Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 1 Matter
Uploaded by
KitsuneOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 1 Matter
Uploaded by
KitsuneCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 1: Matter
• Chemistry tackles matter
Matter
- Is anything that takes space and has mass
- Mass and volume
— Human emotions and ideologies cannot be examined by science because it's not matter.
— Shadow is not matter
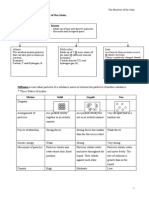
I. States of Matter
Solid Liquid Gas
a. Definite shape ✔ ✘ ✘
b. Volume ✔ ✔ ✘
c. Intermolecular arrangement Compact Far away Very far away
d. Energy →↑E
f. Density D↑←
g. compressibility ✘ ✘ ✔
• The more space in between, the more movement results to high energy.
• Cryogenic
- production and behavior of materials at very low temperatures
• LPG undergoes cryogenic processes where the gas is cooled down to extremely low temperatures to slow
down its molecular movement and make it more compact.
II. Properties of Matter
a. Intensive Property
- Independent to the amount of substance
Example:
→ Color
→ Boiling point
→ Melting point
→ Odor
b. Extensive Property
- Dependent to the amount of substance
Example:
→ Mass
→ Length
→ Volume
• Black formation around the yolk of the egg when overcooked is sulfur formation, which is poisonous.
III. Change in Matter
1. Physical change
- No formation of new substance
Changes can be :
a. Size and shape
b. Phase
— Phase change
S → L = Melting G → L = Condensation S → G = Sublimation
L → S = Solidification L → G = Vaporization G → S = Deposition
- Solidifies under low temperature → freezing
- Solidifies without the low temperature → crystalization
- Vaporize under boiling point → boiling
- Vaporize without high temperature → evaporation
2. Chemical Change
- Formation of new substance
- Cannot return to original form
Changes can be:
a. Formation of bubbles
b. Change in color, odor, and taste
c. Evolution of heat and evolution of gas
d. Precipitate
— Ionic solid products of a chemical reaction
— Solid formed
3. Nuclear change
- Change in nucleus of atom
a. Fusion reaction
General Chemistry Page 1
a. Fusion reaction
– Combining of nucleus to heavier nucleus
– (H + H → He)
Example: Star Formation
b. Fission reaction
– Splitting of nucleus to lighter nucleus
Example: Nuclear bombs and Reactors
IV. Classification of Matter
Matter
Pure Substance Mixture
- Matter composed of only one kind of matter - Physical Combination of 2 or more pure substances
Element Compound Homogenous Heterogeneous
→ Simplest form of → Chemical → 1 phase → 2 or more phase of
matter combination of two the mixtures are
→ 118 known or more elements identifiable
elements
Solution
→ More man-made Chemical
→ Consist of a
elements than combination
solute and a
naturally occurring – Is the total Colloids Suspensions
solvent → "kolla" and → Particles settle
ones change in the
property of "oeides" meaning down upon
the element glue-like standing
respectively
Metals Non- Metal Metalloids 1. Tyndall Effect
→ conductors → insulators → Can be - From John
conductors and Tyndall
insulators in - Scattering of
different light
temperatures 2. Brownian motion
or movement
- Random zig-
zag motion
of colloids
3. Adsorption
Organic Compounds Inorganic Compounds - Mixture
→ With carbon → Without carbon attaches at
Considerations: the surface
→ Oxides of carbon
• CO2
→ Carbonates
→ Cyanides
• HCN (Hydrogen Cyanide)
Acid Neutral or Salt Base or Alkaline
→ pH 1 - 6.9 → pH 7 → pH 7.1 - 14
• 2 liquid solution, the higher amount is the solvent.
○ If equal amount, higher molar mass will be the solvent
• In thermodynamics, randomness can be measured
General Chemistry Page 2
You might also like
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- HS ChemDocument6 pagesHS ChemDorothy CastilloNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1: Physical PropertiesDocument3 pagesChemistry 1: Physical Propertieskeith herreraNo ratings yet
- The States of MatterDocument20 pagesThe States of MatterAyham HassanNo ratings yet
- GenChem 1.3Document12 pagesGenChem 1.3MichelleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Matter and The Atomic Structure: 2.1 Basic Concept of MatterDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Matter and The Atomic Structure: 2.1 Basic Concept of Matterforyourhonour wongNo ratings yet
- Pdfcaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v11.PDF 7Document29 pagesPdfcaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v11.PDF 7aimaan1903No ratings yet
- Matter and Its Properties: Physical Science Week 3 HandoutsDocument2 pagesMatter and Its Properties: Physical Science Week 3 HandoutsBenj Jamieson DuagNo ratings yet
- Semester 1 Gen Chem 1Document21 pagesSemester 1 Gen Chem 1F. Andrea CieloNo ratings yet
- GenChem 1.4Document5 pagesGenChem 1.4MichelleNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL TECHNICIAN EXAM REVIEW: GENERAL CHEM - Introduction To ChemistryDocument2 pagesCHEMICAL TECHNICIAN EXAM REVIEW: GENERAL CHEM - Introduction To ChemistryPrisca Barrientos LimbagNo ratings yet
- Genchem1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenchem1 ReviewerCrystal Anne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic: Classifying MatterDocument11 pagesAtoms and The Periodic: Classifying MattercharlieNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Abbas Kamoona - Caie-Igcse-Chemistry-0620-Theory-V10Document29 pagesKami Export - Abbas Kamoona - Caie-Igcse-Chemistry-0620-Theory-V10Abbas KamoonaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument3 pagesChemistry NotesEain Chan MyaeNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry NotesDocument7 pagesGeneral Chemistry NotesIrish Angel VicencioNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerNishka CarabeoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledAbigail OconNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Reviewer: DecompositionDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry Reviewer: DecompositionMariane Gayle CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 States of Matter - 22-23 - IGDocument12 pagesCh. 1 States of Matter - 22-23 - IGvfdfdNo ratings yet
- Chemistry First SemDocument8 pagesChemistry First SemceeNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument45 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesJade AliyahNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 ScienceDocument14 pagesGrade 8 Scienceleighalbano7No ratings yet
- Gen Chem Chapt.1Document45 pagesGen Chem Chapt.1Dave Cercado BugadorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes BetaDocument47 pagesChemistry Notes BetaKartikeya BishtNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General ChemistryDocument8 pages1.1 General ChemistryAzech Yam ÜNo ratings yet
- PHARM 121: Harmaceutical Norganic Hemistry: TitleDocument5 pagesPHARM 121: Harmaceutical Norganic Hemistry: TitleTrixie Anne FelicitasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ChemistryDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Chemistryabbb25804No ratings yet
- ODB - Chem (Matter)Document2 pagesODB - Chem (Matter)aloevera1994100% (1)
- Gen - Chem 1-Week 1 and 2Document13 pagesGen - Chem 1-Week 1 and 2Mishal NoroñaNo ratings yet
- Matter 65Document13 pagesMatter 65Venkateswar PatroNo ratings yet
- 1GP - Chemistry NotesDocument12 pages1GP - Chemistry NoteseriannenabazengNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Components - 1Document7 pagesMatter and Its Components - 1TenacityNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Ternary Compounds: Physical Change vs. Chemical ChangeDocument7 pagesPhysical Science: Ternary Compounds: Physical Change vs. Chemical ChangeJoshua Jireh SevillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Structure of The Atom.: Atoms Molecules IonsDocument9 pagesChapter 2: The Structure of The Atom.: Atoms Molecules Ionschiet pingNo ratings yet
- Intervention LAS (Matter and Its Properties)Document4 pagesIntervention LAS (Matter and Its Properties)Doll MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry KineticsDocument4 pagesChemistry KineticsmayaNo ratings yet
- 1st Q 1st TopicDocument43 pages1st Q 1st TopicAlexandra TabucanonNo ratings yet
- GENCHEM ReviewerDocument6 pagesGENCHEM ReviewerChricellFNo ratings yet
- MAT T Er in Our SurroundingDocument8 pagesMAT T Er in Our SurroundingBharathNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument51 pagesChemistryj7mv5hskbvNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Structure of AtomsDocument65 pagesTopic 2 Structure of AtomsBainun DaliNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 3Document12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 3shareeandradaNo ratings yet
- Notes Chem Enely 1Document11 pagesNotes Chem Enely 1rickyNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v3Document21 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v3Adenekan Therhophic Orlanshilay100% (2)
- Science: Unit 6 States of MatterDocument3 pagesScience: Unit 6 States of MatterahmedNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry PDFDocument11 pagesSurface Chemistry PDFHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Sheet VI PDFDocument11 pagesSheet VI PDFReady To BurnNo ratings yet
- Sheet VI PDFDocument11 pagesSheet VI PDFyeshwanth padalaNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v1Document24 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v1mohammed darwazehNo ratings yet
- Edgcse TTPP Cc1-2 SB AnswersDocument5 pagesEdgcse TTPP Cc1-2 SB Answersegcarty1009No ratings yet
- 1-Properties of MatterDocument32 pages1-Properties of MatterTrevor NamalawaNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument2 pagesGen ChemLyresh Ellaine VillegasNo ratings yet
- Chem F1 U2 NoteDocument3 pagesChem F1 U2 NoteumaymaupdirahmanmohamedNo ratings yet
- 02 - Modul A + Kimia Tg4Document20 pages02 - Modul A + Kimia Tg4ONG TEIK MING -100% (1)
- Genchem ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenchem ReviewerKarylle PingolNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v8Document24 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v8Rashi GhadiyaNo ratings yet
- Solid State 1Document10 pagesSolid State 1tinachaudhari132No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer q3Document4 pagesScience Reviewer q3Jaye Zielle Angela B. CosinasNo ratings yet
- Design Process in ElectrochemistryDocument92 pagesDesign Process in ElectrochemistryWulan SariNo ratings yet
- Sheeting Structure Verification Input DataDocument26 pagesSheeting Structure Verification Input DataanonimusazNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 6Document4 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 6raju bhowalNo ratings yet
- Product ListDocument17 pagesProduct ListsafinditNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document9 pagesLab Report 2Samsung Note 9No ratings yet
- Virtual Lab ElectrochemistryDocument5 pagesVirtual Lab ElectrochemistryRenneth Rea FloresNo ratings yet
- 300 AS 3679.1 (Australia) : StandardsDocument2 pages300 AS 3679.1 (Australia) : StandardsFrank SunNo ratings yet
- PS4 - 12 30 1 30orcdmmn PDFDocument10 pagesPS4 - 12 30 1 30orcdmmn PDFMarianne Camille de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 578 Oxidation-ReductionDocument41 pagesLecture 578 Oxidation-ReductionDika Virga SaputraNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Quarter 1 Summative Test 1Document6 pagesScience 6 Quarter 1 Summative Test 1ydel pascuaNo ratings yet
- CompactDry TC EDocument4 pagesCompactDry TC EControl de CalidadNo ratings yet
- USN Demolition Material 1944!12!08Document113 pagesUSN Demolition Material 1944!12!08darkNo ratings yet
- Water Quality - Guidelines: SmileDocument12 pagesWater Quality - Guidelines: Smileade muchlasNo ratings yet
- ICE - Bharat Stage Vs Euro Emission NormsDocument27 pagesICE - Bharat Stage Vs Euro Emission Normsmaa1333No ratings yet
- Survey and Risk Assessment of Whitening ProductsDocument96 pagesSurvey and Risk Assessment of Whitening ProductsenNo ratings yet
- Operativa y ComsolDocument16 pagesOperativa y ComsolAnndre RamírezNo ratings yet
- 20231201-India Dyes & Pigments MFG ListDocument27 pages20231201-India Dyes & Pigments MFG Listbatsy4evNo ratings yet
- Ox Idative StressDocument33 pagesOx Idative StressKenNgNo ratings yet
- Iupac Naming Worksheet: Chemical Structure Iupac NameDocument2 pagesIupac Naming Worksheet: Chemical Structure Iupac NameBIANCA PILNo ratings yet
- Toxicity of GrapheneDocument27 pagesToxicity of GrapheneMrudula100% (1)
- 15 TechnicalDocument76 pages15 TechnicalMin Min AungNo ratings yet
- Liquid Solution-04 - Assignments (N)Document16 pagesLiquid Solution-04 - Assignments (N)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Solidification and Crystalline ImperfectionsDocument61 pagesSolidification and Crystalline ImperfectionsstdphdNo ratings yet
- Definition of Modelling and SimulationDocument2 pagesDefinition of Modelling and Simulationjokish100% (1)
- Soal KuantumDocument11 pagesSoal KuantumelianovalinaNo ratings yet
- 1 Year Chemistry Objective: December Tests 2018 Class: Subject: PaperDocument2 pages1 Year Chemistry Objective: December Tests 2018 Class: Subject: PaperKomal ZaffarNo ratings yet
- T4 - Booklet - Copy of EnergeticsDocument32 pagesT4 - Booklet - Copy of EnergeticsKhánh VyNo ratings yet
- Flow of Incompressible Fluids in Conduits and Thin LayersDocument3 pagesFlow of Incompressible Fluids in Conduits and Thin LayersCarlo HafallaNo ratings yet
- CA Lesson 2 AlkanesDocument31 pagesCA Lesson 2 AlkanesAlbaraaAliNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1359646219300363 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S1359646219300363 Mainswaminathan G.No ratings yet