Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supplementary Notes - Cell Structure
Uploaded by
Lance Christian MontalboOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Supplementary Notes - Cell Structure
Uploaded by
Lance Christian MontalboCopyright:
Available Formats
HUMAN
HISTOLOGY – LABORATORY PRACTICALS REVIEWER 2018 Ovum (Ovarian Follicle- Oocyte)
VELEZ COLLEGE – BS MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY • Nucleus: Vesiculated Acidophilic Nucleus (Germinal Vesicle)
Revised by BSMT 3C STUDENT: Oclarit, Aither Benedict C. • Nucleolus: Acidophilic Nucleolus
*General Func. of Nucleus: -controls constructive metabolism of cell (main component of Nucleus: DNA) • Cytoplasm: Reticulated Acidophilic Cytoplasm
-essential for reproduction & transmission of heredity • Neighboring Cells: Granulosa Cells (Blue)
*General Func. of Nucleolus: Synthesis of cytoplasmic rRNA • Function of Granulosa Cells: production of sex steroids and growth factors
EX. 1 – CELL STRUCTURE • Occurence:
Nerve Cells (Neurons) Slide # 56 – Adult Ovary
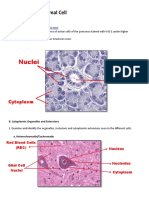
• Nucleus: Vesicular Basophilic Nucleus (fish-eye)
• Nucleolus: Acidophilic Nucleolus
• Cytoplasm: Basophilic Cytoplasm
• Shape: Stellate Shape
• Function: Conduct impulses to/from the sensory organs.
• Occurence:
Slide # 11 - Spinal Cord (Gray Matter)
Granulosa Lutein Cell (Follicular Cells Surrounding the Ovarian Follicle)
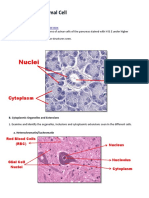
Liver Cells (Hepatocytes)
• Nucleolus: Basophilic Nucleolus
• Nucleus: Granulated Basophilic Nucleus
• Nucleus: Acidophilic Vesicular Nucleus
• Nucleolus: Basophilic Nucleolus (has more than 1 nucleoli)
• Cytoplasm : Granulated Acidophilic Cytoplasm
• Cytoplasm: Granulated Acidophilic Cytoplasm
• Arrangement: Scattered Individually
• Shape: Polyhedral due to pressure from neighboring cells.
• Function: To secrete Estrogen and Progesterone
• Arrangement: Irregular Radiating Columns and Plates
• Occurence:
• Function: To filter the blood.
Slide #57 – Ovary (Corpus Luteum)
• Structure: The plate structure of the liver and high permeability of the sinusoids allows each
hepatocyte to be in close contact with the blood. The hepatic plates are arranged into functional
units called liver lobules (Cord). In the middle of each lobule is a central vein.
• Occurence:
Slide #41 – Human Liver Cells Slide #42 – Pig Liver Cells
You might also like
- Clinical Evaluation of Purified Shilajit On TestosteroneDocument6 pagesClinical Evaluation of Purified Shilajit On TestosteroneAlejandro MüllerNo ratings yet
- Progesterone Is AndrogenicDocument7 pagesProgesterone Is AndrogenicMihai DragomirNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDocument152 pagesDysfunctional Uterine BleedingNavani Tharan100% (2)
- InfertilityDocument42 pagesInfertilityjoycechicagoNo ratings yet
- Oral Contraceptives PresentationDocument19 pagesOral Contraceptives PresentationJoshua DayeNo ratings yet
- MCQ Notes Dr.nadineنساDocument381 pagesMCQ Notes Dr.nadineنساAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Female ReproductivedlpDocument4 pagesFemale ReproductivedlpKathlen Aiyanna Salvan BuhatNo ratings yet
- 4 Nursing Care With Reproduction ProblemsDocument32 pages4 Nursing Care With Reproduction ProblemsSarah Jane MaganteNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Science V 2nd Periodic TestDocument7 pagesGrade 5 Science V 2nd Periodic TestHoneyjo Nette100% (8)
- Histology Laboratory Practicals Velez Medtech Reviewer 2018 FullDocument31 pagesHistology Laboratory Practicals Velez Medtech Reviewer 2018 FullFilicidad EleseoNo ratings yet
- Histo Review 2Document13 pagesHisto Review 2Coy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study Guide For Anatomy and Physiology 1 LabDocument34 pagesMidterm Study Guide For Anatomy and Physiology 1 LabkabukibearNo ratings yet
- Nuclei: Activity 2: The Animal CellDocument7 pagesNuclei: Activity 2: The Animal CellLyx Jady Fyl PerezNo ratings yet
- M2A2 Animal Cell-PEREZ, LYX JADY FYL, 2GDocument7 pagesM2A2 Animal Cell-PEREZ, LYX JADY FYL, 2GLyx Jady Fyl PerezNo ratings yet
