Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 1.1 and 1.2
Unit 1.1 and 1.2
Uploaded by
ysa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesThis document provides an introduction to anatomy and physiology. It describes the different levels of structural organization in the human body from the chemical level up to the organismal level. It then outlines the 11 organ systems of the human body including their main components and functions. The organ systems discussed are the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, reproductive, and urinary systems.
Original Description:
Anaphy
Original Title
UNIT 1.1 AND 1.2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an introduction to anatomy and physiology. It describes the different levels of structural organization in the human body from the chemical level up to the organismal level. It then outlines the 11 organ systems of the human body including their main components and functions. The organ systems discussed are the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, reproductive, and urinary systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesUnit 1.1 and 1.2
Unit 1.1 and 1.2
Uploaded by
ysaThis document provides an introduction to anatomy and physiology. It describes the different levels of structural organization in the human body from the chemical level up to the organismal level. It then outlines the 11 organ systems of the human body including their main components and functions. The organ systems discussed are the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, reproductive, and urinary systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
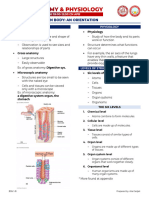
Introduction to AnaPhy
SARAH DE LUNA /8116 MLS 111 R2O6/HAPP
DRA.
○ E: covers body surfaces, lines hollow
organs, and forms glands
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY AND
PATHOLOGY ○ C: connects, supports, and protects
body organs while distributing blood
Anatomy
vessels to other tissues
★ Body structures and relationships among them
○ M: make body parts move and
★ ‘Ana-’ - up ; ‘-tomia’- the process of cutting
generate heat
★ First studied by dissection
○ N: carries information from one part
Andreas Vesalius
to another through nerve impulses
★ Flemish scientist
Organ Level
★ Modern anatomy started during the Renaissance
★ Different types of tissues are joined together
in Europe with him and his contemporaries
★ Organs - two or more different types of tissues;
Gross Anatomy
have specific functions and recognizable shapes
★ Large body structures - heart and bones
★ Liver, heart, stomach, etc
Microscopic Anatomy
★ Study of body structures that are too small to be
System Level (Organ System)
seen with naked eye
★ Related organs with common function
★ Cells and tissues
★ Digestive system, nervous system, etc
Physiology
★ ‘Physi-” - nature ; ‘-logia’ - “study of”
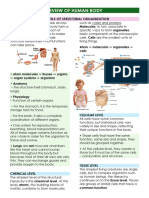
Organismal Level
★ Science of body functions and activities of life /
★ Organism - any living individual; all the parts of
living matter - how the body parts work
human body functioning together
Pathology
★ Science of the causes and effects of diseases
★ Disease: result of disruption to homeostasis ELEVEN SYSTEMS OF HUMAN BODY
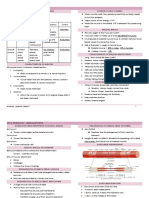
Integumentary System (outermost part)
LEVELS OF STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION AND ★ Comp: Skin, hair, fingernails, toenails, sweat
BODY SYSTEMS (6) glands, and oil glands
★ Func: protects and helps regulate body temp.;
Chemical Level
eliminate wastes; detects pain, warmth, and
★ Atoms, smallest units of matter, molecules -
cold; makes vitamin D; stores fat; provides
two or more atoms joined together
insulation
★ Two familiar molecules found in body: DNA
Skeletal System
and glucose
★ Comp: bones, joints, ligaments and associated
○ DNA: genetic material passed from
cartilages
one generation to the next
★ Func: supports and protects the body; provides
○ Glucose: blood sugar
surface area for muscle attachments; aids body
Cellular Level
movements; houses cells that produce blood
★ Molecules form organelles - makes up cells
cells; stores minerals and lipids (fats).
★ Cells - basic structural and functional units of an
Muscular System
organism that are composed of chemicals
★ Comp: skeletal muscle tissue (attached to
★ Muscle cells, nerve cells, epithelial cells, etc
bones), smooth, and cardiac muscle tissue
Tissue Level
★ Func: body movements - walking, maintains
★ Tissues - group of similar cells and the materials
posture, produce heat
surrounding them that work together to perform
Nervous System
a particular function
★ Comp: eyes and ears(special sense organs),
★ Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Nervous -
nerves, brain, spinal cord
four basic types of tissues
If it’s meant to be, it’ll be.
Introduction to AnaPhy
SARAH DE LUNA /8116 MLS 111 R2O6/HAPP
DRA.
★ Func: send nerve impulses to regulate body Reproductive System
activities; detects, interprets, and responds to ★ Comp: gonads(testes-male; ovaries-female)
body’s internal and external environments by ○ Associated organs (female) - uterine /
causing muscular contractions / gland secretions fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and
Endocrine System mammary glands
★ Comp: glands - pineal, hypothalamus, pituitary, ○ Male - epididymis, ductus / (vas)
thymus, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate,
ovaries, testes penis
★ Func: regulates activities by producing ★ Func: gonads produce gametes (sperm/oocytes)
hormones -unite to form new organisms ; gonads release
Cardiovascular System hormones that regulate reproduction & body
★ Comp: blood, heart, and blood vessels processes; assoc. organs transport and store
★ Func: Carries O2 and nutrients to cells; CO2 gametes; mammary glands produce milk
and wastes away from cells
Lymphatic System and Immunity
★ Comp: Lymphatic fluid, vessels, spleen,
thymus, lymph nodes, tonsils, B and T cells
(carry out immune responses)
★ Func: returns proteins and fluid, and carries
lipids from GI tract to blood
★ Sites of maturation & proliferation of B & T
cells that protect against disease-causing
microbes
Respiratory System
★ Comp: lungs, air passageways - pharynx
(throat), larynx (voicebox), trachea (windpipe),
bronchial tubes (into & out of lungs)
★ Func: O2 (inhaled air) to blood, CO2 (blood) to
exhaled air ; helps regulate acid-base balance of
body fluid; air flowing out of lungs through
vocal cords produces sounds
Digestive System
★ Comp: organs of GI tract - long tube includes
mouth, pharynx, esophagus (food tube),
stomach, small and large intestines, anus ;
accessory organs - salivary glands, liver,
gallbladder, pancreas (behind stomach)
★ Func: physical and chem. Breakdown of food;
absorbs nutrients; eliminates solid wastes
Urinary System
★ Comp: kidneys, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra
★ Func: Produces, stores, and eliminates urine;
eliminates wastes and regulates volume and
chemical composition of blood; helps maintain
the acid–base balance of body fluids; maintains
body’s mineral balance; helps regulate
production of red blood cells
If it’s meant to be, it’ll be.
You might also like
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyDelixae Phoinix80% (5)
- Masters Swimming A ManualDocument184 pagesMasters Swimming A ManualPhuc HienNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 - Orientation To The Human Body Study GuideDocument6 pagesUNIT 1 - Orientation To The Human Body Study GuideEgi Rivas100% (1)
- Question Bank GOCDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank GOCAshutosh Tripathi100% (2)
- Final Anaphy Notes Chapter 1 4Document26 pagesFinal Anaphy Notes Chapter 1 4nicssxxx hshshshsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Reviewer 1Document3 pagesAnatomy Reviewer 1Jeanne Nicci OrcenaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy PhysiologyDOROLA CRIS JANELICA R.No ratings yet
- Prelims Topic 1 - Review of Human BodyDocument18 pagesPrelims Topic 1 - Review of Human BodypanizalesmariajoseNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY REV Chapt 1Document8 pagesANAPHY REV Chapt 1crptzxraffNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Reviewer 2Document5 pagesAnatomy Reviewer 2Jeanne Nicci OrcenaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Body As A Whole: Abdul Quddoos Lecturer SAHARA College of Pharmacy, NarowalDocument23 pagesIntroduction To The Body As A Whole: Abdul Quddoos Lecturer SAHARA College of Pharmacy, NarowalAyeshaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Sci5Document32 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Sci5Joseph CunananNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab TransesDocument57 pagesAnaphy Lab TransesCarl Axel AzurNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY NotesDocument15 pagesANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY NotesAB AlmazoraNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pages01 Introduction Anatomy and PhysiologyLara CalayagNo ratings yet
- Q1.5 Cell TypesDocument17 pagesQ1.5 Cell Typesminimoni kookiesNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Intoduction To Human Body 2022Document54 pagesCHAPTER 1 Intoduction To Human Body 2022Adlyn Shaheera100% (1)
