0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5K views40 pagesMidterm-01 Shear
This document discusses the design principles and calculations for shear strength in reinforced concrete beams. It provides the following information:
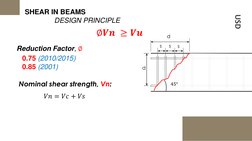
1. The nominal shear strength (Vn) is calculated as the sum of the shear strength provided by concrete (Vc) and shear reinforcement (Vs).
2. Formulas are given for calculating Vc based on the simplified and detailed methods, as well as for calculating Vs based on the amount and properties of shear reinforcement.
3. Minimum requirements for shear reinforcement area (Av,min) and spacing are specified based on the code provisions.
4. Examples demonstrate calculating factored shear (Vu), Vc, Av,min, and required stirrup spacing for given beam
Uploaded by
Xzk MallaboCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5K views40 pagesMidterm-01 Shear
This document discusses the design principles and calculations for shear strength in reinforced concrete beams. It provides the following information:
1. The nominal shear strength (Vn) is calculated as the sum of the shear strength provided by concrete (Vc) and shear reinforcement (Vs).
2. Formulas are given for calculating Vc based on the simplified and detailed methods, as well as for calculating Vs based on the amount and properties of shear reinforcement.
3. Minimum requirements for shear reinforcement area (Av,min) and spacing are specified based on the code provisions.
4. Examples demonstrate calculating factored shear (Vu), Vc, Av,min, and required stirrup spacing for given beam
Uploaded by
Xzk MallaboCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Ultimate Strength Design: Cover page highlighting the title of the presentation on ultimate strength design.
- Shear in Beams: Introduction to the principles of designing for shear in beams, including reduction factors and nominal shear strength.