Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cms-710-02-Fm-05201 - Overhead and Gantry Crane Inspection Form
Uploaded by
Cesar William Aquino AburtoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cms-710-02-Fm-05201 - Overhead and Gantry Crane Inspection Form
Uploaded by
Cesar William Aquino AburtoCopyright:
Available Formats
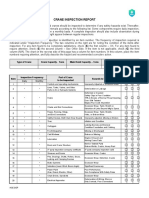
OVERHEAD AND GANTRY CRANE For written reports, respond
in “Conditions Noted”
INSPECTION FORM column.
A Daily - visual inspection, no written report required. Type of Report: Monthly Annual
B Monthly - written report required, use this form.
C Annual - written report required, use this form. Contract No.
Cranes to receive this type inspection also when:
Location
1) New or Altered
2) Idle three to six months Date
3) Stand-by or idle over six months
4) Any major repair. Date of Last Inspection
Item To Be Inspected Inspection Frequency
(“X” indicates frequency. Place ““ beside “X” indicating A B C Conditions
item has been inspected.) Daily Monthly Annual Noted
Report Report
1. Control mechanisms - misadjustment, marking of controls, etc. X X X
2. Limit switches - checked w/o load for operation X X X
3. Air or hydraulic system lines, tanks, valves, drain valves, etc. -
deterioration or leakage
X X X
4. Hooks - deformation or cracks (visual check), NDE if suspect X X X
5. Hoist or load attachment chains - wear, twist, stretch (visual
check). For annual inspection record on back or facility rigging X X X
equipment inspection form.
6. Wire rope slings - wear, stretch, broken wires, kinks, twist (visual
check) - See notes on back. Record inspection on back or facility X X X
rigging equipment inspection form.
7. Wire rope reeving - comply to equipment manufacturing
specifications
X X X
8. Functional operating mechanisms - excessive component wear X X X
9. Structural members – i.e. bridge beam flange, trolley truck runs,
etc. deformed, cracked or corroded members.
X
10. Loose bolts or rivets X X
11. Sheaves and drums - cracked or worn X X X
12. Pins, bearings, shafts, gears, rollers, lock & clamp devices -
damaged or worn
X
13. Brake system parts, linings, pawls, ratchets - excessive wear X
14. Load, wind and other indicators - accuracy X X X
15. Power plants - proper performance X
16. Chain drive sprockets and chains - excess wear & stretch,
alignment
X
17. Electrical apparatus, controller contractors, limit switches, push
button stations - pitting and deterioration, marking of switches X X X
and controls.
18. Wire rope, condition - See notes on back page and record
inspection results on back page.
X X X
Name of Facility
Description of Overhead Crane:
Make Model Serial No.
Capacity: Main Hoist ; Auxiliary Hoist
Comments:
Distribution: Original - Maintenance/Plant Engineer Inspector:
Copy - Supervisor Signature
Copy – Superintendent
Copy – Safety Supervisor Superintendent:
Signature
Parent Document: CMS-710-02-PR-05200
Form Number: CMS-710-02-FM-05201 Issued for Use: 25 Jun 2015 Page 1 of 2
REQUIREMENTS FOR WIRE ROPE INSPECTION
1. Evidence of rope deterioration from corrosion should be cause for (A) Running Wire Rope
replacement. 1. Broken Wires
2. More than one broken wire in any one strand should be cause for (a) Six randomly distributed broken wires in one rope lay
caution. Breaks that occur on the worn crowns of the outside (b) Three broken wires in one strand in one lay
wires indicate normal deterioration. Breaks that occur in the 2. Loss of Rope Diameter
valleys between strands indicate some abnormal condition, (a) Abrasion scrubbing, flattening, peening, or any other
possibly fatigue and breakage of other wires not readily visible. damage resulting in distortion of the rope structure.
One or more valley breaks should be cause for replacement. (b) Reduction from nominal rope diameter of more than
3. Wire breaks generally occur in those portions of a wire rope 5%.
which pass over sheaves, wind onto drums, or receive 3. Other Types of Rope Damage
mechanical abuse. Breaks that occur near attached fittings are (a) Heat or electrical arc damage
apt to result form fatiguing stresses concentrated in these (b) Birdcaging (increased diameter)
localized sections. Breaks of the latter type should be cause for (c) Drum crushing (increased diameter)
replacement of the rope or renewal of the attachment to eliminate (d) High-stranding (increased diameter)
the locally fatigued area. (e) Dog legs or kinks (increased diameter)
4. Heavy wear or broken wires may occur in sections under (f) Corrosion
equalizer sheaves or other sheaves where rope travel is limited, (B) Pendant or Standing Wire Rope
or in contact with saddles. Particular care should be taken to 1 Broken Wires
inspect ropes at these points. (a) Three or more broken wires in one lay in section
5. Rope stretch is generally greatest during initial stages of beyond end connection
operation when the strands are becoming adjusted and seated. (b) Two or more broken wires at end connection
This is accompanied by some reduction in rope diameter, but not (C) Wire Rope Slings
to the extent that the condition of the rope can be judged on this 1 Broken Wires
basis. (a) 10 randomly distributed broken wires in one lay
6. Time for rope replacement is indicated by the extent of abrasion, (b) 5 broken wires in one strand in one lay.
scrubbing and peening on the outside wires, broken wires, (E) Rotation-resistant Wire Rope
evidence of pitting or severe corrosion, kink damage, or other 1. Broken Wires
mechanical abuse resulting in distortion of the rope structure. (a) Two randomly distributed broken wires in six
7. Sheaves, guards, guides, drums, flanges and other surfaces
diameters
contacted by wire rope during operation should be examined at
(b) Four randomly distributed broken wires in thirty
the time of inspections. Any condition harmful to the rope in use
rope diameters
at the time should be corrected. The same equipment, and
particularly sheave and drum grooves, should be inspected and
placed in proper condition before a new rope is installed.
8. Any of the following listed conditions shall be cause for rope
replacement:
RESULTS OF INSPECTION:
Rope Inspected Type and Size Conditions Noted Recommendation
Remarks:
Parent Document: CMS-710-02-PR-05200
Form Number: CMS-710-02-FM-05201 Issued for Use: 25 Jun 2015 Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Guia de Mantenimiento 2535Document54 pagesGuia de Mantenimiento 2535Sebastian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Eot Crane Monthly ChecksheetDocument4 pagesEot Crane Monthly ChecksheetAmit ThakurNo ratings yet
- Audel Guide to the 2005 National Electrical CodeFrom EverandAudel Guide to the 2005 National Electrical CodeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Calidus Periodic Service Worksheet V6 Sep 2021Document9 pagesCalidus Periodic Service Worksheet V6 Sep 2021rpr01No ratings yet
- Fm200 System Test Report Formats Index SL - No Description Document No. A Erection Control Forms For FM200 SystemDocument2 pagesFm200 System Test Report Formats Index SL - No Description Document No. A Erection Control Forms For FM200 SystemAneesh ConstantineNo ratings yet
- CPL Combined SyllabusDocument99 pagesCPL Combined Syllabusshubham chavhanNo ratings yet
- FM-OHS-1700-30 Pre Use Daily Weekly G20 Crane InspectionDocument2 pagesFM-OHS-1700-30 Pre Use Daily Weekly G20 Crane InspectiondavidburkepsNo ratings yet
- Crane Pre Commissioning ITPDocument6 pagesCrane Pre Commissioning ITPAbdul Hamid TasraNo ratings yet
- Crane Inspection ReportDocument2 pagesCrane Inspection ReportbasdNo ratings yet
- Rig Service Lifting Audit UpdatesDocument6 pagesRig Service Lifting Audit UpdatesJorge Humberto Chaparro RamirezNo ratings yet
- Service Loop Incl Manifold(s) in DerrickDocument2 pagesService Loop Incl Manifold(s) in DerrickmhmdtrainingNo ratings yet
- Ramp CheckDocument4 pagesRamp Checka.teamwork2016No ratings yet
- Stem-1 - Frac TankDocument1 pageStem-1 - Frac TankMohamed El-SawahNo ratings yet
- 16 Tractor Inspection ChecklistDocument1 page16 Tractor Inspection ChecklistKoneti JanardhanaraoNo ratings yet
- Daily Equipment Safety ChecklistDocument5 pagesDaily Equipment Safety ChecklistArturo Ramos AlvezoNo ratings yet
- P&G SOWDocument4 pagesP&G SOWsigmaintipurnamaNo ratings yet
- Luffing Tower Crane Preshift InspectionDocument1 pageLuffing Tower Crane Preshift InspectionEdmond KeraNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Mechanic Job DescriptionDocument8 pagesMaintenance Mechanic Job DescriptionBooky BermindashNo ratings yet
- POCKET GUIDE - Wire Rope For Oil FieldDocument2 pagesPOCKET GUIDE - Wire Rope For Oil Field刘 建No ratings yet
- TDC - YER.1.00000 Updated (TDS-3)Document4 pagesTDC - YER.1.00000 Updated (TDS-3)Mohamed AnwarNo ratings yet
- Eot Ibl Crane Yearly ChecksheetDocument3 pagesEot Ibl Crane Yearly ChecksheetAmit ThakurNo ratings yet
- ATG SyllubusDocument13 pagesATG Syllubusjanine GoncalvesNo ratings yet
- BAC Maintenance-VXI MVXIv17EN-SADocument34 pagesBAC Maintenance-VXI MVXIv17EN-SAEurotech Tra TranNo ratings yet
- 01 - 1030 James Rowley - Hydratight PDFDocument17 pages01 - 1030 James Rowley - Hydratight PDFaaNo ratings yet
- 1-Pedestal Crane MONTHLY Checklist Rev 04Document2 pages1-Pedestal Crane MONTHLY Checklist Rev 04ananthNo ratings yet
- Overhead Crane Inspection ProceduresDocument5 pagesOverhead Crane Inspection ProceduresRonniNo ratings yet
- Annual Performance Test Procedure (Circ1222) Rev 3.0Document43 pagesAnnual Performance Test Procedure (Circ1222) Rev 3.0Macro LoveNo ratings yet
- Lifeboat That Will Be Inspected During The Recertification of The Lifeboat (2 Day)Document10 pagesLifeboat That Will Be Inspected During The Recertification of The Lifeboat (2 Day)Justin KallicharanNo ratings yet
- SOP Mobile Crane-Rev.1Document7 pagesSOP Mobile Crane-Rev.1RonniNo ratings yet
- Equipment Checklist PDFDocument34 pagesEquipment Checklist PDFHector IbarraNo ratings yet
- Verif Epi Protraxion Procedure enDocument4 pagesVerif Epi Protraxion Procedure eninternetNo ratings yet
- BLNG TPI ChecklistDocument2 pagesBLNG TPI ChecklistSajith VenkitachalamNo ratings yet
- The Visual Inspection Includes Removal of Inspection Cover Plates As Necessary To Do A Thorough JobDocument6 pagesThe Visual Inspection Includes Removal of Inspection Cover Plates As Necessary To Do A Thorough JobBenjamin HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Inspection CraneDocument2 pagesInspection CranedroidsNo ratings yet
- APPEA ComplianceDocument31 pagesAPPEA ComplianceManuelNo ratings yet
- VT0 Open Cooling Towers VT1 Open Cooling Tower: Operating and Maintenance InstructionsDocument34 pagesVT0 Open Cooling Towers VT1 Open Cooling Tower: Operating and Maintenance InstructionsoussNo ratings yet
- VDR C.O.C. Requirements - 2018.02.27Document17 pagesVDR C.O.C. Requirements - 2018.02.27Macro Love100% (2)
- Forklift safety proceduresDocument5 pagesForklift safety proceduresvictorNo ratings yet
- Wheelchair Lift and Stairlift Annual Maintenance ChecklistDocument2 pagesWheelchair Lift and Stairlift Annual Maintenance ChecklistUmmi HuraizahNo ratings yet
- 3 Monthly PM - OH CraneDocument3 pages3 Monthly PM - OH CraneMuhammad RosihanNo ratings yet
- Tracespec: Global Resources LTDDocument1 pageTracespec: Global Resources LTDTrustEmmaNo ratings yet
- MV. Bahtera Cemerlang - Wreck Removal Oil Pollution Survey ReportDocument11 pagesMV. Bahtera Cemerlang - Wreck Removal Oil Pollution Survey ReportEka Prasetya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Checklist Form: SL No Condition Inspection / Check Point MonthlyDocument1 pageMaintenance Checklist Form: SL No Condition Inspection / Check Point MonthlyAneesh ConstantineNo ratings yet
- CPA Mobile Cranes Wheeled Daily Checks TemplateDocument1 pageCPA Mobile Cranes Wheeled Daily Checks Templateaalaamostafa23No ratings yet
- 2009 Crane Start Up Inspection FormDocument3 pages2009 Crane Start Up Inspection Formsaeed ghafooriNo ratings yet
- MLA Data Sheet - LNG - RevaDocument6 pagesMLA Data Sheet - LNG - RevaLuis Gonzalez0% (1)
- New Removal of Bore Pump SWIDocument11 pagesNew Removal of Bore Pump SWIchrisNo ratings yet
- INSPECCION POR -HARD LANDING-Document4 pagesINSPECCION POR -HARD LANDING-jrdavjhonrom08No ratings yet
- AIS PR INS 29 Rev 01 Crane Inspection Procedure (Repaired)Document11 pagesAIS PR INS 29 Rev 01 Crane Inspection Procedure (Repaired)aymenmoatazNo ratings yet
- Bac - VXC - Operating and Maintenance InstructionsDocument36 pagesBac - VXC - Operating and Maintenance InstructionsLuis Alejandro VásquezNo ratings yet
- Table 3. Recommended Field Tests (B) .: Creating An Effective Maintenance Program GEK 103566hDocument1 pageTable 3. Recommended Field Tests (B) .: Creating An Effective Maintenance Program GEK 103566hRajesh BNo ratings yet
- Crane Construction Verification ITPDocument5 pagesCrane Construction Verification ITPmuhammad afrizalNo ratings yet
- TRACTOR INSPECTION CHECKLIST FOR RFCL CONNECTIVITY PIPELINEDocument2 pagesTRACTOR INSPECTION CHECKLIST FOR RFCL CONNECTIVITY PIPELINEkumar kush100% (1)
- Crane ProceduresDocument67 pagesCrane ProceduresKen RanggaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Maintenance On Hydra RackerDocument4 pagesWeekly Maintenance On Hydra Rackermohamed hamedNo ratings yet
- Crawler Crane Checklist Rev 0Document2 pagesCrawler Crane Checklist Rev 0Maizatul Akmar Manshor100% (2)
- Scheduled Maintenance Allegro-BreezeDocument3 pagesScheduled Maintenance Allegro-BreezeamarcotteNo ratings yet
- Bright Engineering Capability Statement 1Document6 pagesBright Engineering Capability Statement 1Bilal KhanNo ratings yet
- Pressure Relief ValueDocument7 pagesPressure Relief ValueVictor Torres100% (1)
- Level Controls For Scrubbers: L1200 SeriesDocument4 pagesLevel Controls For Scrubbers: L1200 SeriesMEHDINo ratings yet
- WIS 10 Training: Drawing Exercise #1 (Rev. 2)Document1 pageWIS 10 Training: Drawing Exercise #1 (Rev. 2)Doni AfrizalNo ratings yet
- Section ViewDocument22 pagesSection Viewyk_maddyNo ratings yet
- Overboard Valve: Straight, Flanged EndsDocument1 pageOverboard Valve: Straight, Flanged Endsadvantage025No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machine Lab ReportDocument22 pagesMechanics of Machine Lab ReportFaisal MehrbanNo ratings yet
- 50Hz Concealed Duct Unit SpecsDocument3 pages50Hz Concealed Duct Unit SpecsPrimero Valencia LuisNo ratings yet
- ASESORIS HIDROLIK Suction LineDocument7 pagesASESORIS HIDROLIK Suction LineMuhammad Rokhani SalehNo ratings yet
- Regulador Fisher 627Document24 pagesRegulador Fisher 627Ainarut CamargoNo ratings yet
- Landmark Towers 7-8 Cooling Load SummaryDocument17 pagesLandmark Towers 7-8 Cooling Load SummaryAdnan AttishNo ratings yet
- Despiece de Esmeril Dewalt D28490-B3Document3 pagesDespiece de Esmeril Dewalt D28490-B3Kevin Jesus Tadeo Reyes MendezNo ratings yet
- 8-Inch FRP Pressure Vessel User ManualDocument35 pages8-Inch FRP Pressure Vessel User ManualkylealamangoNo ratings yet
- Sip 4th Week c04-059Document3 pagesSip 4th Week c04-059Mugundan N ManiNo ratings yet
- Petesquared Bricksorter Mini Drawing 01-10-2023Document8 pagesPetesquared Bricksorter Mini Drawing 01-10-2023La mera SogaNo ratings yet
- Axces DIN2576 PN10 FlangesDocument1 pageAxces DIN2576 PN10 FlangesAndy SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compressor Inspection GuideDocument7 pagesCentrifugal Compressor Inspection GuideEnergy 2GreenNo ratings yet
- Wiring DiagramDocument1 pageWiring DiagramBayu IsmoyoNo ratings yet
- Online Ass.Document2 pagesOnline Ass.Tesfamichael FufaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Multiple Pig Launching SystemsDocument8 pagesAutomatic Multiple Pig Launching SystemsZackNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet For Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage-Motors SIMOTICS: Motor Type: 7CV3073B Simotics SD - 71M - Im B3 - 4 PDocument1 pageData Sheet For Three-Phase Squirrel-Cage-Motors SIMOTICS: Motor Type: 7CV3073B Simotics SD - 71M - Im B3 - 4 PSHYAM SHARMANo ratings yet
- U3L6 - Dynamics Problem SetDocument3 pagesU3L6 - Dynamics Problem SetLia WallaceNo ratings yet
- 2600 Series Catalog R3Document38 pages2600 Series Catalog R3Mohammad Dzauqi AdamNo ratings yet
- 987559-Product Datasheet-80510-SRS 30XLDocument2 pages987559-Product Datasheet-80510-SRS 30XLZé MirtoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Document4 pagesDiagnostic Assessment B3 (SEC) - November 2022Yoshjordan LambNo ratings yet
- Maintain Boat Davit Safety with Regular InspectionsDocument3 pagesMaintain Boat Davit Safety with Regular InspectionscraponzelNo ratings yet
- Boiler TypeDocument13 pagesBoiler TypeAhemadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Machine AlignmentDocument9 pagesLecture 2 Machine Alignmentodeke aronNo ratings yet
- Cheap Armature TutorialDocument5 pagesCheap Armature TutorialjesseoNo ratings yet
- Material Handling Equipment Chapter on Hoisting EquipmentDocument40 pagesMaterial Handling Equipment Chapter on Hoisting EquipmentSagni GetachewNo ratings yet