Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LEADeXCELS Mod1
Uploaded by
Ray AnzuresOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LEADeXCELS Mod1
Uploaded by
Ray AnzuresCopyright:
Available Formats
What Do You Already Know?
P4
1. Explain three roles of the school head in building a safer school in relation to disasters.
a. Teaching Disaster management to students
b. Serve as an evacuation center
c. If a disaster happens during school hours, schools must consider the risks that
students are exposed to and respond early to such an event.
2. Explain the basic concepts related to disaster risk reduction and management, with
relevant examples.
a. Hazard – an unavoidable danger or risk, even though often foreseeable.
Example
A common way to classify hazards is by category:
biological - bacteria, viruses, insects, plants, birds, animals, and humans, etc.,
chemical - depends on the physical, chemical and toxic properties of the
chemical,
ergonomic - repetitive movements, improper set up of workstation, etc.,
physical - radiation, magnetic fields, pressure extremes (high pressure or
vacuum), noise, etc.,
psychosocial - stress, violence, etc.,
safety - slipping/tripping hazards, inappropriate machine guarding, equipment
malfunctions or breakdowns.
b. Vulnerability - the likelihood that assets will be damaged/destroyed/affected when
exposed to a hazard. Example a building with multiple floors may be more
vulnerable to shaking from an earthquake and more likely to collapse than a one-
story building.
c. Disaster Risk Management is the application of disaster risk reduction policies
and strategies, to prevent new disaster risks, reduce existing disaster risks, and
manage residual risks, contributing to the strengthening of resilience and
reduction of losses. Examples are reducing exposure to hazards, lessening
vulnerability of people and property, wise management of land and the
environment, and improving preparedness for adverse events
3. Identify and explain some of the components contained in the DRRM cycle as it applies
to the school setting.
a. Prevention Mitigation - efforts are made to prevent or mitigate damage
b. Preparedness – Activities and measures for ensuring an effective response to the
impact of hazards
c. Disaster – doing what was prepared during disaster
d. Response – rescue efforts, first aid, fire fighting and evacuation
e. Rehabilitation Reconstruction - considerations of disaster risk reduction should form
the foundations for all activities
4. Briefly discuss two functions of a school disaster risk reduction and management
(DRRM) committee.
a. Spearhead the conduct of multi-hazard drills and other disaster
prevention, mitigation and preparedness activities in school
b. Serve as the point person for collaborations and coordination with
local DRRM Council and other partner organizations
5. Briefly explain three tools that you can use to assess the vulnerability of your school to
disasters.
a. Student-led hazard mapping
b. Baseline data
c. Emergency Response Inventory
6. Explain three important considerations when developing your school DRRM plan.
a. Geological location
b. Socio-economic landscape
c. School Physical Condition
7. Explain three strategies for communicating your school DRRM plan
a. Student awareness and preparedness education
b. Involve parents and other stakeholders
c. Curriculum integration
8. How do you propose to integrate disaster DRRM-related concepts in your school
curriculum?
a. AP DRRM
b. Science Typhoons, Volcanoes and Earthquakes
c. MAPEH First Aide
9. Enumerate and explain some examples of learning materials related to DRRM that you
have observed your teachers using in their classrooms
a. An AP teacher taught Disaster Risk Reduction and Management to her Grade 10
students during the 1st Quarter in which the learning Materials were given by the
LGU.
b. A Science teacher taught Typhoons, Volcanoes and Earthquakes to her grade 10
students during the 1st quarter using materials developed by the RO.
c. A MAPEH Teacher taught First Aide to his Grade 9 students using materials
developed by the teacher during the Division INSET.
10. Suggest some DRRM-related activities that you can plan and organize for your students
to encourage them to become DRRM champions.
a. Organization of School-Based Student-Led DRRM Organization
b. Participation to Red Cross First Aide Interschool Competition
c. Organization of School-Based Training Seminars for students
d. Parents and other stakeholders’ involvement in organizing the said activities
Self-Rating Competency Checklist
I cannot do I am I can do I can do this
this yet. learning this, but very well.
how to do I need
this. to learn
more and
improve.
