Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Triangle and Quadrilateral Formulas
Uploaded by
hasibul rojan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesOriginal Title
ACFrOgD81caqQzxjnXaXPpwyDwkvSDvIs7Ze0oCw4Bci8Kog8hOt8ApZO-p-0m0tJzH2tFNxWga3CwYjh1NY8ud-JEx_hbpyqXYpEa1UIW7_7eUp1OfXxWqGuo3t-PqpVxCMG7WmcG2GmyQfynwU
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesTriangle and Quadrilateral Formulas
Uploaded by
hasibul rojanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
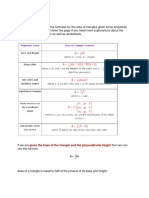
Triangle Related Formulas Quadrilateral Related Formulas
Equilateral Triangle: Parallelogram:
√3 2 Area = Base × Height
Area = 𝑎
4 Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Breadth)
Perimeter = 3a
Rectangle:
Isosceles Triangle: Area = Length × Breadth
1 a2 −b2 Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Breadth)
Area = 2 × √ ×b
4
1
• Diagonals are equal
= 2 absinθ [Here, a = equal sides, b = base,
θ= adjacent angle of a and b] Rhombus:
Area = Product of diagonals
Scalene Triangle: Perimeter = 4a
a+b+c
Semi perimeter (S) = 2
Square:
Area = √S(S − a)(S − b)(S − C) Area = a2
Here, S = semi perimeter; a, b, c are three Perimeter = 4a
sides of triangle
Diagonal = √2a
• Diagonals are equal
Right Angle Triangle:
Pythagoras:
Trapezoid/Trapezium:
(Base)2 + (Perpendicular)2 = (Hypotenuse)2 1
Area = × (Summation of parallel sides) ×
2
If the triangle is isosceles right-angle triangle, height
Base : Perpendicular : Hypotenuse = x ∶ x ∶ x√2
Polygon:
0
If one angle of the right angle is 60 and another Total interior angle = (n − 2) × 1800
angle is 300 ,
Then the angle measurement will be like this. If the polygon is regular polygon, then,
All angles are equal.
Angle measurement of regular polygon =
(𝑛−2)×180
𝑛
𝟐𝒙
300
𝒙√𝟑 Circle Related Formulas
Let the radius of the circle = r, diameter = d = 2r
0 d
60 Area = πr 2 = π(2)2
𝒙 Circumference = 2πr = πd
22
𝜋 = 3.1416 = 7
Here, 𝑥√3 will always be the opposite side of 600 , 𝑥0 𝑥0
and x will be the opposite side of 300 and 2x = Area of a certain portion = 𝐴 × 3600 = πr 2 × 3600
hypotenuse 𝑥0
Length of an arc, AB = 2𝜋𝑟 × 3600
Solid Geometry
Cube:
Total surfaces = 6
Total surface area = 6x 2
Volume = x 3
Short diagonals = x√2
Long diagonals = x√3
Sphere:
Let the radius of sphere = r
4
Volume = 3 πr 3
Total Surface Area = 4πr 3
Cylinder:
Let the height = h, radius of circular surface = r
Total Surface Area = 2πrh + 2πr 2
= 2πr(h + r)
Volume = area of base × height
= πr 2 × h = πr 2 h
Cone:
Let the height = h, radius = r, slant height = l
1
Volume = 3 πr 2 h
Slant height (l) = √r 2 + h2
Surface Area = πr × (r + l)
= πr(r + √r 2 + h2 )
Lateral Surface Area = πr√h2 + r 2
Base area = πr 2
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Math Formula SheetDocument8 pagesMath Formula SheetHidayah TeacherNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet 2 Area and PerimeterDocument8 pagesGrade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet 2 Area and PerimetergeethaNo ratings yet
- 6 Geometry 01apr2009 PDFDocument1 page6 Geometry 01apr2009 PDFNarenNo ratings yet
- Geometry (2D)Document26 pagesGeometry (2D)mnashish619No ratings yet
- Mensuration: This Chapter ''Mensuration'' Is Taken From Our BookDocument11 pagesMensuration: This Chapter ''Mensuration'' Is Taken From Our BookSunil SinghNo ratings yet
- Formulas SheetDocument5 pagesFormulas SheetabdulrehmanNo ratings yet
- Important Points and Formulae: e Markedpric Discount Loss ProfitDocument5 pagesImportant Points and Formulae: e Markedpric Discount Loss ProfitNyasha GweruNo ratings yet
- Important formulae and concepts for maths revisionDocument5 pagesImportant formulae and concepts for maths revisionMata Pronoob100% (1)
- Mensuration IDocument0 pagesMensuration IBalabhadruni SowmyaNo ratings yet
- Mensuration formulas and geometry problemsDocument0 pagesMensuration formulas and geometry problemsBalabhadruni SowmyaNo ratings yet
- Important Points and Formulae: e Markedpric Discount Loss ProfitDocument4 pagesImportant Points and Formulae: e Markedpric Discount Loss ProfitTaha YousafNo ratings yet
- Mensuration PDFDocument33 pagesMensuration PDFSudhanshu Kumar100% (1)
- Formulas for Areas & Volumes of 2D & 3D ShapesDocument3 pagesFormulas for Areas & Volumes of 2D & 3D ShapesAlexandre100% (1)
- Important Points and Formulae: Mathematics Grade 9 BmiDocument6 pagesImportant Points and Formulae: Mathematics Grade 9 BmiZulfiqar Ali MirNo ratings yet
- Mensuration FormulasDocument2 pagesMensuration Formulasayesha.siiddiquiiNo ratings yet
- Review Module 5 Plane and Solid Geometry Part 1Document2 pagesReview Module 5 Plane and Solid Geometry Part 1YeddaMIlagan100% (1)
- Review Module - Plane & Solid Geometry - N2023Document3 pagesReview Module - Plane & Solid Geometry - N2023Mina, KhristineNo ratings yet
- Area of TrianglesDocument7 pagesArea of TrianglesAngelica MontezonNo ratings yet
- G10 - Key Points Formulae 2023Document10 pagesG10 - Key Points Formulae 2023hersheys boiNo ratings yet
- Formulas PDFDocument8 pagesFormulas PDFSubham Paul100% (1)
- FormulaeDocument7 pagesFormulaeVesna NasirNo ratings yet
- 2 MathDocument5 pages2 MathAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Track 2 Important FormulaeDocument3 pagesForm 4 Track 2 Important FormulaePaulette CaruanaNo ratings yet
- Great Math Formula With ExamplesDocument37 pagesGreat Math Formula With Examplessandesh negi100% (1)
- Length, Area, Volume Equation TableDocument2 pagesLength, Area, Volume Equation Tableomar.medbechirNo ratings yet
- Important Formulae For CAT: Ratio, Proportion, VariationDocument10 pagesImportant Formulae For CAT: Ratio, Proportion, Variationvenkatakrishnan srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet Area and Perimeter Answer KeyDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet Area and Perimeter Answer Keygeetha100% (1)
- Formula Booklet PDFDocument16 pagesFormula Booklet PDFBasalic GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Math Formula Chart: Perimeter CircumferenceDocument4 pagesMath Formula Chart: Perimeter CircumferenceBhushan SrivatsaNo ratings yet
- Math Igcse FormulasDocument4 pagesMath Igcse FormulasAbdelrahman MostafaNo ratings yet
- CXC MATHS Formula SheetDocument7 pagesCXC MATHS Formula SheetEric D Medeci100% (1)
- G10 - Key Points & FormulaeDocument10 pagesG10 - Key Points & FormulaePlayer dude65No ratings yet
- A - Sin Cos Tan - Pythagoras THDocument33 pagesA - Sin Cos Tan - Pythagoras THMaroNo ratings yet
- Mensuration 1st ChapterDocument23 pagesMensuration 1st ChaptersanthoshNo ratings yet
- TRIGONOMETRYDocument61 pagesTRIGONOMETRYMapurisa TriciahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document17 pagesLecture 01David OrtegaNo ratings yet
- SBI PO Study Guide: Mensuration Formulas for Geometry ShapesDocument16 pagesSBI PO Study Guide: Mensuration Formulas for Geometry ShapesMann2920No ratings yet
- GCSE-CheatSheet Foundation2019Document2 pagesGCSE-CheatSheet Foundation2019diya pNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Formula BookDocument16 pagesCambridge Formula BookJaymie AnchumNo ratings yet
- Upsc Cds E: Study Material For MathematicsDocument16 pagesUpsc Cds E: Study Material For MathematicsVishwjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- 10th STD - Mathematical Formulae - 2Document4 pages10th STD - Mathematical Formulae - 2ambresh.09No ratings yet
- No Part of This Presentation May Be Reproduced, Copied, or Transmitted in Any Form or by Any Means!Document57 pagesNo Part of This Presentation May Be Reproduced, Copied, or Transmitted in Any Form or by Any Means!Cherry NissNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid Review Module Nov2020finalDocument2 pagesPlane and Solid Review Module Nov2020finalrhodel cosyeloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - Solid MensurationDocument6 pagesReviewer - Solid MensurationLorenz ArdienteNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument2 pagesFormulasCarmen FloresNo ratings yet
- GEOMETRY FORMULA GUIDEDocument27 pagesGEOMETRY FORMULA GUIDEMubassher Ahmed Shoaib100% (1)
- Averages: For Two Numbers A and BDocument26 pagesAverages: For Two Numbers A and BpankajbookNo ratings yet
- Mathematical FormulaeDocument2 pagesMathematical FormulaeRoslina OthmanNo ratings yet
- Algebra FormulasDocument7 pagesAlgebra FormulasAngela David BucangNo ratings yet
- Formulas Pre OlympiadDocument11 pagesFormulas Pre Olympiadbus9No ratings yet
- Trigonometry DAM PDFDocument9 pagesTrigonometry DAM PDFNtombikhonaNo ratings yet
- Matematika - Formule Za A RazinuDocument7 pagesMatematika - Formule Za A RazinuJakov MandicNo ratings yet
- nth term formula, profit, speed, interest, quadratic formulaDocument2 pagesnth term formula, profit, speed, interest, quadratic formulaHikmaNo ratings yet
- CXC MATHS Formula SheetDocument7 pagesCXC MATHS Formula SheetSeleneGoberdhanNo ratings yet
- Geometry FormulasDocument21 pagesGeometry FormulasHyma100% (1)
- ACT FORMULA SHEET MATHDocument2 pagesACT FORMULA SHEET MATHAdit GhosalkarNo ratings yet
- Research in EdMath 2Document18 pagesResearch in EdMath 2Jivson BuayaNo ratings yet
- END OF PRIMARY BENCHMARK MATHEMATICSDocument14 pagesEND OF PRIMARY BENCHMARK MATHEMATICSgururajanNo ratings yet
- Vectors and The Geometry of SpaceDocument81 pagesVectors and The Geometry of Spaceayesha noorNo ratings yet
- FACTORISATIONDocument10 pagesFACTORISATIONPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- 5th IPM 2022 PaperDocument5 pages5th IPM 2022 PaperNamita B SaneNo ratings yet
- OMO Fall 2013 Math Contest Official SolutionsDocument17 pagesOMO Fall 2013 Math Contest Official SolutionskidNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Math Chapter 2 - PolynomialsDocument69 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Math Chapter 2 - PolynomialsFari KhanNo ratings yet
- Solving Algebra Equations With FractionsDocument2 pagesSolving Algebra Equations With FractionsanjumrajgoliNo ratings yet
- Chapter Wise Worksheet Grade - 8Document13 pagesChapter Wise Worksheet Grade - 8Roamin Uchiha (Aarush)No ratings yet
- Full Download Introduction To Mathematical Thinking Algebra and Number Systems 1st Edition Gilbert Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Introduction To Mathematical Thinking Algebra and Number Systems 1st Edition Gilbert Solutions Manualirisybarrous100% (20)
- Topic 2 - Number - and - Algebra - HandoutsDocument22 pagesTopic 2 - Number - and - Algebra - HandoutspcmantilNo ratings yet
- The Associated Harmonic Quadrilateral - Paris PamfilosDocument15 pagesThe Associated Harmonic Quadrilateral - Paris PamfilosAltanany0% (1)
- X Class Calculus SolutionDocument20 pagesX Class Calculus SolutionSamhithaReddyNo ratings yet
- The Project For Human Resource Development Scholarship by Japanese Grant Aid (JDS) Basic Mathematics Aptitude Test 2019 SolutionDocument7 pagesThe Project For Human Resource Development Scholarship by Japanese Grant Aid (JDS) Basic Mathematics Aptitude Test 2019 SolutionShahadat Jamil Shaon100% (1)
- Advance Engineering Mathematics ECE 321Document33 pagesAdvance Engineering Mathematics ECE 321Cllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Relations and FunctionsDocument51 pagesChapter 1 - Relations and Functionssidhusingh24No ratings yet
- Usemo 2022Document2 pagesUsemo 2022Zhugzhuang ZuryNo ratings yet
- 22-Real Analysis Tute 1 PDFDocument4 pages22-Real Analysis Tute 1 PDFNipuna LaksithaNo ratings yet
- Mathsclinic Smartprep GR10 Eng 2023 V2.1Document36 pagesMathsclinic Smartprep GR10 Eng 2023 V2.1Anees ArnoldNo ratings yet
- Oxfordaqa Gcse Mathematics SpecDocument16 pagesOxfordaqa Gcse Mathematics Specjameelah santillanNo ratings yet
- PolygonsDocument3 pagesPolygonsHAMSKULLNo ratings yet
- Solves Surface Area Word Problems Involving Cubes and Rectangular PrismsDocument37 pagesSolves Surface Area Word Problems Involving Cubes and Rectangular PrismsShaharaZ.Mendoza-PañaresNo ratings yet
- Binary OperationsDocument11 pagesBinary Operationsyaw197100% (1)
- 2 MathDocument5 pages2 Mathas_5kNo ratings yet
- Drill Problems On Derivatives and AntiderivativesDocument5 pagesDrill Problems On Derivatives and AntiderivativesLeah Mae FranceNo ratings yet
- Intro College Math TextDocument247 pagesIntro College Math TextPushpendu GhoshNo ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form5Document28 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form5JW LimNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Topic 1 AnglesDocument12 pagesTrigonometry: Topic 1 AnglesDanika MartinezNo ratings yet
- Area Under Curve-02 - Solved ExampleDocument13 pagesArea Under Curve-02 - Solved ExampleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- All 64 GMAT Math Formulas You Need + How To Use Them - PrepScholar GMATDocument19 pagesAll 64 GMAT Math Formulas You Need + How To Use Them - PrepScholar GMATderek_f1980100% (2)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceFrom EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- Assessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6From EverandAssessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)