- CO1Document42 pagesCO1KitNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio SLDocument103 pagesCell Bio SLkrhimkrNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document3 pagesModule 2Grayka QuiapoNo ratings yet
- Prac NotesDocument4 pagesPrac NotesB00RGIR WID FRIESNo ratings yet
- Struktur Sel Dan FungsinyaDocument6 pagesStruktur Sel Dan FungsinyaKim TaelynNo ratings yet
- Slide ObservationDocument31 pagesSlide ObservationV sreenivasaNo ratings yet
- GEN. ZOO (Midterms)Document4 pagesGEN. ZOO (Midterms)mimiNo ratings yet
- A8 Cell Unit of LifeDocument1 pageA8 Cell Unit of LiferajjoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cells Lesson 7Document18 pagesChapter 2 Cells Lesson 7May Khin NyeinNo ratings yet
- Cell+Structure 1Document38 pagesCell+Structure 1madhubalaNo ratings yet
- Lctur 2 BologyDocument9 pagesLctur 2 Bologykarim adelNo ratings yet
- Exam Review05Document3 pagesExam Review05api-26602387No ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument8 pagesCell Notesrandomdomram12No ratings yet
- 16.2 Cell and ClassificationDocument59 pages16.2 Cell and Classificationbabaaijaz01No ratings yet
- Cell Structure ASDocument40 pagesCell Structure ASYasmine HadiastrianiNo ratings yet
- Cell Study GuideDocument8 pagesCell Study GuideJee MascardoNo ratings yet
- Important Cells in NCERTDocument4 pagesImportant Cells in NCERTPragya ParidaNo ratings yet
- Cellular BiologyDocument26 pagesCellular BiologyLynette Guinacaran GanironNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue System-92618Document151 pagesNervous Tissue System-92618gokulkrishnayadhavNo ratings yet
- Dr. Yanga'S Colleges, Inc.: Name: Role: Course - Date Submitted: Group NoDocument3 pagesDr. Yanga'S Colleges, Inc.: Name: Role: Course - Date Submitted: Group NoJamil Samira E. BuizonNo ratings yet
- 2 CellsDocument31 pages2 CellsRashed NadaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell?Document49 pagesWhat Is A Cell?Nor Farhana KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure - Bio - Yr91Document18 pagesCell Structure - Bio - Yr91Aameena FarhanNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Document7 pagesCell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Amrul Zlalu AdaNo ratings yet
- 2: Cell Structure: LM Salazar Human Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument28 pages2: Cell Structure: LM Salazar Human Anatomy & Physiologychoi_salazarNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganizationDocument29 pagesCell Organizationninaninano889No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Atlas ADocument78 pagesChapter 1 Atlas Agabbs_123No ratings yet
- Edit Structure and Functional CellDocument20 pagesEdit Structure and Functional CellArifiaNo ratings yet
- Oral Histology First Grading NotesDocument24 pagesOral Histology First Grading NotesAli,morwan HydarNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument94 pagesThe CellKorean DramaNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of Life BST NotesDocument10 pagesCell - The Unit of Life BST NotesE.AshwinNo ratings yet
- Chaper 12 - PPT - Openstax 2021Document72 pagesChaper 12 - PPT - Openstax 2021Hilary OliverioNo ratings yet
- LP1 - Cells - TissuesDocument36 pagesLP1 - Cells - Tissuesstephcruz0726No ratings yet
- Topic 1 and 2 GenhistoDocument4 pagesTopic 1 and 2 GenhistoShiina MashiroNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument61 pagesMuscle TissueCatherine Joy SalongaNo ratings yet
- Genzoo Reviewer 1st SemDocument4 pagesGenzoo Reviewer 1st SememilpauloquibilanNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument25 pagesThe CellmaryshealshealNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument15 pagesScience Noteslaramatraji45No ratings yet
- lp1 - Cells - TissuesDocument36 pageslp1 - Cells - TissuesBAIDURJYA MONI DEKANo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Kgis Grade 11Document64 pagesCell Structure Kgis Grade 11Katie Al HodaliNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument34 pages3.1 Cell Structure and OrganisationMoza AlaliliNo ratings yet
