Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microbiology & Parasitology 2
Uploaded by
Christine Magbata0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesOriginal Title
MICROBIOLOGY & PARASITOLOGY 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views3 pagesMicrobiology & Parasitology 2
Uploaded by
Christine MagbataCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
MICROBIOLOGY & PARASITOLOGY
Microbiology for the health sciences
CLASSIFICATION OF Algae
MICROORGANISMS
Unicellular or multicellular eukaryotes
Some of them are not alive obtains nourishment by photosynthesis
they are the largest number of living lives in water, damp soil, and rocks
organism on the planet produces oxygen and carbon dioxide by
in 1674 ANTON VAN LEEUWOENHOEK other organisms
observed microorganisms for the first time
MICROORGANISM Virus
the uni-celllar (single celled) or multi cellular Tiny infectious particle that lives inside of a
organisms which are invisible to the naked living organism
eye when taken individually are called noncellular entities that consist of nucleic
microorganisms acid core (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a
bacteria, fungi, protozoa, algae, virus. protein coat.
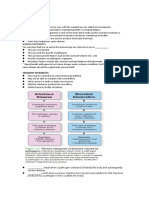
Bacteria Function and structure of
Unicellular organisms Eukaryotic cells
lacks nucleus (prokaryotic)
exist is shapes such as : coccus, bacillus, EUKARYOTIC CELL
spirilla and vibrio. have nucleus enclosed within the nuclear
can either be classified as "GRAM-POSITIVE" membrane and from large and complex
or "GRAM NEGATIVE" organism.
classified under kingdom EUKARYOTA
Fungi
carries out various metabolic reactions
Eukaryotic cells CHARACTERISTICS OF EUKARYOTIC CELL
multicellular and cell walls are composed of 1. have nucleus enclosed within a nuclear
chitin membrane
obtains nutrients by absorbing organic 2. has mitochondria
material in the environment., through 3. flagella and cilia are the locomotory organs
symbiotic with plants, or symbiotic with a 4. cell wall is the outermost layer
host 5. divides by mitosis
Protozoa 6. contains cytoskeletal structure
7. contains single linear DNA, which carries all
Unicellular aerobic eukaryotes the genetic information.
obtains nourishments by absorption or STRUCTURE
ingestion through specialized structures. PLASMA MEMBRANE- separates cell from
the cell walls are made up of cellulose outside environment
divided based on their locomotion CELL WALL- rigid structure present outside
use structures such as cilia, pseudopodia the plant cell.; provides shape and helps in
and flagella for locomotion. cell-to-cell interaction
VIRUSES
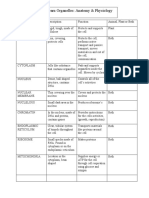
CYTOSKELETON- present inside cytoplasm, made up of genetic code and protected by
provides perfect shape to the cell, anchors protein coating
organelles and stimulate cell movement. PARASITES
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM- divides the cell organisms that behave like tiny animals,
into : luminal and extra luminal living on the host.
NUCLEUS- contains DNA and proteins,
ribosome production takes place here. Modes of disease transmission
GOLGI APPARATUS- Made up of cisternae
RIBOSOMES- main site of protein synthesis, CONTACT
composed of protein and ribonucleic acid. DIRECT- passed on from person to person
MITOCHONDRIA- powerhouse of the cell, without infecting an intermediate object or
helps regulate cell metabolism person. can be skin to skin or mucous
LYSOSOMES- aka suicidal bags, possess membrane to mucous membrane
hydrolytic enzymes to digest protein, lipids, INDIRECT- pathogens are transferred via a
carbohydrates an nucleic acid. contaminated intermediate object or
PLASTIDS- Double membraned structures. person. can be via food, water or fecal
matter, or even fomites that become
Normal Flora contaminated by respiratory secretions. or
via blood transfusion.
microbiota DROPLET
lives on specific locations of the body respiratory droplets carrying pathogens
they can be beneficial or just do nothing. transmits infection when they travel from
prevents the body to be colonized with respiratory tract of an infectious individual.
dangerous bacteria droplet traditionally have been larger than
subjected to phagocytosis and do not 5J.1 m in size.