- HA Module 1Document6 pagesHA Module 1LACANARIA, ELLE BEA N.No ratings yet
- Els Handouts (2ND)Document6 pagesEls Handouts (2ND)Xiena Reyes AlforqueNo ratings yet
- ALectN (Organ System Overview-CellsTissues)Document47 pagesALectN (Organ System Overview-CellsTissues)Elaine MalinayNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY TRANS 1 The Human OrganismDocument7 pagesANAPHY TRANS 1 The Human OrganismDianne TicaNo ratings yet
- M1 HAPP LecDocument6 pagesM1 HAPP LecM SNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument60 pagesTissuesLeo PietroNo ratings yet
- Introduction NotesDocument5 pagesIntroduction Notesenrhe1334No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AnaPhy Notes - ReviewerDocument6 pagesChapter 1 AnaPhy Notes - ReviewerDanielle LeighNo ratings yet
- Bio CHP 7 Sem 1Document60 pagesBio CHP 7 Sem 1Aliaa AkbarNo ratings yet
- Httpseducacionadistancia - Juntadeandalucia.escentroscadizpluginfile - Php671451mod resourcecontent2UNIT2032C.20ORGANIDocument38 pagesHttpseducacionadistancia - Juntadeandalucia.escentroscadizpluginfile - Php671451mod resourcecontent2UNIT2032C.20ORGANIjuanfernandezhormigaNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument2 pagesANATOMYJecie CodillaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chap1 Lec Handout 1Document3 pagesAnaphy Chap1 Lec Handout 1psyche.ladicaNo ratings yet
- L 1 - (I) The Study of Body FunctionsDocument20 pagesL 1 - (I) The Study of Body Functionskaukab azimNo ratings yet
- Anaphy 1aDocument7 pagesAnaphy 1aFheonna De La PeñaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human BodyDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Human Bodyjunitria13No ratings yet
- Anatomy LectureDocument20 pagesAnatomy Lectureshiba ngujo100% (1)
- Introduction Anatomy and Physiology ModuleDocument35 pagesIntroduction Anatomy and Physiology ModuleFebz CanutabNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 TissuesDocument6 pagesActivity 2 TissuesMartina SilerioNo ratings yet
- Act 1 Final RealDocument5 pagesAct 1 Final Realmqdzpmjp2rNo ratings yet
- Body Organization: Sister Ilse Gabriela 7th Grade ScienceDocument11 pagesBody Organization: Sister Ilse Gabriela 7th Grade ScienceIlse AguilarNo ratings yet
- Body Organization: Sister Ilse Gabriela 7th Grade ScienceDocument11 pagesBody Organization: Sister Ilse Gabriela 7th Grade ScienceIlse AguilarNo ratings yet
- PDF - ANAPY LAB ACTIVITIES GEC4Document77 pagesPDF - ANAPY LAB ACTIVITIES GEC4Althea Aubrey AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Fan l1 TransesDocument8 pagesFan l1 TransesRose Marei ArriesgadoNo ratings yet
- Fan l1 TransesDocument8 pagesFan l1 TransesRose Marei ArriesgadoNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Cells Tissues Organs PDFDocument41 pages2.1. Cells Tissues Organs PDFRobert YabutNo ratings yet
- MT1 HSCI LEC L1 Introduction Overview HomeostasisDocument13 pagesMT1 HSCI LEC L1 Introduction Overview HomeostasisSEBASTIEN ANDREI BUENAFENo ratings yet
- MC 1 - Chapter 1Document13 pagesMC 1 - Chapter 1vinceridwan.gumbahaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - AnaphyDocument41 pagesChapter 1 - Anaphyyshie manlapazNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 2Kim Ashley Padernal MandronNo ratings yet
- The Human Organism: 1.1. AnatomyDocument17 pagesThe Human Organism: 1.1. AnatomyBeah Marie AlisosoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument33 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology NotesFLORLYN VERALNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy, Chapter 1: Outline of Class Notes Objectives: After Studying This Chapter You Should Be Able ToDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy, Chapter 1: Outline of Class Notes Objectives: After Studying This Chapter You Should Be Able ToAesthethic finds100% (1)
- Human AnatomyDocument16 pagesHuman AnatomyRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Muscular System 2nd SemDocument6 pagesMuscular System 2nd SemJOANNA MARIE INVENTORNo ratings yet
- ANA1N2 - FIRST QUIZ REVIEWER (AutoRecovered)Document2 pagesANA1N2 - FIRST QUIZ REVIEWER (AutoRecovered)Jacinth ManuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: An Introduction To The Human BodyDocument7 pagesChapter 1: An Introduction To The Human BodyShyra EntradaNo ratings yet
