Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oral Comm 2Q
Uploaded by
Elizander Vergara0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThis document discusses oral communication and communicative strategies. It covers speech context, styles, acts, and delivery methods. The key points are:
1) Oral communication uses speech styles and strategies based on the speech purpose and number of participants.
2) Communicative strategies include plans for sharing information to achieve a social, political, or linguistic goal.
3) Speech context can be intrapersonal, interpersonal, dyadic, small group, public, mass, organizational, or intercultural.
Original Description:
Original Title
ORAL-COMM-2Q
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses oral communication and communicative strategies. It covers speech context, styles, acts, and delivery methods. The key points are:
1) Oral communication uses speech styles and strategies based on the speech purpose and number of participants.
2) Communicative strategies include plans for sharing information to achieve a social, political, or linguistic goal.
3) Speech context can be intrapersonal, interpersonal, dyadic, small group, public, mass, organizational, or intercultural.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOral Comm 2Q
Uploaded by
Elizander VergaraThis document discusses oral communication and communicative strategies. It covers speech context, styles, acts, and delivery methods. The key points are:
1) Oral communication uses speech styles and strategies based on the speech purpose and number of participants.
2) Communicative strategies include plans for sharing information to achieve a social, political, or linguistic goal.
3) Speech context can be intrapersonal, interpersonal, dyadic, small group, public, mass, organizational, or intercultural.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
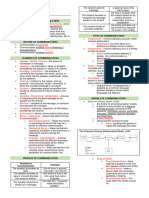
ORAL COMMUNICATION - Used in crafting the types of speech styles or their
1ST SEM 2ND QUARTER combinations
- Used in specific speech context (based on the
Speech Purpose and no. of participants)
COMMUNICATIVE STRATEGIES
● Locutionary (locution or utterance act) - the act
- plans/ways/means of sharing information that is
of making a meaningful utterance, a stretch of
adopted to achieve a particular social, political,
spoken language that is preceded by silence and
psychological, or linguistic purpose
followed by silence or a change of speaker
- Hallmark of communicative competence
● Illocutionary - the act of saying something with
Speech Context
the intention of stating (an opinion), making (a
- All communication, whatever the speech context,
prediction, promise, request), issuing (an order
has to have a purpose
or decision), or giving (advice or permission)
● Intrapersonal - communicating with oneself
● Perlocutionary - seen when a particular effect is
(talking, writing, thinking)
sought from either the speaker or the listener or
● Interpersonal - involves more than one person
both. Response may not necessarily be physical
- Differentiated by its purpose
or verbal and is elicited by inspiring or insulting,
- Communication is always intentional
persuading or convincing, or deterring or scaring
● Dyadic - interaction between two
- Aim is to change feelings, thoughts, or
persons
actions
● Small group - 3-15 people; anyone can
Seven Types of Communicative Strategies
be a speaker
Nomination - presenting a particular topic clearly,
● Public - no interchanging of the speaker
truthfully, and saying only what is relevant
and listeners’ role
Restriction - constraining the response/reaction within a
● Mass - carried out with the mass media
set of categories
technology
Turn-taking - recognizing when and how to speak
● Organizational - interaction of members
because it is one’s turn
along the links in an organizational
Topic control - keeping the interaction by asking
structure; formal and informal
questions and eliciting a response
● Intercultural - exchange of concepts,
Topic Shifting - introducing a new topic followed by the
