Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiration in Plants
Respiration in Plants
Uploaded by
adityaaggarwal821Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiration in Plants
Respiration in Plants
Uploaded by
adityaaggarwal821Copyright:
Available Formats
Flashcards for NEET Biology: Respiration in Plants
EMP (Embden Meyerhof
Parnas) pathway
Occurs in cytoplasm
Glycolysis Common step in both
aerobic and anaerobic
respiration
Hexose is converted to two
molecules of pyruvate
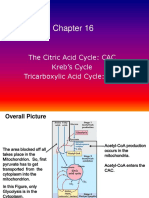
1. Glycolysis (Cytoplasm)
2. Pyruvate to acetyl CoA by
pyretic dehydrogenase
Aerobic respiration (mitochondrial matrix)
3. TCA or Krebs cycle
(mitochondrial matrix)
Pyruvic acid to ethanol
and CO2
Alcoholic
Fermentation Enzymes- pyruvic acid
decarboxylase and
alcohol dehydrogenase
Flashcards for NEET Biology: Respiration in Plants
Pyruvic acid to lactic acid
Lactic acid In muscles and some
bacteria
fermentation
Enzyme- lactate
dehydrogenase
Hans Krebs (Krebs cycle)
Tricarboxylic acid Citric acid cycle- In the first
cycle (TCA) step OAA reacts with acetyl
CoA to produce citric acid
36 or 38 ATP
Glycolysis- 6 or 8 ATP (2
Net gain of ATP per ATP and 2 NADH)
glucose in aerobic Transition reaction- 6 ATP
respiration (2 NADH)
TCA- 24 ATP (2 GTP, 6
NADH, 2 FADH2)
Flashcards for NEET Biology: Respiration in Plants
Pyruvate to acetyl CoA
Isocitrate to 𝛼-
Decarboxylation
ketoglutarate
reactions
𝛼-ketoglutarate to
succinyl CoA
Glycolysis- 1,3-
bisphosphoglyceric acid to
Substrate level PGA
PEP to Pyruvic acid
phosphorylation
(ATP production) TCA- succinyl CoA to
Succinate (GTP is
produced)
Inner mitochondrial membrane
Complex I- NADH dehydrogenase
(FMN, Fe-S)
Complex II- Succinate
Electron transport dehydrogenase (FAD, Fe-S)
system (ETS) Complex III- Cytochrome bc1
Complex IV- Cytochrome c
oxidase (cyt a, a3, two Cu)
Complex V- ATP synthase (F0, F1)
Flashcards for NEET Biology: Respiration in Plants
Cytochrome C and
Mobile electron
ubiquinone (UQ)
carrier
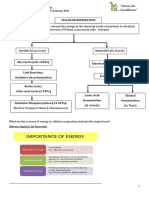
Carbohydrate- 1
Respiratory quotient Fat- 0.7
Protein- 0.9
Net gain of ATP in
2 ATP
fermentation
You might also like
- 1M. 2 - Biochemistry - Glycolysis and KrebsDocument4 pages1M. 2 - Biochemistry - Glycolysis and KrebsKate Lynne Camonayan100% (1)
- Aerobic Anaerobic RespirationDocument29 pagesAerobic Anaerobic RespirationAnonymous e0TdsoxUNo ratings yet
- SurfactantDocument26 pagesSurfactantApapond Jirasirichote100% (1)
- Cell Respiration Glycoloysis and Acetyl CoADocument30 pagesCell Respiration Glycoloysis and Acetyl CoAJ15No ratings yet
- Polymer Modified Asphalt EmulsionsDocument26 pagesPolymer Modified Asphalt EmulsionsdodifaisholNo ratings yet
- MCAT Biology Complete OutlinesDocument34 pagesMCAT Biology Complete OutlinesJacob Mikhail90% (10)
- Glycolysis & Kreb's CycleDocument33 pagesGlycolysis & Kreb's CycleMapple Hernandez BelenNo ratings yet
- PDH Complex and TCA CycleDocument20 pagesPDH Complex and TCA CycleDarrion LouisNo ratings yet
- Learners Activity Sheet in General Biology 1: "Cellular Respiration"Document2 pagesLearners Activity Sheet in General Biology 1: "Cellular Respiration"Cristine TingzonNo ratings yet
- Key Topics: To Know: To Generate Energy by Acetyl Coa OxidationDocument23 pagesKey Topics: To Know: To Generate Energy by Acetyl Coa OxidationIsaiah Emmanuel SuguitanNo ratings yet
- 11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument68 pages11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismcheckmateNo ratings yet
- Cooling Towers Design Feb12 - CHENG PDFDocument6 pagesCooling Towers Design Feb12 - CHENG PDFisosicaNo ratings yet
- 1001B B.P.S. X S.A. I Science Chapterwise 5 Printable Worksheets With Solution 2014 15Document111 pages1001B B.P.S. X S.A. I Science Chapterwise 5 Printable Worksheets With Solution 2014 15RajeevLochanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism 1Document22 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism 1Affie SaikolNo ratings yet
- 18 - Lipid MetabolismDocument26 pages18 - Lipid Metabolismcheckmate100% (1)
- IMA Master List 2021 05Document225 pagesIMA Master List 2021 05DerianSyahNo ratings yet
- AxialFans BifurcatedDocument25 pagesAxialFans Bifurcatedblindjaxx100% (1)
- Bio Reviewer 2Document2 pagesBio Reviewer 2Prince Lawrence Garcia100% (1)
- Fire Extinguisher Safety Checks PDFDocument2 pagesFire Extinguisher Safety Checks PDFvengielNo ratings yet
