Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 4
Uploaded by
simplyPlatinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 4
Uploaded by
simplyPlatinCopyright:
Available Formats
I.D. No.
Student Signature of the
Name Instructor with
Date
Batch No.
Day & Date
Experiment -4
Precision Circuits
Objective:
To study
1. Fast precision half-wave rectifier
2. Precision full-wave rectifier
Components required:
Experiment:
1. Fast precision half-wave rectifier:
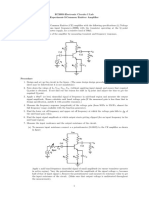
1.1 Design a fast precision half-wave rectifier as shown schematically in Figure
1, for a gain of -3.9. Choose the appropriate resistor values of R 1 and R2.
Consider RL = 10kΩ and R3 = R1 || R2. Use 1N4002 diodes. Assemble the
circuit.
Draw the circuit of Fig12.3 of TB2 Page No. 93
1.2 Feed sinusoidal input of amplitude 200mV and frequency 100 Hz. Observe
the input and output voltages on a CRO. Determine the amplitude and
frequency of the output voltage. Plot the input and output voltages on the
same scale. Increase the frequency of the input signal till distortion appears in
the output. Record this frequency.
fcutoff,H =…………….. Input signal frequency at which distortion appears
1.3 Repeat step 1.2 by reversing the polarity of the diodes.
fcutoff,H =…………….. Input signal frequency at which distortion appears
1
2. Precision full-wave rectifier:
2.1 Design a precision full-wave rectifier as shown schematically in Figure 2 for
a gain of +3.9. Choose the appropriate resistor values of R 4 and R6.
Consider R1 = 1kΩ, R5 = R4 and R3 = R1 || R2 for A1 and R4 || R5 || R6 for
A2. Use 1N4002 diodes. Assemble the circuit.
Draw the circuit of Fig12.4 of TB2 Page No. 94
2.2 Feed Sinusoidal input of amplitude 1 V and frequency 100 Hz. Observe the
input and output voltages on a CRO. Plot the input and output voltages on the
same scale. Determine the amplitude and frequency of the output voltage.
Vpeak to peak] output =………………..
foutput = ……………..
2.3 Increase the frequency of the input signal till distortion appears in the output.
Record this frequency.
fcutoff,H =…………….. Input signal frequency at which distortion appears
3. PSPICE Simulations:
Use the macromodels of the μA741, 1N4002 and 1N750 from the analog
devices library in simulation. The op-amp dc power supply voltages are +15/-15
V.
3.1 Simulate the circuit, as used in experiment (Positive clamping circuit) step 4,
using PSPICE. Plot the input and the output on the same scale. Compare the
results with the experimental results.
3.2 Simulate the circuit, as used in experiment (Peak detector) step 5, using
PSPICE. Plot the input and the output on the same scale. Compare the
results with the experimental results.
You might also like
- Inverter ProjectDocument19 pagesInverter ProjectMohd SamNo ratings yet
- LCD Work BookDocument102 pagesLCD Work BookNR-SANNo ratings yet
- Tan DeltaDocument23 pagesTan DeltaDivya GurukumarNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual Microelectronic Circuits, International 6th Edition, Sadra, SmithDocument10 pagesSolutions Manual Microelectronic Circuits, International 6th Edition, Sadra, SmithSolutionsNo ratings yet
- Eee334 Lab#1 Ltspice and Lab Orientation - Instruments and MeasurementsDocument9 pagesEee334 Lab#1 Ltspice and Lab Orientation - Instruments and Measurementsplaystation0% (1)
- Experiment 1 Tumambing Evan John C PDFDocument31 pagesExperiment 1 Tumambing Evan John C PDFRafael AclanNo ratings yet
- Pure Sine Wave Inverter User ManualDocument12 pagesPure Sine Wave Inverter User Manualjadad100% (1)
- Information On Some of The Parts in PSpice LibrariesDocument8 pagesInformation On Some of The Parts in PSpice Librarieshamza abdo mohamoudNo ratings yet
- B.sc. Generator ProtectionDocument10 pagesB.sc. Generator ProtectionQuazi Mosaddequl HaqueNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document5 pagesExperiment 1ankitchaurasia313No ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document4 pagesExperiment 5simplyPlatinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document3 pagesExperiment 3simplyPlatinNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal and Non-Sinusoidal Oscillators: Experiment 6Document3 pagesSinusoidal and Non-Sinusoidal Oscillators: Experiment 6Prateek PriyadarshiNo ratings yet
