Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Act 6 Anaphy
Uploaded by
Angelica Joyce SinnacoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Act 6 Anaphy
Uploaded by
Angelica Joyce SinnacoCopyright:
Available Formats
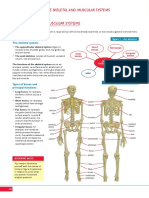
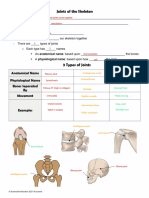
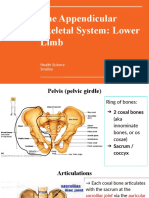
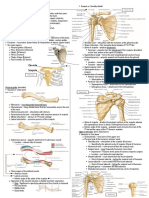
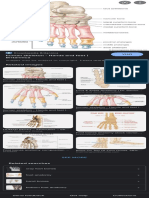
Types of Joints Examples
▪️Planar joint
-acromioclavicular
-sternoclavicular
-intercarpal
-Intertarsal
-vertebrocostal
-sacro iliac
▪️Hinge Joint
-elbow
-knee
-ankle
-interphalangeal
▪️Pivot Joint
-atlas/axis
-proximal radio-ulnar
▪️Ellipsoid Joint
-radiocarpal
-metacarpophalangeal
-metatarsophalangeal
▪️Saddle Joint
-first carpometacarpal
▪️Ball and Socket Joint
-shoulder joints
-hip joints
Questions for Research
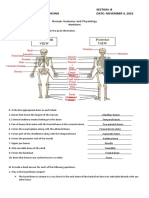
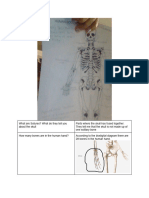
1. Give specific examples for each of the types of joints studied earlier in this exercise. Tabulate your answer.
2. Describe the functions of the synovial fluid.
Synovial fluid is a viscous solution found in the cavities of synovial joints. The principal role of synovial fluid is to
reduce friction between the articular cartilages of synovial joints during movement. The presence of high molar mass
hyaluronan (HA) in this fluid gives it the required viscosity for its function as lubricant solution. Inflammation oxidation
stress enhances normal degradation of hyaluronan causing several diseases related to joints.
The work of synovial fluids is always to lubricate the important joints also to represent a way for vitamins and
minerals to sustain the cartilage. The tissues that uphold the cartilage never have blood flow, senses or lymphatic tubes
hooked up to them, so the synovial fluid is the merely way they may be supplied.
3. Describe the function of the ligaments surrounding the joints.
Ligaments are bundles of fibrous connective tissue that connect one bone to an adjacent bone. Collagen fibers are
the basic building blocks of the ligament. These fibers are very strong, flexible and resistant to pulling or compressing
stress damage. The ligaments of knee joint form a chain link between the femur and the tibia. As in a chain, the individual
links can move freely, but they must remain in sequence and can not move apart. This allows the joint to move while
preventing it from dislocating. Their function is to provide support for the joint at the end of its range of motion and keep
it stable. These ligaments are important for maintaining the stability of the joint while it is in motion.
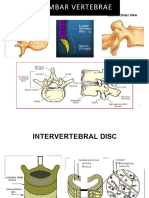
4. What is the function of articular discs?
Articular cartilage has key roles in the function of joints. A major function is to take up and distribute load such that a
given point of the underlying bone can handle very high strain. Another role of cartilage is to provide low-friction
movement. One key feature of joint diseases is deterioration of joint function, which results from progressive damage to
articular cartilage by degradation of the structural components important for properties of the tissue. Progressive joint
destruction may eventually lead to total loss of the cartilage accompanied by alterations in underlying bone in the
common disease of osteoarthritis.
References:
Dick Heinegård, ... Tore Saxne, in Rheumatology (Sixth Edition), 2015
Villa-Forte, A., By, Villa-Forte, A., & Last full review/revision Dec 2019| Content last modified Dec 2019. (n.d.).
Ligaments - Bone, Joint, and Muscle Disorders. Retrieved from https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/bone,-joint,-and-
muscle-disorders/biology-of-the-musculoskeletal-system/ligaments
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3967437/
You might also like
- Natural Healing Secrets of Native AmericansDocument34 pagesNatural Healing Secrets of Native Americansjeff raynor100% (1)
- Muscle and Skeletal FunctionDocument23 pagesMuscle and Skeletal FunctionLuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Internal MedicineDocument13 pagesInternal MedicineTianah davisNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive SystemAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Amano, Miles M. - Human AnaPhyW5-6Document4 pagesAmano, Miles M. - Human AnaPhyW5-6Khalil, Mikaela VictoriaNo ratings yet
- L2 Reading 1Document62 pagesL2 Reading 1Milena RohenkohlNo ratings yet
- 9 Giles B3Document37 pages9 Giles B3Jem Rhod CamenseNo ratings yet
- Depth 2 Concept, Goals, Assessment, Principles ofDocument134 pagesDepth 2 Concept, Goals, Assessment, Principles ofAswathy Aswathy100% (1)
- grp52 UTI PathoDocument3 pagesgrp52 UTI Pathokcdgrvn100% (3)
- Sample Extended Matching QuestionDocument3 pagesSample Extended Matching QuestionDorish Thason100% (1)
- Core 2 PDHPE - Body in Motion Study NotesDocument43 pagesCore 2 PDHPE - Body in Motion Study Notesmarissa.makhNo ratings yet
- Mod 1.3 Synovial Joints UpdatedDocument24 pagesMod 1.3 Synovial Joints UpdatedNandhkishoreNo ratings yet
- Tutorial UNIT 5Document2 pagesTutorial UNIT 5E32 ESTERLINENo ratings yet
- Review On Upper Limb-29!8!23-1Document47 pagesReview On Upper Limb-29!8!23-1Sara BasheerNo ratings yet
- Musculo Skeletal System: Red Bone Marrow in AdultsDocument9 pagesMusculo Skeletal System: Red Bone Marrow in AdultsJasmina BarakovicNo ratings yet
- Lect 3 AlmDocument74 pagesLect 3 AlmHUSSAIN 77No ratings yet
- Week 5 ExerciseDocument7 pagesWeek 5 ExerciseGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Structures To Palpate For 3SE Practical ExamsDocument1 pageStructures To Palpate For 3SE Practical ExamsPat DazaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 SlidesDocument10 pagesLab 2 SlidesMikeNo ratings yet
- Arthrology (Presentation) Author Anatomy PlcnetDocument54 pagesArthrology (Presentation) Author Anatomy PlcnetPredrag NikolicNo ratings yet
- Schamberger2016 220712 110125Document81 pagesSchamberger2016 220712 110125이용기No ratings yet
- Bone Growth: Bone Growth Refers To Increase in Diameter and Length of The Bone.Document16 pagesBone Growth: Bone Growth Refers To Increase in Diameter and Length of The Bone.Jessa RedondoNo ratings yet
- Ana - Joints ClassificationsDocument12 pagesAna - Joints ClassificationsMahmoud hilmyNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1571800842460Document27 pagesOrca Share Media1571800842460Reniel De MesaNo ratings yet
- The Skeleton: Chapter 7 Part ADocument79 pagesThe Skeleton: Chapter 7 Part ADon KeyNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb NotesDocument10 pagesLower Limb Notescorrainnejimenez.24No ratings yet
- Skeletal System 2021Document12 pagesSkeletal System 2021Jad JawhariNo ratings yet
- Joint Classification: - Structure - FunctionDocument12 pagesJoint Classification: - Structure - FunctionMkarthik BraveNo ratings yet
- JointsDocument34 pagesJointsNandhana Kattuparambil SunojNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument42 pagesSeminarJamNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 - Articulations: Richland College Biol. 2401 Marieb A&P Lab Manual - 9 EditionDocument2 pagesExercise 13 - Articulations: Richland College Biol. 2401 Marieb A&P Lab Manual - 9 EditionTHÂN TÂM VUI KHOẺNo ratings yet
- How Animals Move: Skeletal SystemsDocument60 pagesHow Animals Move: Skeletal SystemsKristel Lao-asNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Jeshua Caballero - Student Notes (F)Document3 pagesKami Export - Jeshua Caballero - Student Notes (F)Jeshua CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesSkeletal SystemSOFIA ALEXIS MALIÑANANo ratings yet
- Klouby EngDocument34 pagesKlouby EngMatea RupčićNo ratings yet
- Appendicular Skeleton - Lower LimbDocument22 pagesAppendicular Skeleton - Lower LimbShekeyva SmalleyNo ratings yet
- MRAT 211 - Lumbar Rehabilitation TransDocument11 pagesMRAT 211 - Lumbar Rehabilitation TransLovely GopezNo ratings yet
- 1.1.2 Skeletal Scavenger .1.2SkeletalScavengerDocument4 pages1.1.2 Skeletal Scavenger .1.2SkeletalScavengerarianamcpherson18No ratings yet
- BIO 1133 Exercise 7 (Skeletal System of The Frog)Document7 pagesBIO 1133 Exercise 7 (Skeletal System of The Frog)Tonet LapeNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Dr. Mona Liza N. Valencia, PTRPDocument33 pagesThe Skeletal System: Dr. Mona Liza N. Valencia, PTRPAccount ExtraNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Notes WorksheetDocument2 pagesSkeletal System Notes WorksheetCarla MirandaNo ratings yet
- Gross HSB A - Appendicular Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesGross HSB A - Appendicular Skeletal SystemAngelo BautistaNo ratings yet
- 2 Skeletal and Articular SystemDocument3 pages2 Skeletal and Articular SystemKimberlee Ced NoolNo ratings yet
- Mod 1.5 Knee JointDocument23 pagesMod 1.5 Knee JointNandhkishoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document35 pagesChapter 7s211151339No ratings yet
- Ther150 Week 2 1 StudentDocument27 pagesTher150 Week 2 1 StudentKaashvi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Foot Bone - Google SearchDocument1 pageFoot Bone - Google SearchMasty HemnNo ratings yet
- Joints: Structural ClassificationDocument3 pagesJoints: Structural ClassificationRAMON VILLACRUZADANo ratings yet
- 09:16 - Back & Spinal Cord PDFDocument24 pages09:16 - Back & Spinal Cord PDFVidya BalaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument20 pagesPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology in SportRachelHatcher123No ratings yet
- L2 Joints of Axial Appendicular Skeleton - 2020-2021 - CompressedDocument12 pagesL2 Joints of Axial Appendicular Skeleton - 2020-2021 - CompressedARYSSA BINTI AZRINo ratings yet
- Skeletal System QuestionsDocument44 pagesSkeletal System QuestionsSritama GhoshNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument47 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemZULFIKAR GHOZI MALIKUL AKBAR -No ratings yet
- CFJ Hollingsworth HipDocument8 pagesCFJ Hollingsworth HipAlessandro PetrizzaNo ratings yet
- A&P 1 Lab Exam 2 Review GuideDocument2 pagesA&P 1 Lab Exam 2 Review GuideMakenzie LyonNo ratings yet
- Bones and Joints of Upper LimbDocument34 pagesBones and Joints of Upper LimbNisreen SalameNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Permas Jaya: Prepared By:-Azam SenseiDocument59 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Permas Jaya: Prepared By:-Azam SenseiazamsenseiNo ratings yet
- Sports Science Study (Topics 1 - 6)Document39 pagesSports Science Study (Topics 1 - 6)Jayden OoiNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDocument59 pages2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsFauziah Abu Bakar100% (1)
- Anatomi Tulang Extremitas SuperiorDocument30 pagesAnatomi Tulang Extremitas SuperiorZUHRUF YARISUNA KHOLID FIRDAUSNo ratings yet
- Lectured By: Dr. Jesus J. Gracilla Transcribed By: Beverly YuDocument7 pagesLectured By: Dr. Jesus J. Gracilla Transcribed By: Beverly YuFamela Anne GOmez MadambaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesSkeletal SystemIra George ArcillaNo ratings yet
- SLAB MusculoskeletalCareModalitiesDocument47 pagesSLAB MusculoskeletalCareModalitiesMontero, Ma. Cecilia - BSN 3-BNo ratings yet
- Joints of The Lower Limbs and Joint Classification FinalmDocument27 pagesJoints of The Lower Limbs and Joint Classification Finalmolamidealapa2608No ratings yet
- 1 - Bones and Joints of Upper LimbDocument42 pages1 - Bones and Joints of Upper Limb76nr4m8ndxNo ratings yet
