Professional Documents
Culture Documents
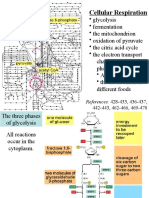
Respiration
Uploaded by
Jayesh patilCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiration
Uploaded by
Jayesh patilCopyright:
Available Formats
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Exercise -1 (NEET Pattern)
Important Instructions
This test contains 45 questions. Each question carries 4 marks. For each correct response the
candidate will get 4 marks. For each incorrect response, one mark will be deducted from the
total scores.
1. Energy obtained by a cell from catabolic reaction is stored immediately in the form of
(1) Pyruvic acid (2) Glucose
(3) ATP (4) DNA
2. Which component of ETS is mobile carrier?
(1) UQ (CO-Q) (2) Cyt - a (3) Cyto - b (4) Cyt - f
3. R.Q. is less than one at the time of respiration of –
(1) Starch (2) Sugarcane (3) Glucose (4) Ground nut
4. Number of ATP produced from one pyruvic acid during conversion to acetyl Co-A –
(1) 6 (2) 3 (3) 12 (4) 15
5. Conversion of pyruvic acid into ethyl alcohol is mediated by –
(1) Phosphatase (2) Dehydrogenase
(3) Decarboxylase & dehydrogenase (4) Catalase
6. The formation of Acetyl Co-A from pyruvic acid is the result of its: -
(1) Reduction (2) Dehydration
(3) Phosphorylation (4) Oxidative decarboxylation
7. Which of the following is link between carbohydrate and fat metabolism?
(1) CO2 (2) Acetyl Co-A
(3) Pyruvic acid (4) Citric acid
8. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is used in converting –
(1) Pyruvate to glucose (2) Glucose to pyruvate
(3) Pyruvic acid to lactic acid (4) Pyruvate to acetyl Co-A
9. The first member of TCA cycle is: -
(1) Oxalo succinic acid (2) Oxalo acetic acid
(3) Citric acid (4) Cis aconitic acid
Digital www.allendigital.in [1]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
NEET : Biology
10. Excess of ATP inhibits the enzyme: -
(1) Phosphofructokinase (2) Hexokinase
(3) Aldolase (Lyases) (4) Pyruvate decarboxylase
11. End product of glycolysis is: -
(1) Citric acid (2) Glyceraldehyde
(3) Phosphoglyceraldehyde (4) Pyruvic acid
12. In the electron transport chain during terminal oxidation, the cytochrome, which donates
electrons to O2 is?