- CellDocument34 pagesCellSadaf JavedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cell 1Document50 pagesChapter 6 Cell 1janardhan aghavNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy-lab ACTSDocument5 pagesAnaPhy-lab ACTSCEEJNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document112 pagesWeek 3Anne nicole P. CasemNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Cell Prepared By: Dexter Dave M. Tariman, RN, MANDocument11 pagesOverview of The Cell Prepared By: Dexter Dave M. Tariman, RN, MANNorjehan BantoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: CELL - : How Were Cells Discovered?Document5 pagesCHAPTER 1: CELL - : How Were Cells Discovered?Joy Mazo FaderagaoNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Specialized CellsDocument60 pagesWeek 5 - Specialized CellsDesiree Pescasio DimasuayNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory and StructureDocument4 pagesCell Theory and StructureKrizhia MacayaonNo ratings yet
- Histology of PancreasDocument12 pagesHistology of PancreasElgilani zaherNo ratings yet
- Pro Bef Ore Karyotic Nucleus: BloodDocument5 pagesPro Bef Ore Karyotic Nucleus: BloodDanielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- SAMPLEPAGES Unit11 1LivingThings topic1CellstissuesandorgansAuthorsMartinHansonwithDiaitiZure ThediscoveryofcellsDocument33 pagesSAMPLEPAGES Unit11 1LivingThings topic1CellstissuesandorgansAuthorsMartinHansonwithDiaitiZure Thediscoveryofcellsrobinasanga09No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles PDFDocument23 pagesCell Organelles PDFEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Functions Revised PowerPointDocument24 pagesCell Organelles Functions Revised PowerPointJanine Ginog FerrerNo ratings yet
- S5Q2MOD2 WK2 Menstrual CycleDocument18 pagesS5Q2MOD2 WK2 Menstrual CycleKring SandagonNo ratings yet
- Short Note Biology Form 5-Chapter 4 Reproduction and GrowthDocument7 pagesShort Note Biology Form 5-Chapter 4 Reproduction and Growthsalamah_sabri50% (2)
- 9 Male Reproductive System LectureDocument20 pages9 Male Reproductive System LectureGhadi RisNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Booster HODocument59 pagesAnatomy Booster HOJo Hn VengzNo ratings yet
- Combined Science 0653 Objectives CoreDocument19 pagesCombined Science 0653 Objectives CoreAzalia Delgado VeraNo ratings yet
- Levonorgestrel: Mechanism of ActionDocument6 pagesLevonorgestrel: Mechanism of ActionAdditi SatyalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Administration ManualDocument6 pagesNursing Administration ManualKenee SamboNo ratings yet
- Question 692676Document7 pagesQuestion 692676rishu5384No ratings yet
- 9109 Manuscrito 52819 1 10 20220523Document9 pages9109 Manuscrito 52819 1 10 20220523Diana MartinezNo ratings yet
- GynecomastiaDocument30 pagesGynecomastiaTania Davis100% (1)
- Student WorkDocument7 pagesStudent Workapi-316130138No ratings yet
- Module NCM 107 Pre LimDocument35 pagesModule NCM 107 Pre Limjanina mykaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction Grade 10Document23 pagesSexual Reproduction Grade 10Carol EscañoNo ratings yet
- General Insect Physiology 3344Document14 pagesGeneral Insect Physiology 3344Shawn BlueNo ratings yet
- Spermatogenesis and FertilizationDocument21 pagesSpermatogenesis and FertilizationAyen FornollesNo ratings yet
- Biologi Gonzaga - Hormon WanitaDocument9 pagesBiologi Gonzaga - Hormon WanitaVinna ZulhelmiNo ratings yet
- Labial AdhesionsDocument2 pagesLabial AdhesionsLydia TsiapleNo ratings yet
- Nematology: Concepts, Diagnosis and ControlDocument194 pagesNematology: Concepts, Diagnosis and Controlrhayahay230000001615No ratings yet
- Androgen and How They Cause Skin AgingDocument4 pagesAndrogen and How They Cause Skin AgingOlaonipekun GbeminiyiNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Anatomi 4 (Sistem Urogenitalia) - 225160100111030 - Almira Carissa Puspita Wijaya (3) - CompressedDocument16 pagesPraktikum Anatomi 4 (Sistem Urogenitalia) - 225160100111030 - Almira Carissa Puspita Wijaya (3) - CompressedAlmira WijayaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology) 21. Female Reproductive Cycle - Ovulation - KeyDocument1 pageEndocrine Physiology) 21. Female Reproductive Cycle - Ovulation - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet