Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transactional Mechanical Motion 2 - Ideal Pulleys
Uploaded by
Salman MasriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transactional Mechanical Motion 2 - Ideal Pulleys
Uploaded by
Salman MasriCopyright:
Available Formats
Dynamic System Analysis
MECH 432
Transactional Mechanical Motion
Ideal Pulley
The Ideal Pulley
• A pulley can be used to change the
direction of motion of a translational
mechanical system.
• An ideal pulley has a no mass and no
friction. Furthermore, we assume that
there is no slippage between the cable and
the surface of the cylinder (i.e., same
velocity).
• We also assume the cable is always in
tension but does not stretch (add spring in
series to the model if necessary).
Example 2.7 Animate the
pulley
• Find the equations of motion
Example 2.7
• Find the equations of motion
For 𝑀1 :
For 𝑀2 :
𝐾1 (𝑥2 − 𝑥1 )
Resistive:
Resistive:
𝐾1 : 𝑓𝐾1 = 𝐾1 (𝑥1 − 𝑥2 )
𝐾2 : 𝑓𝐾1 = 𝐾2 𝑥2 − 𝑥𝑤𝑎𝑙𝑙
𝑀1 : 𝑓𝐼 = 𝑀1 𝑥1ሷ
= 𝐾2 𝑥2
𝐵: 𝑓𝐵 = 𝐵1 𝑥1ሶ
𝐾1 : 𝑓𝐾1 = 𝐾1 𝑥2 − 𝑥1
𝑀2 : 𝑓𝐼 = 𝑀2 𝑥2ሷ
Assistive:
𝑓𝑎 : +𝑓𝑎 (𝑡) 𝐵2 : 𝑓𝐵 = 𝐵2 (𝑥ሶ 2 −
𝑥𝑤𝑎𝑙𝑙
ሶ )=𝐵2 𝑥2ሶ
𝑀1 𝑥ሷ 1 + 𝐵1 𝑥ሶ 1 + 𝐾1 𝑥1 − 𝑥2 = +𝑓𝑎 (𝑡) Assistive:
𝑀𝑔: −𝑀2 𝑔
𝑀2 𝑥ሷ 2 + 𝐵2 𝑥ሶ 2 + 𝐾1 𝑥2 − 𝑥1 + 𝐾2 𝑥2 = −𝑀2 𝑔
Ensure that x2<x1, otherwise the string will be loaded in compression!
Example 2.7
𝑀1 𝑥ሷ 1 + 𝐵1 𝑥ሶ 1 + 𝐾1 𝑥1 − 𝑥2 = +𝑓𝑎 (𝑡)
𝑀2 𝑥ሷ 2 + 𝐵2 𝑥ሶ 2 + 𝐾1 𝑥2 − 𝑥1 + 𝐾2 𝑥2 = 0
𝑀1 𝑥ሷ 1 + 𝐵1 𝑥ሶ 1 + 𝐾1 𝑥1 − 𝑥2 = +𝑓𝑎 (𝑡)
𝑀2 𝑥ሷ 2 + 𝐵2 𝑥ሶ 2 + 𝐾1 𝑥2 − 𝑥1 + 𝐾2 𝑥2 = −𝑀2 𝑔
You might also like
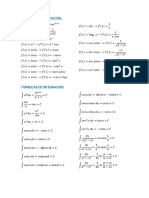
- Formula SheetDocument4 pagesFormula SheetSyasya AziziNo ratings yet
- Formulario Estadistica 4 FinalDocument4 pagesFormulario Estadistica 4 FinalcopiesteriaraquelNo ratings yet
- Application of Partial Differential EquationsDocument7 pagesApplication of Partial Differential EquationsventhiiNo ratings yet
- Lec #5 (Numerical Integration)Document33 pagesLec #5 (Numerical Integration)Hamna YounisNo ratings yet
- Penj El Asan Integral Lipat Dua & Penerapan Pada Momen InersiaDocument26 pagesPenj El Asan Integral Lipat Dua & Penerapan Pada Momen InersiaDevi apNo ratings yet
- Formulário Fisica ModernaDocument2 pagesFormulário Fisica ModernaInes FernandesNo ratings yet
- La Derivada - 01 de Setiembre EjemplosDocument8 pagesLa Derivada - 01 de Setiembre EjemplosAlvaro LeonNo ratings yet
- Engineering Analysis - PDFDocument12 pagesEngineering Analysis - PDFbahast faiqNo ratings yet
- Draw BMD (Use Double Integration and Energy Methods) - Maximum Deflection (Use Double Integration Method)Document5 pagesDraw BMD (Use Double Integration and Energy Methods) - Maximum Deflection (Use Double Integration Method)Nagham MuradNo ratings yet
- Biostatistika FORMULEDocument1 pageBiostatistika FORMULEAjla RekićNo ratings yet
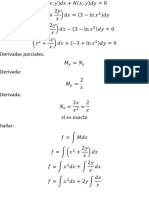
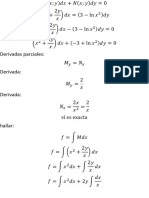
- Integrating Factor For Non-Exact ReducibleDocument3 pagesIntegrating Factor For Non-Exact ReducibleHefri Noer RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Aux 1 PartDocument21 pagesAux 1 PartNelidaNo ratings yet
- Transactional Mechanical Motion 2 - Relative MotionDocument8 pagesTransactional Mechanical Motion 2 - Relative MotionSalman MasriNo ratings yet
- EC2303 Final Formula Sheet PDFDocument8 pagesEC2303 Final Formula Sheet PDFnormanNo ratings yet
- Formulario Derivadas e IntegralesDocument4 pagesFormulario Derivadas e IntegralesJesus G ReNo ratings yet
- 课本附录 (二) - 公式表 Formula Sheet - finalDocument2 pages课本附录 (二) - 公式表 Formula Sheet - finalluoyifei1988No ratings yet
- Hermitian Operators Cont'd:: Quantum Chemistry - Solution Set 3Document9 pagesHermitian Operators Cont'd:: Quantum Chemistry - Solution Set 3mozNo ratings yet
- Diffy Qs 1st Order Linear de Lec (2) (1) ApatDocument19 pagesDiffy Qs 1st Order Linear de Lec (2) (1) ApatClaire G. MagluyanNo ratings yet
- 5volume 2 - 05 - Integral Calculus - 2021 - FinalDocument15 pages5volume 2 - 05 - Integral Calculus - 2021 - FinalRichard TandaguenNo ratings yet
- Financial Statistics - Formula SheetDocument26 pagesFinancial Statistics - Formula Sheetale.ili.pauNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas Cálculo IntegralDocument1 pageFórmulas Cálculo IntegralRicardo AlvesNo ratings yet
- FrmulasClculoIntegral PDFDocument1 pageFrmulasClculoIntegral PDFRicardo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Hafiz Noor-Ul-Amin BMAF17E117Document17 pagesAssignment: Hafiz Noor-Ul-Amin BMAF17E117Haseeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- Coeficientes ConstantesDocument2 pagesCoeficientes ConstantesFernando MurminachoNo ratings yet
- Formuleblad WB1630Document1 pageFormuleblad WB1630Raccoon OneNo ratings yet
- MHLANGA MAZWI - Assignment.1 - 9709Document5 pagesMHLANGA MAZWI - Assignment.1 - 9709MAZWI MHLANGANo ratings yet
- 10 EjerciciosDocument40 pages10 EjerciciosJames Poma ReyesNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentSilvia Rahmi EkasariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 42fourier Series of Discontinuous FunctionsDocument16 pagesLecture 42fourier Series of Discontinuous FunctionsJames PrakashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document29 pagesChapter 3Eyob HabteNo ratings yet
- Alfredj - Zulu 1598868814 ADocument14 pagesAlfredj - Zulu 1598868814 AMike chibaleNo ratings yet
- Integration (Part 1) - MAADocument10 pagesIntegration (Part 1) - MAAMD. ABDULLAH AL MAHMUD 221-33-1630No ratings yet
- Statistics ProofsDocument1 pageStatistics ProofsRaghad Al-ShaikhNo ratings yet
- ME-L04 Fourier Analysis of Continuous-Time Signals and SystemsDocument22 pagesME-L04 Fourier Analysis of Continuous-Time Signals and SystemsYeng VisalNo ratings yet
- ME L04 Fourier Analysis of Continuous Time Signals and SystemsDocument23 pagesME L04 Fourier Analysis of Continuous Time Signals and SystemsYeng VisalNo ratings yet
- ( ) : ( ) ( - ) ( - ) Máxima SimilitudDocument1 page( ) : ( ) ( - ) ( - ) Máxima SimilitudErick XavierNo ratings yet
- Assignement (RA-II)Document1 pageAssignement (RA-II)Adinew GeseseNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii (Part-2)Document26 pagesUnit-Ii (Part-2)M jhansiNo ratings yet
- Formula RioDocument4 pagesFormula RioalejandroNo ratings yet
- Lec10 - Pharm - Math - After Bahdala2Document18 pagesLec10 - Pharm - Math - After Bahdala2Shrouk AbdallahNo ratings yet
- 07.2.0. Fourier - PropiedadesDocument13 pages07.2.0. Fourier - PropiedadesSteven ChávezNo ratings yet
- Graficos EdoDocument12 pagesGraficos EdoJanine CabascangoNo ratings yet
- Graficos EdoDocument12 pagesGraficos EdoJanine CabascangoNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Models of Chemical Processes: Abdul Halim Chemical Engineering Universitas Internasional Semen IndonesiaDocument37 pagesTheoretical Models of Chemical Processes: Abdul Halim Chemical Engineering Universitas Internasional Semen IndonesiathoriqnoviaNo ratings yet
- Wzory StatystykaDocument1 pageWzory StatystykaAbejejNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations L2Document4 pagesDifferential Equations L2AndreaNo ratings yet
- Lecture No, - 1week No, - 1course Code - BSI242 Noor BadshahDocument33 pagesLecture No, - 1week No, - 1course Code - BSI242 Noor BadshahLeo KhanNo ratings yet
- Integration Sine and CosineDocument13 pagesIntegration Sine and CosinemukondimmagodaNo ratings yet
- Final Formula Sheet MArk3120Document2 pagesFinal Formula Sheet MArk3120Sophia RosieeNo ratings yet
- Derivadas ParcialesDocument13 pagesDerivadas ParcialesValentina Duarte GamboaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation: Rule If F (X) Then F' (X) BasicDocument2 pagesDifferentiation: Rule If F (X) Then F' (X) BasicJo-LieAngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Part 3Document10 pagesChapter 1 - Part 3Shahril ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Week 11Document76 pagesWeek 11snaaaoNo ratings yet
- 2850-361 Sample Formulae Sheet v1-0 PDFDocument3 pages2850-361 Sample Formulae Sheet v1-0 PDFMatthew SimeonNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous FunctionDocument11 pagesHomogeneous FunctionJOHN DAVID DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- BC Calculus ReviewDocument29 pagesBC Calculus ReviewKawan EngNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Account Activity: As of 19-01-2024 14:09:38 GMT +0200Document1 pageAccount Activity: As of 19-01-2024 14:09:38 GMT +0200Salman MasriNo ratings yet
- ME412 Heat Transfer Syllabus 2024Document4 pagesME412 Heat Transfer Syllabus 2024Salman MasriNo ratings yet
- Midterm P4 MECH412 2021Document1 pageMidterm P4 MECH412 2021Salman MasriNo ratings yet
- Functions HigherOrderDocument2 pagesFunctions HigherOrderSalman MasriNo ratings yet
- Tuples Lists MutableObjectsDocument4 pagesTuples Lists MutableObjectsSalman MasriNo ratings yet
- Repetition ForDocument2 pagesRepetition ForSalman MasriNo ratings yet
- Transactional Mechanical Motion - VariablesDocument6 pagesTransactional Mechanical Motion - VariablesSalman MasriNo ratings yet
- Functions ListMethodsDocument3 pagesFunctions ListMethodsSalman MasriNo ratings yet
- Chap +5+Cardiovascular+SyDocument39 pagesChap +5+Cardiovascular+SySalman MasriNo ratings yet
- Transactional Mechanical Motion-Free Body DiagramsDocument13 pagesTransactional Mechanical Motion-Free Body DiagramsSalman MasriNo ratings yet
- Transactional Mechanical Motion-Interconnection LawsDocument7 pagesTransactional Mechanical Motion-Interconnection LawsSalman MasriNo ratings yet