(1) Cytochrome-b (2) Cytochrome-C
(3) Cytochrome-a3 (4) Cytochrome-f
13. Respiration in plants: -
(1) Occurs only during day (2) Results in the formation of vitamins
(3) Occurs both during day and night (4) Often requires CO2
14. The end products of respiration in plants are: -
(1) CO2, H2O and energy (2) Starch and O2
(3) Sugar and O2 (4) H2O and energy
15. The incomplete breakdown of sugars in anaerobic respiration results in the formation of
(1) Fructose and water (2) Glucose and CO2
(3) Alcohol and CO2 (4) Water and CO2
16. Common immediate source of energy in cellular activity is: -
(1) glucose (2) aldohexose
(3) ATP (4) NAD
17. The net gain of ATP molecules by glycolysis in aerobic condition is
(1) Zero (2) Two (3) Four (4) Eight
18. Cytochromes are concerned with
(1) Protein synthesis (2) Cellular digestion
(3) Cell division (4) Cell-respiration
19. In respiration pyruvic acid is: -
(1) Formed only when oxygen is available
(2) One of the products of Krebs cycle
(3) Broken down into Acetyl Co-A and CO2
(4) Oxidised into Alcohol
[2] www.allendigital.in Digital
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Respiration in plants
20. Respiratory enzymes are localised in: -
(1) Ribosomes (2) Chloroplast
(3) Mitochondria (4) Chromoplast
21. Number of ATP molecules formed during aerobic respiration in break-down of one glucose
molecule via malate aspartate shuttle, is: -
(1) 38 (2) 18 (3) 28 (4) 4
22. The organism in which Kreb's cycle does not occur in mitochondria is: -
(1) Yeast (2) E. coli (3) Ulothrix (4) Plants
23. What causes R.Q. to vary?
(1) Respiratory Substrate (2) Light & O2
(3) Respiratory Product (4) Temperature
24. The first preferred respiratory substrate is: -
(1) Glucose (2) Fats (3) Proteins (4) Polypeptides
25. Respiration occurs in: -
(1) All living cells both in day and night
(2) Non-green cells only in day
(3) Non-green cells in both day and night
(4) All living cells in day only
26. When the evolution of CO2 is more than the intake of O2, the respired substrate should be:
(1) Fatty acid (2) organic acid
(3) Glucose (4) Polysaccharides
27. Respiration may take place –
(1) In the presence of O2 (2) In the absence of O2
(3) In the presence or absence of O2 (4) Only in the presence of CO2
28. The common phase between aerobic & anaerobic respiration is: -
(1) TCA cycle (2) Krebs cycle
(3) Glycolysis (4) Photo respiration
29. The enzyme which converts glucose to glucose-6-phosphate -
(1) Phosphorylase (2) Gluco-phosphorylase
(3) Hexokinase (4) Phosphoglucomutase
Digital www.allendigital.in [3]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
NEET : Biology
30. Which of the following ETS complex is inhibited by cyanide?
(1) Complex II (2) Complex V
(3) Complex IV (4) Complex III
31. How many molecules of ATP are produced per molecule of FADH2 oxidised?
(1) One (2) Two (3) Three (4) four
32. The full form of NADP is: -
(1) Nicotine adenosine diphosphate phosphate
(2) Nicotinamide adenosine dinucleotide phosphate
(3) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
(4) Nicotinamide adenine diphosphate phosphate
33. How many ATP molecules produced from the complete oxidation of a molecule of active
acetate or acetyl Co-A?
