Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System: Disorders of Adrenal Gland
Endocrine System: Disorders of Adrenal Gland
Uploaded by
RANGSINEE SUWANNASUKOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System: Disorders of Adrenal Gland
Endocrine System: Disorders of Adrenal Gland
Uploaded by
RANGSINEE SUWANNASUKCopyright:
Available Formats
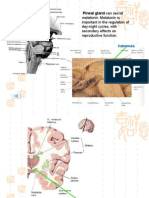
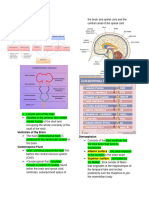
1. Hypothalamus 2.
Pituitary gland (Hypophysis)
inferior to the brain in the hypophyseal fossa
3. Pineal gland 4. Thyroid gland
small region of the brain below the thalamus
the major link between the nervous and endocrine systems stalk called infundibulum connect gland to
hypothalamus synthesize at least nine different hormones hypothalamus
The pituitary gland has 2 basic divisions
1. Anterior lobe has 3 subdivision
- pars distalis
- pars intermedia - pars tuberalis
2. Posterior lobe has 2 subdivisions -
pars nervosa
- infundibular : a small, pine cone shaped Melatonin: regulate circadian rhythms
structure (Darkness of night, the “clock” that controls daily butterfly-shaped
: at the end of a short stalk on star-shaped with long branching processes Anterior neck, inferior to the larynx
the roof of the diencephalon rhythms and melatonin secretion) 2 lateral lobes connected by a median
endocrine cells called pinealocytes bridge called the isthmus
dense particles of calcium “brain sand
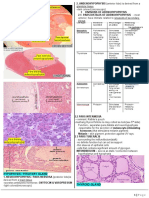
hollow spherical follicles (Thyroid follicles)
epithelial cells called follicular cells -->
5. Parathyroid glands Thyroid hormone --> Metabolism
central lumen filled with a jellylike
substance called colloid consisting of
thyroglobulin
Thyroid follicles
(stain poorly)
Parafollicular (C) cells --> Calcitonin -->
Ca2+ in blood
: small, yellow-brown lie on the posterior surface of the
thyroid g. : may be embedded in the thyroid gland
: have their own connective tissue capsules
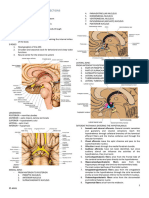
Endocrine system
8. Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
7. Adrenal gland
paired, pyramidal organs perched on the superior surface of the kidneys
6. Thymus gland
an important immune organ, the site which the white blood Note: parathyroid hormone and calcitonin have
cells called T lymphocytes arise from precursor cells. opposite, or antagonistic effects: PTH raises blood
calcium whereas calcitonin lowers it
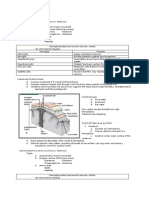
Disorders of Adrenal gland
Cushing’s syndrome
Hypersecretion of glucocorticoid h.
This condition is characterized by - Located in the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity
high level of glucose contains both exocrine and endocrine cells
- swollen face The exocrine acinar cells, secrete digestive enzymes
- redistribution of fat to the The endocrine cells,contained
Diabetes (pancreas related disease) posterior neck; “buffalo hump” in islets of Langerhans (million) : secrete hormones
glucose cannot enter most cells, so blood sugar
remains high and abundant glucose appears in urine
Disorders of the Thyroid gland Pituitary Disorders
Some disorders of the
adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary)
affect the secretion of growth
hormone (GH) .