- Joints PPT NsDocument89 pagesJoints PPT Ns安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument3 pagesCase StudyAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Punicaceae: Pollinated and Cross-PollinatedDocument7 pagesPunicaceae: Pollinated and Cross-PollinatedAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- For The Prosecution, Your Honor, We Are Ready To Present Our WitnessDocument3 pagesFor The Prosecution, Your Honor, We Are Ready To Present Our WitnessAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Botanical Name: Important Genera:: Carrot Family or Celery or Parsley Family or UmbelliferaeDocument4 pagesBotanical Name: Important Genera:: Carrot Family or Celery or Parsley Family or UmbelliferaeAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- A. Ligand Factors: Page - 1Document5 pagesA. Ligand Factors: Page - 1Angelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Supreme Power Especially Over ADocument2 pagesSupreme Power Especially Over AAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Gsts Midterm Group Assignment: Against ScientismDocument2 pagesGsts Midterm Group Assignment: Against ScientismAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Conclusion Org ChemDocument1 pageConclusion Org ChemAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Gcworld PRELIMSDocument4 pagesGcworld PRELIMSAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Reflection GCWORLDDocument1 pageReflection GCWORLDAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Reflection GCWORLDDocument1 pageReflection GCWORLDAngelica Joyce SinnacoNo ratings yet
- Methazolamide-Diuretic (Sar)Document11 pagesMethazolamide-Diuretic (Sar)Laras Haryan LNo ratings yet
- Aoi 2019 05 316Document6 pagesAoi 2019 05 316newtonNo ratings yet
- SCHOOL WORKWEEK PLAN FOR February 1-28, 2021Document2 pagesSCHOOL WORKWEEK PLAN FOR February 1-28, 2021Melrose Gudmaling Manatad-HamoyNo ratings yet
- Health-Professionals Warn COVID Being A Hoax by Big Pharma CartelDocument61 pagesHealth-Professionals Warn COVID Being A Hoax by Big Pharma CartelCarlCordNo ratings yet
- Final Psych Case StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Psych Case StudySheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Atherero 1 Doc Raquid 2021Document50 pagesAtherero 1 Doc Raquid 2021orea0% (1)
- Eric Melillo - Letter To ConstituentsDocument2 pagesEric Melillo - Letter To ConstituentsRayson MartynNo ratings yet
- Breast AtrophyDocument28 pagesBreast AtrophyJehanzeb ZebNo ratings yet
- Critical Jurnal Review: Pendidikan Tata Rias Fakultas Teknik Universitas Negeri Medan 2020Document4 pagesCritical Jurnal Review: Pendidikan Tata Rias Fakultas Teknik Universitas Negeri Medan 2020Silvia NandaNo ratings yet
- Model Question Bank-Ohs Sem.-V Ce & MeDocument8 pagesModel Question Bank-Ohs Sem.-V Ce & MeVipin RajputNo ratings yet
- 10 1089@omi 2019 0192Document12 pages10 1089@omi 2019 0192Raul Morales VillegasNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Cairan Dan Elektrolit Pada PmebedahanDocument34 pagesManajemen Cairan Dan Elektrolit Pada PmebedahanZaniaNo ratings yet
- RAA SampleDocument25 pagesRAA SampleJomar F. RamirezNo ratings yet
- Medical ParacitologyDocument83 pagesMedical ParacitologyariffdrNo ratings yet
- (BS en 16616) - Chemical Disinfectants and Antiseptics. Chemical-Thermal Textile Disinfection. Test Method and Requirements (Phase 2, Step 2)Document35 pages(BS en 16616) - Chemical Disinfectants and Antiseptics. Chemical-Thermal Textile Disinfection. Test Method and Requirements (Phase 2, Step 2)Muhamad Zaky100% (1)
- HA-RLE-WS # 10 Assessing Nutritional StatusDocument4 pagesHA-RLE-WS # 10 Assessing Nutritional StatusJULIE ANNE CORTEZNo ratings yet
- Case StudiesDocument5 pagesCase Studiespragna novaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluatio N SubjectiveDocument58 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluatio N SubjectiveJemina Rafanan RacadioNo ratings yet
- Lecture8 AI Applications Part III Feb07 2022Document23 pagesLecture8 AI Applications Part III Feb07 2022CjdjkekNo ratings yet
- Crohn's DiseaseDocument8 pagesCrohn's DiseaseibrahimNo ratings yet
- B6119 Mosquitoes and The Diseases They TransmitDocument8 pagesB6119 Mosquitoes and The Diseases They Transmitnirmal dNo ratings yet
- Resistance Exercise Dosage in Men With Prostate CancerDocument60 pagesResistance Exercise Dosage in Men With Prostate Cancersilvio da costa guerreiroNo ratings yet
- XI Rancangan Soal PtsDocument8 pagesXI Rancangan Soal PtsHanida Dwi Astuti SuwarnoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microbiology For The Healthcare Professional 2nd Edition by VanmeterDocument35 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology For The Healthcare Professional 2nd Edition by Vanmetershriekacericg31u3100% (38)