Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes Graphing Motion
Uploaded by
glencook0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThis document discusses analyzing position vs. time and velocity vs. time graphs in kinematics. It provides examples of how to determine velocity and acceleration graphs from position graphs or vice versa. The document also lists rules for properly labeling graphs, including labeling axes, titling graphs, choosing an appropriate scale, and determining if the curve is linear or nonlinear. It explains how to find the slope and equation of a line by choosing two points and using the slope formula. Finally, it provides examples of curve straightening problems involving acceleration, gravity, and force.
Original Description:
Original Title
notes_graphing_motion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses analyzing position vs. time and velocity vs. time graphs in kinematics. It provides examples of how to determine velocity and acceleration graphs from position graphs or vice versa. The document also lists rules for properly labeling graphs, including labeling axes, titling graphs, choosing an appropriate scale, and determining if the curve is linear or nonlinear. It explains how to find the slope and equation of a line by choosing two points and using the slope formula. Finally, it provides examples of curve straightening problems involving acceleration, gravity, and force.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesNotes Graphing Motion
Uploaded by
glencookThis document discusses analyzing position vs. time and velocity vs. time graphs in kinematics. It provides examples of how to determine velocity and acceleration graphs from position graphs or vice versa. The document also lists rules for properly labeling graphs, including labeling axes, titling graphs, choosing an appropriate scale, and determining if the curve is linear or nonlinear. It explains how to find the slope and equation of a line by choosing two points and using the slope formula. Finally, it provides examples of curve straightening problems involving acceleration, gravity, and force.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
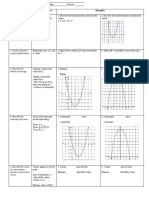
Unit 1: Kinematics in 1D
Curve Straightening Graphs
There is certain information that can be taken from position vs. time (d vs. t) and velocity vs. time (v vs. t) graphs.
For Example:
d vs. t graphs: v vs. t graphs:
Given the information from the v vs. t graph we can complete the x and a vs. t graphs
In Physics 12 you will be expected to perform more advanced graphical analysis on tests and in labs. EVERY time
you make a graph you should follow the following rules.
• Label the axis
_______________________ variable on the x-axis
_______________________ variable on the y-axis
• Give the graph an ______________________ ________________________.
• Scale each axis
Use…
Choose a scale that is…
• Plot the points and draw a __________________ _______ ____________.
• Determine if the curve is ______________ or not
Direct: Quadratic : Inverse Square Root:
Inverse Square
Finding Slope
To find the slope of a straight line: Determine the slope
• Choose… and y-intercept of the
graph shown and write
• Choose them as… the equation describing
this line.
• Use only…
Remember the equation of a line is:
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
Curve Straightening
Ex 1: A car starts at a certain Ex 2: An astronaut standing on an Ex 3: A student pushes a wooden
speed and accelerates uniformly. A asteroid measures the force of block over a rough surface with
student collects data of velocity at gravity acting on a 10 kg mass at different amounts of force and
different displacements. different distances from the center measures the acceleration each
of the asteroid. time.
You might also like
- Chapt 3-VectorsDocument25 pagesChapt 3-VectorsAbdullatif AlbattatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document31 pagesLecture 3Wolf DragonneNo ratings yet
- Shahrul Niza Mokhatar Shahruln@uthm - Edu.myDocument39 pagesShahrul Niza Mokhatar Shahruln@uthm - Edu.myazrinaishakNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Bending Moment DiagramsDocument9 pagesLab 3 - Bending Moment DiagramsTaha KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13, 14 - Chapter 6 Area Moments of InertiaDocument31 pagesLecture 13, 14 - Chapter 6 Area Moments of Inertiarobel metikuNo ratings yet
- Ch06-Deflection of Beams - LectureDocument24 pagesCh06-Deflection of Beams - LectureLeo Wong100% (1)
- Torsion Test: Department of Power Engineering and Turbomachinery Silesian University of Technology, GliwiceDocument8 pagesTorsion Test: Department of Power Engineering and Turbomachinery Silesian University of Technology, GliwiceThe White WolfNo ratings yet
- 12.ch14.transformation 22Document46 pages12.ch14.transformation 22sidsridhar89No ratings yet
