Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp-5 Sep of Losses
Uploaded by
Vamsi RamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp-5 Sep of Losses
Uploaded by
Vamsi RamCopyright:
Available Formats
BEE LAB OBSERVATION
EXPERIMENT-5
SEPERATION OF LOSSES AND DETERMINATION OF
STRAY LOSSES
BVCITS EEE PAGE NO-
BEE LAB OBSERVATION
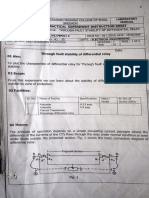
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
BVCITS EEE PAGE NO-
BEE LAB OBSERVATION
EXPT NO: 5 DATE:
SEPERATION OF LOSSES AND DETERMINATION OF
STRAY LOSSES
AIM:
To determine the stray losses in dc shunt machine and separate the different losses
APPARATUS REQURIED:
S no Name of the Range type Quantity
apparatus
1. Ammeter 0-2 A Moving coil 1 No.
0-5 A Moving coil 1 No.
2. Voltmeter 0-300 V Moving coil 1 No.
0-30 v Moving coil 1 No.
3. Tacho meter 0-10000 rpm Digital 1 No.
4. Rheostats 360 ohms/1.6 A Wire wound 1 No.
50 ohms/5 A Wire wound 1 No.
5. Connecting
wires - - -
THEORY:
When a machine is loaded, the load current establishes an M.M.F which appreciably changes the space distribution of air
gap flux density wave. This leads to an increase in the core loss from no load to full load. This increment in core loss caused by
distortion of the air gap flux plus the increment in (i2r) loss due to non-uniform distribution of conductor current is called stray load
loss. In other words, stray load loss consists of two components, one originating in iron parts and other in the armature conductors.
In iron parts, the stray load loss consists of the eddy current loss in the stator frame, end covers etc., caused by the armature leakage
flux load under load and the increased teeth loss due to distortion of the flux density wave. In the conductors, the stray load loss is
due to the circulating currents set up in the conductors by the alternating leakage flux produced by load current. These circulating
currents make the conductor current distribution non uniform and a result effective resistance of conductor increases. This gives
rise to additional conductor loss, called stray load loss. These losses are cannot be determined accurately. In dc machines by
convention, it is taken as 1% of the rated output for rating above 150kw. For synchronous and induction machines, it is taken as
0.5% of their rated output.
BVCITS EEE PAGE NO-
BEE LAB OBSERVATION
TABULAR COLOUMN:
If =0.7A
If = 0.9A
MODEL GRAPH
BVCITS EEE PAGE NO-
BEE LAB OBSERVATION
PROCEDURE:
1. Make the connection are given as per ckt diagram
2. Apply 220 v, dc supply to the motor by closing DPST switch
3. Motor is started with the help of 3 –point starter with no –load.
4. Check the speed of the motor by using tachometer and motor made to run at rated speed
by adjusting armature rheostat and field rheostat
5. The field current is adjusted to desired value, i.e,.0.7amps at no-load the readings of
voltmeter, ammeter and speed are noted down at given field current.
6. By varying armature rheostat in steps and note down V, A, and N at 0.7 amps
7. The armature rheostat brings to initial position (max)and respect the same procedure at
another field current i.e, 0.9 amps by adjusting field rheostat
8. Bring all the rheostats to their original position and open the DPST switch.
9. Now measure armature resistance from the drop test.
PRECAUTIONS:
1. Motor field rheostat must be kept in minimum resistance position.
2. Starter arm must be in OFF position.
3. Connections should be tight and reading should be without any parallax error.
RESULT:
Hence, the stray losses in dc shunt machine and separation of the different losses are
determined.
BVCITS EEE PAGE NO-
You might also like
- Ethernet Cable CrimpingDocument3 pagesEthernet Cable CrimpingsunilsjadhavNo ratings yet
- Witness ManualDocument131 pagesWitness ManualJustin Dean MurrayNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine-Ii Lab ManualDocument33 pagesElectrical Machine-Ii Lab ManualTauhidul Haque100% (1)
- Exp-6 Load Test On DC Series GenDocument5 pagesExp-6 Load Test On DC Series GenVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Exp-1 Mag CharDocument5 pagesExp-1 Mag CharVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Exp-9 Reg of Alternator - RemovedDocument6 pagesExp-9 Reg of Alternator - RemovedVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Exp-7 OC & SC TestDocument7 pagesExp-7 OC & SC TestVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Swinburns'S Test On D.C Shunt MachineDocument15 pagesSwinburns'S Test On D.C Shunt MachineharimadhavareddyNo ratings yet
- Exp-4 Speed ControlDocument5 pagesExp-4 Speed ControlVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Anderson'S Bridge & Schering'S BridgeDocument54 pagesAnderson'S Bridge & Schering'S BridgeSaad Bin MunirNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engg Laboratory ManualDocument25 pagesBasic Electrical Engg Laboratory ManualDheerenNo ratings yet
- Open Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt GeneratorDocument5 pagesOpen Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt Generatorramniwas123No ratings yet
- EM-1 LabDocument49 pagesEM-1 LabApoorvNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory ManualDocument36 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory Manualjith16No ratings yet
- Bee Lab Manual R19Document25 pagesBee Lab Manual R19Sudharshan ChennupalliNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 N 2Document16 pagesExp 1 N 2mallikarjunbpatilNo ratings yet
- 120EE1098 - Vennela Medaboina - Merged BEE Report-CompressedDocument83 pages120EE1098 - Vennela Medaboina - Merged BEE Report-CompressedSahasrabda Sai PradhanNo ratings yet
- Exp-2 Brake Test On Shunt MotorDocument5 pagesExp-2 Brake Test On Shunt MotorVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- EM-I LAB-finalDocument114 pagesEM-I LAB-finalHarimadhavareddy YenireddyNo ratings yet
- Ee2259 LMDocument90 pagesEe2259 LMPradeep KNo ratings yet
- s5 Lab Manual Full FinalDocument45 pagess5 Lab Manual Full FinalananyadeviashokkumarNo ratings yet
- Exp-8 Sump TestDocument7 pagesExp-8 Sump TestVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- EE8311 Electrical Machines Lab - 1 Manual PDFDocument67 pagesEE8311 Electrical Machines Lab - 1 Manual PDFkrishnandrk100% (2)
- 142 No Load and Block Rotor Test 3 PH Ind Motor Dol PDFDocument15 pages142 No Load and Block Rotor Test 3 PH Ind Motor Dol PDFGopinath B L NaiduNo ratings yet
- List of Experiments: Sno Name of The Experiment Date SignatureDocument41 pagesList of Experiments: Sno Name of The Experiment Date SignatureRajeshKanchanaNo ratings yet
- PSP Practical No 3,5,7Document11 pagesPSP Practical No 3,5,7Vivek BendeNo ratings yet
- OCC of DC GeneratorDocument4 pagesOCC of DC GeneratorsivaiahjettiNo ratings yet
- Em-1 LabDocument32 pagesEm-1 LabM Pavankumar PavanNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction Diode Characteristics: Edc Lab ManualDocument72 pagesP-N Junction Diode Characteristics: Edc Lab ManualPraneeth KUMAR.PNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine-II Laboratory Manual B.Tech, 3 Yr, 5 Semester, Electrical Engg. DeptDocument28 pagesElectrical Machine-II Laboratory Manual B.Tech, 3 Yr, 5 Semester, Electrical Engg. DeptMoumi PanditNo ratings yet
- EM-I LAB-finalDocument111 pagesEM-I LAB-finalHarimadhavareddy YenireddyNo ratings yet
- Dev Bhoomi Institute Chakrata Road, Navgaoun Manduwala, UttarakhandDocument32 pagesDev Bhoomi Institute Chakrata Road, Navgaoun Manduwala, UttarakhandRockstar RichNo ratings yet
- 4 Zener Voltage Regulator Diode Clippers ClampersDocument7 pages4 Zener Voltage Regulator Diode Clippers ClampersmakreloadedNo ratings yet
- EE3411 EM-II Lab Manual FinalDocument71 pagesEE3411 EM-II Lab Manual FinalManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8Document3 pagesExperiment 8buhbabfNo ratings yet
- DC Machines Lab ManualDocument5 pagesDC Machines Lab Manualhodeee eeeNo ratings yet
- Open Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt GeneratorDocument10 pagesOpen Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt Generatorramniwas123No ratings yet
- Ism LabDocument67 pagesIsm LabpadmavathiNo ratings yet
- Open Circuit and Short Circuit On Single Phase TransformerDocument9 pagesOpen Circuit and Short Circuit On Single Phase TransformerManju KommojuNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram For Brake Test On D.C.Shunt Motor: EM1 LAB, BVCR, RAJAHMUNDRY Prepared by K. Nagesh & V.D.NeelimaDocument4 pagesCircuit Diagram For Brake Test On D.C.Shunt Motor: EM1 LAB, BVCR, RAJAHMUNDRY Prepared by K. Nagesh & V.D.NeelimaPrabhu MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 N 2Document8 pagesExp 1 N 2mallikarjunbpatilNo ratings yet
- Em-Ii ExperimentDocument19 pagesEm-Ii Experimentprince rajNo ratings yet
- Brake Test On Three Phase Induction MotorDocument31 pagesBrake Test On Three Phase Induction MotorLalam Hari CharanNo ratings yet
- Drop Test For R:: Circuit Diagram For Load Test On D.C. Compound GeneratorDocument4 pagesDrop Test For R:: Circuit Diagram For Load Test On D.C. Compound Generatorالموعظة الحسنه chanelNo ratings yet
- Site Test Report: Accuracy Testing of Energy Meter - ElsterDocument4 pagesSite Test Report: Accuracy Testing of Energy Meter - Elstersalman100% (1)
- 1no Load-And-Blocked-Rotor-Test-On-Single Phase-Induction MotorFF PDFDocument5 pages1no Load-And-Blocked-Rotor-Test-On-Single Phase-Induction MotorFF PDFkobamelo LetowaNo ratings yet
- Binder 1Document48 pagesBinder 1deepanshu rajputNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledUdi AsulinNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Alternators by Emf Method: Ex - NoDocument5 pagesRegulation of Alternators by Emf Method: Ex - NosellakumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 03Document6 pagesLab 0349 - 103 - Umair Hossain100% (1)
- Exp 10 PostlabDocument19 pagesExp 10 PostlabjatinNo ratings yet
- Experiment No - Measurement of ResistanceDocument5 pagesExperiment No - Measurement of ResistanceAppu ParoorNo ratings yet
- Expt IEDocument68 pagesExpt IEDipali Awate KorkeNo ratings yet
- No Load and Block Rotor Test 3 PH Ind Motor DolDocument14 pagesNo Load and Block Rotor Test 3 PH Ind Motor DolalexNo ratings yet
- Site Test Report: Accuracy Testing of Energy Meter - ElsterDocument4 pagesSite Test Report: Accuracy Testing of Energy Meter - ElstersalmanNo ratings yet
- PS Lab Maual 7052 - MasterDocument70 pagesPS Lab Maual 7052 - MasterSunilNo ratings yet
- Magnetization Characteristics of A D.C. Shunt Generator: Exp. No: DateDocument60 pagesMagnetization Characteristics of A D.C. Shunt Generator: Exp. No: DateSuyash SinghNo ratings yet
- KEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEDocument34 pagesKEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEAkshat GuptaNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab Manual EeeDocument106 pagesEDC Lab Manual EeeVishnu Kumar NadarNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignFrom EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- 22 Batch 2 Sem TimetableDocument4 pages22 Batch 2 Sem TimetableVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- UdaysopsDocument6 pagesUdaysopsVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- 9.1 CentralDocument6 pages9.1 CentralVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Geo Tagged Class Rooms: Bonam Venkata Chalamayya Institute of Technology & ScienceDocument4 pagesGeo Tagged Class Rooms: Bonam Venkata Chalamayya Institute of Technology & ScienceVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Skill CourseDocument1 pageSkill CourseVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Bonam Venkata Chalamayya Institute of Technology & Science Library & Information Centre Consolidated ReportDocument1 pageBonam Venkata Chalamayya Institute of Technology & Science Library & Information Centre Consolidated ReportVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Individuals 2023Document7 pagesIndividuals 2023Vamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Exp-4 Speed ControlDocument5 pagesExp-4 Speed ControlVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- S. No. Name of The Experiment Page No. Sig of Faculty Cycle-IDocument1 pageS. No. Name of The Experiment Page No. Sig of Faculty Cycle-IVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Exp-3 Swinburns TestDocument5 pagesExp-3 Swinburns TestVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Exp-2 Brake Test On Shunt MotorDocument5 pagesExp-2 Brake Test On Shunt MotorVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Exp-8 Sump TestDocument7 pagesExp-8 Sump TestVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Work Load 2021-22 IDocument7 pagesWork Load 2021-22 IVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Exp-10 Brake Test On IMDocument8 pagesExp-10 Brake Test On IMVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Bee Cover PageDocument12 pagesBee Cover PageVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Transmission