Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ultrasound Abdomen
Uploaded by
Hey ReelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ultrasound Abdomen
Uploaded by
Hey ReelCopyright:
Available Formats
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed.
, RDMS, RT(R)
▪ Understanding the anatomy and physiology
is crucial to understanding pathology
▪ Two approaches to evaluation
– Transabdominal
Anatomy and Physiology – Endovaginal
▪ TA ▪ Approach varies based on
– Full bladder – Age
– Good overview – Sexually active
– 3.5 to 6.0 mHz
▪ TA
▪ EV – Bladder helps visualization
– Empty
– 7.5 to 12 mHz
▪ EV
– Focused view – Iliac vessels
– Uterus
– Primary landmarks
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
Pelvic LandMarks Bony Pelvis
▪ External Landmarks ▪ Four Bones
– Vulva – 2 innominate
▪ Mons pubis – Sacrum
▪ Labia majora – Coccyx
▪ Labia minora
▪ Clitorus ▪ Innominate
▪ Ureteral opening – Anterior
▪ Vestibule of vagina – Lateral margins
– Vagina separate
▪ Sacum and Coccyx
▪ Forms the canal from vestibule to cervix
– posterior
▪ Anatomically ▪ True pelvis
– 2 parts – Posterior wall
– True pelvis and False pelvis ▪ Sacrum and coccyx
– Posterolateral wall
▪ Piriformis
– Divided by imaginary line ▪ Coccygeus
▪ Superior sarcum – Anterolateral wall
▪ Anterior symphysis ▪ Hip bones
▪ Obturator internus
▪ Ishium
▪ Pubis
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
Muscles
▪ True pelvis ▪ Landmarks
– Inferior – Differentiate from adnexal structures
▪ Levator ani
▪ Coccygeus
– Pelvic diaphram ▪ Vary in shape
▪ Hypoechoic with hyperechoic striations
False Pelvis muscles True pelvis muscles
▪ Psoa Major ▪ Piriformis
– Lumbar vertebra ▪ Obturator internus
– Join iliacus
▪ Pelvic sidewall ▪ Muscles of the pelvic floor
▪ Form iliopsoas
– Anterior to hip ▪ Piriformis
– Attach lesser trochanter – Flat
– Triangular
– Anterior sacrum
– Pass through sciatic notch
– Insert superior greater trochanter
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
▪ Obturater Internus ▪ Levator Ani
– Three muscles
▪ Pubo coccygeus
– Triangle ▪ Iliococcygeus
▪ Puborectalis
– Antero lateral
▪ Surround obturator foramen – Pubococcygeus
▪ Insert greater trochanter ▪ Anterior
▪ medial
Bladder and Ureters
▪ Iliococcygeus ▪ Bladder
– Anterolateral pelvic wall – Anterior
– To coccyx – Post to pubis
▪ Puborectalis – Function
– Lower symphysis ▪ Collect and store urine
– Surround rectum
– Forms a sling – Empty
▪ Entirely in the true pelvis
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
Ureters Vagina
▪ Descend inferiorly ▪ Muscular tube
– Run anterior to psoas
– Behind peritoneum
▪ Collapsed
– Along lateral cervix ▪ External genitalia to cervix
– Upper portion of vagina
– Enter the trigone of the bladder ▪ Posterior to bladder, urethra
▪ Anterior to rectum and anus
– Forms a 90 degree angle with cervix
– Approx. 9 cm long
▪ Longest along posterior wall
Vagina Uterus
▪ Extends upward
▪ Lower half within perineum ▪ Hollow pear shaped
▪ Upper half above pelvic floor
▪ Divided into
– Fundus
▪ Four fornicies – Body
▪ Arterial supply – Cervix
– Vaginal and uterine arteries
– Drains into iliac vein
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
Uterus
▪ Covered with perineum ▪ Normal Anatomy
– Except anterior below os – Derived from Mullerian ducts
– Elongate and fuse about 12th week
▪ Supported by – Pear shaped
– Levator ani – Largest pelvic organ
– Cardinal ligaments ▪ 6 to 8 cm long
– Sacral ligaments ▪ 3 to 5 AP and lat
– Round and anteverted
▪ Varies with age and parity
Cervix
▪ Fundus ▪ Lower portion
– Widest
– Superior
▪ Divided into
– Exocervix
▪ Lateral borders – Endocervix
– Cornua
▪ Exocervix
▪ Body – Squamous epithelium
– Between fundus and cervix – Continuous with vagina
– Largest portion
▪ Endocervix
– Columnar cells
– Excrete mucous
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
Cervix Uterus
▪ Internal Os ▪ Wall
– Opening to the uterine cavity – Consists of
▪ Perimetrium
▪ Serosal layer
▪ External Os ▪ Muscular
– Opening to the vagina ▪ Middle layer
▪ Thickest
▪ Smooth muscle
▪ Mucous
▪ Glandular
▪ endometrium
Endometrium
▪ Two layers ▪ Functional
– Zona Functionalis – Superficial layer of glands
▪ Superficial – Sheds during menses
– Zona Basalis
▪ Deep basal layer ▪ Basal
– Blind ends of endometrial glands
– Regenerates new endometrium
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
Ligaments Broad
▪ Supported by ▪ Lateral aspect to pelvic sidewall
– Broad
– Round
▪ Mesovarium
– Uterosacral – Posterior fold
– Cardinal – Encloses ovary
▪ Mesosalpinx
– Upper fold
– Encloses ovary
Positions
▪ Round ▪ Variable
– Fundus to anterior pelvic side walls
▪ Average position
▪ Cardinal – Anteverted
– Extend across pelvic floor laterally ▪ “verted” Flex at cervix
– Support cervix ▪ Cervical canal forms 90 degree or smaller angle with cervix
– Anteflexed
▪ “flex” at fundus
▪ Canal and fundus curved upon cervix
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
▪ Retroverted
– Tipped backward
– Cervical canal less than 90 degrees from vagina
▪ Retroflexed
– Curve backwards upon cervix
▪ Dextroversion
– Deviates to right
▪ Levoversion
– Deviates to left
Fallopian tubes Tubes
▪ Coiled ▪ Four anatomic portions
▪ Muscular – Infundibulum
▪ Lateral
▪ Open into peritoneal cavity ▪ Widest
▪ Umbrella
▪ 10 -12 cm long ▪ fimbria
– Ampulla
▪ 1 – 4 mm diameter ▪ Middle
▪
▪ Lie superior to ▪
Longest
most coiled
▪ utero –ovarian ligaments ▪ Fertilization occurs
▪ Tubo – ovarian blood vessels
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
Ovaries
▪ Almond shaped
– Isthmus
▪ Medial ▪ 3 cm menarcheal
– Interstitial
▪ Passes through uterine wall ▪ Attached at posterior aspect of broad
ligament by mesovarium
▪ Lie in ovarian fossa
▪ Medial to Iliac vessels
▪ Dual blood supply
– Ovarian artery
▪ Off aorta
– Uterine artery
Ovarian anatomy
▪ Venous drainage ▪ Outer layer
– Ovarian vein – Cortex
▪ Left into renal vein – Surrounds medulla
▪ Right into Inferior Vena Cava – Consists of follicles
▪ Positions
– Anterior to iliac vessels ▪ Produce
– Medial to iliac vessels – Ovum
– Highly variable – Estrogen
▪ Especially after pregnancy
▪ Secreted by follicles
– Progesterone
▪ Secreted by Corpus luteum
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
Ovary Vasculature
▪ Supported by ▪ Common Iliacs
– Ovarian ligaments from cornua – Anterior and medial to psoas
– Suspensory ligaments
▪ laterally ▪ Internal Iliacs
– Extend into pelvis
– Posterior wall
– Multiple branches
– Perfuse pelvic organs
▪ Uterus
▪ Vagina
▪ Rectum
▪ bladder
▪ Uterine artery
– Arises from internal iliac
– Tortuous
– Spirals along side of uterus
– Within the broad ligament
– Courses laterally at cornua and anastomoses with ovarian
– Many branches to feed serosa and myometrium
– Form arcuate
▪ Can be seen as vessels within myometriun sonographically
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
Physiology
▪ Radial arteries ▪ Reproductive
– supply blood to endometrium – 11 – 13 years
– Extend through myometrium to base – end around 50
– Branch into spiral arteries
– Supplies zona basalis
▪ Cycle
– 28 days
– Begins at 1st day of menses
▪ Defined
– Premenarch
– Menarche
– Menopause
Follicular Development
▪ Ovum released once per month
▪ Regulated ▪ Occurs mid cycle
– Hypothalmus
– About day 14
– Production of
▪ Estrogen ▪ Immature = oocyte
▪ Progesterone
– From ovaries ▪ Each ovary about 200,000
▪ Ovulation regulated by the hypothalamus
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
▪ Puberty ▪ FSH
– Cyclical release of – Causes follicles to develop
▪ Gonado tropin releasing hormones – Follicular phase
▪ First day of bleeding to day 14
▪ Stimulate the pituitary gland ▪ Grow and increase estrogen
▪ One reaches maturity
– Secretes varying levels of:
– Graffian follicle (about 2cm)
– Gonadotropins
▪ FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) ▪ LH
▪ LH (luteinizing hormone) – Increases rapidly 24 to 36 hours before ovulation
– Peaks 10 to 12 hours FSH surges trigger ovulation
▪ Luteal Phase
– After ovulation
– 14 days
–Corpus luteum
▪ Starts secreting progesterone
▪ 9 to 11 days after
▪ degeneration
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
Endometrial
Endometrial
▪ Three stages ▪ Estrogen stimulates growth
– Menstrual Phase
▪ 3-5 days
– Begins with declining progesterone ▪ Proliferative phase
– Decreased blood flow – lasts until luteinization of graffian follicle
▪ Progesterone
– Sloughs off zona fucntionalis – Spiral arteries enlarge
– Follicular phase of cycle – Endometrial cells enlarge
– Ovulate
– No conception
– Follicles produce estrogen
▪ Secretory phase
– Luteal phase
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
▪ Proliferative
– 4 – 8mm
– Hypoechoic three line sign
▪ Just before ovulation
– 6 – 10mm
– Isoechoic
▪ Secretory
– 7 – 14mm
– Echogenic
▪ HRT
– <5mm
Abnormal Cycles
▪ Menorrhagia ▪ Amenorrhea
– Abnormally heavy or long – Primary
▪ Oligomenorrhea ▪ Delayed beyond 18 y
– Abnormally short or light – Secondary
▪ Cessation after menses
▪ Polymenorrhagia
– Less than 21 days
▪ Dysmenorrhagia
– Painful
▪ Amenorrhea
– Absence
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
Pelvic Recesses
▪ Vesico-uterine pouch ▪ Recto-uterine
– Anterior cul de sac – Posterior cul de sac
▪ Anterior to fundus between uterus and bladder – Posterior to uterus and cervix and anterior to rectum
Congenital Anomalies
▪ Retro pubic ▪ Mullerian Ducts
– Space of Retzius – Uterus derived from fusion of the caudal part of the duct
– Between bladder and symphysis
▪ Uterus Didelphys
– Complete failure of fusion
– Complete duplication
– rare
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
Salvatore LaRusso, M.Ed., RDMS, RT(R)
▪ Bicornuate ▪ Unicornuate
– Cervix fuses – Development of only one mullerian duct
– Fundus does not – And or varying degrees of contralateral side
▪ Septus
– Fusion occurs ▪ Aplasia
– Median septum fails to reabsorb – Very rare
▪ Total or partial
▪ Frequently associated with GU anomalies
▪ Approx 1/3 will have renal agenesis or
ectopia
©2018. Gulfcoast Ultrasound Institute. All Rights Reserved.
You might also like
- Pregnancy by WeekDocument78 pagesPregnancy by WeekIoana Influencers RebornNo ratings yet
- A&P - 6. Pelvic & Lower Limb Detailed Anatomy (42p)Document42 pagesA&P - 6. Pelvic & Lower Limb Detailed Anatomy (42p)andreeaNo ratings yet
- Estrogen DominanceDocument122 pagesEstrogen DominanceMuthuraman Gurusamy100% (5)
- Sexuality and Reproductive Health HandoutDocument110 pagesSexuality and Reproductive Health HandoutJoshua EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AnatomyDocument7 pagesAbdominal Anatomysarguss14100% (2)
- S2C - SD - SOLO and HOTS in The ClassroomDocument67 pagesS2C - SD - SOLO and HOTS in The ClassroomMaria Eleonor Banares93% (29)
- Development of Frog EmbryoDocument13 pagesDevelopment of Frog EmbryoNexieNo ratings yet
- A Miasmatic Approach To Endometriosis-1Document34 pagesA Miasmatic Approach To Endometriosis-1Suriya OsmanNo ratings yet
- Raphael Rettner - End PMS NowDocument58 pagesRaphael Rettner - End PMS NowYuldash100% (1)
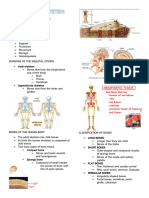
- Skeletal SystemDocument32 pagesSkeletal SystemMatthew HallNo ratings yet
- DEC 2007-NPT 2-Questions and RationaleDocument17 pagesDEC 2007-NPT 2-Questions and RationaleRoy Salvador100% (1)
- The Ncuk International Foundation Year IFYBI002 Biology 2017-18 Mark SchemeDocument16 pagesThe Ncuk International Foundation Year IFYBI002 Biology 2017-18 Mark SchemeFran cNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Positioning and Radiologic Procedures I FinalsDocument13 pagesRadiographic Positioning and Radiologic Procedures I FinalsrozdhagaNo ratings yet
- EJD Physical Assessment Head To ToeDocument4 pagesEJD Physical Assessment Head To ToeErl DrizNo ratings yet
- Gross HSB A - Gluteal Region, Hip Joint, and Posterior ThighDocument2 pagesGross HSB A - Gluteal Region, Hip Joint, and Posterior ThighGaelle Lisette MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Gross HSB A - Appendicular Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesGross HSB A - Appendicular Skeletal SystemAngelo BautistaNo ratings yet
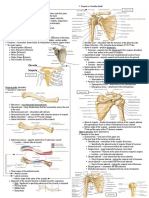
- Gross HSB A - Shoulder Region & Anterior Arm CompartmentDocument2 pagesGross HSB A - Shoulder Region & Anterior Arm CompartmentAngelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment Head To ToeDocument4 pagesPhysical Assessment Head To Toenot your medz duranNo ratings yet
- Structures To Palpate For 3SE Practical ExamsDocument1 pageStructures To Palpate For 3SE Practical ExamsPat DazaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall and Viscera in Situ AtfDocument75 pagesAbdominal Wall and Viscera in Situ AtfArif ullah Arif ullahNo ratings yet
- Lower LimbsDocument45 pagesLower LimbsFagboladeNo ratings yet
- A&P - 7. Shoulder Girdle & Upper Limb Detailed Anatomy (42p)Document42 pagesA&P - 7. Shoulder Girdle & Upper Limb Detailed Anatomy (42p)andreeaNo ratings yet
- Act 6 AnaphyDocument2 pagesAct 6 AnaphyAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Head Neck Osteology PDF Handout (Anatomy Decoded YouTube) PDFDocument22 pagesHead Neck Osteology PDF Handout (Anatomy Decoded YouTube) PDFNijam UdeenNo ratings yet
- Gross HSB A (INCOMPLETE) - The Liver, Gallbladder, Jejunum, and IleumDocument1 pageGross HSB A (INCOMPLETE) - The Liver, Gallbladder, Jejunum, and IleumAngelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- A.S.a - The Skeletal SystemDocument21 pagesA.S.a - The Skeletal Systemkoshiaiko21No ratings yet
- Back and SpineDocument31 pagesBack and Spinesjs6r8wwv9No ratings yet
- Ankleandfoot 2Document10 pagesAnkleandfoot 2Jamilah FlorendoNo ratings yet
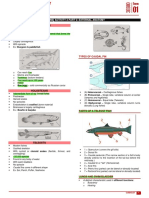
- 4 - CestodesDocument12 pages4 - CestodesEsther Victoria TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Frog AtlasDocument16 pagesFrog AtlasJAYHANNE PSYCHE MONDIANo ratings yet
- Zoology Nicolas Matthews Comparative Anatomy Classification Chart 1Document2 pagesZoology Nicolas Matthews Comparative Anatomy Classification Chart 1api-390660990No ratings yet
- Anfis MuskuloskelatalDocument37 pagesAnfis Muskuloskelataldesyantari6No ratings yet
- MRAT 211 - Lumbar Rehabilitation TransDocument11 pagesMRAT 211 - Lumbar Rehabilitation TransLovely GopezNo ratings yet
- AMALAB Activity2 Reviewer Actinopterygii-EarlyTetrapodsDocument3 pagesAMALAB Activity2 Reviewer Actinopterygii-EarlyTetrapodsDimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Analab Skeletal Reviewer Michie PDFDocument7 pagesAnalab Skeletal Reviewer Michie PDFMichieNo ratings yet
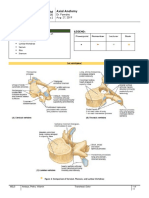
- Axial Anatomy: AY 2019-2020 Dr. Paredes Aug. 27, 2019Document11 pagesAxial Anatomy: AY 2019-2020 Dr. Paredes Aug. 27, 2019Jose Emmanuel DolorNo ratings yet
- BAT Notes - 2017 For 2018Document1,387 pagesBAT Notes - 2017 For 2018Nadun MethwadaneNo ratings yet
- Acetabular FractureDocument7 pagesAcetabular FractureluthfisnetNo ratings yet
- 09:16 - Back & Spinal Cord PDFDocument24 pages09:16 - Back & Spinal Cord PDFVidya BalaNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data:: Inspection & Palpation of HeadDocument11 pagesSubjective Data:: Inspection & Palpation of HeadEllias RoseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: The Boney Skeleton: Chapter 7 and 8Document59 pagesLecture 2: The Boney Skeleton: Chapter 7 and 8lemonNo ratings yet
- Imaging of The Reproductive SystemDocument15 pagesImaging of The Reproductive SystemAbi SulitNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Problem Evaluation: 6 Articulations or JointsDocument4 pagesShoulder Problem Evaluation: 6 Articulations or JointsMARY GIZETH GACHONo ratings yet
- Botany NotesDocument9 pagesBotany NotesLoeyNo ratings yet
- Anne G Osborn MD FACR, Karen L Salzman MD, Jeffrey S Anderson MD-23-44Document22 pagesAnne G Osborn MD FACR, Karen L Salzman MD, Jeffrey S Anderson MD-23-44angulomareling9No ratings yet
- Apparatus Uro Genital IsDocument32 pagesApparatus Uro Genital IsNelli NémethNo ratings yet
- Paper2032 1Document9 pagesPaper2032 1vellyezkaNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Chapter 1 2Document6 pagesANAPHY Chapter 1 2BSN1C John Ashley PastorizoNo ratings yet
- Handouts - Ref PeriopDocument10 pagesHandouts - Ref PerioproseNo ratings yet
- Hip PelvisDocument4 pagesHip PelvisMariz PascualNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Study GuideDocument2 pagesSkeletal System Study GuideyssahmariebongabongNo ratings yet
- 2 System Musculo Sceletal 2014Document41 pages2 System Musculo Sceletal 2014leni sharaNo ratings yet
- Osteologia - Normas CranianasDocument68 pagesOsteologia - Normas Cranianasadrianela cabezaNo ratings yet
- MAIN MUSCLES & DOF Apps of Func AnatomyDocument4 pagesMAIN MUSCLES & DOF Apps of Func AnatomyjoshNo ratings yet
- Heent Exam: Greeting Your PatientDocument12 pagesHeent Exam: Greeting Your PatientJuliana NwokochaNo ratings yet
- Core 2 PDHPE - Body in Motion Study NotesDocument43 pagesCore 2 PDHPE - Body in Motion Study Notesmarissa.makhNo ratings yet
- UERM GROSS Intro Meninges Blood SupplyDocument63 pagesUERM GROSS Intro Meninges Blood Supplyroxanne.viriNo ratings yet
- Gross HSB A - The Facial MusclesDocument4 pagesGross HSB A - The Facial MusclesAngelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Gross HSB A - Stomach, Duodenum, Pancreas, and SpleenDocument2 pagesGross HSB A - Stomach, Duodenum, Pancreas, and SpleenAngelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Types of VertebraDocument2 pagesTypes of VertebramtangcaaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Anatomy 101Document25 pagesSpinal Anatomy 101Monleau céliaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy RR CerebellumDocument106 pagesAnatomy RR Cerebellumभईया भोसडिकाNo ratings yet
- Normal Ob 1Document14 pagesNormal Ob 1Dairyl TagaroNo ratings yet
- Reviewer GHSB - Prelims PDFDocument4 pagesReviewer GHSB - Prelims PDFTj AgudillaNo ratings yet
- Catatan Orthopedi AriefDocument8 pagesCatatan Orthopedi Ariefmiwer 765No ratings yet
- GA&E 5 - Intro To Arthrology & Osteology IIIDocument51 pagesGA&E 5 - Intro To Arthrology & Osteology IIISu ZikaiNo ratings yet
- Prehistory of Saglek Bay, Labrador: Archaic and Palaeo-Eskimo OccupationsFrom EverandPrehistory of Saglek Bay, Labrador: Archaic and Palaeo-Eskimo OccupationsNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System: Development of The Reproductive OrgansDocument11 pagesHuman Reproductive System: Development of The Reproductive OrgansDhion Ardhian NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Amenorrhoea NotesDocument17 pagesAmenorrhoea NotesPrasadNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Histology LectureDocument46 pagesFemale Reproductive System Histology LectureMwaeNo ratings yet
- Maternal Practice Test 1Document21 pagesMaternal Practice Test 1Cj AguilarNo ratings yet
- Week 7-LS2 (Human Reproductive System) - WorksheetsDocument7 pagesWeek 7-LS2 (Human Reproductive System) - WorksheetsRheymund CañeteNo ratings yet
- Infertility - Female 2021Document51 pagesInfertility - Female 2021Nikky SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Mid-Semester Test English in Nursing - Dysfunctional of Menstrual Cycle (Menorrhagia, Metrorrhagia, Meno-Metrorrhagia) - 190411Document5 pagesMid-Semester Test English in Nursing - Dysfunctional of Menstrual Cycle (Menorrhagia, Metrorrhagia, Meno-Metrorrhagia) - 190411Chalida HayulaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 LFSC Informal Test Reproduction MemoDocument4 pagesGrade 12 LFSC Informal Test Reproduction Memomokgopofranklin75No ratings yet
- OB Exam 1 Study GuideDocument23 pagesOB Exam 1 Study GuideAlvin ManiagoNo ratings yet
- 55 Q&a Antepartum NclexDocument9 pages55 Q&a Antepartum Nclexkrystelle jade labineNo ratings yet
- Markscheme: (244 Marks)Document25 pagesMarkscheme: (244 Marks)Eva TNo ratings yet
- Fast Food Habit Among UUMDocument10 pagesFast Food Habit Among UUMbizcootNo ratings yet
- Reproduction (Human & Plant) KODocument6 pagesReproduction (Human & Plant) KODearbhla HubbardNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Biology Time: 90 Minutes General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper (Term I) 2021-22Document20 pagesClass Xii Biology Time: 90 Minutes General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper (Term I) 2021-22Xyz XyzNo ratings yet
- OB Power Point Presntation 001Document50 pagesOB Power Point Presntation 001RitamariaNo ratings yet
- HahahaDocument16 pagesHahahaJohn BretanaNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Ablutions For WomenDocument24 pagesThe Ritual Ablutions For WomenShahid.Khan1982No ratings yet
- 4.recent Advancement in Infertility TreatmentDocument23 pages4.recent Advancement in Infertility TreatmentVeena DalmeidaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction 2Document36 pagesReproduction 2Emanuel John BangoNo ratings yet
- Migraine - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Triggers, and MoreDocument35 pagesMigraine - Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Triggers, and MoreKarlla SuarezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Biomedical Perspective in Gender Sexuality 2Document28 pagesLesson 4 Biomedical Perspective in Gender Sexuality 2Nikka GoenettNo ratings yet
- Unitive and Procreative Health Procreation, Creation and EvolutionDocument9 pagesUnitive and Procreative Health Procreation, Creation and EvolutionJustJ ThingsNo ratings yet