traditions, values, and practices between
continuation of that topic
people from different nationalities and
Repair - overcoming communication breakdown to send
ways of life
more comprehensible messages
Speech Style
Termination - using verbal and nonverbal signals to end
- Variation of speech used when people
the interaction
communicate with other people
- Each type is used according to the Purpose and
DELIVERY OF SPEECH
Speech Context
- Uses Speech Acts to enhance communication
Methods of Delivery
● Intimate - casual type that happens between
A. Extemporaneous
close family members, friends, and couples
B. Impromptu
● Casual - used among friends and acquaintances
C. Manuscript
w/o background information. Used when there
D. Memory
are no social barriers to consider
Speaker’s Voice
● Consultative - opposite of intimate; requires
- Aspects to control: volume, pitch, rate, pauses,
two-way participation; people don’t share the
variety, pronunciation, articulation, dialect
common experiences or meaning
Nonverbal Communication
● Formal - only for imparting information; does not
- Posture, facial expression, gestures, eye contact
allow interruptions
- Personal appearance
● Frozen - quality is static, ritualistic, and may even
- Bodily actions
be archaic
Speech Acts
- Refer to the action performed by producing
utterances
You might also like
- Reviewer in Oral ComDocument2 pagesReviewer in Oral ComMarjorie PabloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer of Purposive Com. (PRELIM)Document7 pagesReviewer of Purposive Com. (PRELIM)fabarracoso24No ratings yet
- Reviewer Midterms PcommDocument13 pagesReviewer Midterms PcommKlouie KohNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication NotesDocument5 pagesOral Communication NotesAlfie Lyn PedregosaNo ratings yet
- GEC-PC Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesGEC-PC Midterm ReviewerSarah Mae EmbudoNo ratings yet
- Purcom HandoutsDocument5 pagesPurcom HandoutsEloisa BrailleNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH NotesDocument22 pagesENGLISH NotestempoNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm. 1st Sem FinalsDocument2 pagesOral Comm. 1st Sem FinalsAlexarae CasaneNo ratings yet
- Speech Oralcom REVIEWERDocument16 pagesSpeech Oralcom REVIEWERWhatever WhatwhoNo ratings yet
- Aneeza NadineDocument10 pagesAneeza NadineElyssa ReahnaNo ratings yet
- SMILE L.P Q2 ORAL COM. WK 3Document7 pagesSMILE L.P Q2 ORAL COM. WK 3Angelie Espartero Araneta LobitañaNo ratings yet
- Nature, Elements & Functions of Communication: Kristine B. Viñas InstructorDocument17 pagesNature, Elements & Functions of Communication: Kristine B. Viñas InstructorDanielle Kate MadridNo ratings yet
- MIL RevDocument7 pagesMIL Revsydneyroxas03No ratings yet
- Grammatical - Morphology and Syntax Discourse - Connection of Sentences of Utterance. Sociolinguistic - Interaction of Language To Society or ToDocument2 pagesGrammatical - Morphology and Syntax Discourse - Connection of Sentences of Utterance. Sociolinguistic - Interaction of Language To Society or ToysaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Language and Communication 2023 03Document41 pagesUnit 1 Language and Communication 2023 03Rezelle Mae TrongcoNo ratings yet
- Speech Context & Speech StylesDocument2 pagesSpeech Context & Speech StylesLyresh Ellaine VillegasNo ratings yet
- Speech Oralcom REVIEWER 1Document20 pagesSpeech Oralcom REVIEWER 1Whatever WhatwhoNo ratings yet
- J. Paul LeaganDocument15 pagesJ. Paul LeaganAries C. GavinoNo ratings yet
- OralCom - Lesson 1 PDFDocument4 pagesOralCom - Lesson 1 PDFShadowGlimmer PedroNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PURC111Document10 pagesReviewer PURC111priya garciaNo ratings yet
- SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL-Oral Communication in ContextDocument13 pagesSENIOR HIGH SCHOOL-Oral Communication in ContextTrixie Mae CabadinNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm ReviewerDocument10 pagesOral Comm ReviewerLucille Marie SabioNo ratings yet
- Types of CommuDocument2 pagesTypes of CommuFATIMA AYRAA SALIHNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesReviewer in Purposive CommunicationENCARNACION Princess MarieNo ratings yet
- PCM Notes and AssignmentsDocument9 pagesPCM Notes and Assignmentshan mamarilNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in Context Types of Speech ContextDocument5 pagesOral Communication in Context Types of Speech ContextRainee Anne DeveraNo ratings yet
- Pancit CantonDocument13 pagesPancit CantonAgatha Cristie AndradaNo ratings yet
- Jerilyn Rafols Activity 2Document5 pagesJerilyn Rafols Activity 2Danica RafolsNo ratings yet
- PurpComTranses CollegeDocument15 pagesPurpComTranses Collegelainezalthea15No ratings yet
- Purposive Communication PrelimsDocument21 pagesPurposive Communication PrelimsMichiiee Batalla0% (1)
- ENGLISHDocument11 pagesENGLISHgabezneNo ratings yet
- Oc CM Week 3Document19 pagesOc CM Week 3Zasha Denise LunarNo ratings yet
- Purposive - Module 1Document4 pagesPurposive - Module 1Glecy Ann MagnoNo ratings yet
- PurcomDocument6 pagesPurcomproxima midnightxNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology - For RemovalDocument23 pagesAbnormal Psychology - For RemovalPrue Shania JacoboNo ratings yet
- Oral Com - Final Term (A4)Document3 pagesOral Com - Final Term (A4)James David ganteNo ratings yet
- Chen Jet Eric 12 - Agate ICT Review in Oral CommDocument3 pagesChen Jet Eric 12 - Agate ICT Review in Oral CommJet Eric LeeNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Midterms ReviewerDocument3 pagesOral Com Midterms ReviewerPia AlineaNo ratings yet
- Gec 115 Lec 1 - 2 Pre MidDocument3 pagesGec 115 Lec 1 - 2 Pre MidArchjune Aubrey AbellaNo ratings yet
- Ged 106 Lesson 2Document5 pagesGed 106 Lesson 2shiftdohyonsNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesOral CommunicationKaith Ashlee De LeonNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument3 pagesPurposive CommunicationjennygumafelixNo ratings yet
- Purc111 Prelim ReviewerDocument8 pagesPurc111 Prelim ReviewerJamaica EstorninosNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication 1Document6 pagesPurposive Communication 1Jasmine Fritz CabreraNo ratings yet
- Types of Communication StrategyDocument3 pagesTypes of Communication StrategyJoshua Lander Soquita CadayonaNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesPurposive Communicationreen leighNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument2 pagesOral CommunicationJenRose Gadon SoliguenNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication - Second Sem - Midterms: Community. They Share Same Set of Rules in TheDocument7 pagesPurposive Communication - Second Sem - Midterms: Community. They Share Same Set of Rules in TheDA SulitNo ratings yet
- Nature of CommunicationDocument4 pagesNature of CommunicationAgtina, Angela Claudine A.No ratings yet
- PCOMDocument9 pagesPCOMXhiana ParkNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Diass 4QDocument2 pagesReviewer in Diass 4QJuniel TabaderoNo ratings yet
- Oral CommDocument5 pagesOral CommKaireen OzNo ratings yet
- 1st Semester Q1 Oral Communication (Notes)Document4 pages1st Semester Q1 Oral Communication (Notes)vince.resultay07No ratings yet
- Cor 001 2ND QTRDocument2 pagesCor 001 2ND QTRKassandra Gayle Olmodo SardoncilloNo ratings yet
- Handouts For Report DiscourseDocument2 pagesHandouts For Report DiscourseMary Joyce BautistaNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument8 pagesOral CommunicationAlliah ManilaNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument4 pagesOral CommunicationPrincess Cherry C. EstradaNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication For Finals NotesDocument11 pagesOral Communication For Finals NotesPullos, Gillian C.No ratings yet
- Conversation Strategies: Pair and Group Activities for Develping Communicative CompetenceFrom EverandConversation Strategies: Pair and Group Activities for Develping Communicative CompetenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Mindful Communicator: Effective Communication for Relationships and SuccessFrom EverandThe Mindful Communicator: Effective Communication for Relationships and SuccessNo ratings yet
