Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DLL Els Quarter 1 Week 8
Uploaded by
alyssa.ballon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesThis daily lesson log outlines an Earth and Life Science lesson for 11th grade students about natural hazards. The objectives are for students to understand geological, hydrometeorological, and coastal hazards and be able to conduct a community survey to identify hazards. The lesson content includes hazard maps of tropical cyclones, monsoons, floods, and coastal processes. Students will learn to use hazard maps to identify hazard-prone areas in their community. They will also learn how coastal processes can cause erosion, submersion, and saltwater intrusion.
Original Description:
Original Title
DLL ELS QUARTER 1 WEEK 8 - Copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis daily lesson log outlines an Earth and Life Science lesson for 11th grade students about natural hazards. The objectives are for students to understand geological, hydrometeorological, and coastal hazards and be able to conduct a community survey to identify hazards. The lesson content includes hazard maps of tropical cyclones, monsoons, floods, and coastal processes. Students will learn to use hazard maps to identify hazard-prone areas in their community. They will also learn how coastal processes can cause erosion, submersion, and saltwater intrusion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesDLL Els Quarter 1 Week 8
Uploaded by
alyssa.ballonThis daily lesson log outlines an Earth and Life Science lesson for 11th grade students about natural hazards. The objectives are for students to understand geological, hydrometeorological, and coastal hazards and be able to conduct a community survey to identify hazards. The lesson content includes hazard maps of tropical cyclones, monsoons, floods, and coastal processes. Students will learn to use hazard maps to identify hazard-prone areas in their community. They will also learn how coastal processes can cause erosion, submersion, and saltwater intrusion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
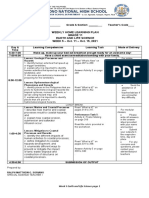
SOLOTSOLOT NATIONAL HIGH
DAILY LESSON LOG School
SCHOOL
Grade Level 11
Department of Education Teacher KENNEDY F. VAGAY Learning Area EARTH & LIFE SCIENCE
Teaching Dates and Time Week 8 Quarter First Quarter |1st Semester
Session 1: Session 2: Session 3: Session 4:
I. OBJECTIVES
The learners demonstrate understanding of…
1. the different hazards caused by geological processes (earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landslides)
A. Content Standards
2. the different hazards caused by hydrometeorological phenomena (tropical cyclones, monsoons, floods, and tornadoes or ipo-ipo)
3. the different hazards caused by coastal processes (waves, tides, sea-level changes, crustal movement,
The learners should be able to …
B. Performance Standards
Conduct a survey to assess the possible geologic/ hydrometeorological hazards that your community may experience.
1. Using hazard maps, identify areas prone to hazards brought about by tropical cyclones, monsoons, floods, or ipo-ipo.
C. Learning
2. Describe how coastal processes result in coastal erosion, submersion, and saltwater intrusion.
Competencies/Objectives
3. Cite ways to prevent or mitigate the impact of land development, waste disposal, and construction of structures on control coastal processes.
HAZARD MAPS OF TROPICAL MITIGATION ON COASTAL
II. CONTENT COASTAL PROCESSES
CYCLONE, MONSOONS & IPO-IPO PROCESSES
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
1. TG’s Pages
2. LM’s Pages
3. Textbook’s Pages
B. Other Resources Modules in Earth and Life Science
IV. PROCEDURES
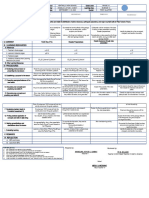
1. Ask students if they have experienced
a natural calamity before and if they
can recall any news or reports about
natural disasters that have occurred in
Today, we will discuss ways to prevent or
the Philippines recently.
A. Reviewing previous lesson or mitigate the impact of land development,
2. Introduce the new lesson by telling Briefly review the concept of erosion and its types.
presenting the new lesson waste disposal, and construction of
the students that they will be learning
structures on controlling coastal processes.
how to use hazard maps to identify
areas prone to hazards brought about
by tropical cyclones, monsoons,
floods, or ipo-ipo.
The purpose of this lesson is to help
students understand how to use hazard
By the end of the lesson, the students
maps to identify areas prone to hazards
should be able to identify ways to prevent
brought about by tropical cyclones,
B. Establishing the purpose of the The purpose of this lesson is to enable students to describe how coastal processes or mitigate the impact of land
monsoons, floods, or ipo-ipo. By the end
lesson result in coastal erosion, submersion, and saltwater intrusion. development, waste disposal, and
of this lesson, students should be able to
construction of structures on controlling
identify areas in their community that are
coastal processes.
prone to these hazards and take steps to
prepare for them.
1. Show the students different types of
1. Human activities such as land
hazard maps, including those that
development, waste disposal, and
show flood-prone areas, storm surge
construction of structures near the
areas, landslide-prone areas, and ipo-
C. Presenting examples/instances of coast can lead to erosion, submersion,
ipo prone areas. Show pictures of eroded coastlines, submerged areas, and saltwater intrusion.
the new lesson and saltwater intrusion.
2. Discuss the characteristics of each
2. These activities can also lead to a
natural hazard and how they can
reduction in beach width, loss of
affect the environment and the people
habitat, and damage to infrastructure.
living in the affected areas.
1. Discuss the different ways to
prevent or mitigate the impact of
land development on controlling
coastal processes, such as
avoiding development in
vulnerable areas, preserving
1. Explain how hazard maps are created, natural barriers, and
using data from different sources such implementing strict regulations
as satellite images, ground surveys, on development.
and historical records. 1. Introduce the concept of coastal processes, including wave action, tides, and 2. Discuss the different ways to
2. Show the students how to read and currents. prevent or mitigate the impact of
interpret hazard maps, including the 2. Explain how these processes lead to erosion, submersion, and saltwater waste disposal on controlling
D. Discussing new concepts and
different symbols and colors used to intrusion. coastal processes, such as proper
practicing new skills #1
indicate the level of risk in a certain 3. Discuss the factors that affect the severity of coastal erosion, such as the waste management, reducing
area. strength and frequency of waves, the type of beach material, and the shape of waste production, and recycling.
3. Provide examples of hazard maps and the coastline. 3. Discuss the different ways to
ask the students to identify the areas prevent or mitigate the impact of
that are prone to different types of construction of structures on
natural hazards. controlling coastal processes,
such as designing structures that
do not obstruct natural coastal
processes, implementing strict
regulations on construction, and
using sustainable building
materials.
1. Discuss the importance of disaster
preparedness and the role of hazard Discuss the importance of collaboration
1. Introduce strategies for managing coastal erosion, such as beach nourishment,
maps in helping communities prepare among different stakeholders, such as
seawalls, and vegetation.
E. Discussing new concepts and for natural disasters. local communities, government agencies,
2. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of these strategies.
practicing new skills #2 2. Show the students how to use hazard and environmental organizations, in
3. Engage students in a discussion of the impact of coastal erosion on the
maps to identify evacuation routes, implementing effective coastal
environment and human activities, such as agriculture, tourism, and fishing
safe areas, and potential hazards in management strategies.
their communities.
F. Developing Mastery To develop mastery, the teacher can divide 1. Engage students in a group activity where they will create a presentation on the
the class into groups and provide each impact of coastal erosion in a specific coastal area.
group with a different hazard map. Each 2. Provide them with resources and tools to research and collect data, such as
group can then identify the hazard-prone maps, articles, and websites.
areas in their map and present their
findings to the class. The class can then
3. Each group will present their findings and conclusions, as well as their
discuss similarities and differences
proposed strategies to address coastal erosion in the area they studied.
between the hazard-prone areas identified
by each group.
