Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class Rules School Education Infographic
Uploaded by
Stephanie Nichole Ian Casem0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views3 pagesThe document summarizes the stages of the cell cycle including interphase and mitosis. It describes the important events that occur during each phase such as DNA replication in S phase, cell growth and preparing for division in G2 phase. It then explains the key stages of mitosis in detail: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Chromosomes condense and align at the metaphase plate before separating and moving to opposite poles in anaphase. Finally, the nucleus and cell divide through cytokinesis to form two identical daughter cells each with a full set of chromosomes.
Original Description:
bio
Original Title
Class Rules School Education Infographic (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the stages of the cell cycle including interphase and mitosis. It describes the important events that occur during each phase such as DNA replication in S phase, cell growth and preparing for division in G2 phase. It then explains the key stages of mitosis in detail: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Chromosomes condense and align at the metaphase plate before separating and moving to opposite poles in anaphase. Finally, the nucleus and cell divide through cytokinesis to form two identical daughter cells each with a full set of chromosomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views3 pagesClass Rules School Education Infographic
Uploaded by
Stephanie Nichole Ian CasemThe document summarizes the stages of the cell cycle including interphase and mitosis. It describes the important events that occur during each phase such as DNA replication in S phase, cell growth and preparing for division in G2 phase. It then explains the key stages of mitosis in detail: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Chromosomes condense and align at the metaphase plate before separating and moving to opposite poles in anaphase. Finally, the nucleus and cell divide through cytokinesis to form two identical daughter cells each with a full set of chromosomes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
GENERAL BIOLOGY
STEPHANIE NICHOLE IAN A.CASEM(STEM 11-MERCURY)WEEK 6 ACTIVITY
ACTIVITY 1
ACTIVITY 2A :Directions: Study the given diagram and answer
the table below.
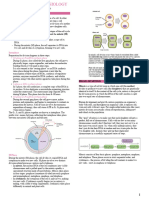
STAGES OF
CELL CYCLE
IMPORTANT EVENTS
G1 is an intermediate phase occupying the
time between the end of cell division in mitosis
G1 and the beginning of DNA replication,the cell
grows in size and synthesizes mRNA and
protein that are required for DNA synthesis
The S phase of a cell cycle occurs during
interphase, before mitosis or meiosis, and is
responsible for the synthesis or replication of
S DNA. In this way, the genetic material of a cell
is doubled before it enters mitosis or meiosis,
allowing there to be enough DNA to be split
into daughter cells the cell synthesizes a
complete copy of the DNA in its nucleus. It also
duplicates a microtubule-organizing structure
called the centrosome. The centrosomes help
separate DNA during M phase
The last part of interphase is called
the G2 phase. The cell has grown, DNA
G2 has been replicated, and now the cell
is almost ready to divide. This last
stage is all about prepping the cell for
mitosis or meiosis where it organizes
and condenses the genetic material,
or starts to condense the genetic
material, and prepares to divide.
Karyokinesis is mitotic nuclear
division,it is the division of the
nucleus that occurs in four
stages. They are prophase,
metaphase, anaphase and
KARYO- Telophase. During prophase, the
KINESIS chromatin condenses to form
chromosomes. centrioles develop
into asters and move towards the
opposite poles.
Cytokinesis is a division of the
cytoplasm following mitosis that
forms two daughter cells.It
takes place in four stages: initiation,
contraction, membrane insertion and
completion. The events occurring
within these stages differ in animal
CYTOKI- and plant cells.During cytokinesis,
NESIS the cytoplasm splits in two and the
cell divides.
ACTIVITY 2B:Directions: Study the diagram and tell something about it. Write your
answer on the box
MOTHER CELL
TWO DAUGHTER
CELLS
DNA REPLICATION
CELL DIVISION
THE DIAGRAM SHOWS THE CELL CYCLE OF MITOSIS,Mitosis is a process of
nuclear division in eukaryotic cells that occurs when a parent cell divides to
produce two identical daughter cells.Let’s start by looking at a cell right
before it begins mitosis.This cell is in interphase late G2 start
subscript,2,end subscript phase and has already copied its DNA,so the
chromosomes in the nucleus each consist of two connected copies,
called sister chromatids.You can’t see the chromosomes very clearly at this
point,because they are still in their long,stringy,decondensed form.
