Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COMMUNICATION
Uploaded by
ramoskynch0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesGrade 11 Oralcom notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGrade 11 Oralcom notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesCOMMUNICATION
Uploaded by
ramoskynchGrade 11 Oralcom notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
ORALCOM NOTES
COMMUNICATION
- Process of sharing and conveying messages or information from one person to another.
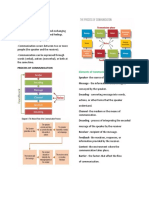
COMMUNICATION PROCESS
ENOCODING
MESSAGE
DECODING
FEEDBACK
THE ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION
VERBAL/NON-VERBAL
SPEAKER – the source of information or message
MESSAGE – the information, ideas, or thoughts conveyed by the speaker in words or in
actions.
ENCODING - the process of converting the message into words, actions, or other forms
that the speaker understands.
CHANNEL – the medium and the means.
DECODING – the process of interpreting the encoded message of the speaker by the
receiver.
RECEIVER – the recipient of the message, or someone who decodes the message.
FEEDBACK - the reactions, response, or information provided by the receiver.
CONTEXT – the environment where communication takes place.
BARRIER – the factors that affect the flow of communication.
MODELS OF COMMUNICATION
SHANNON- WEAVER MODEL - Mother of all communication models.
INTERACTIVE MODEL - Exchange of roles in communication.
THE TRANSACTIONAL MODEL - Two-way process with the inclusion of feedback as one
element.
3 PARTICULAR LAYERS OF COMMUNICATION PROBLEM
Technical: How accurately can the message be transmitted?
Semantic: How precisely can the meaning be conveyed?
Efficacy-related: How effectively does the received meaning affect behavior?
TYPE OF NOISE
Environmental Noise - physically disrupts communication.
Physiological-Impairment Noise - Physical conditions that can impede effective
communication and interfere with messages being clearly and accurately received.
Semantic Noise - refers to when a speaker and a listener have different interpretations of
the meanings of certain words.
ORALCOM NOTES
Syntactical Noise - Communication can be disrupted by mistakes in grammar, such as an
abrupt change in verb tense during a sentence.
Organizational Noise - poorly structured messages can also be a barrier.
Cultural Noise - making stereotypical assumptions.
Psychological Noise - certain attitudes can also make communication difficult.
FUNCTION OF COMMUNICATIONS
CONTROL – communication function to control behavior
SOCIAL INTERACTION – communication allows individuals to interact with others
MOTIVATION – communication motivates or encourage people to live better.
DEMOTIONAL EXPRESSION – communication facilitates peoples expression of their feelings
and emotions.
INFORMATION DISSEMINATION – used when the speaker wants to make others aware of
certain data, concepts, and other processes.
FEUTURES OF SOMMUNICATION
COMPLETENESS – who, when, why, what, where
CONCISENESS – straight to the point.
CONSIDERATION - Give consideration on relevant information
CONCRETENESS - The message should be concrete and supported by facts, figures, and real
life
COURTESY - Respect the culture, values, and beliefs of his/her receivers
CLEARNESS - use of simple and specific words to express ideas
CORRECTNESS - eliminates negative impact on the audience
NON-VERBAL COMMUNICATION
Example : smile, stare, style, attire, and attitude
DIFFERENT NON-VERBAL
KINESIS – body movement
PROXEMICS – closeness/personal space
POSTURE – body posture
EYE CONTACT – make a contact with your eyes in a short/long period
YOUCH/HAPTICS – physical touch
PARALANGUAGE – tone of voice
FINANCIAL EXPRESSION – face expression when you are emotional
PHYSIOLOGY – deliberately control
You might also like
- Oral CommunicationDocument6 pagesOral CommunicationPaul RobertNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument14 pagesOral CommunicationBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication (Reviewer)Document14 pagesOral Communication (Reviewer)Harchelo AndayaNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm HandoutDocument25 pagesOral Comm HandoutRina Tubera100% (1)
- Fundamentals of CommunicationDocument2 pagesFundamentals of CommunicationMaryjoy PaladanNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesOral CommunicationJAS MAGHARINo ratings yet
- Oral 1Document10 pagesOral 1ROWENA PALACIONo ratings yet
- Performance Task - Tiu, Eva CarlieDocument6 pagesPerformance Task - Tiu, Eva CarlieKimmehhloves VlogxxxNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocument2 pagesOral Communication ReviewerJeocel Saramosing100% (10)
- Lesson 1 Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument18 pagesLesson 1 Nature and Elements of CommunicationKervie AntonioNo ratings yet
- Process of Communication ReportDocument31 pagesProcess of Communication ReportmysterioushumaneNo ratings yet
- Oral ComDocument5 pagesOral ComVenise RevillaNo ratings yet
- DIASS Fourth Quarter ModuleDocument18 pagesDIASS Fourth Quarter ModuleMikex Mike100% (2)
- COMMUNICATIONDocument2 pagesCOMMUNICATIONwannabeeurzNo ratings yet
- Communication Process: Is Also Like The Importance of BreathingDocument12 pagesCommunication Process: Is Also Like The Importance of BreathingElla JaneNo ratings yet
- California: Wadsworth Publishing Company) : Ge Comm Purposive Communication Definition of CommunicationDocument2 pagesCalifornia: Wadsworth Publishing Company) : Ge Comm Purposive Communication Definition of CommunicationMarinela MitraNo ratings yet
- Nature and Elements of Communication: Miss Riza O. VillanuevaDocument45 pagesNature and Elements of Communication: Miss Riza O. VillanuevaBea Dacillo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Oral Com - MidtermDocument9 pagesOral Com - MidtermKate CustodioNo ratings yet
- Oral CommDocument5 pagesOral CommJorge GanzonNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocument5 pagesOral Communication ReviewerSofia Rose Saniel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Nature and Process of CommunicationDocument6 pagesNature and Process of CommunicationHessah Balmores DupitasNo ratings yet
- Basic Purposive CommunicationDocument38 pagesBasic Purposive CommunicationDimple EstacioNo ratings yet
- Communication (Notes)Document5 pagesCommunication (Notes)zariyahriegoNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocument6 pagesOral Communication ReviewerArmhay Loraine DuavezNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument5 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerMikaela MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Reviewer Unit 1&2Document4 pagesOral Communication Reviewer Unit 1&2Leigh Anne CaminceNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm Reviewer First Quarter White BGDocument2 pagesOral Comm Reviewer First Quarter White BGWarren PagsuyuinNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument32 pagesOral CommunicationchichiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocument2 pagesOral Communication ReviewereukiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CommunicationDocument2 pagesReviewer CommunicationJaimNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication (Grade 11)Document22 pagesOral Communication (Grade 11)leviduranteeNo ratings yet
- 2ND Day ReviewerDocument4 pages2ND Day ReviewerJasmine de LeonNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Prelim ReviewerDocument6 pagesPurposive Communication Prelim ReviewerJade PaulosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Fundamentals of CommunicationDocument5 pagesLesson 1 - Fundamentals of CommunicationCedrick Lei BalaagNo ratings yet
- Oral CommDocument5 pagesOral CommJairah CastilloNo ratings yet
- POINTS TO REMEMBER IN ORAL COMMUNICATION PrelimDocument5 pagesPOINTS TO REMEMBER IN ORAL COMMUNICATION PrelimMarco Antonio MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication ReferenceDocument5 pagesOral Communication ReferenceAndaya, Karl Christian D.No ratings yet
- Oral ComDocument1 pageOral Commarcosrose1935No ratings yet
- Oral Communication (Reviewer)Document4 pagesOral Communication (Reviewer)Frances Nicole ArceNo ratings yet
- Ommunication Nalysis Ature: Silliman UniversityDocument22 pagesOmmunication Nalysis Ature: Silliman UniversityKressol ChavezNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocument5 pagesOral Communication ReviewerMaureen AkimoriNo ratings yet
- Oral ComDocument3 pagesOral ComNova Jane EdradNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Purposive CommunicationDocument12 pagesReviewer For Purposive CommunicationJohn Rey GalichaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Oral Cominication 11Document10 pagesReviewer in Oral Cominication 11Nicole BirjNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm NotesDocument18 pagesOral Comm NotesArianne Courtney NacarNo ratings yet
- Oral Com 1ST Quarter LessonsDocument9 pagesOral Com 1ST Quarter Lessonsangelobasallote66No ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument2 pagesOral CommunicationCharlene DanaNo ratings yet
- NOES2Document5 pagesNOES2HighsNo ratings yet
- Rev. Oral ComDocument3 pagesRev. Oral ComFrances A. JumarangNo ratings yet
- Purcomm Lesson 1: The Nature, Process and Basics of CommunicationDocument9 pagesPurcomm Lesson 1: The Nature, Process and Basics of CommunicationPirate CaribbeanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Process of CommunicationDocument2 pagesChapter 2 - Process of CommunicationCarolyn NacesNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm Nat and Periodical ReviewerDocument3 pagesOral Comm Nat and Periodical ReviewerApricus BenciNo ratings yet
- PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION ReviewerDocument10 pagesPURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION ReviewerAngel AlipioNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument52 pagesPurposive CommunicationArlene Rose GonzaloNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Chapter 1Document23 pagesPurposive Communication Chapter 1Gwyneth Lei ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Chapter 1Document23 pagesPurposive Communication Chapter 1Gwyneth Lei ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication 2Document23 pagesIntroduction To Communication 2Rodney Takundanashe MandizvidzaNo ratings yet
- Barriers To CommunicationDocument29 pagesBarriers To CommunicationGuneet AulakhNo ratings yet
- Purc Week 2-5 (Prelim)Document8 pagesPurc Week 2-5 (Prelim)Mary Mae Antoinette Perez ChanNo ratings yet
- Grade 1: Writing RubricsDocument3 pagesGrade 1: Writing RubricsCarol GlenNo ratings yet
- SRS - PBL6 - Nhóm 5Document4 pagesSRS - PBL6 - Nhóm 5Duy LêNo ratings yet
- CS3691 - Embedded Systems and Iot Lab ManualDocument30 pagesCS3691 - Embedded Systems and Iot Lab Manualp01591124No ratings yet
- CEREC AC Omnicam: Installation Instructions For Windows 10 Performance PackDocument10 pagesCEREC AC Omnicam: Installation Instructions For Windows 10 Performance PackdirkfalkNo ratings yet
- The Legal Status of Following A Madhab by Sheikh Mufti Taqi Usmani PDFDocument84 pagesThe Legal Status of Following A Madhab by Sheikh Mufti Taqi Usmani PDFMUSALMAN BHAI100% (1)
- VanadurgaDocument3 pagesVanadurgaBangaru Babu50% (2)
- Lecture 02 - POP vs. OOP, Java Features, Class, ObjectDocument2 pagesLecture 02 - POP vs. OOP, Java Features, Class, ObjectSanjoy PathakNo ratings yet
- ExcelDocument8 pagesExcelucieNo ratings yet
- SAP Learning System Access1Document35 pagesSAP Learning System Access1Nguyễn BảoNo ratings yet
- Otto Bohlmann Auth. Yeats and Nietzsche An Exploration of Major Nietzschean Echoes in The Writings of William Butler Yeats PDFDocument243 pagesOtto Bohlmann Auth. Yeats and Nietzsche An Exploration of Major Nietzschean Echoes in The Writings of William Butler Yeats PDFDanja Tešić100% (1)
- AlghazzaliDocument24 pagesAlghazzaliapi-247725573No ratings yet
- Hum 002 Sas 1-2Document8 pagesHum 002 Sas 1-2Elmer BoybantingNo ratings yet
- Use of EnglishDocument6 pagesUse of EnglishLorena DoduNo ratings yet
- Session 2 Principles of Effective CommunicationDocument22 pagesSession 2 Principles of Effective CommunicationANIRUDDHA JADHAVNo ratings yet
- Comp. Sup. QuizDocument2 pagesComp. Sup. QuizCaro CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Background of The StudyDocument15 pagesBackground of The StudyJensi AsiNo ratings yet
- Calendar Thematic Plan For Grade 3 Within The Framework of Updating The Secondary Education Content 2021 - 2022 Academic YearDocument6 pagesCalendar Thematic Plan For Grade 3 Within The Framework of Updating The Secondary Education Content 2021 - 2022 Academic YearAkonya AnarbekovaNo ratings yet
- Bugfix Build 18.10 English PDFDocument6 pagesBugfix Build 18.10 English PDFHakim BenmajidNo ratings yet
- Node-Lock ProceduresDocument3 pagesNode-Lock ProceduresgeneraljomoNo ratings yet
- 0478 m17 QP 22Document12 pages0478 m17 QP 22Kiron DebNo ratings yet
- Aef4 - 02B - WBDocument3 pagesAef4 - 02B - WBRussellNo ratings yet
- Daily Recorder Exercises (In C) PDFDocument7 pagesDaily Recorder Exercises (In C) PDFkuang100% (1)
- TugaskuDocument6 pagesTugaskuputri noer auliantyNo ratings yet
- LogDocument53 pagesLogNahudin SNo ratings yet
- King LearDocument12 pagesKing LearAyaat ElmelegyNo ratings yet
- Training Course Datastage (Part 1) : V. Beyet 03/07/2006Document122 pagesTraining Course Datastage (Part 1) : V. Beyet 03/07/2006gangadhar1310100% (1)
- Pentecost: Lesson 2 For July 14, 2018Document9 pagesPentecost: Lesson 2 For July 14, 2018Martinez YanNo ratings yet
- Ontotheological Turnings? Joeri SchrijversDocument288 pagesOntotheological Turnings? Joeri SchrijversAna Piljic Mitrovic100% (1)
- Tasm User's Manual Tasm - A TableDocument86 pagesTasm User's Manual Tasm - A TablehovukiemNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Board Position Test System Plan For Class 10 As Per PBCC 2022Document7 pagesSyllabus: Board Position Test System Plan For Class 10 As Per PBCC 2022zaeemNo ratings yet