- Auto Reform Ad orDocument17 pagesAuto Reform Ad orAlan Flores RamirezNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument15 pagesRespiration in Plantsyahake5036No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Points To RememberDocument6 pagesChapter 14 Points To RememberSaksham YadavNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument12 pagesCellular RespirationZhu Ying TingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cellular Respiration and FermentationDocument68 pagesChapter 5 Cellular Respiration and Fermentationbm-3272No ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument19 pagesCell RespirationPauline FrascaNo ratings yet
- TCA CycleDocument47 pagesTCA CycleMita SeptianiNo ratings yet
- BIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Document39 pagesBIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Shariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument34 pagesRespiration in PlantsPukazhvanthen ParamanandhanNo ratings yet
- Microbial MetabolismDocument49 pagesMicrobial MetabolismOmelNo ratings yet
- Bio LectureDocument38 pagesBio LectureDaniel ZederNo ratings yet
- 228 Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument43 pages228 Carbohydrate MetabolismAmanullahNo ratings yet
- KH MetabolismeDocument87 pagesKH MetabolismeAlicia AngelinaNo ratings yet
- ADP, ATP and Cellular RespirationDocument16 pagesADP, ATP and Cellular RespirationHerman Henson [Northwest CTA]No ratings yet
- How Did Saccharomyces Evolve To Become A Good Brewer?Document4 pagesHow Did Saccharomyces Evolve To Become A Good Brewer?ciaoNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Aerobic Cellular RespirationDocument5 pagesGroup 5 - Aerobic Cellular Respirationditucalan.ha2003No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 19 Tricarboxylic Acid CycleDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 19 Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle楊畯凱No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument11 pagesRespirationthushyanthNo ratings yet
- Colegio de San Juan de LetranDocument9 pagesColegio de San Juan de Letranking untalanNo ratings yet
- 생화학 6ed (Chpt-16)Document48 pages생화학 6ed (Chpt-16)마서빈No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesCellular RespirationAirene JabagatNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XI Botany Ch10 RespirationDocument4 pagesHsslive XI Botany Ch10 RespirationAlfiya ShereefNo ratings yet
- 34 Nutritiongrowthmetabolism 2009Document5 pages34 Nutritiongrowthmetabolism 2009ariffdrNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 20 Class Notes Saakaar 20 Batch For IIT JAM 2Document46 pagesBiochemistry 20 Class Notes Saakaar 20 Batch For IIT JAM 2Adeeti RaiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument42 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismMurali RajagopalNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Cellular Respiration CompleteDocument31 pagesCH 7 Cellular Respiration CompleteWilly WonkaNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - GenBio1 CELL RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document3 pagesWeek 8 - GenBio1 CELL RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Mbs1 - k3 - Carbohydrate Metabolism 1. NewDocument18 pagesMbs1 - k3 - Carbohydrate Metabolism 1. NewDian Permana BurlandNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Hingher PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in Hingher PlantsTrillionare HackNo ratings yet
- Energy and RespirationDocument35 pagesEnergy and RespirationHà Nguyễn Thị ViệtNo ratings yet
- The Krebs CycleDocument10 pagesThe Krebs CycleHenry MafuaNo ratings yet
- Ho10 Tca & EtsDocument26 pagesHo10 Tca & EtstresnowahyudienNo ratings yet
- UGEB2363-1718-week 5 To 6Document70 pagesUGEB2363-1718-week 5 To 6Gladys Gladys MakNo ratings yet
- Edited & Recomposed by DR - Liniyanti D.Oswari, Msc. For Medical Students in Block 8Document40 pagesEdited & Recomposed by DR - Liniyanti D.Oswari, Msc. For Medical Students in Block 8YUFFANo ratings yet
- BiokimNut 10 Siklus Asam SitratDocument19 pagesBiokimNut 10 Siklus Asam SitratM Ziyad UlhaqNo ratings yet
- METABOLISMDocument11 pagesMETABOLISMking untalanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument19 pagesBiochemistry: Carbohydrate MetabolismALINo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesChapter 16 Cellular RespirationLisa AllisyaNo ratings yet
- Respiration and PhotorespirationDocument29 pagesRespiration and PhotorespirationThảo UyênNo ratings yet
- The Krebs Cycle - Harnessing Chemical Energy For Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesThe Krebs Cycle - Harnessing Chemical Energy For Cellular RespirationTami AbordoNo ratings yet