(1) 38 ATP (2) 15 ATP (3) 12 ATP (4) 4 ATP
34. How many ATP equivalents are produced by the oxidation of succinate into fumarate?
(1) 1 ATP (2) 2 ATP (3) 3 ATP (4) 4 ATP
35. Product formed by the activity of malic dehydrogenase is: -
(1) Fumaric acid (2) Malic acid
(3) Oxaloacetic acid (4) Succinic acid
36. Which of the following is 5 -carbon compound of Krebs cycle?
(1) Citric acid (2) Fumaric acid
(3) Oxalosuccinic acid (4) a - Ketoglutaric acid
37. How many net ATP generates in aerobic respiration via glycerol phosphate shuttle in
eukaryotes
(1) 38 ATP (2) 36 ATP (3) 40 ATP (4) 80 ATP
38. Cyanide resistant respiration is found in –
(1) Homo sapiens (2) Brassica (3) Spinach (4) Bacteria
39. SLP net gain of ATP from one molecule of glucose during glycolysis or EMP pathway –
(1) 2 ATP (2) 6 ATP (3) 36 ATP (4) 38 ATP
40. Which enzyme breaks the fructose-1, 6-Bisphosphate?
(1) Hexokinase (2) Phosphatase
(3) Aldolase (4) Phosphofructokinase
[4] www.allendigital.in Digital
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Respiration in plants
41. Acceptor of acetyl Co-A in Krebs-cycle is: -
(1) Malic acid (2) Fumaric acid
(3) a – ketoglutaric acid (4) Oxalo acetic acid
42. Enzymes concerned with transfer of electrons are: -
(1) Hydrolases (2) Dehydrogenases
(3) Transaminases (4) Proteases
43. Anaerobic respiration takes place in: -
(1) Ribosome (2) Mitochondria
(3) Cytoplasm (4) Vacuole
44. During the formation of bread, it becomes porous due to release of CO2 by the action of: -
(1) Yeast (2) Bacteria
(3) Virus (4) Protozoans
45. In which one of the following do the two names refer to one and the same thing?
(1) Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle
(2) Tricarboxylic acid cycle and citric acid cycle
(3) Citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle
(4) Tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle
46. Chemiosmotic theory of ATP synthesis in the chloroplast and mitochondria is based on: -
(1) Proton gradient (2) Accumulation of K ions
(3) Accumulation of Na ions (4) Accumulation of Cl ions
Answer key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
Answer 3 1 4 2 3 4 2 4 2 1 4 3 3 1 3
Question 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
Answer 3 4 4 3 3 1 2 1 1 1 2 3 3 3 3
Question 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45
Answer 2 3 3 2 3 4 2 3 1 3 4 2 3 1 2
Question 46
Answer 1
Digital www.allendigital.in [5]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
NEET : Biology
Exercise - 2 (NEET PYQs)
1. Curing of tea leaves is brought about by the activity of –
(1) viruses (2) fungi
(3) bacteria (4) mycorrhiza
[AIPMT 2006 (+4 /–1)]
2. How many ATP molecules could maximally be generated from one molecule of glucose, if
the complete oxidation of one mole of glucose to CO2 and H2O yields 686 kcal and the useful
chemical energy available in the high energy phosphate bond of one mole of ATP is 12 Kcal?
(1) 57 (2) 1 (3) 2 (4) 30
[AIPMT 2006 (+4 /–1)]
3. The overall goal of glycolysis, Krebs cycle and the electron transport system is the
formation of:
(1) Nucleic acids
(2) ATP in small stepwise units
(3) ATP in one large oxidation reaction
(4) Sugars
[AIPMT 2007 (+4 /–1)]
4. All enzymes of TCA cycle are located in the mitochondrial matrix except one which is
located in inner mitochondrial membrane in eukaryotes and in cytosol in prokaryotes. This
enzyme is: -
(1) Succinate dehydrogenase (2) Lactate dehydrogenase
(3) Isocitrate dehydrogenase (4) Malate dehydrogenase
[AIPMT 2007 (+4 /–1)]
5. Which one of the following mammalian cells are not capable of metabolising glucose to
carbon-dioxide aerobically?
(1) Red blood cells (2) White blood cells
(3) Unstriated muscle cells (4) Liver cells
[AIPMT 2007 (+4 /–1)]
6. The chemiosmotic coupling hypothesis of oxidative phosphorylation proposes that
adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is form because: -
(1) A proton gradient forms across the inner membrane
(2) There is a change in the permeability of the inner mitochondrial membrane toward
adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
(3) High energy bonds are formed in mitochondrial proteins
(4) ADP is pumped out of the matrix into the intermembrane space
[AIPMT 2008 (+4 /–1)]
[6] www.allendigital.in Digital
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Respiration in plants
7. The energy-releasing process in which the substrate is oxidised without an external
electron acceptor is called: -
(1) Aerobic respiration (2) Glycolysis
(3) Fermentation (4) Photorespiration
[AIPMT 2008 (+4 /–1)]
8. Aerobic respiratory pathway is appropriately termed: -
(1) Parabolic (2) Amphibolic
(3) Anabolic (4) Catabolic
[AIPMT 2009 (+4 /–1)]
9. The energy-releasing metabolic process in which substrate is oxidised without an external
electron acceptor is called:
(1) Glycolysis
(2) Fermentation
(3) Aerobic respiration
(4) Photorespiration
[AIPMT Pre 2010 (+4 /–1)]
10. In mitochondria, protons accumulate in the:
(1) Matrix (2) Outer membrane
(3) Inner membrane (4) Intermembrane space
[AIPMT mains 2011 (+4 /–1)]
11. Which of the metabolites is common to respiration- mediated breakdown of fats,
carbohydrates and proteins?
(1) Acetyl CoA
(2) Glucose–6–phosphate
(3) Fructose-1,6–bisphosphate
(4) Pyruvic acid
[NEET-UG 2013 (+4 /–1)]
12. The three boxes in this diagram represent the three major biosynthetic pathways in
aerobic respiration. Arrows represent net reactants or products.
