Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen Chem
Uploaded by
Lyresh Ellaine VillegasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gen Chem
Uploaded by
Lyresh Ellaine VillegasCopyright:
Available Formats
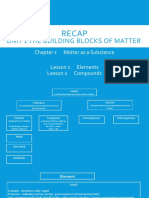
LESSON 1: MATTER & ITS PROPERTIES PURE SUBSTANCE MIXTURE
Matter - anything that has mass & volume - Fixed composition - 2 or more components
Ancient Greek Philosophers - first to speculate - Single component - Physically combined
the nature of matter ex: Oxygen, water, - Variable composition
mercury, carbon - Retains its chemical identity
> Aristotle: matter is continuous, all space filled dioxide ex: Cup of coffee, Air, bronze,
up with matter has no empty spaces. soft drink
> Democritus: Matter is made up of indivisible
particles. This paved the way in establishing that > Homogenous: cannot be seen
matter is made up particles instead of primal separately
material. > Heterogeneous: can easily be
> Anaximenes: Matter is made up of air through seen separately
rarefication/condensation (thinning/thickening)
> Heraclitus: Matter is composed of fire, the Element: pure substance composed of one type
basic material principle of an orderly universe. of atom.
> Thales: water is the primal material of matter. Compound: substances formed by 2 or more
Things are varying forms of one primary and types of elements
ultimate element ELEMENTS COMPOUNDS
> Empidocles: Materials are made up of 1 Oxygen Table salt
primal matter Iron nail Baking soda
> Leucippus & Democritus: referred matter as Copper wire Hydrogen peroxide
atom, "atomos" meaning indivisible.
GENERAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER:
Continuity of Matter: matter is not void 1. Mass: the amount of matter in an object
meaning its divisible and can be cut into pieces 2. Weight: gravitational force that acts on an
repeatedly. object. Greater force = heavier weight
3. Volume: amount of space occupied by matter
DISCONTINUITY OF MATTER = Liters (liquids) Cubic length (I3) solid
1. Matter is composed of discrete particles 4. Density: ratio between mass & volume
2. There is an empty space between particles of = kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m3) or grams
matter per cubic centimeter (g/cm3)
3. particles of matter are in constant motion
4. There are forces that act between the Physical Properties: qualities readily
particles observed/measurable w/o changing the
matter’s composition
When particles of matter are heated > Melting point
- heat energy increases, kinetic energy increases > Boiling point
too > Freezing point
> Solubility: solute can dissolve in a solvent.
Varies depending on its composition
> Metallic properties: qualities observed in
metals
- conductivity: ability of a material to allow
heat/electrical charges pass easily
- malleability: ability to be flattened
- ductility: ability to be easily drawn into wires
Physical properties of matter may be How to know what separation method to use?
categorized into these 2 based on its
dependence on the amount of matter.
Extensive Properties: Depends on the amount
of matter in substance.
= size, mass, length, shape, volume
Intensive Properties: Does not depend on the
amount of matter in the substance
= color, smell. Temperature, boiling/melting
point.
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
- characteristics that can only be seen when the
chemical identity of a material is altered.
>Biodegradability – capacity of a material to
decompose by the actions of microorganisms
> Combustion – chemical reaction between a
substance (fuel) & oxygen by heat and light to
form flame
> Combustibility – ability of a material to burn
> Flammability – ability of a combustible
material to catch flame easily.
Difference: ease & rate of how an object burns
>Reactivity: tendency of a substance to undergo
chemical reaction.