- ADPATPand Cellular RespirationDocument43 pagesADPATPand Cellular RespirationJessa CabusaoNo ratings yet
- Biology: Biochemistry, Genetics and Evolutionary TrendsDocument20 pagesBiology: Biochemistry, Genetics and Evolutionary TrendsRosalyn Marie SugayNo ratings yet
- Life Processes SummaryDocument20 pagesLife Processes SummaryKlara EmperadoNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument49 pagesCellular RespirationJohn Paul RoaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument9 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plantsadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Metabolism 1 BGJE 2017Document30 pagesMetabolism 1 BGJE 2017Gîrneţ AlinaNo ratings yet
- Cell RespiDocument30 pagesCell Respi11009911No ratings yet
- Metabolisme KatabolismeDocument3 pagesMetabolisme KatabolismeGiska AliyaNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument6 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasesadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisiongbuDocument7 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Divisiongbuadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesdfDocument9 pagesBio Moleculesdfadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- 1plant Growth and DevelopmentDocument8 pages1plant Growth and Developmentadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument11 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plantsadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument10 pagesStructural Organisation in Animalsadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Locomotion and MovementDocument13 pagesLocomotion and Movementadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocument12 pagesBody Fluids and Circulationadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Neural Control and CoordinationDocument16 pagesNeural Control and Coordinationadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument14 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument9 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plantsadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan SceDocument4 pagesLesson Plan ScesalinahNo ratings yet
- CLASS 11 Vacation Assignment CHEMISTRY PDFDocument12 pagesCLASS 11 Vacation Assignment CHEMISTRY PDFGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Bio Chem Prelims Hand OutsDocument18 pagesBio Chem Prelims Hand Outsnina grace joyNo ratings yet
- FT AspxDocument11 pagesFT Aspxحمزة الفنينيNo ratings yet
- Abs and Fluor of TPPH2Document11 pagesAbs and Fluor of TPPH2morikao21No ratings yet
- 201201142811122Document360 pages201201142811122MuhammadIqbalMughal0% (1)
- Secutex - Geotextile IntroductionDocument4 pagesSecutex - Geotextile IntroductionoanaariadnaNo ratings yet
- Cathodic ProtectionDocument8 pagesCathodic ProtectionHmid AljbreNo ratings yet
- Main Definitions of Pharmacology. Classifications of Drugs.Document36 pagesMain Definitions of Pharmacology. Classifications of Drugs.Mihika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry: SciencedirectDocument11 pagesFood Chemistry: Sciencedirectratri nurNo ratings yet
- Skin Mechanical Properties - ArinSDocument26 pagesSkin Mechanical Properties - ArinSJack Flow ClickNo ratings yet
- Zn-Containing Ionic Liquids For The Extractive Denitrogenation of A Model Oil - A Mechanistic ConsiderationDocument7 pagesZn-Containing Ionic Liquids For The Extractive Denitrogenation of A Model Oil - A Mechanistic ConsiderationJohnSmithNo ratings yet
- Test 3 Chem.Document2 pagesTest 3 Chem.Uday BhartiyaNo ratings yet
- Ecosurf SA-7Document2 pagesEcosurf SA-7Saepul Indra MulyanaNo ratings yet
- IsotiosianateDocument8 pagesIsotiosianateGerardine EmeraldaNo ratings yet
- Water: Shield Polyethylene Piping SystemDocument8 pagesWater: Shield Polyethylene Piping SystemRajiv R'n'bNo ratings yet
- Carbofill Dec08Document4 pagesCarbofill Dec08Cristian Andres Araya CisternasNo ratings yet
- Sika Ferrogard 901Document2 pagesSika Ferrogard 901thepilot2No ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument24 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Carissa Estrada Activity No. 9 EnzymesDocument3 pagesCarissa Estrada Activity No. 9 EnzymesCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- Dommeti Pujitha Mrs. G.MANGADEVI (M.Pharm) : Presented BY (Reg. No:19JQ1S1603)Document40 pagesDommeti Pujitha Mrs. G.MANGADEVI (M.Pharm) : Presented BY (Reg. No:19JQ1S1603)LikithaNo ratings yet
- Updated Private DTLDocument8 pagesUpdated Private DTLMayur MulyeNo ratings yet