And as you can see to the second phase the cell starts to break down some
structures and build others up,setting the stage for division of the
chromosomes.The chromosomes start to condense.The mitotic spindle
begins to form.The spindle is a structure made of microtubules strong
fibers that are part of the cell’s skeleton.The spindle grows between the
centrosomes as they move apart.The nucleolus or nucleoli,part of the
nucleus where ribosomes are made,disappears this is a sign that the
nucleus is getting ready to break down.The mitotic spindle begins to capture
and organize the chromosomes.Chromosomes become even more
condensed,so they are very compact.The nuclear envelope breaks
down,releasing the chromosomes.Mitotic spindle grows more and some of
the microtubules start to capture chromosomes.As you can see at the third
picture the spindle has captured all the chromosomes and
lined them up at the middle of the cell,ready to divide.All the chromoso
mes align at the metaphase plate .At this stage,the two kinetochores of
each chromosome should be attached to microtubules from opposite
spindle poles.the sister chromatids separate from each other and are pulled
towards opposite ends of the cell.The protein glue that holds the sister
chromatids together is broken down,allowing them to separate.
Each is now its own chromosome. The chromosomes of each pair are pulled
towards opposite ends of the cell.Microtubules not attached to
chromosomes elongate push apart,separating the poles and making the cell
longer.the cell is nearly done dividing,and starts to re-establish its normal
structures as cytokinesis division of the cell contents takes place.The
mitotic spindle is broken down into its building blocks.Two new nuclei
form,one for each set of chromosomes. Nuclear membranes and nucleoli
reappear.The chromosomes begin to decondense and return to their stringy
form.The last stage the cytokinesis finishes,we end up with two new
cells,each with a complete set of chromosomes identical to those of the
mother cell.The daughter cells can now begin their own cellular lives,and
depending on what they decide to be when they grow up may undergo
mitosis themselves, repeating the cycle.
You might also like
- Cell Cycle To MeiosisDocument13 pagesCell Cycle To MeiosisSOPHIA ALESNANo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument12 pagesCell CycleCharmaine AngaraNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document48 pagesModule 1Saalif RahmanNo ratings yet
- E1.2a Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument3 pagesE1.2a Cell Cycle and MitosishzntrpNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument12 pagesThe Cell CycleCharmaine AngaraNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument39 pagesCell CycleBuyco, Nicole Kimberly M.No ratings yet
- Cell Growth and DivisionDocument15 pagesCell Growth and DivisionJohn Lester BerdinNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth and DivisionDocument15 pagesCell Growth and DivisionJohn Lester BerdinNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 MitosisDocument5 pagesGrade 8 MitosisJay r DomingoNo ratings yet
- Module in EnglishDocument28 pagesModule in EnglishIannNo ratings yet
- Cell Division in PlantsDocument13 pagesCell Division in PlantsKizzie Mae DacanayNo ratings yet
- Mitosis - Cell MembraneDocument12 pagesMitosis - Cell MembraneJeanelle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Cell CycleDocument25 pagesCell Division and Cell CycleZamantha Zaynn100% (1)
- Ch07 CellCyclesDocument10 pagesCh07 CellCyclesAna GujabidzeNo ratings yet
- General-Biology-1 - Q1 - Week 4-1-9Document9 pagesGeneral-Biology-1 - Q1 - Week 4-1-9Paul James Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 4 FinalDocument13 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 4 FinalJamille Jam BoholNo ratings yet
- Most Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GDocument8 pagesMost Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GfredNo ratings yet
- Biology Is The Only Subject in Which Is The Same Thing As : Multiplication DivisionDocument23 pagesBiology Is The Only Subject in Which Is The Same Thing As : Multiplication DivisionKate Ashly Mae AteradoNo ratings yet