1. Describe the √
roles of the
school head in
disaster risk
reduction and
management
(DRRM).
2. Explain the √
basic concepts
related to
DRRM.
3. Describe the √
DRRM cycle.
4. Organize a √
school DRRM
committee.
5. Assess the √
vulnerability
of your
school to
both natural
and human
induced
hazards.
6. Develop a √
school DRRM
plan involving
school
stakeholders.
7. Communicate √
the school
DRRM plan.
8. Integrate √
DRRM
concepts in
the school
curriculum.
9. Lead and √
guide your
teachers in
developing
learning
materials
related to
DRRM.
10. Plan and √
organize
student
activities
leading
towards a
safer school.
Legal basis for schools as evacuation centers
In accordance with DepEd Memo No. 58, s. 2015 that states the Guidelines on Evacuation Center
Coordination and Management, the Department of Education shall provide temporary shelters to
evacuees affected by calamity.
DEPED-DSWD-DILG-DOH JOINT MEMORANDUM CIRCULAR NO. 1, s. 2013
GUIDELINES ON EVACUATION CENTER COORDINATION AND MANAGEMENT
You might also like
- Preparing for Disaster: What Every Early Childhood Director Needs to KnowFrom EverandPreparing for Disaster: What Every Early Childhood Director Needs to KnowNo ratings yet
- PART 2 School Disaster Risk Reduction and ManagementDocument15 pagesPART 2 School Disaster Risk Reduction and ManagementPAOLA LUZ CRUZNo ratings yet
- Ready for Anything : A Guide to Disaster Preparedness and Family SafetyFrom EverandReady for Anything : A Guide to Disaster Preparedness and Family SafetyNo ratings yet
- School Disaster Management Contingency Plan 1Document20 pagesSchool Disaster Management Contingency Plan 1Rizalyn Tatotz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Planning and Preparedness in Early Childhood and School-Age Care SettingsFrom EverandDisaster Planning and Preparedness in Early Childhood and School-Age Care SettingsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Week 8 CU 7 DN-M2-CU7 School Mitigation and Preparedness, Evaluation-2 - 1460360581 PDFDocument9 pagesWeek 8 CU 7 DN-M2-CU7 School Mitigation and Preparedness, Evaluation-2 - 1460360581 PDFArlyn MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Week 9 CU 8 School Disaster Risk Reduction Planning, EvaluationDocument4 pagesWeek 9 CU 8 School Disaster Risk Reduction Planning, EvaluationMAUREIN ANNE TEPACENo ratings yet
- Final Updated CU7 School Mitigation and Preparedness EvaluationDocument10 pagesFinal Updated CU7 School Mitigation and Preparedness EvaluationKathleen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Sci-Eng SDM HandbookDocument104 pagesSci-Eng SDM Handbookkitderoger_391648570No ratings yet
- DRRM DepED Management PlanDocument69 pagesDRRM DepED Management PlanJofit Dayoc100% (1)
- PART 1 School Disaster Risk Reduction and ManagementDocument26 pagesPART 1 School Disaster Risk Reduction and ManagementPAOLA LUZ CRUZ100% (1)
- School Disaster Management Planning TemplateDocument8 pagesSchool Disaster Management Planning TemplateMargie AmoinNo ratings yet
- DRRM OfficerDocument2 pagesDRRM OfficerShanee ArguellesNo ratings yet
- School Based DRRM PlanDocument17 pagesSchool Based DRRM PlanHERMINIGILDO ATIENZANo ratings yet
- School Disaster MGMT PlanDocument39 pagesSchool Disaster MGMT PlanDhruv Bhardwaj100% (1)
- SSP Presentation PDFDocument57 pagesSSP Presentation PDFTine CristineNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) Framework PlanDocument5 pagesComprehensive Disaster Risk Reduction and Management (DRRM) Framework PlanFERNANDEZ ZACAL LEARNING CENTER INC100% (1)
- Asic Chool LAN: (School Name) (Document8 pagesAsic Chool LAN: (School Name) (Leonardo PalominoNo ratings yet
- School Disaster 2018Document20 pagesSchool Disaster 2018Allan Tangkihay100% (1)
- DRRR Quarter 1 - Module 6Document4 pagesDRRR Quarter 1 - Module 6Shelly Ryn Saligumba86% (36)
- DLP Hazard MappingDocument7 pagesDLP Hazard Mappingaleah siducon100% (1)
- Questionnaire DRRMDocument4 pagesQuestionnaire DRRMjuliamark78% (9)
- School Disaster MGMT PlanDocument39 pagesSchool Disaster MGMT Planramshere2003165No ratings yet
- SCHOOL DISASTER MANAGEMENT PLANNING Workshop June 25-26, 2019Document62 pagesSCHOOL DISASTER MANAGEMENT PLANNING Workshop June 25-26, 2019Albert MarzanNo ratings yet
- Education Cluster Operations ProtocolDocument9 pagesEducation Cluster Operations ProtocolSIP DCNHS Official100% (2)
- DRRRM TeamDocument10 pagesDRRRM TeamRey Julius RanocoNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesArgie Joy Marie AmpolNo ratings yet
- School Disaster Preparedness PlanDocument53 pagesSchool Disaster Preparedness PlanMaan GasmenNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Schools Safety Monitoring ChecklistDocument5 pagesComprehensive Schools Safety Monitoring ChecklistKriss Paran100% (1)
- Concept PaperDocument14 pagesConcept PaperJOHANNES LATRASNo ratings yet
- LP DRRR Teaching PrinciplesDocument5 pagesLP DRRR Teaching PrinciplesArgie Joy Marie AmpolNo ratings yet
- Drrmo Suggested Inputs On Field Testing of The New School Improvement Planning Process and ToolsDocument4 pagesDrrmo Suggested Inputs On Field Testing of The New School Improvement Planning Process and ToolsAnonymous f1Dn9aNo ratings yet
- Mock Drills - Guidance Note For Schools (29-03)Document22 pagesMock Drills - Guidance Note For Schools (29-03)A.k. SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar - Camiso Grace CotDocument7 pagesLesson Exemplar - Camiso Grace CotJhoan ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Disaster RoutingDocument57 pagesDisaster RoutingAnonymous 52ChTZ100% (1)
- DISASTER RESPONSE AND RISK REDUCTION - Q3 - SLM3-without Answer KeyDocument14 pagesDISASTER RESPONSE AND RISK REDUCTION - Q3 - SLM3-without Answer KeyDeceree Mae RemeticadoNo ratings yet
- SJWCS-DRRM MagazineDocument6 pagesSJWCS-DRRM MagazineIrish Capili LaquiNo ratings yet
- Criteria For Best Safety School Program Implementer 1Document7 pagesCriteria For Best Safety School Program Implementer 1nanethangelesNo ratings yet
- 3.5 - Safe Schools Project Building Safe Learning EnvironmentDocument56 pages3.5 - Safe Schools Project Building Safe Learning EnvironmentAbet LaborteNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Emergency Preparedness and Safety ManagementDocument9 pagesModule 1 Emergency Preparedness and Safety ManagementRaffy CioconNo ratings yet
- Background of The StudyDocument75 pagesBackground of The StudyroemarNo ratings yet
- SWT Accomplishment 2016 2017Document6 pagesSWT Accomplishment 2016 2017Brylee PascualNo ratings yet
- SDRRM Completion ReportDocument2 pagesSDRRM Completion ReportJoy Cano Butlay100% (1)
- ABUSO Disaster - in The Time of K To 12-Summary AdvanceDocument8 pagesABUSO Disaster - in The Time of K To 12-Summary AdvanceKlent CalunsagNo ratings yet
- S2S Awareness ProgramDocument24 pagesS2S Awareness ProgramAaron James Mutia MabuyoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 DRRM MANUAL PDFDocument58 pagesModule 2 DRRM MANUAL PDFMichelle Revilla BeltranNo ratings yet
- School Crisis MGMTDocument34 pagesSchool Crisis MGMTJester Ambojnon Tukling100% (1)
- Module-1-Emergency Preparedness and Safety ManagementDocument8 pagesModule-1-Emergency Preparedness and Safety ManagementGrace AngNo ratings yet
- SDRRM Manual 1 InsideDocument26 pagesSDRRM Manual 1 InsideNORMAN BREGENTENo ratings yet
- Raagas, Ma - Cristina N. Bped 2-ADocument3 pagesRaagas, Ma - Cristina N. Bped 2-ASagaar Airam AnitsircNo ratings yet
- DRRR q2 Mod13 Fireemergencyandevacuationplan v2Document27 pagesDRRR q2 Mod13 Fireemergencyandevacuationplan v2Mordecai SaceNo ratings yet
- School Disaster Management Contingency PlanDocument28 pagesSchool Disaster Management Contingency PlanJayzel Joy Juanico94% (83)
- Session Guide: Alternative Learning System For Senior High School Als-ShsDocument3 pagesSession Guide: Alternative Learning System For Senior High School Als-ShsDharwin Jhay LinatocNo ratings yet
- DRRM Manual - Booklet 1 - Final 1Document32 pagesDRRM Manual - Booklet 1 - Final 1MICHAEL JIMENONo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed. 22 Learning Episode 7.4Document6 pagesProf. Ed. 22 Learning Episode 7.4Jomar DiegoNo ratings yet
- DRRR q1 Mod1 Basicconceptofdisasteranddisasterrisk v2Document26 pagesDRRR q1 Mod1 Basicconceptofdisasteranddisasterrisk v2Kymbherleigh100% (1)
- School Disaster Risk Reduction and Management PlanDocument2 pagesSchool Disaster Risk Reduction and Management PlanMin Hyun ParkNo ratings yet
- School Disaster Management Contingency PlanDocument26 pagesSchool Disaster Management Contingency PlanR-Yel Labrador Baguio94% (54)
- DRR - 1 WeekDocument4 pagesDRR - 1 WeekJayrLinsanganManuelNo ratings yet
- Letter of RequestDocument1 pageLetter of RequestRay AnzuresNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test For School HeadsDocument8 pagesPre-Test For School HeadsRay AnzuresNo ratings yet
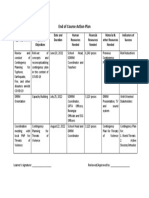
- LEAD Action Plan ANZURES, Wilson RayDocument1 pageLEAD Action Plan ANZURES, Wilson RayRay AnzuresNo ratings yet
- CLP and UDL Training MatrixDocument2 pagesCLP and UDL Training MatrixRay AnzuresNo ratings yet
- Assignement 1 LEADeXCELS Anzures WRDocument1 pageAssignement 1 LEADeXCELS Anzures WRRay AnzuresNo ratings yet
- (Jill E. Thistlethwaite) Values-Based Interprofess (B-Ok - CC)Document192 pages(Jill E. Thistlethwaite) Values-Based Interprofess (B-Ok - CC)Ria Qadariah AriefNo ratings yet
- Unit 18: Calculating Food Costs, Selling Prices and Making A ProfitDocument4 pagesUnit 18: Calculating Food Costs, Selling Prices and Making A Profitkarupukamal100% (2)
- MediclaimDocument3 pagesMediclaimPrajwal ShettyNo ratings yet
- Pay Structure of Public Employees in PakistanDocument28 pagesPay Structure of Public Employees in PakistanAamir50% (10)
- Continuous Microbiological Environmental Monitoring For Process Understanding and Reduced Interventions in Aseptic ManufacturingDocument44 pagesContinuous Microbiological Environmental Monitoring For Process Understanding and Reduced Interventions in Aseptic ManufacturingTorres Xia100% (1)
- Guarantor Indemnity For Illness or DeathDocument2 pagesGuarantor Indemnity For Illness or Deathlajaun hindsNo ratings yet
- Tropical Fruit CHAPTER-3Document32 pagesTropical Fruit CHAPTER-3Jeylan FekiNo ratings yet
- Sore Throat, Hoarseness and Otitis MediaDocument19 pagesSore Throat, Hoarseness and Otitis MediaainaNo ratings yet
- Tarot Cards: Cheat SheetDocument1 pageTarot Cards: Cheat SheetDipti100% (7)
- Summative Test SolutionsDocument1 pageSummative Test SolutionsMarian Anion-GauranoNo ratings yet
- Mrunal Handout 12 CSP20Document84 pagesMrunal Handout 12 CSP20SREEKANTHNo ratings yet
- Ideal Discharge Elderly PatientDocument3 pagesIdeal Discharge Elderly PatientFelicia Risca RyandiniNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing 7 BulletsDocument4 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing 7 BulletsHoneylie PatricioNo ratings yet
- Optimization Process of Biodiesel Production With Ultrasound Assisted by Using Central Composite Design MethodsDocument47 pagesOptimization Process of Biodiesel Production With Ultrasound Assisted by Using Central Composite Design MethodsMiftahFakhriansyahNo ratings yet
- Resume - Arun BhartiDocument3 pagesResume - Arun BhartiArun AbNo ratings yet
- November 2013 (v3) QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSEDocument12 pagesNovember 2013 (v3) QP - Paper 6 CIE Biology IGCSEAfra AhamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.2 Futures HedgingDocument19 pagesChapter 3.2 Futures HedginglelouchNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Nano BookDocument44 pagesTransdermal Nano BookMuhammad Azam TahirNo ratings yet
- Ems em FW Paneel Firetec enDocument2 pagesEms em FW Paneel Firetec enzlatkokrsicNo ratings yet
- Nammcesa 000008 PDFDocument197 pagesNammcesa 000008 PDFBasel Osama RaafatNo ratings yet
- Giardiasis PDFDocument14 pagesGiardiasis PDFSaad Motawéa0% (1)
- The Allied Valve Spares Manufacturer Company Maharashtra IndiaDocument10 pagesThe Allied Valve Spares Manufacturer Company Maharashtra IndiaThe Allied Valve Spares Manufacturer CompanyNo ratings yet
- Subhead-5 Pump Motors & Related WorksDocument24 pagesSubhead-5 Pump Motors & Related Worksriyad mahmudNo ratings yet
- A-V300!1!6-L-GP General Purpose Potable Water Commercial Industrial Hi-Flo Series JuDocument2 pagesA-V300!1!6-L-GP General Purpose Potable Water Commercial Industrial Hi-Flo Series JuwillgendemannNo ratings yet
- Advances in Agronomy v.84Document333 pagesAdvances in Agronomy v.84luisiunesNo ratings yet
- TextDocument3 pagesTextKristineNo ratings yet
- தமிழ் உணவு வகைகள் (Tamil Cuisine) (Archive) - SkyscraperCityDocument37 pagesதமிழ் உணவு வகைகள் (Tamil Cuisine) (Archive) - SkyscraperCityAsantony Raj0% (1)
- UntitledDocument18 pagesUntitledSpace HRNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 8 RadioactivityDocument19 pagesScience Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 8 Radioactivitysakinah100% (1)
- HOME (2021) - Fransivan MacKenzieDocument21 pagesHOME (2021) - Fransivan MacKenzieFransivan MacKenzie100% (1)