1 5 9 10
Glucose Pathway A 2 Pathway B 6 Pathway C 11
7
3 8 12
4
Arrow numbered 4, 8 and 12 can all be:
(1) FAD+ or FADH2 (2) NADH
(3) ATP (4) H2O
[NEET-UG 2013 (+4 /–1)]
Digital www.allendigital.in [7]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
NEET : Biology
13. In which one of the following processes CO2 is not released?
(1) Aerobic respiration in plants
(2) Aerobic respiration in animals
(3) Alcoholic fermentation
(4) Lactate fermentation
[AIPMT 2014 (+4 /–1)]
14. Which of the following biomolecules is common to respiration-mediated breakdown of
fats, carbohydrates and proteins?
(1) Pyruvic acid
(2) Acetyl CoA
(3) Glucose-6-phosphate
(4) Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
[NEET-UG-II 2016 (+4 /–1)]
15. Which statement is wrong for Krebs' cycle?
(1) There is one point in the cycle where FAD+ is reduced to FADH2
(2) During conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid, a molecule of GTP is synthesised
(3) The cycle starts with condensation of acetyl group (acetyl CoA) with pyruvic acid to
yield citric acid
(4) There are three points in the cycle where NAD+ is reduced to NADH+ H+
[NEET-UG 2017 (+4 /–1)]
16. What is the role of NAD+ in cellular respiration?
(1) It functions as an enzyme
(2) It functions as an electron carrier
(3) It is a nucleotide source for ATP synthesis
(4) It is the final electron acceptor for anaerobic respiration
[NEET-UG 2018 (+4 /–1)]
17. Which of these statements is incorrect?
(1) Enzymes of TCA cycle are present in mitochondrial matrix.
(2) Glycolysis occurs in cytosol.
(3) Glycolysis operates as long as it is supplied with NAD that can pick up hydrogen atoms.
(4) Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in outer mitochondrial membrane.
[NEET-UG 2018 (+4 /–1)]
[8] www.allendigital.in Digital
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Respiration in plants
18. Respiratory Quotient (RQ) value of tripalmitin is:
(1) 0.9 (2) 0.7 (3) 0.07 (4) 0.09
[NEET-UG 2019 (+4 /–1)]
19. Conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, the first irreversible reaction of glycolysis,
is catalyzed by:
(1) Aldolase
(2) Hexokinase
(3) Enolase
(4) Phosphofructokinase
[NEET-UG 2019 (+4 /–1)]
20. Where is respiratory electron transport system (ETS) located in plants?
(1) Mitochondrial matrix
(2) Outer mitochondrial membrane
(3) Inner mitochondrial membrane
(4) Intermembrane space
[NEET-UG 2019 (Odisha) (+4 /–1)]
21. The number of substrate level phosphorylations in one turn of citric acid cycle is :
(1) Three (2) Zero (3) One (4) Two
[NEET-UG 2020 (+4 /–1)]
22. Pyruvate dehydrogenase activity during aerobic respiration requires :-
(1) Calcium (2) Iron (3) Cobalt (4) Magnesium
[NEET-(UG)[COVID-19] 2020 (+4 /–1)]
23. Which of the following statements is incorrect ?
(1) During aerobic respiration, role of oxygen is limited to the terminal stage.
(2) In ETC (Electron Transport Chain), one molecule of NADH + H+ gives rise to 2 ATP
molecules, and one FADH2 gives rise to 3 ATP molecules.
(3) ATP is synthesized through complex V.
(4) Oxidation-reduction reactions produce proton gradient in respiration.
[NEET-UG 2021 (+4 /–1)]
24. What is the net gain of ATP when each molecule of glucose is converted to two molecules
of pyruvic acid ?
(1) Six (2) Two
(3) Eight (4) Four
[NEET-UG 2022 (+4 /–1)]
Digital www.allendigital.in [9]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
NEET : Biology
25. What amount of energy is released from glucose during lactic acid fermentation?
(1) More than 18% (2) About 10%
(3) Less than 7% (4) Approximately 15%
NEET-UG 2022 (+4 /–1)]
27. The number of time(s) decarboxylation of isocitrate occurs during single TCA cycle is :
(1) One (2) Two (3) Three (4) Four
[Re-NEET-(UG) 2022 (+4 /–1)]
Answer Key
Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
Answer 3 1 2 1 1 1 3 2 2 4 1 3 4 2 3
Question 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
Answer 2 4 2 2 3 3 4 2 2/3 3 2
[ 10 ] www.allendigital.in Digital
You might also like
- Proof of HeavenDocument146 pagesProof of Heavenkrisztaboti100% (3)
- Respiration 90 QuestionsDocument92 pagesRespiration 90 QuestionsNITISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Chapter-11 Respiration in Plants PDFDocument26 pagesChapter-11 Respiration in Plants PDFVedavathi100% (1)
- The Heart - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesThe Heart - Print - Quizizzosama100% (1)
- Cellular RespirationDocument38 pagesCellular RespirationItsYaBoiRZ YTNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Middle Ear CavityDocument235 pagesDiseases of Middle Ear CavityDr. T. BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration - ReviewerDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration - ReviewerJoyce Cañal100% (1)
- Cellular RespirationDocument44 pagesCellular RespirationGhizlane El FazaziNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet Biotechnology 8Document11 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Biotechnology 8Jaeda BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument10 pagesRespiration in PlantspattnaikdibyashreeNo ratings yet
- class 11 BIODocument7 pagesclass 11 BIOVector AcademyNo ratings yet
- Respiration EXE 1Document12 pagesRespiration EXE 1AdityaNo ratings yet
- p2Document4 pagesp2Vector AcademyNo ratings yet
- 2-Poll BotanyDocument2 pages2-Poll Botanydnamazing1702No ratings yet
- POLL 2 P+C+B+Z OYM Batch Que Paper @CET - JEE - NEETDocument10 pagesPOLL 2 P+C+B+Z OYM Batch Que Paper @CET - JEE - NEETKrins GopaniNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules ExerciseDocument16 pagesBiomolecules ExerciseMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants DPP 04of Lec 06 PDFDocument4 pagesRespiration in Plants DPP 04of Lec 06 PDFkavin12345ananNo ratings yet
- Target Test PariDocument23 pagesTarget Test PariAditya ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule - Polymer - & Practical - ExDocument22 pagesBiomolecule - Polymer - & Practical - ExAnuvrat SharmaNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument17 pagesPhotosynthesisJayesh patilNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell Respiration SiteDocument73 pagesPlant Cell Respiration SiteGovind Mani BhattNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants QuestionsDocument4 pagesRespiration in Plants QuestionsGourav SinghNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal NutritionDocument3 pagesPlant and Animal NutritionRamesh KandagatlaNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 15 16 XIII Bot Study Package 3 Set 1 Chapter 11 PDFDocument26 pagesCLS Aipmt 15 16 XIII Bot Study Package 3 Set 1 Chapter 11 PDFMoumita SarkarNo ratings yet
- Botany 4Document4 pagesBotany 4Vibushitha KabardineshwarNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants QuestionsDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants Questionsbajrangkashyap2020No ratings yet
- Mitochondria: By-Akshita Nautiyal Kashyap Panchal Yogesh VishwakarmaDocument23 pagesMitochondria: By-Akshita Nautiyal Kashyap Panchal Yogesh VishwakarmasekharurlaNo ratings yet