Discuss the importance of individual
actions in preventing or mitigating the
1. Engage students in a discussion of the relevance of coastal erosion to their
Discuss with the students how they can impact of land development, waste
G. Finding practical applications of daily lives.
use hazard maps to prepare for natural disposal, and construction of structures on
concepts and skills in daily living 2. Ask them to think of ways they can contribute to mitigating the impact of
disasters. controlling coastal processes, such as
coastal erosion in their communities.
proper waste management and reducing
consumption.
Summarize the main points of the lesson,
including the importance of hazard maps Ask the students to reflect on the
1. Ask students to summarize the key concepts and ideas discussed in the lesson.
H. Generalizing and abstractions in disaster preparedness, how to read and importance of coastal management and the
2. Engage them in a discussion of the broader implications of coastal erosion and
about the lesson interpret hazard maps, and how to use role of individuals and communities in
the need for sustainable management of coastal areas.
hazard maps to identify safe areas and implementing effective strategies.
evacuation routes.
1. Ask the students to create their own
hazard map of their community or
school.
Conduct a quiz or an assessment to
2. Have them identify the different
evaluate the students' understanding of the
I. Evaluating Learning hazards in the area and to locate safe Assess students' understanding of the lesson through a quiz or a written reflection.
concepts and strategies discussed in the
areas and evacuation routes.
lesson.
3. Evaluate their hazard maps based on
accuracy, completeness, and
creativity.
1. Students can research and present
case studies of successful coastal
1. For application, ask students to research and present case studies of successful management strategies implemented
coastal management strategies that address the problems caused by coastal in different parts of the world.
J. Additional Activities for
processes. 2. Students can also participate in a
Application or Remediation
2. For remediation, provide additional readings and resources for students who beach clean-up activity or a waste
need more support in understanding the topic. reduction campaign in their
community to apply the concepts
learned in the lesson.
V. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who earned 80%
in the evaluation.
B. No. of learners who require
additional activities for
remediation who scored below
80%.
C. Did the remedial lessons work?
No. of learners who have caught
up with the lesson.
D. No. of learners who continue to
require remediation.
E. Which of my teaching strategies
worked well? Why did this work?
F. What difficulties did I encounter
which my principal or supervisor
can help me solve?
G. What innovation or localized
materials did I use/discover which
I wish to share with other
teachers?
Prepared by: Checked by: Approved by:
KENNEDY F. VAGAY LEILANI R. SARMIENTO, EdD VILMA P. AVILA, EdD
Teacher II Head Teacher III School Principal II
You might also like
- DLL 3Document6 pagesDLL 3jullienneNo ratings yet
- Estimating Peak DischargeDocument9 pagesEstimating Peak DischargeioanciorneiNo ratings yet
- Computer Models Water Resources WurbsDocument228 pagesComputer Models Water Resources WurbsDiego Montaña PNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science: I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science: I. ObjectivesJT SaguinNo ratings yet
- Engineering Hydrology 4E by WilsonDocument362 pagesEngineering Hydrology 4E by Wilsonska5193% (14)