You might also like
- The BrainDocument7 pagesThe BrainCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to The Pineal Gland (The Third Eye) And Its FunctionFrom EverandA Simple Guide to The Pineal Gland (The Third Eye) And Its FunctionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Dental Anatomy IntroductionDocument33 pagesDental Anatomy Introductioneyezblind100% (3)
- Diploma in Occupational TherapyDocument47 pagesDiploma in Occupational TherapyAzmi Plus100% (2)
- Washington State Cat Project Unit 3Document44 pagesWashington State Cat Project Unit 3CatalinAlbuNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Movements ModifiedDocument50 pagesMandibular Movements ModifiedMohamed Gamal100% (1)
- NeuropsychologyDocument7 pagesNeuropsychologyAbby Orioque IINo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesChapter 8: Nervous SystemAndrea BoocNo ratings yet
- Newborn AssesmentDocument10 pagesNewborn Assesmentgandhialpit100% (2)
- 300 Dental Anatomy Facts - NBDEDocument13 pages300 Dental Anatomy Facts - NBDEmilagros falconNo ratings yet
- L15 CerebrumDocument27 pagesL15 CerebrumEvilneko1No ratings yet
- Bated Head To Toe ScriptDocument9 pagesBated Head To Toe ScriptChrisie50% (2)
- 1 Nervous SystemDocument155 pages1 Nervous Systemsonali sundramNo ratings yet
- 10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabDocument4 pages10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum & DiencephalonDocument21 pagesCerebellum & Diencephalonprasun_vNo ratings yet
- Yoga Preparatory MovementsDocument20 pagesYoga Preparatory MovementsnkbarwakhtNo ratings yet
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- Electroacupuctura VollDocument32 pagesElectroacupuctura Vollminunat50% (2)
- Lab 3Document31 pagesLab 3melmotta1005No ratings yet
- Hypothalamus Infundibulum: (Adenohypophysis)Document3 pagesHypothalamus Infundibulum: (Adenohypophysis)jaira_joshbieNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland: 2.2 BasophilsDocument15 pagesPituitary Gland: 2.2 BasophilsJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- NetterDocument2 pagesNetternclov.00No ratings yet
- SistemendokrinDocument26 pagesSistemendokrinNazwa AuliaNo ratings yet
- Basal GangliaDocument9 pagesBasal Gangliasalmankhan09215No ratings yet
- Adrenal GlandDocument7 pagesAdrenal GlandAbdullah Yeamin PeyalNo ratings yet
- Parts of The BrainDocument106 pagesParts of The BrainbechichemelissaNo ratings yet
- Parts:: Diencephalon InferiorDocument5 pagesParts:: Diencephalon InferiorThanat PetchrodNo ratings yet
- The Brain: Functional Divisions: Primary and Secondary Vesicles of The Developing CNSDocument6 pagesThe Brain: Functional Divisions: Primary and Secondary Vesicles of The Developing CNSKelly FariaNo ratings yet
- Lec.5 Brain Structure and Function 2Document47 pagesLec.5 Brain Structure and Function 2sofiaNo ratings yet
- Course 3.1 Diencephalon 3 L 6 THALAMUSDocument74 pagesCourse 3.1 Diencephalon 3 L 6 THALAMUSSuman MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of The Nervous SystemDocument34 pagesFundamentals of The Nervous SystemEthan Dreiz BaltazarNo ratings yet
- 116 - Concept of Perception and CoordinationDocument3 pages116 - Concept of Perception and Coordinationalaisahmae02No ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument1 pageCentral Nervous Systemlez2No ratings yet
- Homeostasis and Higher Brain FunctionsDocument84 pagesHomeostasis and Higher Brain Functionsbodeadumitru9261No ratings yet
- 0-Review File (FINAL)Document40 pages0-Review File (FINAL)kaputostanleyNo ratings yet
- Bates CH 17 NeuroDocument11 pagesBates CH 17 NeurokandeeNo ratings yet
- L20-Thalamus & Limbic SystemDocument33 pagesL20-Thalamus & Limbic SystemSk JsNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument53 pagesNervous SystemBhebhe Lyra Hiponia ElgincolinNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Adrenal GlandsDocument1 pageHistology of The Adrenal GlandsSabrina NodariNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PDFDocument9 pagesNervous System PDFAfif Al BaalbakiNo ratings yet
- Neurohistology Lecture 3 Endocrine SystemDocument32 pagesNeurohistology Lecture 3 Endocrine Systemisicheipraise3No ratings yet
- Action Potential Propagation of Action Potential: Central Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesAction Potential Propagation of Action Potential: Central Nervous Systemlez2No ratings yet
- Di Encephalo NDocument6 pagesDi Encephalo NbolivarsefNo ratings yet
- Anaphy NS-BrainCranialNervesDocument13 pagesAnaphy NS-BrainCranialNervesYo1No ratings yet
- Exercise 15 PDFDocument3 pagesExercise 15 PDFJason Greyzon Boligao IndianaNo ratings yet
- Nervous + Animal DiversityDocument7 pagesNervous + Animal DiversityMaisonette MichNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction NOTESDocument46 pagesHuman Reproduction NOTESawatifaizan7No ratings yet
- Inbound 2262520782433835641Document5 pagesInbound 2262520782433835641Jannah MoralesNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System (CNS)Document10 pagesCentral Nervous System (CNS)Ma Roni Paula VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Fundamentals of The Nervous SystemDocument18 pages1.1 Fundamentals of The Nervous Systemno nameNo ratings yet
