKissiedu YirenkyiNo ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers 08 EDocument12 pagesSuggestedAnswers 08 ERaiNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry AssignmentDocument11 pagesInorganic Chemistry AssignmentK VIKASNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sample Paper Coordination CompoundDocument14 pagesChemistry Sample Paper Coordination Compoundbachpankapyar071No ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Structured QuestionsDocument22 pagesChapter 12 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Structured QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 10 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Assertion-Reason QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 12 Assertion-Reason Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Structured QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Structured QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Structured Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document59 pagesBook 2tony ho100% (1)
- 3 Domestic Electricity: Practice 3.1 (p.133)Document8 pages3 Domestic Electricity: Practice 3.1 (p.133)teresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- 1 Electrostatics: Practice 1.1 (p.20)Document11 pages1 Electrostatics: Practice 1.1 (p.20)Jerry ChanNo ratings yet
- TM 402Document12 pagesTM 402ArPo HoNo ratings yet
- NSSBIO3E Skills Data Handling Intrepret Line Graph Ts&Ss eDocument8 pagesNSSBIO3E Skills Data Handling Intrepret Line Graph Ts&Ss eramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- QB 1A ch05 e QuestionsDocument12 pagesQB 1A ch05 e Questionsteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Level of Organization: Powerpoint Lecture Presentations Prepared by Jason LapresDocument125 pagesThe Chemical Level of Organization: Powerpoint Lecture Presentations Prepared by Jason LapresRindNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 f4 KSSM - Student 2021Document101 pagesChap 3 f4 KSSM - Student 2021Koo Rui CheeNo ratings yet
- Curphy-Morrison Additivity Constant For H NMRDocument2 pagesCurphy-Morrison Additivity Constant For H NMRDeshan WolfeyNo ratings yet
- TEST-17: JEE MainDocument20 pagesTEST-17: JEE MainRdNo ratings yet
- OMFDocument16 pagesOMFDuy AnhNo ratings yet
- 2 CLab ManualDocument129 pages2 CLab ManualMomerNo ratings yet
- Chlorosulfuric AcidDocument2 pagesChlorosulfuric AcidChristine Juliana CiembolonzNo ratings yet
- Biospada Plus 60 Technical Data Sheet - CopiarDocument2 pagesBiospada Plus 60 Technical Data Sheet - CopiarPablo CuellarNo ratings yet
- Biological Corrosion FailuresDocument10 pagesBiological Corrosion FailuresJose QuiinteroNo ratings yet
- BPI Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesBPI Exam QuestionsKatarina ElezNo ratings yet
- Mor Et Al., (2006)Document22 pagesMor Et Al., (2006)Fatin Al-Khuza'iNo ratings yet
- Single Bond Universal - TPP - CEE-LA-APAC - PDFDocument40 pagesSingle Bond Universal - TPP - CEE-LA-APAC - PDFNabel ramiNo ratings yet
- Ferro Manganese Slag PDFDocument2 pagesFerro Manganese Slag PDFDebraNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane WSDocument2 pagesCell Membrane WSDana FransenNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6:: Write and Balance Chemical EquationsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 6:: Write and Balance Chemical EquationsMARIEL PULBOSANo ratings yet
- Chemical Formula NamesDocument8 pagesChemical Formula NamesJeni PNo ratings yet
- Products Beverage AllDocument7 pagesProducts Beverage AllMariane KaiNo ratings yet
- 2000-2019 Nesa Chemistry Advanced Level-1Document269 pages2000-2019 Nesa Chemistry Advanced Level-1Jeff AlbaNo ratings yet
- Use of Biogas in Fuel CellsDocument18 pagesUse of Biogas in Fuel CellsManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- BMCDocument24 pagesBMCAhsan Sial AhsanNo ratings yet
- Primary Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and PotassiumDocument3 pagesPrimary Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and PotassiumPoonam JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Fenvik, მარტი 2012Document50 pagesFenvik, მარტი 2012emediageNo ratings yet
- Sydney Grammar 2014 Chemistry Prelim HY & SolutionsDocument52 pagesSydney Grammar 2014 Chemistry Prelim HY & SolutionsgihanbajitheNo ratings yet