- Earth and Life DLLDocument4 pagesEarth and Life DLLlex marantalNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Hazard Severity Risk Risk Level PreventionDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment: Hazard Severity Risk Risk Level Preventionrajal11No ratings yet
- LC 37Document4 pagesLC 37JT SaguinNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: (S11/12ES-Ig-36)Document3 pagesI. Objectives: (S11/12ES-Ig-36)JT Saguin100% (1)
- Problem Based Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesProblem Based Lesson PlanLichelCaitaNo ratings yet
- DRRR 11 & 12 Module 6.1Document8 pagesDRRR 11 & 12 Module 6.1Ryan BersaminNo ratings yet
- 1979-2015 Geography Optional Questions of Last 37 Years PDFDocument101 pages1979-2015 Geography Optional Questions of Last 37 Years PDFanil kumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar in Earth and Life Science G11 Cristina V. Maquinto, LPTDocument5 pagesLesson Exemplar in Earth and Life Science G11 Cristina V. Maquinto, LPTcristina maquinto100% (1)
- W8 DLP ELS Oct 26 2022Document5 pagesW8 DLP ELS Oct 26 2022Anne RiveroNo ratings yet
- LC 31Document3 pagesLC 31JT SaguinNo ratings yet
- DLL Earth and Life Science Week 8 Ok PDocument3 pagesDLL Earth and Life Science Week 8 Ok PLily Mar Vinluan100% (2)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionCharls John Ercillo100% (1)
- DRRR 2nd Quarter - Week 1 Day 2Document3 pagesDRRR 2nd Quarter - Week 1 Day 2Kristal Pearl Rosete100% (1)
- Lesson Exemplar in Earth and Life Science G11 Cristina V. Maquinto, LPTDocument9 pagesLesson Exemplar in Earth and Life Science G11 Cristina V. Maquinto, LPTcristina maquinto100% (1)
- DLL Earth and Life Science Week 6 Ok PDocument3 pagesDLL Earth and Life Science Week 6 Ok PMark Hernand Galapate100% (1)
- Naatural Hazard DLLDocument3 pagesNaatural Hazard DLLAnnliz EstebanNo ratings yet
- How Typhoons Develop Categories of Tropical Cyclone PAR and Path of Tropical Cyclones Safety Measures Before, During, After An EarthquakeDocument3 pagesHow Typhoons Develop Categories of Tropical Cyclone PAR and Path of Tropical Cyclones Safety Measures Before, During, After An EarthquakeRichard VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- DLL Sept 9-13, 2019Document5 pagesDLL Sept 9-13, 2019Aq Nga ToNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log in Earth and Life ScienceDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Log in Earth and Life Sciencejanice alquizarNo ratings yet
- DLL Aug 3-10-ElsDocument3 pagesDLL Aug 3-10-ElsCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 11Document3 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 11Austin Capal Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Storm Water Pump Station Design GuideDocument69 pagesStorm Water Pump Station Design GuideAbraham JyothimonNo ratings yet
- Landslide Prevention: Module in Earth and Life ScienceDocument22 pagesLandslide Prevention: Module in Earth and Life ScienceKenn ProvidaNo ratings yet
- Tsunamis in the European-Mediterranean Region: From Historical Record to Risk MitigationFrom EverandTsunamis in the European-Mediterranean Region: From Historical Record to Risk MitigationNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: Grade 12 Charity DRRR 4 Quarter/2 SemesterDocument4 pagesI. Objectives: Grade 12 Charity DRRR 4 Quarter/2 SemesterMichael DeniegaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter - Week 4 Day 1 - 35Document2 pages2nd Quarter - Week 4 Day 1 - 35Kristal Pearl Rosete100% (1)
- DLL Els Quarter 1 Week 7Document3 pagesDLL Els Quarter 1 Week 7alyssa.ballonNo ratings yet
- DLL 6Document2 pagesDLL 6Rizalyn Tatotz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesKim GenandaNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Sciences Week 7 8Document11 pagesEarth Life Sciences Week 7 8ginayumo0No ratings yet
