Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dev Read 2
Uploaded by
Joanna Ventura0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views8 pagesDev Read Module
Original Title
DEV READ 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDev Read Module
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views8 pagesDev Read 2
Uploaded by
Joanna VenturaDev Read Module
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Republic of the Philippines
Ramon Magsaysay Technological University
(Colegio de Castillejos building/Castillejos National High School Compound)
Castillejos Campus, Castillejos, Zambales
Tel/Fax No. (047) 602-1548
crmtu@yahoo.com.ph
COLLEGE OF TEACHERS EDUCATION
Course Syllabus
DEVELOPMENTAL READING 1
First Semester 2017 – 2018
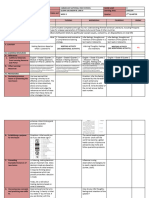
XI. LEARNING PLAN
LEARNING METHODO- TIME
TOPIC RESOURCES ASSESSMENT
OUTCOMES LOGY FRAME
Define reading I. What is Reading -Powerpoint -LCD -Quizzes 11
clearly and A. Reading is a skill presentation Projector -Worksheets
scientifically; B. Reading is a process -Lecture -Laptop -Assignments
Identify the various C. Reading is a tool -Discussion -Blackboard/ -Recitation
factors affecting D. Reading is strategic Whiteboard
reading abilities; E. Reading is continuous -Chalk /
Analyze situations II. What Reading Can do? Marker
to find out what III. Characteristics of a Good Reader
causes reading IV. Why Reading is Important
disabilities; V. Essential Components of Reading
Underscore the role A. Phonemic Awareness
of “nature” and B. Phonics
“nurture” in the C. Fluency
reading process; D. Vocabulary
Acquire functional E. Comprehension
understanding of the F. Spelling
various VI. Factors Affecting Reading
developmental A. Physical and Clinical Factors
stages in reading B. Predictors of School Entry
process; C. Family-based Risk Factors
D. Acquired Knowledge of
Literacy
E. Neighborhood, Community,
and School-Based Factors
VII. Stages of Reading Process
A. Process 1: Making Early
Connections – Describing
Pictures
B. Process 2: Forming a Story by
Connecting Pictures
C. Process 3: Transitional Picture
Reading
D. Process 4: Advance Picture
Reading
E. Process 5: Early Print Reading
F. Process 6: Early Strategic
Reading
G. Moderate Strategic Reading
VIII. Developmental Reading Stages
A. Stage 0: Reading
Readiness/Pre-Reading
B. Stage 1: Initial Reading or
Decoding
C. Stage 2: Fluency
D. Stage 3: Reading for Learning
the New Stage
E. Stage 4: Multiple View-points
Stage
F. Construction and
Reconstruction Stage
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION
Understand the I. Reading Models -Powerpoint -LCD -Quizzes 22
underlying A. Bottom-up Reading Model presentation Projector -Worksheets
principles of reading B. Top-down Reading Model -Lecture -Laptop -Assignments
strategies and C. Interactive Reading Model -Discussion - -Recitation
models and apply II. Comprehension and Levels of Blackboard
them when you read Comprehension /
in different content A. What is Comprehension? Whiteboard
areas; B. Indicators of Learners’ Reading -Chalk /
Identify and Comprehension Marker
describe the C. Comprehension Levels
different C.1. Level One: Literal
C.2. Level Two: Interpretative
comprehension C.3. Level Three: Applied
levels arranged D. Skills that are Important for
according to Comprehension
complexity of III. Comprehension Strategies
reading skills A. Skimming
required and read B. Scanning
short and longer C. Extensive Reading
texts with full D. Intensive Reading
comprehension; E. Visualizing
Efficiently employ F. Monitoring and Repairing
reading Understanding
comprehension G. Synthesizing
strategies; H. Determining Important Ideas
Define, discuss the I. Synthesizing
importance of J. Inferring
vocabulary; K. Using Background Knowledge
Identify an array of L. Questioning
vocabulary learning IV. Expanding Your Vocabulary
strategies; A. Facts about Vocabulary
Expand your Acquisition
vocabulary by B. Vocabulary Learning Strategies
