Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Reviwer
Uploaded by
Alejandro Peralta IIIOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Reviwer
Uploaded by
Alejandro Peralta IIICopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE
- Pressure
- Volatile
REVIEWER MAIN SOURCE OF GEOTHERMAL ENERGY
-presence of magma
-presence of water
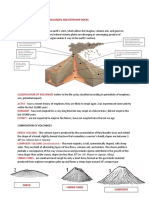
TYPES OF VOLCANOES -reservoirs
COMPOSITE VOLCANO -cap rock
- borad bases, steep sides, large crater, crater was created
during the last eruption. 3 DIFF DESIGNS OF GEOPLANT
SHIELD VOLCANO DRY STEAM PLANTS - steam
- bowl or shield, long gentle slopes, basaltic lava flows, low- FLASH PLANTS - high pressure of hot water
viscosity of lava flows. BINARY PLANTS - hot water
LAVA DOMES
- lava was too thick, steep-sided, highly viscous lava. Direct-use application
CINDER CONES Geothermal heat pumps (GHP’s)
- circular or oval cones, single vent, small pieces of scoria and Geothermal power plants
pyroplastic.
VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS INACTIVE - doesn’t erupt in 10000 years
- lava & gas are released from a volcano -sometimes
explosively.
HAWAIIAN
- thrown into the air in jets, fire fountains
STROMBOLIAN
- periodic weak to violent eruption, distinct burst of fluid lava.
VULCANIAN
- short violent, relatively small explosion of viscous lava, 20
km (tephra- rock ejected)
PLINIAN
- largest, most violent, release enormous amounts of energy,
50 km.
PHREATIC
- steam-driven explosion, occur when water beneath the
ground on the surface is heated by magma.
PELEAN
- eruption formes domes, glowing avalanches.
MAGMA
- molten rock found beneath earth surface.
BASALTIC MAGMA (MAFIC)
- Si02 44-55%
- 1000 to 1200 c
- distribution : divergent - divide
- viscosity: Low
ANDESITIC MAGMA (INTERMEDIATE)
- Si02 55-65%
- 800 to 1000 c
- distribution : convergent - collide
- viscosity: Intermediate
RHYOLITIC MAGMA (FELSIC)
- Si02 65-75%
- 650 to 800 c
- hot spots in continental crust
- viscosity: High
SILICA DIOXIDE (SILICA)
- basic building block of volcanic rocks, most important
factor.
3 WAYS TO GENERATE MAGMA
- Decompression melting
- Heat transfer
- Flux melting
SPECIAL CONDITION:
- Temperature
GEOTHERMAL POWER PLANT
- hot water
- steam
- turbine
- generator
- cooling tower
- injection well
RENEWABLE ENERGY
- can be replenished naturally over relatively short period of
time.
Solar energy-sun rays (solarpanel)
Wind energy-movement of air (windmill)
Hydro energy-movement of water (dam)
Geothermal energy-heat of the earth’s core
Biomass energy-organic matter
NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY
- cannot be replenished naturally over short period of time.
Coal -- Oil -- Natural gas -- Nuclear energy
(Fossil Fuels)
CLIMATE & WEATHER
CLIMATE - refers to the long term pattern of weather
condition.
WEATHER - refers to the condition of atmosphere.
FACTORS AFFECTING CLIMATE:
LATITUDE - distance from equator.
ALTITUDE - above sea level.
TOPOGRAPHY - shape & features of land.
OCEAN CURRENTS - flow of water in ocean
GREENHOUSE EFFECT
- trap heat from sun keeping planet warm
*human activities
*deforstation
*burning of fossil fuels
*intensive farming
GLOBAL WARMING
- increase in the average global temp.