- Extra Grammar: Extension Units 7 & 8Document1 pageExtra Grammar: Extension Units 7 & 8Emiliano AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Dhea MulyaniDocument70 pagesSkripsi Dhea MulyaniDhea AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument12 pages1 SMAhmad BusyairiNo ratings yet
- Business English 2, (ML, PI, U1, C3)Document2 pagesBusiness English 2, (ML, PI, U1, C3)Ben RhysNo ratings yet
- Admitere Conditional ClausesDocument6 pagesAdmitere Conditional ClausesGeorgiana Argentina DinuNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Check Answers: Part 1: Non-FictionDocument45 pagesDiagnostic Check Answers: Part 1: Non-FictionMay Youssef100% (2)
- Integrate Reading Writing Building 1 Student 39 S Book PDFDocument114 pagesIntegrate Reading Writing Building 1 Student 39 S Book PDFKathy Di Rosa100% (1)
- Sample of Comment For Online ESLDocument6 pagesSample of Comment For Online ESLRodel Namayan100% (1)
- The Road - Cormac McCarthy - Lesson 1Document13 pagesThe Road - Cormac McCarthy - Lesson 1Alejandro James D'AbreauNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses - 10 AnoDocument10 pagesRelative Clauses - 10 AnoAna Sofia SantosNo ratings yet
- Pegagogical Documentation - Ece 242 Reflective ProfessionalDocument10 pagesPegagogical Documentation - Ece 242 Reflective Professionalapi-603620299No ratings yet
- 11 Classe 3T FirstDocument2 pages11 Classe 3T FirstFernando SabinoNo ratings yet
- Learn JapaneseDocument7 pagesLearn JapaneseEstera ButnariucNo ratings yet
- Westaway, F.W. - Quantity and Accent in The Pronunciation of LatinDocument140 pagesWestaway, F.W. - Quantity and Accent in The Pronunciation of LatinKevin HarrisNo ratings yet
- (Cambridge Books Online) Subbārāo, Kārumūri V - South Asian Languages - A Syntactic Typology-Cambridge University Press (2012)Document392 pages(Cambridge Books Online) Subbārāo, Kārumūri V - South Asian Languages - A Syntactic Typology-Cambridge University Press (2012)taryumanNo ratings yet
- Improving Systematic Generalization Through Modularity and Augmentation - Laura Ruis Brenden LakeDocument9 pagesImproving Systematic Generalization Through Modularity and Augmentation - Laura Ruis Brenden LakeluizNo ratings yet
- Pygmalion - Script PDFDocument27 pagesPygmalion - Script PDFArisetya Hafiz75% (4)
- OjibwefgdDocument128 pagesOjibwefgdMáirtín Ó hUallacháin100% (1)
- Degrees of Comparison of AdjectivesDocument2 pagesDegrees of Comparison of AdjectivesCarlynArgentinaPaitanCarduzaNo ratings yet
- Cahaya Try Hartaty - H1041201008 - Biologi B - Subject of SentenceDocument6 pagesCahaya Try Hartaty - H1041201008 - Biologi B - Subject of SentenceCahayatryhartaty YayaNo ratings yet
- Bolyán Anita, Ahriman ('The Devil') Means The Shaman of The Onogur-Manju Tribal Alliances (Neither Good, Nor Bad), 2023.Document8 pagesBolyán Anita, Ahriman ('The Devil') Means The Shaman of The Onogur-Manju Tribal Alliances (Neither Good, Nor Bad), 2023.Anita BolyánNo ratings yet
- 2 03 Smarttime 3 Unit 3 PDFDocument12 pages2 03 Smarttime 3 Unit 3 PDFKalin67% (3)
- Relative ClauseDocument27 pagesRelative ClauseꂅᏒꂅภ ᕱᏒᏕᎥภNo ratings yet
- STD 10 TH Maths Bridge CourseDocument64 pagesSTD 10 TH Maths Bridge Coursedarshan kawareNo ratings yet
- 1.0: Introduction of Role PlayDocument12 pages1.0: Introduction of Role PlayMuhd Hilmi AkhirNo ratings yet
- Ilocano LitratureDocument23 pagesIlocano LitratureMichaella Shane Daniel ApostolNo ratings yet
- CSC 415 Comminication Skills (Service Course)Document96 pagesCSC 415 Comminication Skills (Service Course)karan sapateNo ratings yet
- 1ST Periodical Eng 7Document2 pages1ST Periodical Eng 7Zoren RefusarNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2 Grammar Revision AnswerkeyDocument3 pagesAssessment 2 Grammar Revision AnswerkeyKarunya RaoNo ratings yet
- "and" in Chinese - 与 (yǔ), 和 (hé) or 跟 (gēn) 4. Sentence structure differencesDocument27 pages"and" in Chinese - 与 (yǔ), 和 (hé) or 跟 (gēn) 4. Sentence structure differencesJane FrostNo ratings yet