- Pocket Eyewitness Human Body Facts at Your Fingertips (D.K. Publishing) (Z-Library)Document155 pagesPocket Eyewitness Human Body Facts at Your Fingertips (D.K. Publishing) (Z-Library)Tamouh ZakrtNo ratings yet
- The Introduction of PHYSIOLOGY-1Document14 pagesThe Introduction of PHYSIOLOGY-1Ramadan Physiology100% (2)
- My Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument8 pagesMy Introduction To Human AnatomyIannah Corazon FadugaNo ratings yet
- BMD-3201 - Trans 1 - Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument16 pagesBMD-3201 - Trans 1 - Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyOwen RoldanNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument1 pageAnimal TissuesEdrea T. LimNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lectures ScheduleDocument7 pagesAnatomy Lectures SchedulecelecosibNo ratings yet
- 2nd - Human Organ SystemsDocument26 pages2nd - Human Organ SystemsJaeshelle Florendo100% (1)
- The Chapeter That Is TissueDocument36 pagesThe Chapeter That Is TissuereemNo ratings yet
- Congreso - Cierre de Minas PDFDocument531 pagesCongreso - Cierre de Minas PDFYordy AlejandroNo ratings yet
- MM2 Cellular DifferentiationDocument2 pagesMM2 Cellular DifferentiationSafiya James100% (1)
- Marstall Katalog-English WEBDocument80 pagesMarstall Katalog-English WEBeovidiuNo ratings yet
- 3.6.1 Busduct (Jis)Document29 pages3.6.1 Busduct (Jis)Kristine Grace LimatoNo ratings yet
- LightNeedle Manual EnglishDocument29 pagesLightNeedle Manual EnglishLiliana ŢehanciucNo ratings yet
- 2 - States of Matter PDFDocument26 pages2 - States of Matter PDFRisialyn ManalangNo ratings yet
- PGP/PGM300 Series PGP/PGM400 Series: Cast Iron Bushing DesignDocument28 pagesPGP/PGM300 Series PGP/PGM400 Series: Cast Iron Bushing DesignMario SouzaNo ratings yet
- Distribution Board - TUTORIALDocument28 pagesDistribution Board - TUTORIALVinod RohillaNo ratings yet
- Sab Foundation Innovation Award 2011Document24 pagesSab Foundation Innovation Award 2011Paul KimNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-24-12 - 11th (PQRS) Code-A WADocument12 pagesCHEMISTRY-24-12 - 11th (PQRS) Code-A WARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- SEBTS Spring CatalogDocument5 pagesSEBTS Spring CatalogidlewildchurchNo ratings yet
- Pastor Gonzalo G. Pe Jr. Pastor Gonzalo G. Pe JR.: Date DateDocument1 pagePastor Gonzalo G. Pe Jr. Pastor Gonzalo G. Pe JR.: Date DateJewel Alayon CondinoNo ratings yet
- The Mental Health Status of Grade 11 ABM Students During The Online Learning Set Up in Davao CityDocument19 pagesThe Mental Health Status of Grade 11 ABM Students During The Online Learning Set Up in Davao CityALYANNA SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Dr. Kee OngDocument2 pagesDr. Kee OngDr. Kee OngNo ratings yet
- DG1 Installation Manual 2018Document128 pagesDG1 Installation Manual 2018Mario LopezNo ratings yet
- ADDENDUM To IOM - Tech Notes: Electronically Commutated Motor (ECM) - Test & InfoDocument1 pageADDENDUM To IOM - Tech Notes: Electronically Commutated Motor (ECM) - Test & Infojaime palenzuela rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Capstone Project Update 4Document15 pagesCapstone Project Update 4api-631585778No ratings yet
- TheoryDocument2 pagesTheoryjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Convotherm-4 ManualDocument11 pagesConvotherm-4 ManualJean RamosNo ratings yet
- BS en ISO 17226-1-2019 - HCHO in Leather - LC MethodDocument16 pagesBS en ISO 17226-1-2019 - HCHO in Leather - LC MethodMinh Tien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Electricity Generation Cost Report 2020Document72 pagesElectricity Generation Cost Report 2020Sanuwar RahmanNo ratings yet
- L P G Part 1-Safety-LPG Short Course-5-05-Rev1Document18 pagesL P G Part 1-Safety-LPG Short Course-5-05-Rev1liveconnectionz282No ratings yet
- Laboratory Associated Infections: Tania Chintya IKD BiomedikDocument16 pagesLaboratory Associated Infections: Tania Chintya IKD BiomedikTania Chintya Dewi KarimaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 121 - General Chemistry Chapter 1Document14 pagesCHEM 121 - General Chemistry Chapter 1kingdom12828No ratings yet
- Food in Italy BlaDocument8 pagesFood in Italy BlajaniNo ratings yet
- Eco FriendlyDocument50 pagesEco FriendlySivakumar K100% (1)
- Peo SSP PDFDocument108 pagesPeo SSP PDFshwetaNo ratings yet
- Education Vs TrainingDocument3 pagesEducation Vs TrainingMark Lyndon M OrogoNo ratings yet