- Cell Life Cycle and Reproduction SummaryDocument3 pagesCell Life Cycle and Reproduction SummaryblairNo ratings yet
- Reproduksi Sel RingkasanDocument2 pagesReproduksi Sel RingkasanMulyadi SPdNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Discussion - Cell Cycle and Mitosis OnlyDocument56 pagesCell Division Discussion - Cell Cycle and Mitosis Onlymarimay.lumabanNo ratings yet
- MustakDocument3 pagesMustakMh Mari HereNo ratings yet
- Mystical Rose College of Science and Technology: Stage 1: InterphaseDocument4 pagesMystical Rose College of Science and Technology: Stage 1: InterphaseLaarni ToleteNo ratings yet
- Overview of Cell Cycle by Javali.GDocument15 pagesOverview of Cell Cycle by Javali.GJavali.GNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis PresentationDocument53 pagesCell Cycle and Mitosis Presentationbisma nadeemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Cell Cycle Cell Cycle: A. G1 PhaseDocument17 pagesChapter 2: Cell Cycle Cell Cycle: A. G1 PhaseIrish GatpoNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument4 pagesMitosisJeanelle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- GENBIO1MOD3Document11 pagesGENBIO1MOD3Renzsoc JalmascoNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer 2Document9 pagesBiology Reviewer 2John Arnel BunquinNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument17 pagesMitosisadamahmad20007No ratings yet
- C C C D C 10: ELL Ycle AND ELL IvisionDocument11 pagesC C C D C 10: ELL Ycle AND ELL IvisionbjjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document20 pagesChapter 21Uzma AdnanNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Worksheet AnswersDocument3 pagesCell Division Worksheet AnswersDanaNo ratings yet
- I. Binary FissionDocument4 pagesI. Binary FissionMarielle GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle: Prepared By: Ms. Charis D. Juanico, General Biology 1 TeacherDocument59 pagesCell Cycle: Prepared By: Ms. Charis D. Juanico, General Biology 1 TeacherTrisha Loise VillacampaNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment PDFDocument13 pagesBiology Assignment PDFmohd mehartaj100% (1)
- Technical Definition and Description Final DraftDocument5 pagesTechnical Definition and Description Final Draftapi-252711494No ratings yet
- Class - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionDocument13 pagesClass - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionANIRBAN PALNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document9 pagesLec 1د. محمد زهير المرعب Dr. Mohammed Zuhair Al-Muri’bNo ratings yet
- Burgos, John Adrian Ingco General Biology 1 STEM 12-21Document5 pagesBurgos, John Adrian Ingco General Biology 1 STEM 12-21Lorie Austria DinoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - Short Notes - Arjuna NEET 2024Document2 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - Short Notes - Arjuna NEET 2024shraddha2572sharmaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division DNA Replication Bacteria Cell NucleusDocument2 pagesCell Division DNA Replication Bacteria Cell NucleusJhon Navarro SabordoNo ratings yet
- The Phase of Growth and DNADocument4 pagesThe Phase of Growth and DNARedNo ratings yet
- 2.5 - Cell DivisionDocument5 pages2.5 - Cell DivisionAlvin JovanNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Division Lecture NotesDocument16 pagesCell Cycle Division Lecture NotesZachary HamidNo ratings yet
- Module 4-The Cell's Life CycleDocument4 pagesModule 4-The Cell's Life Cycle10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle NotesDocument12 pagesCell Cycle NotesMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Cell DivisionDocument5 pages1.6 Cell DivisionmariamNo ratings yet
- 2.5 The Cell CycleDocument5 pages2.5 The Cell CycleAntoline Natasha RayappanNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Lesson 4Document2 pagesGen Bio 1 Lesson 4Ric SantosNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell Cyclewebpixel servicesNo ratings yet
- UZAItfinalDocument18 pagesUZAItfinalYasirNo ratings yet
- Biology Ch. 9 (2136)Document49 pagesBiology Ch. 9 (2136)lianneNo ratings yet