*
CLIMATE CHANGE
- long term changes in earth’s climate
*animals *human health *melting glaciers *plants *change in
precipitation
CH4
N2O
H2O
CO2
LA NINA
- 9-12 months , El Viejo , more rains
EL NINO
- 2-7 years , strong typhoons , draught
You might also like
- VOLCANOESDocument40 pagesVOLCANOESQueenie Bars OgirdorNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Compaction ManualDocument25 pagesCaterpillar Compaction ManualSiegfred RaccaNo ratings yet
- Gas-Liquid Mass Transfer in Cellular Systems: A A AB ADocument7 pagesGas-Liquid Mass Transfer in Cellular Systems: A A AB AChristian Jay SabladaNo ratings yet
- Science 9Document4 pagesScience 9Mary Therese LimoconNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Unit 3 Module 1Document3 pagesScience 9 Unit 3 Module 1Jeddie SuanNo ratings yet
- RbbebDocument6 pagesRbbebauvqliaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesEarth Science ReviewerClarence DeitaNo ratings yet
- Volcano: Disrrr - MidtermsDocument13 pagesVolcano: Disrrr - MidtermsPrincess Gabrielle BrotonelNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer Q3 Grade 9 - Volcanic Eruptions and GeothermalDocument1 pageScience Reviewer Q3 Grade 9 - Volcanic Eruptions and GeothermalzaijiantalanNo ratings yet
- Science 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 3rd Quarter ReviewerXyra TabarinaNo ratings yet
- Science 3RD Quarter ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience 3RD Quarter Reviewer-Rain Santos-No ratings yet
- Science 9 ReviewerDocument6 pagesScience 9 ReviewerRenz Cedric MasaudlingNo ratings yet
- VOLCANO MendeleevDocument62 pagesVOLCANO MendeleevJuliana deLunaNo ratings yet
- Q3 Sci Rev FinalDocument10 pagesQ3 Sci Rev FinalReigne Daniella OgatisNo ratings yet
- Geology ReviewerDocument7 pagesGeology Reviewerpauljust.8080No ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equations Notes and Practice Problems Worksheet Pastel PrintableDocument6 pagesBalancing Chemical Equations Notes and Practice Problems Worksheet Pastel Printableawroo321No ratings yet
- Science 9 ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience 9 ReviewerJan Carlo Esmero100% (1)
- Lecture 5 - VolcanoesDocument45 pagesLecture 5 - VolcanoesDaniel MogorosiNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument25 pagesVolcanoesjenjang yannieNo ratings yet
- Science VolcanoDocument61 pagesScience VolcanoMiomi Venice LeongNo ratings yet
- Science 3rd Q RevDocument6 pagesScience 3rd Q Revethan elizaldeNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes g9Document33 pagesVolcanoes g9rvnsj28No ratings yet
- Classifications of VolcanoDocument53 pagesClassifications of VolcanoAthena Bermundo100% (1)
- Science Notes 1st MqeDocument4 pagesScience Notes 1st MqekarnsofiabNo ratings yet
- EARTH SCIENCE - 2Q - LessonsDocument1 pageEARTH SCIENCE - 2Q - LessonsMargarette MartinNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer: Lesson 1Document2 pagesScience Reviewer: Lesson 1AMIEL MOIRA BERNARDONo ratings yet
- DN Volcanic EruptionDocument3 pagesDN Volcanic EruptionArabellaNo ratings yet
- Science RevDocument8 pagesScience RevAndrea BascaraNo ratings yet
- Topics:: - Settings - Products - Eruptive Style of Volcanoes - Volcanism OccurrencesDocument38 pagesTopics:: - Settings - Products - Eruptive Style of Volcanoes - Volcanism OccurrencesPee JayNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science: Structure IsomersDocument2 pagesReviewer in Science: Structure IsomersSharlaine TandinganNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Reviewer-3rd Quarter SRSTHSDocument5 pagesGrade 9 Science Reviewer-3rd Quarter SRSTHSKaryll Heart Layug67% (3)
- Earthsci First Quarter ReviewerDocument3 pagesEarthsci First Quarter ReviewerLala CoronelNo ratings yet
- 9 QST 3 ScienceDocument9 pages9 QST 3 ScienceJhaniella QuinlogNo ratings yet
- MODULE 02: Earth's Processes: Differentiating Weathering and ErosionDocument15 pagesMODULE 02: Earth's Processes: Differentiating Weathering and ErosionAllyson Brianna MosqueraNo ratings yet
- VOLCANOESDocument45 pagesVOLCANOESCyrus Bantugon GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (3RD Quarter)Document9 pagesScience Reviewer (3RD Quarter)Smilingchae TomatominNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument37 pagesVolcanoesSHERRIE MAE BIJASANo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument3 pagesEarth Scienceromie bayetaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 ReviewerDocument2 pagesScience 9 ReviewerSamuel Arthur G. DomingoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of The Kamojang Geothermal Reservoir (West Java) As Revealed by Its Hydrothermal Alteration MineralogyDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of The Kamojang Geothermal Reservoir (West Java) As Revealed by Its Hydrothermal Alteration MineralogyMuhammad IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes PDFDocument2 pagesVolcanoes PDFRaphael Ivan FernandezNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sciencevolcanic EruptionsDocument46 pagesEarth and Life Sciencevolcanic EruptionsAngelou LagazonNo ratings yet
- Types of Volcanic EruptionsDocument1 pageTypes of Volcanic EruptionsDodong BagolorNo ratings yet
- Chapter05 VolcanoesDocument42 pagesChapter05 Volcanoes뚜뚜DDUDDUNo ratings yet
- Science MidtermsDocument3 pagesScience MidtermsGwynette Kei HernandezNo ratings yet
- DRRR Volcanoes ReviewerDocument27 pagesDRRR Volcanoes ReviewerAtria Mariz OrbistaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Earth and LifeDocument28 pagesScience 9 Earth and LifeJulliannah Claire GoteraNo ratings yet
- Nature and Types of Volcanoes Autosaved 1Document31 pagesNature and Types of Volcanoes Autosaved 1jairolostreNo ratings yet
- EALSFinalsDocument3 pagesEALSFinalsHannah EstebarNo ratings yet
- Volcanic HazardsDocument45 pagesVolcanic HazardsAlyanna ManaloNo ratings yet
- Week 1 TYPES OF VOLCANOESDocument2 pagesWeek 1 TYPES OF VOLCANOESNorraine Denice Jabalde NoricoNo ratings yet
- DRRR Mod 16 Mod 10 ReviewerDocument5 pagesDRRR Mod 16 Mod 10 ReviewerjohnzenurielalquisadaNo ratings yet
- Dostal 2008 Geosci Can KomatiiteDocument12 pagesDostal 2008 Geosci Can KomatiiteLIANo ratings yet
- Volcanoes - Module 1 FinalDocument69 pagesVolcanoes - Module 1 FinalAngel rose OrbeNo ratings yet
- Wiuhrq 2 IwDocument2 pagesWiuhrq 2 IwJhanna Gil BuctolanNo ratings yet
- Completion Keys PDFDocument2 pagesCompletion Keys PDFAishe Bheb EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes: ° °F) or Above, Found inDocument3 pagesVolcanoes: ° °F) or Above, Found innoah allenNo ratings yet
- Volcano TopicDocument63 pagesVolcano TopicannepauleentabangcurdaNo ratings yet
- CSSCI02Document2 pagesCSSCI02Bey VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Geol 100 VolcanoDocument16 pagesGeol 100 VolcanoTamio, Marc Angelo100% (1)
- Layers of The EarthDocument3 pagesLayers of The EarthZGB VlogsNo ratings yet
- InterferenceDocument13 pagesInterferenceYugandhar VeeramachaneniNo ratings yet
- Resume - Sanket D MankarDocument2 pagesResume - Sanket D MankariyergvNo ratings yet