- Crash Course-4Document4 pagesCrash Course-4Praveen ReddyNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Practice Test-1 (Iit-Jee (Main Pattern) ) : Important InstructionsDocument18 pagesPart - I: Practice Test-1 (Iit-Jee (Main Pattern) ) : Important InstructionsSamridh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Xii DPPDocument18 pagesChemistry Xii DPPRakshi PadhanNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 15 16 XIII Zoo Study Package 2 Set 1 Chapter 3Document30 pagesCLS Aipmt 15 16 XIII Zoo Study Package 2 Set 1 Chapter 3Santu Karmakar100% (1)
- Biology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 1Document105 pagesBiology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 1SDO BSNL NALAGARHNo ratings yet
- 26.12.2023 -Biomolecule.pdf. JEEDocument2 pages26.12.2023 -Biomolecule.pdf. JEERittamNo ratings yet
- BBBBBDocument7 pagesBBBBBDr. Pradeep SakeNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule & Polymer - Exercise (E)Document19 pagesBiomolecule & Polymer - Exercise (E)aleena'No ratings yet
- Biology MCQ Standard 11Document19 pagesBiology MCQ Standard 11VirendraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Points To RememberDocument6 pagesChapter 14 Points To RememberSaksham YadavNo ratings yet
- Repeater Test BiomoleculeDocument2 pagesRepeater Test BiomoleculeDharmvir TantyNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument15 pagesRespiration in Plantsyahake5036No ratings yet
- Respiration and Enzymes 2Document11 pagesRespiration and Enzymes 2Ganesh ManikandanNo ratings yet
- (2017-19) XI TWT - Biomolecules - Prof SCZ, RSZ - FinalDocument5 pages(2017-19) XI TWT - Biomolecules - Prof SCZ, RSZ - FinalRiteshNo ratings yet
- Lactobacillus Nostoc, Chara Nitrosomonas, Nitrobacter, Streptomyces, Sacharomyces, JiypanosomaDocument4 pagesLactobacillus Nostoc, Chara Nitrosomonas, Nitrobacter, Streptomyces, Sacharomyces, Jiypanosomamechanical_lecturerNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XIII Zoo Study Package 1 SET 1 Chapter 2Document30 pagesCLS Aipmt 18 19 XIII Zoo Study Package 1 SET 1 Chapter 2Saravanan RajuNo ratings yet
- 14.respiration New BioHackDocument8 pages14.respiration New BioHackAnush KhillareNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Hingher PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in Hingher PlantsTrillionare HackNo ratings yet
- Respiration Combustion: Glycolysis Krebs CycleDocument7 pagesRespiration Combustion: Glycolysis Krebs CycleParulNo ratings yet
- Ncert Page Wise Q RespirationDocument34 pagesNcert Page Wise Q RespirationSagarNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Neet RespirationDocument8 pagesClass 11 Neet RespirationViswaNo ratings yet
- 9.Biomolecules 140mcq AakashDocument30 pages9.Biomolecules 140mcq Aakashmd.ali.sharukhnawazNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules 10+2, 2023-24Document7 pagesBiomolecules 10+2, 2023-24pushkargarg14No ratings yet
- 10 Metabolisme MikrobiaDocument51 pages10 Metabolisme MikrobiaHastomo Nur HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantspattnaikdibyashreeNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument19 pagesCell RespirationPauline FrascaNo ratings yet
- Dopa - 22Document6 pagesDopa - 22hhNo ratings yet
- Respiration and PhotorespirationDocument29 pagesRespiration and PhotorespirationThảo UyênNo ratings yet
- Plant RespirationDocument4 pagesPlant RespirationSoumit PaulNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration Quiz SCDocument2 pagesAerobic Respiration Quiz SCapi-323720899No ratings yet
- Glycolysis MCQs: Net ATP Yield & Key EnzymesDocument7 pagesGlycolysis MCQs: Net ATP Yield & Key Enzymessherazahmedroy0% (1)
- Cellular Respiration: References: 428-433, 436-437Document45 pagesCellular Respiration: References: 428-433, 436-437Ciania KimNo ratings yet
- Science Daily Lesson l44Document48 pagesScience Daily Lesson l44Audie Nocedo MontecastroNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION: THE BREAKDOWN OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS FOR ENERGYDocument4 pagesRESPIRATION: THE BREAKDOWN OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS FOR ENERGYAlfiya ShereefNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya NEET Weekend Test KeyDocument8 pagesSri Chaitanya NEET Weekend Test KeyLade VarshithaNo ratings yet
- BIO 181 Lab Quiz 9-Respiration - AnswersDocument1 pageBIO 181 Lab Quiz 9-Respiration - Answersjenna ibanezNo ratings yet
- CBTA FOCUS AREA REVISION QUESTIONS ON RESPIRATIONDocument3 pagesCBTA FOCUS AREA REVISION QUESTIONS ON RESPIRATIONMolly KuttyNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesFrom EverandTransition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19. The Social InsectsDocument18 pagesChapter 19. The Social Insectsalberto saenzNo ratings yet
- Biosensing Technology A Brief HistoryDocument4 pagesBiosensing Technology A Brief HistoryIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drug GuideDocument42 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drug GuideRamadi PrameelaNo ratings yet
- Infancy: Developmental Psychology by Aamna Tayyaba Khan Psychology Dept., Lahore Garrison UniversityDocument17 pagesInfancy: Developmental Psychology by Aamna Tayyaba Khan Psychology Dept., Lahore Garrison UniversityZeeshan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Why Do We LaughDocument2 pagesWhy Do We LaughzabkzuidktagoyriqfNo ratings yet
- Overview of Phototrophic ProteobacteriaDocument49 pagesOverview of Phototrophic ProteobacteriaTyra NNo ratings yet
- Formulation, Development and Evaluation of Herbal Antiaging CreamDocument6 pagesFormulation, Development and Evaluation of Herbal Antiaging CreamEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Journal of Bodywork & Movement TherapiesDocument10 pagesJournal of Bodywork & Movement TherapiesCarol MansurNo ratings yet
- Naas Rating 2011Document32 pagesNaas Rating 2011salmaan_bhat83% (6)
- Musculoskeletal System Assessment: - OverviewDocument5 pagesMusculoskeletal System Assessment: - OverviewDenise BarayogaNo ratings yet
- Lipds and CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesLipds and CarbohydratesMilenaNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Bbabio 2018 01 005Document7 pages10 1016@j Bbabio 2018 01 005Michi TristeNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lect. (4) : Preparation of Solutions For Wet MountDocument5 pagesParasitology Lect. (4) : Preparation of Solutions For Wet MountAbdul hadiNo ratings yet
- Capillary Puncture (Materials and Procedure)Document36 pagesCapillary Puncture (Materials and Procedure)Angelica Camille B. AbaoNo ratings yet
- Beta Oxidation of Fatty AcidDocument5 pagesBeta Oxidation of Fatty Acidkshaf muzammilNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 - Biology - AR2.Document11 pagesGrade 7 - Biology - AR2.Jay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congenital Heart Disease in The Adult: Special ReportDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of Congenital Heart Disease in The Adult: Special ReportLwin ThantNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document40 pagesLesson 5Eiluj AjaranNo ratings yet
- Historia de AuriculoterapiaDocument10 pagesHistoria de AuriculoterapiaDessirhe LaraNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The Oral Cavity-3Document33 pagesCysts of The Oral Cavity-3Mostafa El GendyNo ratings yet
- Crisan Larisa RenataDocument8 pagesCrisan Larisa RenataCleaver BrightNo ratings yet
- Connect With Me!: Have Any Questions?Document23 pagesConnect With Me!: Have Any Questions?Jennie Ann Sciarrotta BoudreauxNo ratings yet
- Cfasmsumain Fplereview2022 PhycologyDocument149 pagesCfasmsumain Fplereview2022 PhycologyPilihp Elessej Yaj NiuqidcidNo ratings yet
- Psychology Complete Unit 4Document210 pagesPsychology Complete Unit 4VeekeshGuptaNo ratings yet
- LH Rapid Quantitative Test COA - F2441530BADDocument1 pageLH Rapid Quantitative Test COA - F2441530BADTerakola VictorNo ratings yet