- The Process of Cell Division: Lesson ObjectivesDocument4 pagesThe Process of Cell Division: Lesson ObjectivesManuel DiazgranadosNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument67 pagesCell DivisionRylle SimonNo ratings yet
- 0 BooksDocument20 pages0 Bookslaraib zahidNo ratings yet
- IB Biology - Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesIB Biology - Cell DivisionPriyani GuptaNo ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Oc Module-2Document18 pagesOc Module-2Stephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Perdev Week3Document2 pagesPerdev Week3Stephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Perdev Week 2Document1 pagePerdev Week 2Stephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Oc Module-3Document16 pagesOc Module-3Stephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Oc Module-5Document13 pagesOc Module-5Stephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- PERDEVDocument2 pagesPERDEVStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- 21st Conventional and 21st Century Genres Week 3 PDFDocument25 pages21st Conventional and 21st Century Genres Week 3 PDFStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- What Is Cancer Cellhow Does It DevelopDocument1 pageWhat Is Cancer Cellhow Does It DevelopStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- What Is Cancer Cellhow Does It DevelopDocument2 pagesWhat Is Cancer Cellhow Does It DevelopStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- 21ST Century LiteratureDocument1 page21ST Century LiteratureStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionDocument1 pageDisaster Readiness and Risk ReductionStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Perdev Week 2.1Document3 pagesPerdev Week 2.1Stephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- 21ST Century LiteratureDocument6 pages21ST Century LiteratureStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Lamyak 6Document1 pageLamyak 6Stephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- What Is Cancer Cellhow Does It DevelopDocument3 pagesWhat Is Cancer Cellhow Does It DevelopStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- FITT Calendar HOPEDocument1 pageFITT Calendar HOPEStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionDocument4 pagesContemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- You Should Not Teach Your Kids To Believe in Santa ClausDocument5 pagesYou Should Not Teach Your Kids To Believe in Santa ClausStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Classification of RocksDocument5 pagesClassification of RocksStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction-5Document2 pagesDisaster Readiness and Risk Reduction-5Stephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- The Media and Public Opinion Media and Elections: What Causes Bias?Document3 pagesThe Media and Public Opinion Media and Elections: What Causes Bias?Stephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Cells 10 00463 v2Document40 pagesCells 10 00463 v2Stephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Peta DRRRDocument2 pagesPeta DRRRStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Assignment DRRRDocument1 pageAssignment DRRRStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Father of Bride SpeechDocument4 pagesFather of Bride SpeechStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Template ImmersionDocument1 pageTemplate ImmersionStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Peta DRRR Final NaDocument2 pagesPeta DRRR Final NaStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Untitled Design-16Document1 pageUntitled Design-16Stephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- G16. Macatangay Marielle Kyle D. Activity 1 What S More PDFDocument3 pagesG16. Macatangay Marielle Kyle D. Activity 1 What S More PDFStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- Purple and White Simple February 2023 Monthly CalendarDocument2 pagesPurple and White Simple February 2023 Monthly CalendarStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNo ratings yet
- EnduranceDocument76 pagesEnduranceBethany W. Nelson100% (1)
- Eukaryotic Origins and The ProterozoicDocument81 pagesEukaryotic Origins and The ProterozoicgonzaloNo ratings yet