- Struc 1Document17 pagesStruc 1keeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - STRESSES IN BEAMS-11-11-2020Document84 pagesChapter 2 - STRESSES IN BEAMS-11-11-2020JoaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 BDocument35 pagesLecture 2 BWolf DragonneNo ratings yet
- FinalpresentationDocument21 pagesFinalpresentationapi-617547727No ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Learning Guide For Module 10 TrigDocument7 pagesAlgebra 2 Learning Guide For Module 10 TrigSmart StudyManNo ratings yet
- L29 - Beam DeflectionsDocument13 pagesL29 - Beam DeflectionsVince CabugNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Math Menu: Drinks DessertsDocument1 pageUnit 2 Math Menu: Drinks DessertsStephanie HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - 1Document43 pagesLab Manual - 1Nabeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual MOS-2 Revised 2017 PDFDocument10 pagesLab Manual MOS-2 Revised 2017 PDFSohaib ZaibNo ratings yet
- EXP4 Bending and TorsionDocument2 pagesEXP4 Bending and Torsionaman chopraNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Deformation of Statically Determinate Beam 2 Double IntegrationDocument37 pagesUnit 6 Deformation of Statically Determinate Beam 2 Double IntegrationJojnojie DannyzNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions Topic SummaryDocument13 pagesTrigonometric Functions Topic SummaryPerson GainableNo ratings yet
- Interior Pixels Along A Scan Line Passing Through A Polygon AreaDocument32 pagesInterior Pixels Along A Scan Line Passing Through A Polygon AreaNivedita kNo ratings yet
- EMF Theory by Sangeen PanezaiDocument100 pagesEMF Theory by Sangeen PanezaiSangeen Panezai0% (1)
- Chapter 6.4-5 Modeling Shapes With Polygonal MeshesDocument40 pagesChapter 6.4-5 Modeling Shapes With Polygonal MeshesFranklinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document32 pagesLecture 6Muhammad Usama Bin TahirNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument37 pagesEngineering MechanicsManikandan SriramNo ratings yet
- Junior6 Transformations LessonDocument16 pagesJunior6 Transformations LessonaraymundomNo ratings yet
- EL215-COA Lab Manual Fall 19Document29 pagesEL215-COA Lab Manual Fall 19Ibrahim ZahidNo ratings yet
- Points and Planes in 3DDocument30 pagesPoints and Planes in 3DAbsarNo ratings yet
- L4 - 3DForcesMoments 2007 - 0810 For Me and The DLSDocument19 pagesL4 - 3DForcesMoments 2007 - 0810 For Me and The DLSabhiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials: Chapter 5: Analysis of Beams For BendingDocument44 pagesMechanics of Materials: Chapter 5: Analysis of Beams For Bendingاحمد يوسفNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Polygons - Simple Convex - Simple Concave - Non-Simple: Self-Intersecting - With HolesDocument38 pagesDifferent Types of Polygons - Simple Convex - Simple Concave - Non-Simple: Self-Intersecting - With HolesthirumalaikumaranNo ratings yet
- Unsymmetrical Bending of Unsymmetrical SectionsDocument21 pagesUnsymmetrical Bending of Unsymmetrical Sectionsaqib sohailNo ratings yet
- Nota Fizik AtolDocument62 pagesNota Fizik AtolKhairun HusnaNo ratings yet
- Maths 3 Application Powerpoint (Amended)Document27 pagesMaths 3 Application Powerpoint (Amended)lerato guguNo ratings yet
- Topic # 4 Bending Theory (SF & BM)Document17 pagesTopic # 4 Bending Theory (SF & BM)Muhammad HabibNo ratings yet
- Vectors: An Introduction To Vector QuantitiesDocument13 pagesVectors: An Introduction To Vector QuantitiesggmmnmcncnnmNo ratings yet
- MC591 Manipulator Mechanism Design RequirementsDocument32 pagesMC591 Manipulator Mechanism Design Requirementsfranklin ChikuwaNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in - Introduction To Tensors Max Planck Why Tensors A Tensors Can Be Used When MatricesDocument35 pagesFdocuments - in - Introduction To Tensors Max Planck Why Tensors A Tensors Can Be Used When Matricesmanjunath RamachandraNo ratings yet
- Emg 2303 - 5Document28 pagesEmg 2303 - 5steve ogagaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials For Technicians Chapter6Document110 pagesStrength of Materials For Technicians Chapter6MR150No ratings yet
- Tensor PseudoDocument22 pagesTensor PseudoArut KeerthiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Vectors and ScalarsDocument42 pagesEngineering Mechanics Vectors and ScalarssatwantNo ratings yet
- Idealización de Estructuras II (Sección Cerrada) .Document23 pagesIdealización de Estructuras II (Sección Cerrada) .David Felipe Vargas OrtizNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 180616192627Document55 pagesChapter3 180616192627SALEEM MALIKNo ratings yet
- Geometry Unit 3: Worksheet #5 Linear Equations Review: ST THDocument5 pagesGeometry Unit 3: Worksheet #5 Linear Equations Review: ST THmukesh_k95No ratings yet
- Núcleo de Diseño D: InámicaDocument2 pagesNúcleo de Diseño D: InámicaDaniel Felipe Rodriguez ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Unit 3b - Quadratic Functions - Study GuideDocument6 pagesUnit 3b - Quadratic Functions - Study GuidegurpreetNo ratings yet
- Review of Statics Solutions For ExamplesDocument53 pagesReview of Statics Solutions For ExamplesAnisyahira khalidNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight Line JEE EnzzDocument64 pagesMotion in A Straight Line JEE EnzzfailurewasteworthlessNo ratings yet
- 13.ch14.transformation 22Document49 pages13.ch14.transformation 22sidsridhar89No ratings yet
- Robotics Control L3Document105 pagesRobotics Control L3Lavesh GoyalNo ratings yet
- Math 4 CompetenciesDocument5 pagesMath 4 CompetenciesRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- Module 4 TOSDocument11 pagesModule 4 TOSPrince IbanezNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 CentroidDocument20 pagesUnit 3 CentroidCrazy SoldierNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 (Kinematics)Document27 pagesGrade 11 (Kinematics)-Bleh- WalkerNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 PDFsarangaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10-Shear-and-Moment-in-BeamsDocument28 pagesLesson 10-Shear-and-Moment-in-BeamsNicole SerquiñaNo ratings yet
- 1680 Maps & Strat Week 5 PRACTICAL Handout - 2023Document8 pages1680 Maps & Strat Week 5 PRACTICAL Handout - 2023Shahad AlwahaibNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Sequence and Series - DPP 2 (Of Lec 03) - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024Document2 pagesSequence and Series - DPP 2 (Of Lec 03) - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024prajitafernandesNo ratings yet
- Module 5 (Traversing and Travers Computation)Document21 pagesModule 5 (Traversing and Travers Computation)Marvie NivalNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Vacuum Tube Logic CircuitsDocument191 pagesBasic Principles of Vacuum Tube Logic Circuitswbblair3100% (5)
- Using The HP35sDocument51 pagesUsing The HP35syuhrygNo ratings yet
- Programming With NuSOAPDocument5 pagesProgramming With NuSOAPConstantin ConstantiusNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mathematics C1 Recitation: Bingquan Fang November 13th, 2020Document7 pagesAdvanced Mathematics C1 Recitation: Bingquan Fang November 13th, 2020Christina XuNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Well StimulationDocument2 pagesAcoustic Well StimulationCristian BarbuceanuNo ratings yet
- Exploring C PDFDocument494 pagesExploring C PDFprasath_676303No ratings yet
- G6 Polynomial CurvesDocument13 pagesG6 Polynomial CurvesMaxine AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Machine Drawing PPT1 Part1Document25 pagesMachine Drawing PPT1 Part1Shubham KaushikNo ratings yet
- FE1073-C1 Resultants and Equilibrium of Forces - May 2014 PDFDocument13 pagesFE1073-C1 Resultants and Equilibrium of Forces - May 2014 PDFDicky DjayadiNo ratings yet
- Technical Memorandum: Hexagonal Close Packed (Document16 pagesTechnical Memorandum: Hexagonal Close Packed (Müge YılmazNo ratings yet
- Problem Hypothesis PDFDocument18 pagesProblem Hypothesis PDFShah RukhNo ratings yet
- Estimating Discount Rates: DCF ValuationDocument60 pagesEstimating Discount Rates: DCF Valuationyadavmihir63No ratings yet
- Wet GranulationDocument40 pagesWet GranulationYolanda PerezNo ratings yet
- Problem-3 1Document4 pagesProblem-3 1Jay UmaliNo ratings yet
- Sample Format of Meeting Minutes ExampleDocument3 pagesSample Format of Meeting Minutes ExamplePaolo O. LozadaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Engineering-A Brief IntroDocument14 pagesIndustrial Engineering-A Brief IntroWilly K. Ng'etich100% (1)
- Randomised Controlled Trials (RCTS) - Sample Size. The Magic NumberDocument4 pagesRandomised Controlled Trials (RCTS) - Sample Size. The Magic NumberrazoblancoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Theory of NumbersDocument312 pagesIntroduction To The Theory of NumbersJames LanhamNo ratings yet
- PHY 113 C General Physics I 11 AM-12:15 PM TR Olin 101 Plan For Lecture 3Document29 pagesPHY 113 C General Physics I 11 AM-12:15 PM TR Olin 101 Plan For Lecture 3Jagadish BabuNo ratings yet
- EIM 116 Course Outline FinalDocument4 pagesEIM 116 Course Outline FinalTAKUDZWA TERRENCE MAREGERENo ratings yet
- JMI - 2020 (Questions With Answer) : Inps ClassesDocument7 pagesJMI - 2020 (Questions With Answer) : Inps ClassesNaresh NNo ratings yet
- Two Fair Dice, One Red and One Blue, Are Rolled. A Score Is - QuizletDocument11 pagesTwo Fair Dice, One Red and One Blue, Are Rolled. A Score Is - QuizletHemank SoniNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Accuracy and PrecisionDocument34 pagesDifference Between Accuracy and PrecisionNiveniveNo ratings yet
- Tutorial SantuBabaTricksDocument64 pagesTutorial SantuBabaTricksArvsrv100% (14)
- Lecture Note - Counting and Combinatorics1Document41 pagesLecture Note - Counting and Combinatorics1Oriola KolawoleNo ratings yet
- 2) C1 Algebra and Functions and Quadratic Functions QuestionsDocument15 pages2) C1 Algebra and Functions and Quadratic Functions QuestionsTimNo ratings yet
- Kurushetra Problem SetDocument16 pagesKurushetra Problem Setjayaprakash89No ratings yet