- Neuro 0411-1323Document21 pagesNeuro 0411-1323Lea Jane ArmeñaNo ratings yet
- Brain Structure and FunctionDocument61 pagesBrain Structure and FunctionBINITANo ratings yet
- Neurolec ReviewerDocument48 pagesNeurolec ReviewerMarianneNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument9 pagesRespiratoryAhmad NoorNo ratings yet
- CEREBELLUMDocument5 pagesCEREBELLUMAIRA BIANCA B. MANALANGNo ratings yet
- The Human Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesThe Human Nervous SystemMichelle RiveraNo ratings yet
- The BrainDocument103 pagesThe Brainrenzvalorant28No ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesCentral Nervous Systemlez2No ratings yet
- Skull Anterior View: The Frontal Bone (Or Forehead Bone) CurvesDocument22 pagesSkull Anterior View: The Frontal Bone (Or Forehead Bone) CurvesFatima JamalNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and CoordinationDocument16 pagesNeural Control and CoordinationAnonymous -No ratings yet
- NeuroDocument71 pagesNeuroSaily JaquezNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and Its ConnectionsDocument5 pagesHypothalamus and Its Connectionst4gjzhpfjcNo ratings yet
- Auditory ReceptorsDocument15 pagesAuditory ReceptorsJeanette RiosNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System EditedDocument80 pagesEndocrine System EditedKyle Gwyneth BobierNo ratings yet
- Physiology11 - Central Nervous SystemDocument56 pagesPhysiology11 - Central Nervous Systemfarhanaali1771No ratings yet
- Brain AnatomyDocument56 pagesBrain AnatomymirelahanganuNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Cortex (1) (Autosaved)Document18 pagesCerebral Cortex (1) (Autosaved)Stars and MoonNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System WordDocument4 pagesPeripheral Nervous System WordJesi QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Vertigo and DizzinessDocument14 pagesVertigo and Dizzinessa7mad thunaibatNo ratings yet
- Shanahan TEJ (1956)Document7 pagesShanahan TEJ (1956)Ali Faraz SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- DDDD PDFDocument1 pageDDDD PDFRalucaIoanaOpreaNo ratings yet
- Bab Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesBab Daftar PustakaElly LutfiasariNo ratings yet
- Nonsyndromic Delayed EruptionDocument3 pagesNonsyndromic Delayed EruptionRista LewiyonahNo ratings yet
- Level1 PHYSICAL-ASSESSMENTDocument11 pagesLevel1 PHYSICAL-ASSESSMENTShyra Mae Riano MarinNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Biomedical: The Origin of Bio-PotentialsDocument32 pagesInstrumentation Biomedical: The Origin of Bio-PotentialsNitin PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal and Nervous SystemDocument50 pagesSkeletal and Nervous SystemDAKSHINA NAIRNo ratings yet
- DR Serban Arghir Popescu - Recuperarea Membrului Superior Dupa Neurorafiile Nervilor Periferici PDFDocument115 pagesDR Serban Arghir Popescu - Recuperarea Membrului Superior Dupa Neurorafiile Nervilor Periferici PDFAnca MantuNo ratings yet
- Physical Characteristics of The NewbornDocument3 pagesPhysical Characteristics of The NewbornNica Mariz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Mnemonics (Upper Limbs) - Mnemonics - MosaicedDocument4 pagesAnatomy Mnemonics (Upper Limbs) - Mnemonics - MosaicedMDreamer50% (2)
- Penatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Kondisi Frozen ShoulderDocument11 pagesPenatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Kondisi Frozen ShoulderSasti aliciaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note - Skull and Visceral SkeletonDocument4 pagesLecture Note - Skull and Visceral SkeletonLopez Manilyn CNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Heart Questions Mark SchemeDocument4 pages5.2 Heart Questions Mark SchemeLesley Boulton100% (2)
- The Frenzel TechniqueDocument22 pagesThe Frenzel TechniqueMarius SahajNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Care of The Newborn Guide QuestionDocument5 pagesNCM 107 Care of The Newborn Guide QuestionMiguel LigasNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Brain Tumor: Guagua National Colleges Sta. Filomena, Guagua, Pampanga College of NursingDocument39 pagesCase Study of Brain Tumor: Guagua National Colleges Sta. Filomena, Guagua, Pampanga College of Nursingeliza luisNo ratings yet
- Other:: Listed Repetitions Are A Guide, 2 Perfect Reps Is Bettter Than 8 PoorDocument4 pagesOther:: Listed Repetitions Are A Guide, 2 Perfect Reps Is Bettter Than 8 PoorMatt SiniscalchiNo ratings yet
- Implant-Retained Cantilever Fixed Prosthesis: Where and WhenDocument4 pagesImplant-Retained Cantilever Fixed Prosthesis: Where and WhenSitiKhadijahNo ratings yet
- Krok 5Document53 pagesKrok 5Wolf WolforNo ratings yet
- Bony Framework of Thorax : Anterior ViewDocument1 pageBony Framework of Thorax : Anterior ViewKun HanifahNo ratings yet
- Skin 1: The Structure and Functions of The SkinDocument4 pagesSkin 1: The Structure and Functions of The SkinJohanNo ratings yet