- Lorentz Psk2 Cs FDocument51 pagesLorentz Psk2 Cs FSINES France100% (1)
- Chm131 Chapter 1 Atoms Molecules Ions Chemical EqDocument106 pagesChm131 Chapter 1 Atoms Molecules Ions Chemical EqAdibah Qistina QistinaNo ratings yet
- Vortex Tube PDFDocument9 pagesVortex Tube PDFGerryNo ratings yet
- Dehydrogenase Activity 3Document9 pagesDehydrogenase Activity 3Jesús FernandezNo ratings yet
- Odum Book5 - 6338920722970182133Document560 pagesOdum Book5 - 6338920722970182133Rajesh Upadhyay0% (1)
- Economics of Power GenerationDocument9 pagesEconomics of Power GenerationNitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CV Writing Style PDFDocument4 pagesCV Writing Style PDFgu_khanNo ratings yet
- General Education - Set B - Part 3Document6 pagesGeneral Education - Set B - Part 3Zhtem CruzadaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test-EcologyDocument4 pagesPractice Test-EcologyTracey MusclowNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Volume of Liquid PDFDocument8 pagesWorksheet Volume of Liquid PDFAzilawati YusofNo ratings yet
- 2010 NJC Prelim Physics H2 Paper 2 Suggested Solution For GÇDocument8 pages2010 NJC Prelim Physics H2 Paper 2 Suggested Solution For GÇcjcsucksNo ratings yet
- Author's Accepted Manuscript: Nano EnergyDocument52 pagesAuthor's Accepted Manuscript: Nano EnergySteven KmiecNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Edge BuildingDocument14 pagesJurnal Edge Buildingardina hendrianiNo ratings yet
- Solar Plan 10 KW-DR - Sudha PDFDocument7 pagesSolar Plan 10 KW-DR - Sudha PDFAravind PandianNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy: Ahmed Amine Hachicha, Israa Al-Sawafta, Dhouha Ben HamadouDocument14 pagesRenewable Energy: Ahmed Amine Hachicha, Israa Al-Sawafta, Dhouha Ben HamadouJuan ApzNo ratings yet
- Designs and Math For Self Sufficient Living 1981Document385 pagesDesigns and Math For Self Sufficient Living 1981MoreMoseySpeedNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Using Peltier Effect: Presented By, P.Selva Kumar K.VinoDocument12 pagesRefrigeration Using Peltier Effect: Presented By, P.Selva Kumar K.Vinovino kNo ratings yet
- Thesis Environmental LawDocument7 pagesThesis Environmental Lawafktmbstdtiobg100% (2)
- Kabeel, El-Samadony, El-Maghlany - 2018 - Comparative Study On The Solar Still Performance Utilizing Different PCM-annotatedDocument9 pagesKabeel, El-Samadony, El-Maghlany - 2018 - Comparative Study On The Solar Still Performance Utilizing Different PCM-annotatedFatma Saad Ep JellaliNo ratings yet
- Broadcast Engineering and Acoustics Expt. #3 FINALDocument15 pagesBroadcast Engineering and Acoustics Expt. #3 FINALMark Joshua DiamseNo ratings yet
- ! The Wavelike Properties of ParticlesDocument20 pages! The Wavelike Properties of ParticlesMLalli5340No ratings yet
- Lithium Titanate (LTO) Cells - Technical Advantages - Shop - GWL.euDocument9 pagesLithium Titanate (LTO) Cells - Technical Advantages - Shop - GWL.euBurak KucukkelesNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2772397621000265 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S2772397621000265 MainANAND KUMARNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals On HVAC Systems PresentationDocument52 pagesFundamentals On HVAC Systems PresentationJane NixonNo ratings yet
- Hysys ManualDocument26 pagesHysys ManualvasdevharishNo ratings yet
- Thesis Title: "Designing of A Green Roof Engineering: Systems"Document7 pagesThesis Title: "Designing of A Green Roof Engineering: Systems"marlon moralesNo ratings yet