- fluorine: most reactive element
- noble gases: no to little reactivity
You might also like
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chem 1 L1 W1Document51 pagesChem 1 L1 W1Desire JoyNo ratings yet
- The Phases of Matter - Chemistry Book Grade 1 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Phases of Matter - Chemistry Book Grade 1 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1st Year MTDocument12 pagesChemistry 1st Year MTENo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1Document60 pagesModule 1 Lesson 107 JAVIER LLYOD GENELSON B.No ratings yet
- GR 10 Matter and Materials Booklet Part 1Document38 pagesGR 10 Matter and Materials Booklet Part 1tcd11ytNo ratings yet
- Handout On Matter (2018)Document9 pagesHandout On Matter (2018)scientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument8 pagesScience ReviewerIT'S JAY STEPHEN0% (1)
- MatterDocument2 pagesMatterBilledo ClarkNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument10 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesGerald CatiponNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem1-Week1Document58 pagesGen Chem1-Week1llamasballsNo ratings yet
- GENCHEM ReviewerDocument6 pagesGENCHEM ReviewerChricellFNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument40 pagesMatterMarianne B. HingpesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Inorganic ChemistryDocument5 pagesReviewer in Inorganic ChemistryPrincess Aleia SalvadorNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 LessonsDocument75 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 LessonsVon DiocenaNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument7 pagesGen ChemBrian MirandaNo ratings yet
- Genchem1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenchem1 ReviewerCrystal Anne CastilloNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument32 pagesChemistryAndrei Angelo PantigNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chem IDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Chem IStudy LionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Study of ChangeDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Study of ChangeMark Julius Felix PagudNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Unit 2 Chemistry (Matter)Document40 pagesLesson 4 Unit 2 Chemistry (Matter)Evelyn Battuac de AustriaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter Lesson 1Document39 pagesProperties of Matter Lesson 1mika3laac0sta14No ratings yet
- Sci8 Qtr3 Lesn1 MatterDocument26 pagesSci8 Qtr3 Lesn1 MatterDaniel LorioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Matter and Its PropertiesDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Matter and Its PropertiesJennelyn BaylonNo ratings yet
- Biochem LecDocument10 pagesBiochem LecRachell Joy FloresNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument112 pagesMatterjoshsiquig12No ratings yet
- Chem. Lesson 1Document31 pagesChem. Lesson 1Ashlee Talento100% (1)
- Week 2Document3 pagesWeek 2Prima LebananNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document19 pagesModule 1Romel AlojadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Matter and Its PropertiesDocument13 pagesLesson 1: Matter and Its Propertiesricky100% (1)
- Module 5 Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyDocument3 pagesModule 5 Mathematics, Science, and TechnologyMarianne Bag-aoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 ScienceDocument14 pagesGrade 8 Scienceleighalbano7No ratings yet
- Matter and Its Properties: Physical Science Week 3 HandoutsDocument2 pagesMatter and Its Properties: Physical Science Week 3 HandoutsBenj Jamieson DuagNo ratings yet
- Science 7 (Third Quarter Module) : Science 7: Module by Rodel T. Alimurong, RN - Man, LPTDocument24 pagesScience 7 (Third Quarter Module) : Science 7: Module by Rodel T. Alimurong, RN - Man, LPTFlashOn DNo ratings yet
- Matter Group 2: I. Definition of Matter and Its ExampleDocument8 pagesMatter Group 2: I. Definition of Matter and Its ExampleMichael S LeysonNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument46 pagesScience Reviewerrowannenicole.jaudianNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument12 pagesGen ChemGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Matter Unit NotesDocument7 pagesMatter Unit NotesAnonpcNo ratings yet
- Matter: Gracie Ann M. DyDocument24 pagesMatter: Gracie Ann M. DyLee Claudine BonifacioNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Matter, MeasurementsDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 1 Matter, MeasurementsRusher SigueNo ratings yet
- 3 1Document90 pages3 1Joy MercadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Gen. ChemDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Gen. Chemsunny sonejaNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument1 pageStates of Mattervimbai choweNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 3Document12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 3shareeandradaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Reviewer: DecompositionDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry Reviewer: DecompositionMariane Gayle CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry 11th NotesDocument10 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry 11th NotesRʌĸɘsʜ GɘʜɭotNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry NotesDocument7 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notesdeveravanessa01No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1Document4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1Jelou LumakinNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Reviewer: Mass - Amount of Matter Constant Weight - Force That The Gravity ExertsDocument13 pagesGeneral Chemistry Reviewer: Mass - Amount of Matter Constant Weight - Force That The Gravity ExertsMariane Gayle CaballeroNo ratings yet
- What Are Physical Properties of Matter?Document32 pagesWhat Are Physical Properties of Matter?Tomasian100% (1)
- Science LT1 IsDocument4 pagesScience LT1 IsManoli MontinolaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer MATTERDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer MATTERRACHELL SATSATINNo ratings yet
- Recap: Unit 1 The Building Blocks of MatterDocument6 pagesRecap: Unit 1 The Building Blocks of MatterAira TerradoNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument5 pagesGeneral ChemistryBon AshleeNo ratings yet
- Lecciones Sobre La MateriaDocument21 pagesLecciones Sobre La Materiaavalkvin04No ratings yet
- Matter and It - S Properties Learning Material PDFDocument12 pagesMatter and It - S Properties Learning Material PDFikennahtNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument7 pagesChemistry Reviewerback upNo ratings yet
- 3rd MASTERY - CHEM 1Document3 pages3rd MASTERY - CHEM 1Rhasher YbañezNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem NatennnDocument5 pagesGen Chem NatennnAriaane Grace DaquioagNo ratings yet
- Matter and It's Properties PDFDocument55 pagesMatter and It's Properties PDFLemuel Glenn BautistaNo ratings yet
- Jet Stream and Long Waves in A Steady Rotating-Dishpan Experiment Structure of The CirculationDocument18 pagesJet Stream and Long Waves in A Steady Rotating-Dishpan Experiment Structure of The CirculationDamien Lune BleueNo ratings yet
- Fission Track Dating PDFDocument3 pagesFission Track Dating PDFzaqiNo ratings yet
- All Is SelfDocument2 pagesAll Is SelfMichaelNo ratings yet
- Landslides and SinkholesDocument50 pagesLandslides and SinkholesRafuncell Rivera100% (2)
- 50 de Thi Thu THPT Quoc Gia 2020 Mon Tieng Anh Co Dap An Va Giai Chi Tiet 4154Document20 pages50 de Thi Thu THPT Quoc Gia 2020 Mon Tieng Anh Co Dap An Va Giai Chi Tiet 4154khanh nguyenNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument26 pagesLife ProcessesThamaraiPandiyanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Law: N.L.S I.UDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Law: N.L.S I.UShrikant BudholiaNo ratings yet
- Env Awareness ProblemsDocument2 pagesEnv Awareness ProblemsPaula FontesNo ratings yet
- E L S Chapter TestDocument7 pagesE L S Chapter TestMark John EspongaNo ratings yet
- Sustainability AutoDocument2 pagesSustainability Autorebekah reyesNo ratings yet
- The Cleaning Operations Study of Gas Wells Blowing Lines From Fluid Sand Mechanical ContaminationDocument19 pagesThe Cleaning Operations Study of Gas Wells Blowing Lines From Fluid Sand Mechanical ContaminationNazarii HedzykNo ratings yet
- Inside Our Earth Class 7 MCQs Questions With AnswersDocument5 pagesInside Our Earth Class 7 MCQs Questions With AnswersKalai Selvi MohanNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Water ResourcesDocument18 pagesCH 6 Water ResourcesVishesh RajputNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Examination Grade 9 RegularDocument6 pagesThird Quarter Examination Grade 9 RegularFelisa Andamon60% (5)
- 1st Half PhysicsDocument1 page1st Half PhysicsTHE A plus ACADMYNo ratings yet
- Automobile Ac by Utilising Waste Heat & GasesDocument18 pagesAutomobile Ac by Utilising Waste Heat & Gasesraveesh11150% (2)
- EHB en File 6.5.3 Calculation of The Reaction ForceDocument3 pagesEHB en File 6.5.3 Calculation of The Reaction ForceGuillermo CorderoNo ratings yet
- Save The Penguins Storyboard UseDocument21 pagesSave The Penguins Storyboard Useapi-306869230No ratings yet
- On Wind TurbineDocument17 pagesOn Wind TurbineAshfiya YazdaniNo ratings yet
- Case Studies PDFDocument12 pagesCase Studies PDFDhruv BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Session 07 Sewage Treatment (2021-22) PDFDocument42 pagesSession 07 Sewage Treatment (2021-22) PDFLeslie LeeNo ratings yet
- Application of GIS in Disaster ManagementDocument10 pagesApplication of GIS in Disaster ManagementPRAVIN ANNAMALAINo ratings yet
- Electrical Transmission and DistributionDocument832 pagesElectrical Transmission and DistributionkapilNo ratings yet
- Technical Standard For SolarDocument44 pagesTechnical Standard For SolarAbhinav SinhaNo ratings yet
- The Electrical Worker July 2010Document20 pagesThe Electrical Worker July 2010Kathryn R. ThompsonNo ratings yet
- The Serpentine Mineral GroupDocument3 pagesThe Serpentine Mineral GroupYudhi PrawiraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19w Groundwater 1 Darcy PowerpointDocument19 pagesLecture 19w Groundwater 1 Darcy PowerpointAmir ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Biology R01Document2 pagesGrade 7 Biology R01He NiNo ratings yet
- Sales Proposal 291KW Karachi Club Annex v1Document7 pagesSales Proposal 291KW Karachi Club Annex v1junaid ahmadNo ratings yet
- Concept Summary: Batesville High School PhysicsDocument20 pagesConcept Summary: Batesville High School PhysicssbdmanNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalFrom EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodFrom EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (20)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireFrom EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (129)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsFrom EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet