Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Community and Public Health For MLS - Laboratory
Community and Public Health For MLS - Laboratory
Uploaded by
torreb8396Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Community and Public Health For MLS - Laboratory
Community and Public Health For MLS - Laboratory
Uploaded by
torreb8396Copyright:
Available Formats
COMMUNITY AND PUBLIC HEALTH FOR MLS FIRST SEMESTER
LABORATORY TRANSCRIPT SY. 2023 - 2024
LESSON 1: DEMOGRAPHY DATA COLLECTION METHODS
DEMOGRAPHY SURVEYS
● Administration of an interview form to a portion of a target
DEFINITION population that has been systematically selected.
● Mathematical & statistical study of SIZE, CENSUS
COMPOSITION, & SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION of HUMAN ● Complete count of individuals or entities residing in a
POPULATIONS & of changes over time in these aspects specific place at a specific time
through the operation of 5 processes of: ○ Registries - data from barangay centers, have the
○ Fertility - how does it affect population size number of individuals in the community as well as
■ High Fertility = high population voters registration
○ Mortality - the number of deaths ■ Ex
■ High mortality= low population ● Voter’s registration - does not collect
○ Migration the complete population within the
■ Immigration - individuals coming in, community because hindi naman lahat
increases population 18 and above with voters
■ Emigration - individuals coming out ● PSA - can contain data about mortality,
decreases population morbidity, etc.
○ Marriage ○ Synthetic Data
■ Affects population and characteristics
○ Social Mobility POPULATION DISTRIBUTION
■ Social status and changes ● Dispersal of population, usually by country
● 3 phenomena ● Describes how people are spread across a specific area
○ Observe and describe the population size, ● Measures of Population distribution
composition and distribution (geographically) ○ By Type of Community
DEMOGRAPHY AIMS TO: ○ By Barangay, Municipality, City, Province, or Region
● Determine the number & distribution of a population in
certain area for planning, priority, setting and for
purposes of fund allocation
○ Based on sex, age, socio demographic profile and
other variables in describing a population
■ Helps in formulation and prioritization of
health programs
■ Example: low fertility rate and high life
expectancy - meaning aging population is
high
● Therefore we do not prioritize maternity
health but the geriatric health,
● By this we can determine why the
fertility rate is low an how it can affect POPULATION CONCENTRATION
the population resulting to low ● AKA population density
independent/productive population ● Ratio of number individuals to physical space
resulting to low economy ● Measure of distribution that indicates the level of
● Determine growth and/or decline and dispersal of concentration or dispersion
population in the past. ● Measured in terms of density
● Establish a causal relationship between population trends ○ Population in the area / total land area
and various aspects of social organization ○ Unit: Person per square km
● Predict future developments & their possible
consequences.
POPULATION SIZE
● Total number individuals in a population
● First “demographic fact” employed in describing a
population
● Measured in terms of the number of individuals who
reside within a defined geographic area at a specified
time
● Other measures: number of households or families
● Methodology
○ Census complete collection or identification of
population size
■ Binibilang lahat ng members
Prepared by: TORRE, Bill Ritchie C., MT2C PAGE 1
COMMUNITY AND PUBLIC HEALTH FOR MLS FIRST SEMESTER
LABORATORY TRANSCRIPT SY. 2023 - 2024
POPULATION COMPOSITION DESCRIBING POPULATION COMPOSITION
● Combined demographic characteristics of persons within SEX COMPOSITION
a geographical data 1. Sex Ratio
DEMOGRAPHIC CHARACTERISTICS 2. Sex Structure
● Attributes that give a population its character AGE COMPOSITION
● Biosocial Characteristics 1. Median Age
○ Age, Sex, Race, & Ethnicity - three major 2. Dependency Ratio
elements AGE–SEX COMPOSITION
● Sociocultural Characteristics - part of social 1. Population Pyramid
determinants of health, extrinsic non-medical factors that SEX COMPOSITION
drive the health of the population
○ Marital SEX RATIO
○ Status / Family Structure
● Compares number of males to the number of females
○ Income 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠
■ Low class ● Formula: 𝑆𝑒𝑥 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜 = ( 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑓𝑒𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠 ) × 100
■ Middle class ● Number of males per 100 males
● low income ● Importance of describing and determining the sex ratio:
● high income ○ Fertility rate lowers when male or female individuals
■ High class are lowered causing an increase in death rate or
○ Education - depends on the the population is decreasing which translates to
■ Quality and level of education dictates the lowered work force which leads to low economy
job you get EXAMPLE
■ Educational attainment: highschool Ex. Calculate the sex ratio for the year 2020 in the Philippines
graduate, masteral if there were 55,741,000 males and 55,306,000 females.
○ Occupation/Industry/Employment - employed or
𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠
unemployed plus industry ● 𝑆𝑒𝑥 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜 = ( 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑓𝑒𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠 ) × 100
○ Religion - actually a social determinant of health 55,741,000
● 𝑆𝑒𝑥 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜 = ( 55,306,000 ) × 100
● 𝑆𝑒𝑥 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜 = 100. 87 = 101 - wala naman kasing
decimal na individuals
● Interpretation: In 2020, there were 101 males for every
100 females in the Philippines or For every 100 females
in the Philippines in 2020, there were about 101 males
COUNTRIES WITH HIGH SEX RATIO (WORLD
POPULATION REVIEW)
● Due to high immigrant workers especially filipinos
1. Qatar : 266 males per 100 females - 88% of
population are migrant workers
2. UAE : 228 males per 100 females
3. Bahrain : 164 males per 100 females
4. Oman : 157 males per 100 females
WHY DO YOU NEED TO KNOW THE POPULATION 5. Kuwait: 156 males per 100 females
COMPOSITION OF THE COMMUNITY? COUNTRIES WITH HIGH SEX RATIO (WORLD
POPULATION REVIEW)
1. Qatar : 302 males per 100 females
2. UAE : 224 males per 100 females
3. Oman : 194 males per 100 females
4. Maldives : 174 males per 100 females
5. Bahrain : 154 males per 100 females
COUNTRIES WITH LOW SEX RATIO (WORLD
POPULATION REVIEW)
1. China : 84.48 M per 100 F
2. Martinique : 85.00 per 100 F
● So that we can allocate the health resources to those 3. Curacao : 85.28 per 100 F
who really needs it and can’t afford it, proper allocation of 4. Nepal : 85. 48 per 100 F
resources so that we can practice equity and not equality 5. Guadeloupe : 85.49 per 100 F
DIFFERENCE OF EQUALITY AND EQUITY
● Equity - giving resources/opportunities to those that need SEX STRUCTURE / SEX DISTRIBUTION
it ● Aka Sex ratio in different categories
● Equality - same resources are given despite the ● Compares sex ratio across different categories (age,
background community type)
● Age-Sex Distribution – most common
Prepared by: TORRE, Bill Ritchie C., MT2C PAGE 2
COMMUNITY AND PUBLIC HEALTH FOR MLS FIRST SEMESTER
LABORATORY TRANSCRIPT SY. 2023 - 2024
EXAMPLE EXAMPLE
Calculate the median age Median Age and provide
interpretation with the given table
● Just get the total male population of 0-14 and 65 and
above divide it to total population of female of 0-14 and
65 and above and that is your sex ratio ● Median Population:
○ 19,995,800/19442800 ○ 𝑀𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛 𝐶𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠 =
𝑛
2
● 15-64 referred to as the productive group 108,274,800
● Interpretation : There is usually a higher sex ratio in the ○ 𝑀𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛 𝐶𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠 = 2
= 54, 137, 400
younger age groups and lower sex ratio at the older age ○ 54, 137, 400 falls between 25-29 age group
groups. ● Median Age:
𝑛
−𝑐
○ 𝑀𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛 𝐴𝑔𝑒 = 𝑙 + 2
× ℎ
AGE COMPOSITION 𝑐𝑓
■ 𝑙 = 25
MEDIAN AGE ■ 𝑐 = 9, 970, 100
● Get total of final cumulative frequency which will be used ■ 𝑓 =9
in finding the median class as well as the median age ■ ℎ = 29 − 25 = 4
108,274,800
● Value which cuts off the upper 50% and lower 50% of the −9,970,100
○ 𝑀𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛 𝐴𝑔𝑒 = 25 + 2
× 4
ages of the population 62,593,200
● Formulas ● Interpretation : The median age of the population is 28
𝑛 years. Or 50% of the population is younger than 28 years
○ 𝑀𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛 𝐶𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠 = 2
of age.