- Pancreas Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument34 pagesPancreas Anatomy and PhysiologySourabh MishraNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Lecture 6 - Digestive SystemDocument39 pagesBiology 2 Lecture 6 - Digestive Systemryle34No ratings yet
- ANPH Midterm NotesDocument44 pagesANPH Midterm NotesClaudine Jo B. TalabocNo ratings yet
- Biology 30Document6 pagesBiology 30Marah AlsurkhyNo ratings yet
- Profil Hematologi Dan Gambaran Morfologi Darah Sapi Bali (Bos Sundaicus) Yang Dipelihara Di Tempat Pembuangan Akhir Alak Kota KupangDocument13 pagesProfil Hematologi Dan Gambaran Morfologi Darah Sapi Bali (Bos Sundaicus) Yang Dipelihara Di Tempat Pembuangan Akhir Alak Kota KupangKeju Mozarella ChizzuNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP - Activity IntoleranceRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- VAD PercutanDocument1 pageVAD PercutanandreaNo ratings yet
- Tructure and Functions of Animal Tissues and CellmodificationDocument53 pagesTructure and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cellmodificationako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Arterial Tortuosity SyndromeDocument11 pagesArterial Tortuosity SyndromeNawal RaiNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary BypassDocument40 pagesCardiopulmonary BypassParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Pelargonidin-PLGA Nanoparticles: Fabrication, Characterization, and Their Effect On Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats1Document13 pagesPelargonidin-PLGA Nanoparticles: Fabrication, Characterization, and Their Effect On Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats1Alyna AlynaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes - What Are The Similarities, Differences, and Examples - RS' ScienceDocument1 pageEukaryotes and Prokaryotes - What Are The Similarities, Differences, and Examples - RS' ScienceCandela Sierra ThomasaNo ratings yet
- Biological Nitrogen FixationDocument16 pagesBiological Nitrogen FixationDiego Nicolas ManceraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4.2Document4 pagesTutorial 4.2Rosa FinizioNo ratings yet
- Friedenberg Silverman (2011) Ch11 Social CognitionDocument9 pagesFriedenberg Silverman (2011) Ch11 Social Cognitionsoheilesm456No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Human Disease Pathology and Pathophysiology Correlations 8th Edition Crowley Test BankDocument13 pagesAn Introduction To Human Disease Pathology and Pathophysiology Correlations 8th Edition Crowley Test Bankmaryjohnsonjkcadytnqe98% (48)
- Massage For Therapists. A Guide To Soft Tissue TherapyDocument218 pagesMassage For Therapists. A Guide To Soft Tissue TherapyKate Trusova100% (5)
- Phospholipids & Their FunctionsDocument13 pagesPhospholipids & Their Functionskulsum fatimaNo ratings yet
- The Vascular SystemDocument7 pagesThe Vascular SystemMiguel GumatayNo ratings yet
- Biology Model Examination For Grade 12 in The Year 2007 E.CDocument15 pagesBiology Model Examination For Grade 12 in The Year 2007 E.CDanielNo ratings yet
- New Era University: Bundoc, Althea Marie Con-1D (Bs Nursing)Document4 pagesNew Era University: Bundoc, Althea Marie Con-1D (Bs Nursing)Bundoc Althea MarieNo ratings yet
- Immuno Hema - EX 2 ACT - Veloso, Mary Raffaele G - BSMT 3D PDFDocument3 pagesImmuno Hema - EX 2 ACT - Veloso, Mary Raffaele G - BSMT 3D PDFAnneNo ratings yet
- ACSM Certified Personal Trainer (010-111) 200+ Exam Practice Review Questions For ACSM Certified Personal Trainer (010-111) (Ace It (It, Ace) )Document221 pagesACSM Certified Personal Trainer (010-111) 200+ Exam Practice Review Questions For ACSM Certified Personal Trainer (010-111) (Ace It (It, Ace) )ASHOK P KNo ratings yet
- 2 MosquitoesDocument41 pages2 MosquitoesAnmut AschaleNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy - Module 1 & 2 - Final TermDocument46 pagesHuman Anatomy - Module 1 & 2 - Final TermwelpNo ratings yet
- Microsystem NoteDocument18 pagesMicrosystem Noteyayanica100% (1)
- Year 7 Biology Scheme.Document3 pagesYear 7 Biology Scheme.Diana ororiNo ratings yet
- 04-03 Using Plant Tissues and Pigments in Forensic Studies - Leaf PDFDocument23 pages04-03 Using Plant Tissues and Pigments in Forensic Studies - Leaf PDFAsif AliNo ratings yet