analyzing roots, B.1. Determination (DET)
affixation, use of B.2. Social (SOC)
antonyms and B.3. Memory (MEM)
synonyms. B.4. Cognitive (COG)
Explain, know the B.5. Metacognitive (MET)
different types, and V. Analyzing Roots
unlock unfamiliar VI. Affixes
words with the use VII. Antonyms
of context clues. VIII. Synonyms
IX. Context Clues
MIDTERM EXAMINATION
Explain what is I. Understanding Idiomatic -Powerpoint -LCD -Quizzes
idiomatic Expressions presentation Projector -Worksheets 21
expressions and II. Skimming and Scanning -Lecture -Laptop -Assignments
decipher the III. Reading Technique – SQ3R -Discussion - -Recitation
meaning of it A. Survey Blackboard
independently; B. Question /
Differentiate C. Read Whiteboard
between skimming D. Recite -Chalk /
and scanning; IV. Noting Details Marker
Discuss and employ A. Examples
SQ3R in reading B. Facts
texts; C. Statistics
Note details in texts D. Reasons
read; E. Definitions
Discuss and identify F. Descriptions
what topics, main V. Identifying Topics, Main Ideas,
ideas, and and Supporting Details
supporting details in VI. Making Inferences
texts read; VII. Drawing Conclusions
Discuss and make VIII. Summarizing
inferences based on IX. Critical Thinking and Reading
the texts read; A. What is Critical Thinking
B. Uses of Critical Thinking
Discuss and draw
C. Attributes of a Critical
conclusions from
Thinker
texts reads;
D. What is Critical Reading
Discuss what is
E. Characteristics of Critical
summarizing is and
Readers
describe effective
F. Steps in Critical Reading
summaries;
X. Recognizing Author’s Purpose
Discuss what and and Point of View
apply critical XI. Identifying Arguments
thinking in reading XII. Content Area Reading
texts;
Discuss why it is A. Definition
necessary and B. Reasons for Teaching
identify an author’s Content Area Reading
purpose and point of C. Content Area Texts vs.
view; Literary Texts
Tell what a good D. How to understand Content
argument is and Area Texts
identify authors’ E. Content Area Vocabulary
arguments in texts XIII. Reading Expository Texts
read; A. Problem and Solution
Discuss what B. Cause and Effect
content area reading C. Comparison
is; D. Sequence
Discuss what E. Description
expository text is; XIV. Reading Essays
Discuss, give the A. Suggestions on effectively
classifications, and read essays
read essays B. Understanding Essays
effectively; XV. Figurative Language
Discuss what Figures of Speech
figurative language A. Simile
is, give and describe B. Metaphor
the most commonly C. Metonymy
used figures of D. Synecdoche
speech; E. Personification
F. Apostrophe
Differentiate
G. Overstatement (Hyperbole)
between tone and
H. Understatement
mood;
I. Alliteration
Discuss what poetry
J. Assonance
is and interpret
K. Onomatopeia
poems effectively;
XVI. Identifying Author’s Tone
Discuss, give and A. Author’s Tone and Mood
describe a short
story and its B. Nostalgic Tone
elements; C. Sentimental Tone
Demonstrate D. Moralizing Tone
understanding of E. Cynical Tone
graphs, charts, and XVII. Reading Poetry
tables. A. Poetry
B. Specific poetic devices
C. Steps to reading a poem
XVIII. Reading Short Stories
A. Setting
B. Plot
C. Conflict
D. Characters
E. Point of View
FINAL EXAMINATION
XII. SUGGESTED READING AND REFERENCES:
Developmental Reading 1 by Alejandro S. Bernardo
XIII. COURSE REQUIREMENTS & GRADING SYSTEM
Class Attendance 10%
Homeworks/Quizzes 10%
Activities 20%
Term Projects 30%
Prelim, Midterm, & Final Examination 30%
TOTAL 100%
FINAL GRADE:
Preliminary 30%
Midterm 30%
Final 40%
Total 100%
XV. CLASSROOM POLICIES:
1. A student who misses any of the major tests must present a valid reason why he/she
was absent before he/she can take the special examination
2. Allowance of 15 minutes is considered before one will be marked absent
3. All other policies stipulate in the Student’s Handbook related to academics and proper
decorum are also included (haircut, uniform, no. of allowable absences, etc.)