- Ec Ex 4 DarlingtonDocument4 pagesEc Ex 4 DarlingtonDeepikaa PoobalarajaNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal and Non-Sinusoidal Oscillators: Experiment 6Document3 pagesSinusoidal and Non-Sinusoidal Oscillators: Experiment 6Mohit DhayalNo ratings yet
- E.G. Per Set/group of StudentDocument4 pagesE.G. Per Set/group of StudentKiritoNo ratings yet
- Ica and HDL LabDocument94 pagesIca and HDL LabBhagya SriNo ratings yet
- EC Lab ManualDocument29 pagesEC Lab ManualAshwath NadahalliNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 05: RC Coupled Multistage CE-CC Cascade AmplifierDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 05: RC Coupled Multistage CE-CC Cascade AmplifierM. Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- World University of Bangladesh: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesWorld University of Bangladesh: ObjectiveshajibNo ratings yet
- Ece 334 ManualDocument37 pagesEce 334 ManualZelalem GirmaNo ratings yet
- CE Amplifier SoftwareDocument3 pagesCE Amplifier SoftwareSreepadh ChittiNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits Lab Manual1Document83 pagesAnalog Circuits Lab Manual1mansoorpasha.ece2020.ncNo ratings yet
- Ex05 Lim OpampDocument9 pagesEx05 Lim OpampLIM Sheryl M.No ratings yet
- Practice Questions Unit 1,2 and 3Document22 pagesPractice Questions Unit 1,2 and 3gowshik ramNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Integrator, Differentiator and Non-Linear Properties of OpampsDocument7 pagesExperiment 5 Integrator, Differentiator and Non-Linear Properties of OpampsEnes AyduranNo ratings yet
- Ty Man V ACDocument17 pagesTy Man V AC10 Joshua MasterNo ratings yet
- Expt No 3Document3 pagesExpt No 3puja maneNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiDocument28 pagesLaboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiAtul SainiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector AmplifierDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector AmplifierSajawal AliNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT #2 Frequency Response of Common Emitter AmplierDocument6 pagesEXPERIMENT #2 Frequency Response of Common Emitter AmplierGhabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument38 pagesLab ManualsivaNo ratings yet
- Long Report Lab 7Document15 pagesLong Report Lab 7Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- IC and ECAD LabDocument88 pagesIC and ECAD LabVeerayya JavvajiNo ratings yet
- Center For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electronics LabDocument9 pagesCenter For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electronics LabHussain HadiNo ratings yet
- EC Lab ManualDocument27 pagesEC Lab ManualMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1: Wiring of RC Coupled Single Stage AmplifierDocument7 pagesExperiment No 1: Wiring of RC Coupled Single Stage AmplifierShweta GadgayNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document4 pagesExperiment 5Jay LopezNo ratings yet
- Experiment-1 Power ElectronicsDocument7 pagesExperiment-1 Power ElectronicsMedhavi RajvanshyNo ratings yet
- MEB704 - Mechatronics Semester 1 2023: Derrick CampusDocument8 pagesMEB704 - Mechatronics Semester 1 2023: Derrick CampusDanilo BahorNo ratings yet
- EE2CJ4 Lab3Document4 pagesEE2CJ4 Lab3Eftakher Alam WasiNo ratings yet
- Inverting and Non-Inverting Amplifiers: Pre-Lab QuestionsDocument13 pagesInverting and Non-Inverting Amplifiers: Pre-Lab QuestionsBereket TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Wein Bridge Oscillator: f =1/2π√R1C1R2C2Document11 pagesWein Bridge Oscillator: f =1/2π√R1C1R2C2krishna goggiNo ratings yet
- Lab02 Electronic Instruments II - 104Document6 pagesLab02 Electronic Instruments II - 104LSNo ratings yet
- EE201 Experiment 10Document5 pagesEE201 Experiment 10Mohammed TAOUSSINo ratings yet
- EC Ex 3 Current SeriesDocument4 pagesEC Ex 3 Current SeriesDeepikaa PoobalarajaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 AmplifiersDocument46 pagesUnit 1 Amplifiersvimalaspl7831No ratings yet
- ST - Joseph College of Engineering: SriperumbudurDocument45 pagesST - Joseph College of Engineering: SriperumbudurSuryaNo ratings yet
- AC Lab Oscilloscope Rev03Document8 pagesAC Lab Oscilloscope Rev03Abdelaziz AbdoNo ratings yet
- Ecgr3155-Experiment 4-Diodes and Bridge RectifiersDocument8 pagesEcgr3155-Experiment 4-Diodes and Bridge RectifiersPhạm Đào Hoàng LongNo ratings yet
- 566 LIC Expt 2Document22 pages566 LIC Expt 2Hrivu Dasmunshi (RA1911004010566)No ratings yet
- Lab 1-Bjt AmplifierDocument8 pagesLab 1-Bjt Amplifierhasnain3257100% (1)
- EC1 Lab Exp3 PDFDocument2 pagesEC1 Lab Exp3 PDFRitu RoyNo ratings yet
- Lica Lab ManualDocument53 pagesLica Lab ManualGowtham KannegantiNo ratings yet
- PHY 112L Activity 8 Series RLC Circuit - 2: ResonanceDocument3 pagesPHY 112L Activity 8 Series RLC Circuit - 2: Resonanceقويه TasmanNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier and Full Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier and Full Wave RectifierAdvyth Vaman AkalankamNo ratings yet
- EC - Lab Manul With Viva Questions and AnswersDocument83 pagesEC - Lab Manul With Viva Questions and AnswerssunandaalurNo ratings yet
- EC &LD-Lab ManualDocument50 pagesEC &LD-Lab Manualdevirpasad100% (1)
- LAB 2 RectifiersDocument2 pagesLAB 2 Rectifiersamerican dxb memesNo ratings yet
- Lab 05Document3 pagesLab 05Juan TarquiNo ratings yet
- LIC Manual MDocument76 pagesLIC Manual MjananirajuNo ratings yet
- Experiment No-1: OBJECTIVE:-Design A Second Order MFB Band Pass Filter With A Mid Frequency of FM 1Document5 pagesExperiment No-1: OBJECTIVE:-Design A Second Order MFB Band Pass Filter With A Mid Frequency of FM 1AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Ec FinalDocument46 pagesEc FinalManjunath YadavNo ratings yet
- Density of States in Graphene: Periodic Boundary ConditionDocument7 pagesDensity of States in Graphene: Periodic Boundary ConditionGemechis D DegagaNo ratings yet
- Transmission and DistributionDocument4 pagesTransmission and DistributionMuthamizhan ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Electrician IntroductionDocument33 pagesElectrician Introductionsnadeem07No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Semester - III Subject Name: Digital ElectronicsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Semester - III Subject Name: Digital ElectronicsBhargavsinh ParmarNo ratings yet
- SDL 4Document4 pagesSDL 4ZbNo ratings yet
- Features Outline Dimensions: L-Band Gaas Power FetDocument4 pagesFeatures Outline Dimensions: L-Band Gaas Power Fethadi545nNo ratings yet
- Planck's ConstantDocument7 pagesPlanck's ConstantAngy100% (1)
- Pioneer Pdp433Document177 pagesPioneer Pdp433Marco AntonioNo ratings yet
- AQ12FANDocument9 pagesAQ12FANhdave32No ratings yet
- Panasonic Car Stereo System CQ-CP134U PDFDocument16 pagesPanasonic Car Stereo System CQ-CP134U PDFJuan Carlos SoHeNo ratings yet
- Hall Effect ManualDocument30 pagesHall Effect ManualHabib LaskarNo ratings yet
- Fairchild - Semiconductor FAN73611MX DatasheetDocument14 pagesFairchild - Semiconductor FAN73611MX DatasheetDeddy WilopoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Ciruit Analysis PDFDocument582 pagesElectrical Ciruit Analysis PDFMohammed SabeelNo ratings yet
- LM10 PDFDocument21 pagesLM10 PDFflo0909rinNo ratings yet
- ABSTRACTDocument4 pagesABSTRACTharithaNo ratings yet
- C 1 BDocument26 pagesC 1 BmaiyonisNo ratings yet
- FACTS Devices: and Effect of UPFC On 500 KV Transmission SystemDocument78 pagesFACTS Devices: and Effect of UPFC On 500 KV Transmission SystemLaeeq Ahmad FaizNo ratings yet
- Jazz Models - Onboard I/O: NotesDocument1 pageJazz Models - Onboard I/O: NotesRubén MelgarNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Comparison of DVR and DSTATCOM Used For Voltage Sag Mitigation at Distribution Side-359Document9 pagesSimulation and Comparison of DVR and DSTATCOM Used For Voltage Sag Mitigation at Distribution Side-359Nirav RanaNo ratings yet
- Rockwell AutomationDocument128 pagesRockwell Automationluisgama22No ratings yet
- Re: What Is The Basic Principle of Vibration Measurement by BENTLY NEVADA Vibration Measurement System? and Why It Gives The - Ve Voltage OutputDocument13 pagesRe: What Is The Basic Principle of Vibration Measurement by BENTLY NEVADA Vibration Measurement System? and Why It Gives The - Ve Voltage Outputydv1947No ratings yet
- PIC16F8X: 8-Bit CMOS Flash/EEPROM MicrocontrollersDocument122 pagesPIC16F8X: 8-Bit CMOS Flash/EEPROM MicrocontrollersCagatay KaynakNo ratings yet
- HC Serial Bluetooth Products User Instructional ManualDocument16 pagesHC Serial Bluetooth Products User Instructional ManualDaniel Norberto DemariaNo ratings yet