■ Age Group with Cumulative frequency
AGE-DEPENDENCY RATIO
greater than the computed value is the
median class ● # of dependents to be supported for every 100
𝑛
−𝑐 economically-productive person.
○ 𝑀𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛 𝐴𝑔𝑒 = 𝑙 + 2
× ℎ 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑑𝑒𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑝𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
𝑐𝑓 ● Formula: 𝐴𝐷𝑅 = ( 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑝𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 ) × 100
■ l = lower limit of median class
○ Dependent Population : 0-14 y/o and >65 y/o
■ c = frequency of class preceding the median
○ Productive Population : 15 –64 y/o
class
■ cf = cumulative frequency of median class
■ h = width of median class
Prepared by: TORRE, Bill Ritchie C., MT2C PAGE 3
COMMUNITY AND PUBLIC HEALTH FOR MLS FIRST SEMESTER
LABORATORY TRANSCRIPT SY. 2023 - 2024
EXAMPLE AGE-SEX COMPOSITION
Calculate the ADR and provide interpretation with the given
table POPULATION PYRAMID
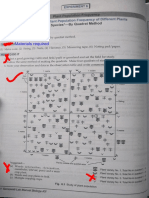
● Graphical presentation of the age and sex composition of
the population
● Reading the pyramid:
○ Malawak sa taas - high aging population or life
expectancy
○ Makipot namans baba - mababa ang fertility rate,
bumababa ang population community
○ Based sa picture,
■ Malawak sa baba then pa-narrow siya sa
taas
● Compute for the number of dependent population
■ Therefore, it is high fertility rate, younger
○ #𝐷𝑃 = 𝐴𝑔𝑒 0 𝑡𝑜14 + 𝐴𝑔𝑒 65 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑎𝑏𝑜𝑣𝑒 population is higher and lower aging
■ To get ng mabilisan, tumingin ka sa population, translates to lower life
cumulative frequency sa 10-14 expectancy
● 𝐴𝑔𝑒 0 𝑡𝑜 14 = 33, 126, 400 ■ Prediction: since there is high young
■ To get this ng mabilisan, tingin ka cf ng sa 80 population, then workforce will increase
and above at sa 60-64, subtract the 80 and ● Characteristics and composition of the population
above cf to 60-64 cf ● Explains and describes demographic trends of the
● 𝐴𝑔𝑒 65 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑎𝑏𝑜𝑣𝑒 = 5, 818, 995 population in the past
○ #𝐷𝑃 = 𝐴𝑔𝑒 0 𝑡𝑜 14 + 𝐴𝑔𝑒 65 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑎𝑏𝑜𝑣𝑒 ● Provides inference about the lifespan and economical
○ #𝐷𝑃 = 33, 126, 400 + 5, 818, 995 status of a community or a country
○ #𝐷𝑃 = 38, 942, 899 ● Factors
● Compute for the number of productive population ○ Fertility Rate, mortality, migration
○ To get this ng mabilisan subtract cf 10-14 to cf
POPULATION PYRAMID TYPES
60-64
■ #𝐷𝑃 = 69, 329, 900 EXPANSIVE/EXPANDING PYRAMID
● Solve for the ADR
𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑑𝑒𝑝𝑒𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑝𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
○ 𝐴𝐷𝑅 = ( 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑝𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 ) × 100
38,942,899
○ 𝐴𝐷𝑅 = ( 69,329,900 ) × 100
○ 𝐴𝐷𝑅 = 56. 2%
● Interpretation: For every 100 economically-productive
persons, 56 persons are to be supported.
● Broad Base, Pointed Star shape, Christmas-tree /
triangular shape
● High Fertility - mataas sa baba
● High Mortality - mababa sa taas
● Low Life Expectancy - wala masyado productive
population, common in developing countries
● High Population Growth Rate
● Common for developing countries
DOME-SHAPED PYRAMID
Prepared by: TORRE, Bill Ritchie C., MT2C PAGE 4
COMMUNITY AND PUBLIC HEALTH FOR MLS FIRST SEMESTER
LABORATORY TRANSCRIPT SY. 2023 - 2024
● Late-Expanding Stage POPULATION PYRAMID & CONCEPT OF DEMOGRAPHIC
● Early Stationary Phase TRANSITION
● Declining birth rate
STATIONARY PYRAMID
POPULATION PYRAMID CONSTRUCTION USING MS
EXCEL
1. Encode your Data. The ff. data are needed
● Age-Sex Distribution (Class Interval of 4)
● % Male = -(# of male in age group / total # of males) x
100
○ Set it to negative value by adding – sign on the
formula
● share of the population remains constant in different age
● % Female = (# of female in age group / total # of
groups
females) x 100
● Barrel-shaped
● There is not much changes in the younger population to
the productive age group, only decreases in the old age
because of mortality
● Low Fertility
● Low Mortality
● High life expectancy
● Slow population growth 2. Highlight the % Male and % Female Data set.
CONSTRICTIVE PYRAMID 3. Click on Insert on the Menu Tabs.
● Select Insert Column or Bar Graph.
● Choose Stack Bar on the 2D-Bar Graphs selection
pane.
● Elder and Shrinking Population
● Urn or bulb-shaped which can turn into an inverted
pyramid
● Low birth rate
IRREGULAR SHAPED PYRAMIDS
● The Baby Boom Pattern 4. Click on either the blue or red bar area and select Format
● Migration Data Series.
○ Winged, Diamond, Indented
● We can blame the sudden migration of individuals in and
out of the country mostly (immigrants)
Prepared by: TORRE, Bill Ritchie C., MT2C PAGE 5
COMMUNITY AND PUBLIC HEALTH FOR MLS FIRST SEMESTER
LABORATORY TRANSCRIPT SY. 2023 - 2024
5. Change the Gap Width to 0%
6. Click on the paint bucket icon (Fill & Line icon), select
Border, and change it to solid line, color black, width 1 pt. 8. Click on the x-axis area, right click and choose the format
7. Repeat for the other bar area, simply right click, format axis.
data series, change the border fill to solid line. 9. Select
● Bounds and make necessary adjustment of the scale
(12)
● Units and change major to 1.0.
● “Numbers” change category to custom, Type to 0;0,
and Format code to 0.0;[Black]0.0 and click Add.
10. Click on the x-axis area, right click and choose select
data.
11. Change the Series names.
● a. Series 1 %Male
● b. Series 2 %Female33
Prepared by: TORRE, Bill Ritchie C., MT2C PAGE 6
COMMUNITY AND PUBLIC HEALTH FOR MLS FIRST SEMESTER
LABORATORY TRANSCRIPT SY. 2023 - 2024
12. Click on the y-axis area, right click and choose format
axis.
13. Click Labels. Set the position to Low
14. Click on the y-axis area, right click and choose select
data.
15. Click Edit under the Horizontal (Category) Axis Labels.
Highlight the Age groups and Click Ok.
16. Change Chart title appropriately.
17. Adjust axis units if needed.
Prepared by: TORRE, Bill Ritchie C., MT2C PAGE 7
COMMUNITY AND PUBLIC HEALTH FOR MLS FIRST SEMESTER
LABORATORY TRANSCRIPT SY. 2023 - 2024
Prepared by: TORRE, Bill Ritchie C., MT2C PAGE 8
COMMUNITY AND PUBLIC HEALTH FOR MLS FIRST SEMESTER
LABORATORY TRANSCRIPT SY. 2023 - 2024
WEEK 2:
● ●
● ●
● WEEK 8:
●
WEEK 3:
● ●
● ●
● WEEK 9:
●
WEEK 4:
● ●
● ●
● WEEK 10:
●
WEEK 4:
● ●
● ●
● WEEK 11:
●
WEEK 5:
● ●
● ●
● WEEK 12:
●
WEEK 6:
● ●
● ●
● WEEK 13:
●
WEEK 7:
● ●
Prepared by: TORRE, Bill Ritchie C., MT2C PAGE 9
COMMUNITY AND PUBLIC HEALTH FOR MLS FIRST SEMESTER
LABORATORY TRANSCRIPT SY. 2023 - 2024
WEEK 14:
●
WEEK 15:
●
Prepared by: TORRE, Bill Ritchie C., MT2C PAGE 10
You might also like
- In What Year Does The Transition Stages StartedDocument6 pagesIn What Year Does The Transition Stages StartedNavasca Jhey Ann100% (1)
- Assessing The Impact of Urbanisation On Water Bodies Using GisDocument22 pagesAssessing The Impact of Urbanisation On Water Bodies Using GisCrispin Cris Nspm100% (1)
- 9 - Urban & Rural Development in BangladeshDocument21 pages9 - Urban & Rural Development in BangladeshMd Omar Kaiser MahinNo ratings yet
- CPH LEC Demography and Pop Estimates ReviewerDocument4 pagesCPH LEC Demography and Pop Estimates ReviewerCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Demography - CHN 2Document4 pagesElements of Demography - CHN 2trisha marieNo ratings yet
- CHN 2Document23 pagesCHN 2Erica JoyNo ratings yet
- Growth ProjectionDocument35 pagesGrowth ProjectionMonica Galuh DhiharsiwiNo ratings yet
- 3 4Document4 pages3 4Sicad, Jhenny DNo ratings yet
- Administrators Roles in Demographic Aspect of Educational PlanningDocument40 pagesAdministrators Roles in Demographic Aspect of Educational PlanningImel Aguado TalagNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 - Changing Population (Unit 1) - Global ChangeDocument65 pagesPaper 2 - Changing Population (Unit 1) - Global Changevomawek227No ratings yet
- CHN - Vital Statistics 1Document5 pagesCHN - Vital Statistics 1CARL ANGEL JAOCHICONo ratings yet
- Health StatisticsDocument2 pagesHealth StatisticsACERET, IVAN LAURENTINE G.No ratings yet
- 9th Geography - Chapter 6 PopulationDocument25 pages9th Geography - Chapter 6 Populationd.kbansal23122008No ratings yet
- Global Demography G 1Document27 pagesGlobal Demography G 1Jemuel Luc JavierNo ratings yet
- CHN Transes Week 2Document2 pagesCHN Transes Week 2cheskalyka.asiloNo ratings yet
- DemographyDocument56 pagesDemographykosalaiNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 Demography Full UnitDocument240 pagesUnit-6 Demography Full UnitKairali puthoor100% (1)
- Health Statistics and EpidemiologyDocument4 pagesHealth Statistics and EpidemiologyAna SoleilNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Term3 0 4 Teacher Final Doc Edward-2Document68 pagesGr10 Term3 0 4 Teacher Final Doc Edward-2Naledi MokoenaNo ratings yet
- Demography StudyDocument53 pagesDemography StudyJAMIL ASUMNo ratings yet
- Global DemographyDocument29 pagesGlobal DemographySarah FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Demography: Environmental Planning Capability Building For Architects Dates: March 8/9/15/16/22/23Document61 pagesDemography: Environmental Planning Capability Building For Architects Dates: March 8/9/15/16/22/23Arnold DominguezNo ratings yet
- Population DynamicsDocument31 pagesPopulation DynamicsIqbal MuzzamilNo ratings yet
- WK 2 PPT FORMAT Demography CHN2Document61 pagesWK 2 PPT FORMAT Demography CHN2VAL ASHLIE ACEBARNo ratings yet
- DemographyDocument30 pagesDemographyzodiackiller1960sNo ratings yet
- Social Planning PDFDocument92 pagesSocial Planning PDFShiela SorinoNo ratings yet
- Hand Out Public Health ToolsDocument19 pagesHand Out Public Health ToolsNicole Sherry M. CHEENo ratings yet
- DS 113 Module 4 Population&DvtDocument57 pagesDS 113 Module 4 Population&DvtKELVIN MAIMUNo ratings yet