produce toxins AIRBORNE
in case of weak immune system, normal occurs with dissemination of either airborne
flora van become pathogenic droplet nuclei or small particles containing
might cause infection if they move outside pathogens
of their normal habitat VEHICULAR
RESIDENT FLORA involves contaminated inanimate objects
Occupy a particular body site VECTOR
TRANSIENT FLORA includes bites of insects or arachnids
found on the outer surface of the skin and
easily removed by hand washing
Pathogens
an organism causing disease
can cause health issues
adhere to the cell and tissues and invades
the cell
resistant against phagocytosis
produces toxins and can alter metabolism of
the host cell
BACTERIA
microorganism made of single cell
FUNGI
can be found everywhere even in human
skin
How infections develop in humans SPLEEN
blood filtering organ that removes microbes
BACTERIA and destroys and removes old and damaged
when bacteria enters the body and increase RBC
number inside BONE MARROW
FUNGI spongy tissue found inside the bones,
inhalation or landed spores on the skin, produces RBC and WBC and platelets
most likely to happen in those who have THYMUS
weakened immune system filter and monitors blood content
PRIONS producces T- lymphocytes
spread throughout lymphatic tissue and the
How immune system eliminates
enteric nervous system, finally reaching the
CNS, infects neurons then replicate microbes
PARASITES ANTIBODIES HELP THE BODY FIGHT THE
intake of water contaminated by parasites. MICROBES OR TOXINS THEY PRODUCE
they recognize antigens on the surface of
Immune system the microbes which marks them as foreign
they then destroy the microbes.
helps the body fight infections and other
diseases.
includes WBC and organs and tissues of
lymphatic system
differentiate non-self and self, and destroy
non-self
3rd line of defense.
Component of Immune system
WBC
made on the bone marrow and is part of the
lymphatic system.
move throughout the body looking for
foreign invaders
includes lymphocytes (B-cell, T- cell and
natural killer cells)
ANTIBODIES
protective proteins produced by the
immune system
attaches to antigens and remove them from
the body
COMPLEMENT SYSTEM
made up of proteins whose actions
complements the work of antibodies
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
network or delicate tubes all throughout the
body.
made up of lymph nodes, lymph vessels and
WBC
You might also like
- The Antibiotic Alternative: The Natural Guide to Fighting Infection and Maintaining a Healthy Immune SystemFrom EverandThe Antibiotic Alternative: The Natural Guide to Fighting Infection and Maintaining a Healthy Immune SystemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To MicrobiologyKarryle AbinanNo ratings yet
- Prelims Micropara LecDocument14 pagesPrelims Micropara LecBSN1F- JACILDO, KUH KYLA C.No ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology OverviewDocument50 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology OverviewmichaelNo ratings yet
- Yeast Fermentation: Investigatory Project Class 12Document31 pagesYeast Fermentation: Investigatory Project Class 12avantika rajeev69% (29)
- The Microbial World & You: NomenclatureDocument9 pagesThe Microbial World & You: NomenclatureApryll DarlineNo ratings yet
- Modern Biology ReviewerDocument3 pagesModern Biology Reviewer22-02442No ratings yet
- Types of Pathogen Infographic/Poster)Document3 pagesTypes of Pathogen Infographic/Poster)merliahranNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Amino AcidDocument5 pagesVocabulary Amino AcidbenjaminNo ratings yet
- Diseased Cause by BacteriaDocument2 pagesDiseased Cause by BacteriaGraciaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Notes Final-2Document58 pagesMicrobiology Notes Final-2arvindk962706No ratings yet
- Microbiology: FungiDocument6 pagesMicrobiology: FungiJohn CedricNo ratings yet
- Form 4Hk/Year 10 Biology Characteristics and Diagrams of Bacteria, Viruses and FungiDocument12 pagesForm 4Hk/Year 10 Biology Characteristics and Diagrams of Bacteria, Viruses and FungiShadreck MagangaNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms: Compulsory TextDocument8 pagesMicroorganisms: Compulsory TextAna CecansciucNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Life Sciences Remote Learning Booklet - Term 1Document56 pagesGrade 11 Life Sciences Remote Learning Booklet - Term 1lungstachapterNo ratings yet
- Compare microbes in cells, shapes and reproductionDocument5 pagesCompare microbes in cells, shapes and reproductionJemima Kesia ApallaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.2 Chapter 4: Acellular and Prokaryotic Microbes Chapter No. & TitleDocument4 pagesAssignment No.2 Chapter 4: Acellular and Prokaryotic Microbes Chapter No. & TitleBridgette ArandilaNo ratings yet
- Life Science StudyGuideDocument113 pagesLife Science StudyGuideNthabeleng RamotseoaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction to Microbiology and ParasitologyROBYLYN C. GAVINNo ratings yet
- Definition, Scope and History of MicrobiologyDocument13 pagesDefinition, Scope and History of MicrobiologySakshiNo ratings yet
- Cell Cell The Cell Cycle: (Before) NucleusDocument2 pagesCell Cell The Cell Cycle: (Before) NucleusRyan ForteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells (Dalman, Jhaziel)Document9 pagesChapter 2: Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells (Dalman, Jhaziel)Jhaziel Elizabeth C. DalmanNo ratings yet
- Crizzel Ruth Padernal Castor GWAPADocument73 pagesCrizzel Ruth Padernal Castor GWAPACrizzel Ruth CastorNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function PPT 4LRDocument21 pagesCell Structure and Function PPT 4LRKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- C5 - Eukayotic MicrobesDocument5 pagesC5 - Eukayotic MicrobesSchool driveNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument12 pagesBiodiversityDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Excreta Related Pathogen, Pathogen Treatment and Control in Wastewater and Sludge Treatment ProcessDocument28 pagesTopic 5 Excreta Related Pathogen, Pathogen Treatment and Control in Wastewater and Sludge Treatment ProcessSyarifah Anis AqilaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.1 CellDocument9 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.1 CellJosebeth CairoNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: BacteriaDocument11 pagesBiodiversity: BacteriaKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesMicrobiologycoolinkenanatamNo ratings yet
- The Eukaryotes: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, & HelminthsDocument14 pagesThe Eukaryotes: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, & HelminthsApryll DarlineNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To MicrobiologyPringle Garcia CulinaNo ratings yet
- 2300 Module 3 Infection and MicrobiologyDocument33 pages2300 Module 3 Infection and Microbiologymegan.abbinkNo ratings yet
- Microbes in Our Lives: A Guide to MicroorganismsDocument12 pagesMicrobes in Our Lives: A Guide to MicroorganismsBeatrix Adrianna PabulayanNo ratings yet
- Micropara ReviewerDocument9 pagesMicropara ReviewerTricia Maxine DomingoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Microbiology UNIT 1Document43 pagesEnvironmental Microbiology UNIT 1Esai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Protist and FungiDocument19 pagesProtist and FungiNesel AlacarNo ratings yet
- Medical Microbiology: Microbial Colonization May Result inDocument4 pagesMedical Microbiology: Microbial Colonization May Result inHossam HafezNo ratings yet
- Clnical Bacteriology Chapter 1Document11 pagesClnical Bacteriology Chapter 1miguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2ngelo.garolNo ratings yet
- Micro 1st ProkaryotesDocument16 pagesMicro 1st ProkaryotesMatahari SempurnaNo ratings yet
- 1 Lec HistoryDocument10 pages1 Lec Historycharizepascual110899No ratings yet
- Kingdom Monera: Bacteria Structure, Growth, Reproduction & ClassificationDocument5 pagesKingdom Monera: Bacteria Structure, Growth, Reproduction & ClassificationMSNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To MicrobiologySeon u 'No ratings yet
- 1 IntroDocument5 pages1 IntroJeanjayannseptoemanNo ratings yet
- FUNGI AND PROTOZOA FACTSDocument46 pagesFUNGI AND PROTOZOA FACTSNelson michaelNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - INTRO TO BIOCHEM (LESSON 2)Document6 pagesMODULE 1 - INTRO TO BIOCHEM (LESSON 2)janmariefernandez0No ratings yet
- 1 BiodiversityDocument10 pages1 BiodiversityjoyuqueioNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Course OverviewDocument34 pagesMicrobiology Course OverviewSELVI ANo ratings yet
- Micropara ReviewerDocument12 pagesMicropara ReviewerAlyssa Mae Azarcon100% (1)
- Chapter 1 ReviewDocument6 pagesChapter 1 ReviewDung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Microbiology (Laden Saleh) FinalDocument240 pagesMicrobiology (Laden Saleh) FinalLaden SalehNo ratings yet
- Understanding Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument17 pagesUnderstanding Prokaryotes and EukaryotesjasminedevesaNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Cell OrganisationDocument3 pagesGeneral Principles of Cell Organisation22194No ratings yet
- Unit 1 MICROORGANISMSDocument68 pagesUnit 1 MICROORGANISMSNatayNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and BiotechniquesDocument8 pagesMicrobiology and BiotechniquesAlanie RakimNo ratings yet
- History of Microbiology: Cell TheoryDocument3 pagesHistory of Microbiology: Cell TheoryPrince Jireh MoralesNo ratings yet
- Normal Flora of the Human BodyDocument8 pagesNormal Flora of the Human BodyProssy Arks100% (1)
- ENMANUEL MC 3 BSN1 Assignment No. 2 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic First TrinalDocument6 pagesENMANUEL MC 3 BSN1 Assignment No. 2 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic First TrinalJason Carbon EnmanuelNo ratings yet
- Self-Study Guide Questions #1: Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocument4 pagesSelf-Study Guide Questions #1: Prokaryotes EukaryotesDaniel EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Medical Microbiology GuideDocument5 pagesMedical Microbiology GuideChristine MagbataNo ratings yet
- Microbiology & Parasitology 3Document3 pagesMicrobiology & Parasitology 3Christine MagbataNo ratings yet
- Medical Microbiology GuideDocument13 pagesMedical Microbiology GuideChristine MagbataNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Practice Medication GuideDocument23 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Practice Medication GuideChristine MagbataNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics (How The Body Converts Food To Energy)Document59 pagesBioenergetics (How The Body Converts Food To Energy)Mary Rose Bobis Vicente100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Test BankDocument11 pagesChapter 11 Test Bankanon_747148947No ratings yet
- Free Radicals: Understanding the BasicsDocument4 pagesFree Radicals: Understanding the BasicsRavi PreethiNo ratings yet
- Sbi 4U1 Exam Evaluation Outline: Section Marks Time (Min) Student Score Knowledge Thinking/InvestigationDocument2 pagesSbi 4U1 Exam Evaluation Outline: Section Marks Time (Min) Student Score Knowledge Thinking/InvestigationEmanNo ratings yet
- Methanobacterium BryantiiDocument1 pageMethanobacterium Bryantiimino loliNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document11 pagesLec 1Ahmed JamalNo ratings yet
- 2 PharmacodynamicsDocument51 pages2 PharmacodynamicsKriziaoumo P. Orpia100% (1)
- Glencoe Biology Textbook Glossary 2010Document84 pagesGlencoe Biology Textbook Glossary 2010Bradford McCallNo ratings yet
- S11.12LT IIbd 6Document16 pagesS11.12LT IIbd 6merliza caguisaNo ratings yet
- MICRODocument9 pagesMICROCyrelle Heart YoshikawaNo ratings yet
- Botanica Lab Virtual 1Document8 pagesBotanica Lab Virtual 1Equalis SantosNo ratings yet
- Transes Anaphy BloodDocument5 pagesTranses Anaphy BloodPia LouiseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Animal Cell Types and TissuesDocument67 pagesLecture 1 - Animal Cell Types and TissuesEthel Gerardo PabloNo ratings yet
- Unit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFDocument47 pagesUnit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFanuksha aroraNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics of Exercise and TrainingDocument62 pagesBioenergetics of Exercise and Trainingswordplay716No ratings yet
- Highly-Purified Exosomes and Shed Microvesicles Isolated From The Human Colon Cancer Cell Line LIM1863 by Sequential Centrifugal Ultrafiltration Are Biochemically and Functionally DistinctDocument15 pagesHighly-Purified Exosomes and Shed Microvesicles Isolated From The Human Colon Cancer Cell Line LIM1863 by Sequential Centrifugal Ultrafiltration Are Biochemically and Functionally DistinctLidia RLNo ratings yet
- MEDBIO KROK-1 English 2019-2020Document65 pagesMEDBIO KROK-1 English 2019-2020Катерина КабишNo ratings yet
- Unit: Genetics and Biotechnology: NYCTA Unit Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesUnit: Genetics and Biotechnology: NYCTA Unit Plan Templateapi-466659492No ratings yet
- DNA Isolation from Bacteria and YeastDocument7 pagesDNA Isolation from Bacteria and Yeastdyalcin2No ratings yet
- Enzyme Commission Number (EC Number)Document1 pageEnzyme Commission Number (EC Number)Sunil BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Manifestation of Life A. Structural Organization: Catherine Genevieve Barretto-LagunzadDocument5 pagesManifestation of Life A. Structural Organization: Catherine Genevieve Barretto-LagunzadNoelle HarrisonNo ratings yet
- 2nd Open Book Exam, Aseel AlharbiDocument6 pages2nd Open Book Exam, Aseel Alharbiعبدالرحمن الحربيNo ratings yet
- XL22 - Basic HaematologyDocument18 pagesXL22 - Basic HaematologyAdi TrisnoNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Genetic InformationDocument13 pagesTransfer of Genetic InformationjaneNo ratings yet
- Organelle Review PackageDocument6 pagesOrganelle Review Packageapi-345120999No ratings yet
- Antibody Structure and Functions in Humoral ImmunityDocument30 pagesAntibody Structure and Functions in Humoral Immunitymohammed agungNo ratings yet
- Notes To Learn Organelles: Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument2 pagesNotes To Learn Organelles: Anatomy & PhysiologyJordane JordineNo ratings yet
- Targeted Genome Editing With A DNA-dependent DNA Polymerase and Exogenous DNA-containing TemplatesDocument21 pagesTargeted Genome Editing With A DNA-dependent DNA Polymerase and Exogenous DNA-containing TemplatesSabranth GuptaNo ratings yet
- Intracrine Sex Steroid Synthesis and Signaling in HumanDocument17 pagesIntracrine Sex Steroid Synthesis and Signaling in HumanMarcela DiasNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanism Involved in Process of Inflammation and RepairDocument32 pagesBasic Mechanism Involved in Process of Inflammation and RepairDeepakNo ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)