LineDocument9 pagesTransmission LineVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Iii Eee TTDocument1 pageIii Eee TTVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- II B.tech Time Tables NewDocument1 pageII B.tech Time Tables NewVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- II B.tech Time Tables NewDocument1 pageII B.tech Time Tables NewVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Individual Time TableDocument8 pagesIndividual Time TableVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- L U N C H: B V C Institute of Technology and Science::AmalapuramDocument1 pageL U N C H: B V C Institute of Technology and Science::AmalapuramVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- L U N C H: B V C Institute of Technology and Science: AmalapuramDocument4 pagesL U N C H: B V C Institute of Technology and Science: AmalapuramVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- IAENG Membership 234119Document1 pageIAENG Membership 234119Vamsi RamNo ratings yet
- III Yr Time Tables NewDocument1 pageIII Yr Time Tables NewVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Iv B.Tech I Sem Eee Inst Mid IiDocument1 pageIv B.Tech I Sem Eee Inst Mid IiVamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Literature Survey: Product DescriptionDocument6 pagesLiterature Survey: Product DescriptionBryan Rex AnggaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Environment of AirtelDocument7 pagesMarketing Environment of AirtelTakauv-thiyagi Thiyagu0% (1)
- 74LVC2G240Document17 pages74LVC2G240Hamzah JaNo ratings yet
- P6NK90ZDocument13 pagesP6NK90ZVictor ChangNo ratings yet
- SoundLink Revolve +Document32 pagesSoundLink Revolve +Vicente FernandezNo ratings yet
- A Briefing On IEEE 1149.1 - 1990 Standard Test Access Port and Boundary-Scan Architecture (AKA JTAG)Document12 pagesA Briefing On IEEE 1149.1 - 1990 Standard Test Access Port and Boundary-Scan Architecture (AKA JTAG)Raghul SambathkumarNo ratings yet
- PG HandbookDocument106 pagesPG HandbookYusri JumatNo ratings yet
- Tas 5142Document34 pagesTas 5142Dragan SurlanNo ratings yet
- FH-P4200MP: Connecting The UnitsDocument4 pagesFH-P4200MP: Connecting The UnitsJeremy NordenNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet: Acti 9 - MIN - Electromechanical Timer - Adjustable From 1 To 7 MinutesDocument2 pagesProduct Data Sheet: Acti 9 - MIN - Electromechanical Timer - Adjustable From 1 To 7 MinutesSamsung JosephNo ratings yet
- Jr. Engineer Power Electrical WAPDA 2018Document50 pagesJr. Engineer Power Electrical WAPDA 2018Hamza IzharNo ratings yet
- Ict114 Lecture 2Document7 pagesIct114 Lecture 2Shirley LohNo ratings yet
- PA308 Installation ManualDocument80 pagesPA308 Installation Manualvene333No ratings yet
- Toshiba Satellite C650 Inwertec Manaus Mas10m Premp Build Rev A02 PDFDocument52 pagesToshiba Satellite C650 Inwertec Manaus Mas10m Premp Build Rev A02 PDFThomas DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Application of WLAN To Automatic VehiclesDocument25 pagesApplication of WLAN To Automatic VehiclesClassic PrintersNo ratings yet
- Sweep GeneratorDocument9 pagesSweep GeneratorHaridas C SNo ratings yet
- P340 Opman Eng - 06Document91 pagesP340 Opman Eng - 06Matias Contreras KöbrichNo ratings yet
- Determining Burden For CTDocument2 pagesDetermining Burden For CTajaysitaula8478No ratings yet
- COD Unit 3 PDFDocument46 pagesCOD Unit 3 PDFYash Gupta MauryaNo ratings yet
- 1MRK509007-BEN en Directional Time-Overcurrent Relays and Protection Assemblies Based On Single Phase Elements RXPDK2HDocument22 pages1MRK509007-BEN en Directional Time-Overcurrent Relays and Protection Assemblies Based On Single Phase Elements RXPDK2HAffanFathurNo ratings yet
- MAX232x Dual EIA-232 Drivers/Receivers: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument26 pagesMAX232x Dual EIA-232 Drivers/Receivers: 1 Features 3 DescriptionIlson JuniorNo ratings yet
- Yahclick: Satellite InternetDocument6 pagesYahclick: Satellite InternetVasco JosephNo ratings yet
- Any Any Inverter M Model: Compatible With Al L Models of Inverter ProductsDocument2 pagesAny Any Inverter M Model: Compatible With Al L Models of Inverter Productsmanlu1001565100% (1)
- VPNDocument44 pagesVPNShahzaib RaufNo ratings yet
- Mobile CommunicationsDocument31 pagesMobile Communicationssuid111100% (1)
- Bird Senors Test Measurement CatalogDocument84 pagesBird Senors Test Measurement CatalogrustyNo ratings yet
- Synopsis Format 6th Sem JDCOEM GRP 4Document17 pagesSynopsis Format 6th Sem JDCOEM GRP 4Prajwal BhajeNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument1 pageGujarat Technological University: InstructionsHardik PatoliyaNo ratings yet