- Population Study of SMKCDocument20 pagesPopulation Study of SMKCAshish DeotaleNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Demography, Health Statistics & EpidemiologyDocument4 pages1.2 Demography, Health Statistics & Epidemiologyライ0% (1)
- Unit 1 - Population 2Document19 pagesUnit 1 - Population 2l97158889No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Notes1Document1 pageMacroeconomics Notes1GODFREY SIDWAKANo ratings yet
- Demographic Studies NotesDocument1 pageDemographic Studies NotesGODFREY SIDWAKANo ratings yet
- Chap-One - Updated Lecture NoteDocument30 pagesChap-One - Updated Lecture Notedesalegn abyeNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - Human Population Dynamic - IssuesDocument8 pagesLESSON 2 - Human Population Dynamic - IssuesDalupire, Jhonryl A.No ratings yet
- Demography 171220090930Document207 pagesDemography 171220090930Shankar GanigNo ratings yet
- L10 Crux F Population and Poverty Developmental Issues 1672180027Document68 pagesL10 Crux F Population and Poverty Developmental Issues 1672180027Atul SinghNo ratings yet
- DimensionsDocument24 pagesDimensionsAltaf TapuNo ratings yet
- CHN Demography-1Document5 pagesCHN Demography-1CARL ANGEL JAOCHICONo ratings yet
- Demografi Inter 2022Document77 pagesDemografi Inter 2022ummufawwazNo ratings yet
- Community Study OverviewDocument20 pagesCommunity Study OverviewShereen Mohamed Soliman HammoudaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DemographyDocument16 pagesIntroduction To DemographyCherry Ng100% (1)
- Enquiry Questions Key Ideas and Concepts Guidance and Possible ExamplesDocument2 pagesEnquiry Questions Key Ideas and Concepts Guidance and Possible Examplesjacksosj05100% (2)
- CHN2 Module 3 Health StatiticsDocument65 pagesCHN2 Module 3 Health StatiticsJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Health Statistics and EpidemiologyDocument12 pagesHealth Statistics and EpidemiologyFrannie Alyssa MataNo ratings yet
- 02 Scope of Demography Study PoolDocument3 pages02 Scope of Demography Study PoolMuhammad AlamNo ratings yet
- Demography and Vital Statistics: MR - Naveena J H Asst. Professor Acon, AuhDocument207 pagesDemography and Vital Statistics: MR - Naveena J H Asst. Professor Acon, AuhPriyanka JangraNo ratings yet
- Sources of Data: - Demographic Data Cover: - Demographic Events IncludeDocument27 pagesSources of Data: - Demographic Data Cover: - Demographic Events Includesafraj5003No ratings yet
- 3 Seminar 3 Population Size Distribution 30may2021Document37 pages3 Seminar 3 Population Size Distribution 30may2021Nurain sayutiNo ratings yet
- Ar Jay AgdonDocument26 pagesAr Jay AgdonRjay AgdonNo ratings yet
- APHuG Unit 2 - Population and MigrationDocument108 pagesAPHuG Unit 2 - Population and MigrationSrujan MaNo ratings yet
- Social Probs Cont..Document11 pagesSocial Probs Cont..Natalie RuthNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document9 pagesGroup 1ayylmaoNo ratings yet
- Population Health & InfrastructureDocument27 pagesPopulation Health & Infrastructureaqsa iqbalNo ratings yet
- Health and DemographyDocument16 pagesHealth and DemographyNojoudNo ratings yet
- Sociology II - Session 11 & 12Document51 pagesSociology II - Session 11 & 12Arsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Philippine Demographic Trends and Patterns - Cruz&CruzDocument244 pagesPhilippine Demographic Trends and Patterns - Cruz&Cruz'Thon SysadminNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 EconomicsDocument4 pagesUnit 2 EconomicsCamille Anne GalvezNo ratings yet
- DEMOGRAPHYDocument4 pagesDEMOGRAPHYPhranxies Jean BlayaNo ratings yet
- Class 9th Geography Population Full Chapter 240124 193322Document30 pagesClass 9th Geography Population Full Chapter 240124 193322rudrapatel7729No ratings yet
- DemographyDocument3 pagesDemographymikobarakoNo ratings yet
- PAEE Reviewer FinalsDocument24 pagesPAEE Reviewer FinalsBea MercadoNo ratings yet
- Postwar Fertility Trends and Differentials in the United StatesFrom EverandPostwar Fertility Trends and Differentials in the United StatesNo ratings yet
- Club of Rome ReportDocument8 pagesClub of Rome Reportmatrixexposed100% (2)
- Demographic Status of Komodo Dragons Populations in Komodo National ParkDocument15 pagesDemographic Status of Komodo Dragons Populations in Komodo National ParkPermata Windra DeasmaraNo ratings yet
- Ganiyu Et Al. (2019) - Assessment of Water Resources Availability and Demand in Malete Watershed, NorthCentral Nigeria PDFDocument8 pagesGaniyu Et Al. (2019) - Assessment of Water Resources Availability and Demand in Malete Watershed, NorthCentral Nigeria PDFisholaoladimejiNo ratings yet
- 2022 Battisti Et Al. Aggregative Oviposition Ecol EntomolDocument10 pages2022 Battisti Et Al. Aggregative Oviposition Ecol EntomolAndrea BattistiNo ratings yet
- Urban Sociology Definition of Terms and Urban EcologyDocument31 pagesUrban Sociology Definition of Terms and Urban EcologyCJ OngNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Sample Task 1Document31 pagesAcademic Writing Sample Task 1sharonkaurNo ratings yet
- Cape Geography SyllabusDocument9 pagesCape Geography SyllabusKern Grant100% (2)
- Interpretation Nadeem SirDocument2 pagesInterpretation Nadeem SirDENZYL D'COUTHONo ratings yet
- Davao City (Philippines) - Barangays - Population Statistics, Charts and MapDocument1 pageDavao City (Philippines) - Barangays - Population Statistics, Charts and MapKristin Faye OlaloNo ratings yet
- Costanza. 1999. The Ecological, Economic, and Social Importance of The OceanDocument15 pagesCostanza. 1999. The Ecological, Economic, and Social Importance of The OceanDennis Panayotis Ostrensky SaridakisNo ratings yet
- Thesis OverpopulationDocument7 pagesThesis Overpopulationafkollnsw100% (2)
- LKDSB Pupil Accommodation ReportDocument18 pagesLKDSB Pupil Accommodation ReportThe London Free PressNo ratings yet
- DesignDocument14 pagesDesignLorena DazaNo ratings yet
- Hometown Brochure DesignDocument2 pagesHometown Brochure DesignTiffanymcliu100% (1)
- Global CountermovementDocument7 pagesGlobal CountermovementDee DyatrieNo ratings yet
- SW Portland Post - Need For UpZoning in The Multnomah Neighborhood Should Be QuestionedDocument1 pageSW Portland Post - Need For UpZoning in The Multnomah Neighborhood Should Be QuestionedLivablePDXNo ratings yet
- Non Pesticide ManagementDocument34 pagesNon Pesticide Managementapi-441599558No ratings yet
- 2008 Erismanetal NatureGeoDocument5 pages2008 Erismanetal NatureGeoKarol GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Plant Population FrequencyDocument2 pagesPlant Population FrequencyPrince Kumar100% (1)
- Malthusianism WikipediaDocument16 pagesMalthusianism WikipediavalensalNo ratings yet
- Lecture No.1 CEDDocument34 pagesLecture No.1 CEDekhtisham ul haqNo ratings yet
- Blueprint For Survival-Ecologist-1972-01Document48 pagesBlueprint For Survival-Ecologist-1972-01Oscar WindsNo ratings yet
- Has The Philippines Undergone The Demographic Transition? Why or Why Not?Document2 pagesHas The Philippines Undergone The Demographic Transition? Why or Why Not?Charres LanuevoNo ratings yet
- Berber Phonology PDFDocument15 pagesBerber Phonology PDFTiddukla Tadelsant ImedyazenNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Globalization and Diversity Geography of A Changing World 6th Edition Marie Price Lester Rowntree Martin Lewis William WyckoffDocument43 pagesTest Bank For Globalization and Diversity Geography of A Changing World 6th Edition Marie Price Lester Rowntree Martin Lewis William Wyckoffjosephestradakmbaizgpyj100% (26)
- Week 4-6 - Uloc AnswersDocument5 pagesWeek 4-6 - Uloc AnswersJohn Mark MadrazoNo ratings yet
- Town IdentificationDocument19 pagesTown IdentificationKellybert FernandezNo ratings yet