- Lebico Camille Sci 3a LP in Plate BoundariesDocument7 pagesLebico Camille Sci 3a LP in Plate BoundarieswannieNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan-3rd WeekDocument16 pagesLesson Plan-3rd WeekCharmen PabilonaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science104Document4 pagesEarth and Life Science104trexia autidaNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: NATURAL HAZARDS, MITIGATION, AND ADAPTATION: Hydro-Meteorological Phenomena and HazardsDocument20 pagesI. Objectives: NATURAL HAZARDS, MITIGATION, AND ADAPTATION: Hydro-Meteorological Phenomena and HazardsRhyz Mareschal DongonNo ratings yet
- g10 1qtr Week9 Day3 PabalinasDocument5 pagesg10 1qtr Week9 Day3 PabalinasRhudz Jai Jian MulatoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science103ADocument4 pagesEarth and Life Science103Atrexia autidaNo ratings yet
- DLL 5Document2 pagesDLL 5Rizalyn Tatotz GarciaNo ratings yet
- DLP - SHSDocument7 pagesDLP - SHSmaryjoymadredijo173No ratings yet
- Sample Format WLPDocument7 pagesSample Format WLPMosdie Mary SaracanlaoNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan in Science 10: Estefania Montemayor National High SchoolDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Plan in Science 10: Estefania Montemayor National High SchoolChristian BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Malativas National High School Fatima M. Limbaga SCIENCE - Unit 2 MODULE 2 Understanding Typhoon January 22, 2022Document2 pagesMalativas National High School Fatima M. Limbaga SCIENCE - Unit 2 MODULE 2 Understanding Typhoon January 22, 2022Fatima Ybanez Mahilum-LimbagaNo ratings yet
- EARTH SCIENCE Week 3, Day 4Document5 pagesEARTH SCIENCE Week 3, Day 4Leah Marie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesAdonis BesaNo ratings yet
- WLP@2nd Quarter Week 1uploadDocument5 pagesWLP@2nd Quarter Week 1uploadLia FernandezNo ratings yet
- WLP@2nd Quarter Week 1upDocument5 pagesWLP@2nd Quarter Week 1upLia FernandezNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan: (Formerly Bohol Institute of Technology - Jagna) Achacoso St. Poblacion, Jagna, BoholDocument14 pagesLearning Plan: (Formerly Bohol Institute of Technology - Jagna) Achacoso St. Poblacion, Jagna, BoholCync KlayNo ratings yet
- Eal 8th Week DLLDocument5 pagesEal 8th Week DLLmary annNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson Plan - 1Document3 pagesSample Lesson Plan - 1Cyrus Junio AmbatNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: School TeacherDocument2 pagesI. Objectives: School TeacherCarla NicolasNo ratings yet
- Science: Curriculum Map For Distance LearningDocument5 pagesScience: Curriculum Map For Distance LearningGil Victor MerzaNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Week 2Document6 pagesScience 6 - Week 2Pressy Leen LimaNo ratings yet
- Es1 - Unit 3-TGDocument4 pagesEs1 - Unit 3-TGClang MabiogNo ratings yet
- Week 5 ELS WHLP WorksheetDocument3 pagesWeek 5 ELS WHLP WorksheethatdogNo ratings yet
- Science 10 First Quarter LP Week 1 To 8Document25 pagesScience 10 First Quarter LP Week 1 To 8Misha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document3 pagesWeek 2JoeNo ratings yet
- Specific Learning Outcome: Grade 12 - South Korea 10:00 - 11:00 (M-TH) Grade 12 - Turks & Caicos 11:00 - 12:00 (M-TH)Document2 pagesSpecific Learning Outcome: Grade 12 - South Korea 10:00 - 11:00 (M-TH) Grade 12 - Turks & Caicos 11:00 - 12:00 (M-TH)Joshua ManalonNo ratings yet
- DLL10 - Q1 - 3 - September 11-15Document2 pagesDLL10 - Q1 - 3 - September 11-15Angelika GabayNo ratings yet
- DLL10 - Q1 - 2 - September 4-8Document2 pagesDLL10 - Q1 - 2 - September 4-8Angelika GabayNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1.1Document3 pagesLesson Plan 1.1Raphael SamsonNo ratings yet
- +++GRADES 1 To 12 Detailed Lesson Plan: Nanhs 11 Jonaida B. Laureta Earth and Life Science Mon-Tue-Wed - Thu 3 QuarterDocument3 pages+++GRADES 1 To 12 Detailed Lesson Plan: Nanhs 11 Jonaida B. Laureta Earth and Life Science Mon-Tue-Wed - Thu 3 QuarterJonaida LauretaNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Week 2Document7 pagesScience 6 - Week 2CHARMAINE MONTESNo ratings yet
- Schools Division Grade Level School Learning Area Teacher Quarter Teaching Date Time AllotmentDocument3 pagesSchools Division Grade Level School Learning Area Teacher Quarter Teaching Date Time Allotmentjozette zamoraNo ratings yet
- Hydro Meteorological HazardsDocument2 pagesHydro Meteorological HazardsGivby DollenteNo ratings yet
- Affidavit For AppealDocument14 pagesAffidavit For AppealKristen NicoleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HydrologyDocument51 pagesIntroduction To HydrologyAnns tomNo ratings yet
- Natural DisastersDocument18 pagesNatural DisastersApoorva ShenoyNo ratings yet
- HRC SAOFFG SCM1 03 20170711 FFG ApproachDocument18 pagesHRC SAOFFG SCM1 03 20170711 FFG ApproachSalam DamitNo ratings yet
- (Balkema-Proceedings and Monographs in Engineering Water and Earth Sciences) Campus, Stefano - Evaluation and Prevention of Natural Risks-Taylor Francis (2007)Document470 pages(Balkema-Proceedings and Monographs in Engineering Water and Earth Sciences) Campus, Stefano - Evaluation and Prevention of Natural Risks-Taylor Francis (2007)Miguel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Non-Residential Floodproofing - Requirements and CertificationDocument17 pagesNon-Residential Floodproofing - Requirements and CertificationgrahambrasicNo ratings yet
- OTA Et Al 2018 - Peixes Da Planície de Inundação Do Alto ParanáDocument111 pagesOTA Et Al 2018 - Peixes Da Planície de Inundação Do Alto ParanáLuiz DuarteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Integrated Watershed ManagementDocument27 pagesChapter 9 - Integrated Watershed ManagementSudharsananPRS100% (1)
- Landscape and Land Use in Postglacial Greece - (4. Holocene Climate Change in Crete An Archaeologist's View)Document10 pagesLandscape and Land Use in Postglacial Greece - (4. Holocene Climate Change in Crete An Archaeologist's View)Simos GinoudisNo ratings yet
- Feasibility OutlineDocument20 pagesFeasibility OutlineAlyyssa Julfa ArcenoNo ratings yet
- ARRB Permeable Pavements 23rdDocument14 pagesARRB Permeable Pavements 23rdPWQGroupNo ratings yet
- 2018-08-05 - Guideline For Detail Feasibility Studies of MHPs 2018Document137 pages2018-08-05 - Guideline For Detail Feasibility Studies of MHPs 2018मनिसभेटुवालNo ratings yet
- City of Miami Flooding Hot Spots Action PlanDocument16 pagesCity of Miami Flooding Hot Spots Action PlanDavid DworkNo ratings yet
- RRL To CanalsDocument5 pagesRRL To CanalsVirgilio VelascoNo ratings yet
- Flood Risk Modeling in Jakarta DissertationDocument154 pagesFlood Risk Modeling in Jakarta DissertationIfan MopNo ratings yet
- 1 The Meaning of DisasterDocument15 pages1 The Meaning of Disasterperlyn oduya25No ratings yet
- VDMP Plan (Pilot)Document11 pagesVDMP Plan (Pilot)dineshmarginalNo ratings yet
- ADVANCE COPY 20230728 DILG ADVISORY On TS KHANUN FALCONDocument3 pagesADVANCE COPY 20230728 DILG ADVISORY On TS KHANUN FALCONBarangay MabuloNo ratings yet
- Essay Writing (HSC 2018)Document11 pagesEssay Writing (HSC 2018)Prabir Kumer RoyNo ratings yet
- HurricaneDocument10 pagesHurricaneNoor AftabNo ratings yet
- Making Paper From WoodchipsDocument3 pagesMaking Paper From WoodchipsDian NovitasariNo ratings yet
- Adapting To Climate Change: A Guide For The Mining IndustryDocument10 pagesAdapting To Climate Change: A Guide For The Mining IndustryPutu Candra DarmansyahNo ratings yet