4. Usage of cellular phones and other communication/entertainment gadgets are not
allowed inside the classroom during the class hours
5. Any form of cheating are strongly prohibited.
6. Students are not allowed to have more than 11 hours absences semester (20% of
allocated hours), she/he may be automatically be dropped in the subject.
XVI. CONSULTATION HOURS:
Monday/Wednesday - 1:00 – 2:00 PM
You might also like
- Tq-Academic Reading and Writing 1ST QuarterDocument4 pagesTq-Academic Reading and Writing 1ST QuarterRhyz Mareschal Dongon100% (1)
- Developmental Reading 2Document10 pagesDevelopmental Reading 2Jaireh CardamaNo ratings yet
- The New Bloom's Taxonomy: An Interactive Quiz GameDocument28 pagesThe New Bloom's Taxonomy: An Interactive Quiz GameSaymon Casilang SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Office Administration Lesson Plan1Document3 pagesOffice Administration Lesson Plan1Donald FaganNo ratings yet
- FRCPath Chemical Pathology CurriculumDocument109 pagesFRCPath Chemical Pathology Curriculummonday125No ratings yet
- Field Study 5.FULLDocument39 pagesField Study 5.FULLAna Bendanillo ArandiaNo ratings yet
- Dev RadDocument9 pagesDev RadJoanna VenturaNo ratings yet
- Language & Power Syllabus - NewDocument4 pagesLanguage & Power Syllabus - NewMarsGilNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS Developmental Reading 2Document3 pagesSYLLABUS Developmental Reading 2Sandy Medyo Gwapz67% (3)
- DLL - Eng10 - Week 2Document4 pagesDLL - Eng10 - Week 2Hilrem L. BayucotNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: A. Content StandardsDocument3 pagesI. Objectives: A. Content Standardsrommel100% (1)
- LP MODELS OF COMM. Sept. 19-23 2022Document3 pagesLP MODELS OF COMM. Sept. 19-23 2022Jean CatandijanNo ratings yet
- Outlining 2Document3 pagesOutlining 2Tane MBNo ratings yet
- Week 12 SHS - JHSDocument7 pagesWeek 12 SHS - JHSCeasar Ryan AsuncionNo ratings yet
- English 5 DLL - Q2 - W10Document9 pagesEnglish 5 DLL - Q2 - W10Jessica bernalNo ratings yet
- DLL - MTB 3 - Q1 - W1Document2 pagesDLL - MTB 3 - Q1 - W1Jazzel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Week 6-8 - Eng 1Document4 pagesWeek 6-8 - Eng 1Julien Ace TongolNo ratings yet
- VR English Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesVR English Lesson PlanMy Darling ChannelNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument9 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayRaee ShaajNo ratings yet
- Cot 2 Eng AATDocument5 pagesCot 2 Eng AATAB TGNo ratings yet
- Day 4Document6 pagesDay 4Mark Gil Jandusay YpantoNo ratings yet
- DLL in English 9 #2Document4 pagesDLL in English 9 #2Ghieft GaeaNo ratings yet
- DLL - MTB 3 - Q1 - W1Document3 pagesDLL - MTB 3 - Q1 - W1FAYE PONGASINo ratings yet
- 4-3 Academic WritingDocument4 pages4-3 Academic WritingMica Jenika VillarNo ratings yet
- Questionnnaire 2Document5 pagesQuestionnnaire 2forsythiachrysanthemumNo ratings yet
- Mendoza, Margott Macie - Lesson Exemplar (Opinions or Assertion)Document10 pagesMendoza, Margott Macie - Lesson Exemplar (Opinions or Assertion)Janice GaboteroNo ratings yet
- RWS 11.1.2 (Selecting and Organizing Info)Document2 pagesRWS 11.1.2 (Selecting and Organizing Info)roxann djem sanglayNo ratings yet
- DLP-G8-Organizational PatternsDocument12 pagesDLP-G8-Organizational PatternsDemmie belle CaluyaNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log JUNE 3 - 7, 2019 (WEEK 1)Document3 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log JUNE 3 - 7, 2019 (WEEK 1)Liezel Marcelo100% (1)
- RWS 11.1.2 (Selecting and Organizing Info)Document3 pagesRWS 11.1.2 (Selecting and Organizing Info)Robert Frio100% (2)
- Obe dr2Document8 pagesObe dr2jonard rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Developmental Reading Syllabus: - Adopted From: Ms. Robwela M. NoronhaDocument3 pagesDevelopmental Reading Syllabus: - Adopted From: Ms. Robwela M. Noronhaupskill socialNo ratings yet
- LE Oral Com - Speech DeliveryDocument3 pagesLE Oral Com - Speech DeliverySigrid FadrigalanNo ratings yet
- DLL English 5 q2 w10Document11 pagesDLL English 5 q2 w10Lilian Elescupides - DayritNo ratings yet
- Q1Wk8 English 9 Communicative StylesDocument3 pagesQ1Wk8 English 9 Communicative StylesLORIE BROCOYNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Friday DLLDocument2 pagesCatch Up Friday DLL5zg2yysjy2No ratings yet
- DLL 1.1Document4 pagesDLL 1.1Honey Brylle TandayagNo ratings yet
- 3i's Lesson Plan (Different Reading Styles)Document7 pages3i's Lesson Plan (Different Reading Styles)BlinDspotted FinaleNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Quarter 4 Week 4Document16 pagesGrade 9 Quarter 4 Week 4Paula Andrea PalacolNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 9 Q2 W2 Make Connections Between Texts (PART 2)Document4 pagesENGLISH 9 Q2 W2 Make Connections Between Texts (PART 2)glenn salvador iv limNo ratings yet
- Features of Academic WritingDocument5 pagesFeatures of Academic WritingKATE SHELOU TABIAN100% (2)
- DLP-Q3W5-LEGGIE-M (Quiz-2)Document3 pagesDLP-Q3W5-LEGGIE-M (Quiz-2)Mark Leggie Feliciano RontaleNo ratings yet
- DLL - MTB 3 - Q1 - W1Document3 pagesDLL - MTB 3 - Q1 - W1Rachel GendranoNo ratings yet
- Melc DLL Eng 9 Week 3 q1 DoneDocument6 pagesMelc DLL Eng 9 Week 3 q1 DonePauLyn ViadoNo ratings yet
- Cot - 1 May 2023 Jeff DLLDocument8 pagesCot - 1 May 2023 Jeff DLLJefferson Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument74 pagesReading and WritingLoren Marie LemanaNo ratings yet
- Young Ji College: Bridging The Gap Between Traditional and Whole Language Perspective in Teaching ReadingDocument4 pagesYoung Ji College: Bridging The Gap Between Traditional and Whole Language Perspective in Teaching ReadingKathMae BoaNo ratings yet
- College of Education: Republic of The Philippines Leyte Normal University Tacloban CityDocument2 pagesCollege of Education: Republic of The Philippines Leyte Normal University Tacloban CityOrlando Jr. VinculadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 12: Andres Bonifacio Integrated SchoolDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in English 12: Andres Bonifacio Integrated SchoolVhergel Mhartinez100% (1)
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument9 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogNora De Guzman HerreraNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work For Form 4 English Unit TDocument30 pagesScheme of Work For Form 4 English Unit TsyzwniNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan (MACANDOG - 3EDFIL6A)Document4 pagesLesson Plan (MACANDOG - 3EDFIL6A)Lyka MacandogNo ratings yet
- RW-Q1-W3 DemoDocument7 pagesRW-Q1-W3 DemoGretchenNo ratings yet
- Tittle Variable SUB Variable Indicators Source of Data Research Method Reasearch QuestionsDocument2 pagesTittle Variable SUB Variable Indicators Source of Data Research Method Reasearch QuestionsM. Hilmi Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Eng10 Nov20 24Document7 pagesEng10 Nov20 24Chaii Madlangsakay TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Claim of FactDocument11 pagesClaim of FactXeb UlritzNo ratings yet
- Q2 - Eng10 - WK8 - Day 1Document5 pagesQ2 - Eng10 - WK8 - Day 1Josette AsentistaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Interventionday DLLDocument3 pagesQ2 Interventionday DLLJo Ann Chrysol IringanNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 3 - Q2 - W9Document3 pagesDLL - English 3 - Q2 - W9Linelle Jane PerezNo ratings yet
- EAPPQ1-1ST SummativeDocument3 pagesEAPPQ1-1ST SummativeRomnickCelestinoNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument9 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayKathleen SollanoNo ratings yet
- DLL 2nd Quarter Wk8Document12 pagesDLL 2nd Quarter Wk8Richelle CantongNo ratings yet
- COT - 1 For May 2023 Jefferson Del RosarioDocument8 pagesCOT - 1 For May 2023 Jefferson Del RosarioJefferson Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Cec StandardsDocument10 pagesCec Standardsapi-508099786No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesRollie LynNo ratings yet
- AiML 1 1Document10 pagesAiML 1 1grosvin.sanchezNo ratings yet
- Cot1 DLP KindergartenDocument6 pagesCot1 DLP Kindergartenmarbieocampo0711No ratings yet
- Jurnal Minggu 4Document2 pagesJurnal Minggu 4MATHAVI A/P RAMASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- Outcome-Based Education: An Approach For Teaching and Learning DevelopmentDocument10 pagesOutcome-Based Education: An Approach For Teaching and Learning DevelopmentNur HafizahNo ratings yet
- LFC Assignment (Claire)Document3 pagesLFC Assignment (Claire)ClaireNo ratings yet
- Subject: Language 1 Semester Lesson Planning SY 2017-2018 Prepared By: - Grade: KG 3/1 Approved By: - Week / Date Content Evaluation After ClassDocument3 pagesSubject: Language 1 Semester Lesson Planning SY 2017-2018 Prepared By: - Grade: KG 3/1 Approved By: - Week / Date Content Evaluation After Classclarence acostaNo ratings yet
- EmilymartinezlormanningDocument1 pageEmilymartinezlormanningapi-310448954No ratings yet
- Jean LaveDocument8 pagesJean LaveJohn Louie TabbunNo ratings yet
- A Semi - Detailed Lesson Plan English For Academics and Professional Purposes 11Document3 pagesA Semi - Detailed Lesson Plan English For Academics and Professional Purposes 11Stephanie Aturdido0% (1)
- Word Flippers: A Sample From All AboutDocument20 pagesWord Flippers: A Sample From All AboutMari Rañada Santos100% (4)
- Sped 203 Assign 2Document15 pagesSped 203 Assign 2asprillaNo ratings yet
- WHLP EmptechDocument2 pagesWHLP EmptechEdison OrgilNo ratings yet
- Orientation ProgramDocument1 pageOrientation ProgramAirishAinneNo ratings yet
- Difficulties of Students Encountering TLEDocument5 pagesDifficulties of Students Encountering TLEKyla Claire Manuba50% (2)
- Cambridge Primary English Resource List Stage 3 To 6Document14 pagesCambridge Primary English Resource List Stage 3 To 6Tumwesigye robertNo ratings yet
- Rules and Procedures PresentationDocument17 pagesRules and Procedures Presentationapi-484192673No ratings yet
- BANDURADocument26 pagesBANDURAJose Espinosa Evangelista Jr.No ratings yet
- Art Teacher Resume 2020Document1 pageArt Teacher Resume 2020api-270319467No ratings yet
- Science 4th QTR CotDocument4 pagesScience 4th QTR Cotsofia gamer girlNo ratings yet
- Technology Scavenger HuntDocument2 pagesTechnology Scavenger Huntapi-431630423No ratings yet
- Abstract 2017Document222 pagesAbstract 2017alan brandambassadorNo ratings yet
- Front PagesDocument4 pagesFront Pages9125103046No ratings yet
- Physical EducationDocument3 pagesPhysical EducationCHARIZE MAE NAVARRONo ratings yet
- DLL General Biology 1 Quarter 1 WeekDocument3 pagesDLL General Biology 1 Quarter 1 WeekRubin RubinNo ratings yet