Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AGK Crammer
Uploaded by
karl bohn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesThe document provides a risk assessment matrix for classifying safety risks. It categorizes risks based on their probability of occurrence and potential effects. The categories range from "no safety effect" and "minor" for very unlikely events with limited consequences, to "hazardous", "catastrophic", and "multiple fatalities" for extremely rare but high impact events. The matrix can be used to help prioritize safety issues and ensure higher risks receive more attention and resources for mitigation.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides a risk assessment matrix for classifying safety risks. It categorizes risks based on their probability of occurrence and potential effects. The categories range from "no safety effect" and "minor" for very unlikely events with limited consequences, to "hazardous", "catastrophic", and "multiple fatalities" for extremely rare but high impact events. The matrix can be used to help prioritize safety issues and ensure higher risks receive more attention and resources for mitigation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesAGK Crammer
Uploaded by
karl bohnThe document provides a risk assessment matrix for classifying safety risks. It categorizes risks based on their probability of occurrence and potential effects. The categories range from "no safety effect" and "minor" for very unlikely events with limited consequences, to "hazardous", "catastrophic", and "multiple fatalities" for extremely rare but high impact events. The matrix can be used to help prioritize safety issues and ensure higher risks receive more attention and resources for mitigation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
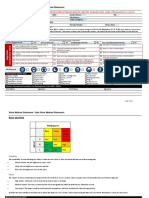
Category No safety effect Minor Major Hazardous Catastrophic
Probability N/A <10-3 <10-5 <10-7 <10-9
Effect on Aircraft No effect Slight reduction Significant Large reduction in Normally with hull
in functional reduction in functional loss
capabilities or functional capabilities or
safety margins capabilities or safety margins
safety margins
Effect on Inconvenience Physical Physical distress, Serious or fatal Multiple fatalities
occupants discomfort possibly including injury to a small
injuries number of
passengers or
cabin crew
Effect on Crew No effect Slight increase Physical Physical distress or Fatalities or
in workload discomfort or a excessive workload incapacitation
significant impairs ability to
increase in perform tasks
workload
Qualitative N/A Probable Remote Extremely Remote Extremely
Probability improbable
Equations Honeycomb – lightweight, strong but no point loads
Force = Area x Pressure Power fac = Kw / Kva Maintenance – hard time = replaced after set hours, on
Volume = Area x Length Freq = RPM X pole pairs / 60 condition when deemed to be un-serviceable
Length = Volume / Area Power = (force X distance) / Pressurisation loads, number of cycles more important
Voltage = Current (I) X time than time.
Resistance Thrust = M x (Vjet – Vflight)
Load max at wing roots, Spars and skin form torsion box
Capacitance = DP X
area/distance Frq = RPM x pole pairs/60
Airframes
Primary flight controls – Aileron (or roll control spoilers,
elevator, rudder.
Secondary – flaps, slats, speedbrakes and trimming
devices
Hydraulics
Shuttle valve – Allows 1 service be operated by 2
supplies i.e. primary and emergency
Hydraulic fuse – Shuts down flow if there is a leak
Colour Code Seals Flammable
Mineral Red DTD58 Synthetic Yes
5 rubber
Synthetic Purple 500A Butyl No
rubber,
Teflon,
propylene
Modern fuselage = semi-monocoque Fluid is irritant to skin and eyes
Stringers absorb longitudinal compressive loads Accumulators – Dampen fluctuations, limited emergency
Pressurisation loads taken on skin supply. Pressure of gas same as system
Stress – force applied, fatigue result of stress
Failure leads to 50% increase in distance
Flight controls Tyres
Reversible – Require gust locks and provide feedback Ply rating = strength of tyre
Irreversible – need artificial feedback (in parallel) Marstand tyre reduces shimmy
Trimming Low pressure up to 200PSI, high 200-315PSI
- Normally centreing devices Loss of 5% okay over 24 hours
- Zero force position of control column does not Hydroplaning increases with higher tyre pressure
change using elevator trim Pneumatics
- ZF pos changes position of control wheel with Bleed air from compressor stage. Also used to prevent
aileron trim stall at low compressor speeds
Fly-by-wide – lighter, less maintenance and safer Airconditioning
Landing gear
Ram air is used to cool the heat exchangers
Cooling is by heat exchange and making it do work in the
turbine. On the ground fans may be used to force air
through. Recirculation fans direct air around the cabin
Pressurisation systems
Air comes in from bleed air. Ram air in emergencies
Outflow valve controls cabin pressure (cabin altitude)
Max differential 9PSI. If 0.5 PSI over max safety valves
open. Cannot exceed 1,800fpm climb
Cannot take positive pressure on hull
Categories of decompression. Normal (6 to 10 seconds),
Rapid (4 to 6) Explosive (0 to 3)
>10,000ft cabin alt visual warning CABIN ALT
>13,850ft AUTO FAIL light
> 14,000ft oxygen masks drop
Ice and rain protection
Used on Aerofoils, engine intake, windscreens, static and
pitot tubes
Detection – Vibrating rod 40Khz, ice illuminates warning
light then heats to melt ice and goes out.
Pressure detectors – Ice blocks holes and pressure
triggers warning then heats to melt ice
Rotor – knife cuts ice and detects torque
Wings are normally hot bleed air, on turbo props
pneumatic boots.
Red gear lights show gear is in different position to Engine intakes hot air or oil. Propellers electric or fluid.
switch Windows heated to 35oC. Makes them malleable.
Emergency lowering – blow down, mechanical, gravity Rain repellent CFC based
and emergency hydraulics Fuel systems
Brakes LP 115v AC pumps submerged to keep cool. If off LOW
Brake wear checked with brakes on PRESSURE light
Steel brakes work best cold, carbon best hot (long Fuel heated by oil to prevent waxing and water crystals
braking vs short braking) Fuel flow measured after the Fuel Control Unit
Anti-skid inputs – Idle wheel speed, braked wheel speed Smoke and fire detection
and desired slip rate Smoke detectors are duplicated, both must register
Smoke detection required in non-manned areas and Transformers – Step up or down voltage twice the turns
toilets twice the voltage
Ion detection – Smoke absorb alpha particles V drop Rectifiers – convert AC to DC
Optical – smoke scatters light Invertor – DC to AC
Fire detection in Jet engine, APU and main gear bays Zenier diode – Breakdown with too much reverse
Resistive loops use 28v DC and detect short circuit current, used for voltage stabilisation
Systron Donner – gas pressure in pipe increases. Pipe is Generator control unit protects against under / over
heated to test. Failure if low pressure voltage, under frequency etc
Pulling fire handle closes LP/HP valves, hydraulics and In fault it trips the excitation Breaker and isolates the
electrics generator
Oxygen systems Logic circuits
Portable oxygen for medical purposes
Chemical generation for passengers, bottled for crew
Gas stored @ 1800PSI delivered at 8PSI to mask
In smoke crew oxygen select 100% <32,000ft O2 mixes
Electrics
Joule – Unit of work
Watt – unit of power
Ampere – unit of current
Ohm – unit of resistance
DC electrics
Recharging voltage 112% of Bat voltage
Primary cell = 1.5V
Lead Acid cell 2.2v dropping to 2v under load
If close to discharged voltage falls under load
NiCad – 1.3v per cell. Wider temp range, fast charge
rate, can be stored discharged and hold voltage under
load
Disadvantage thermal runaway
DC Motors Piston Engines
Series Wound – Most common starter motors. Voltage Inlet valve opens before TDC (valve lead)
increases under load Ignition occurs just before TDC
Shunt wound – low torque, fans etc. Voltage decreases Compression ratio = Volume at BDC / TDC
under load 80% efficient
Compound wound – bit of both – constant voltage Mags cutout by grounding to earth
Split field – can run both directions with 2 sets of coils Fuel
AC electricity
Uses slip rings rather than commutator
The rotor rotates the stator is fixed
Alternator is AC generator and rectifier to produce DC
3 phase Stator pairs are 120o from each other
Capacitors act as high resistance to low frequencies
Need more on AC!
AC generator and motors
Frequency wild generator no control of RPM
Constant Speed Drives (CSD) keeps generator running at
same speed to keep frequency the same
Synchronous motor – runs at speed related to frequency
and maintains speed as load varies. Inductive systems High Octane = less chance of detonation = higher
starts them compression ratio
Induction motor – loses speed as load increases but are Gas turbine engines
self starting. Used for fuel pumps etc
AC Devices
Feather position provides min drag on failed engine
Range between flight fine pitch and feather is called
alpha range. Range from FFP to reverse is Beta
The Constant Speed unit (CSU) has a simple rule:
Compressor – divergent duct
- If propeller RPM falls the CSU will cause the propeller
Diffuser after compressor before combustion chamber
blades to move to a finer pitch
reduced velocity and increases pressure
- If prop RPM rises the CSU will cause the prop blades to
Combustion chamber – continuous at constant pressure.
move to a coarser pitch
Exit is convergent duct
Turbine causes drop in temp, pressure and velocity as
the air is doing work
Exhaust – divergent duct – pressure reduces velocity
increases
Total pressure never changes as does total temperature
Axial flow more mass flow than centrifugal
Free turbine engine drive not connected to turbine
Rotor accelerates air towards stator
creating a divergent duct. Pressure
rises, velocity decreases. The rotor
moves the stator does not. Looks
like a wave if drawn.
Inner stage bleed may be required
to start the engine
Arrangement called Impulse blades
Gas Turbine handling
Dry start – no fuel no lightup
Hung start – stays at 20% high EGT low fuel flow
Hot start – Rapid rise in EGT
Wet start – Fails to light up, low RPM, no EGT some flow
Propeller Systems
You might also like
- TTEC Fencing RADocument7 pagesTTEC Fencing RAGeml TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Cummins - ISL CM2150 (2007-09)Document11 pagesCummins - ISL CM2150 (2007-09)Paquito Lozano100% (2)
- Jha RebarsDocument7 pagesJha RebarsJaycee QuinNo ratings yet
- Activity Being Assessed: Risk Assessment For Skate Park ConstructionDocument9 pagesActivity Being Assessed: Risk Assessment For Skate Park ConstructionTerence Tsam0% (1)
- Hazard RegisterDocument146 pagesHazard RegisterMirwali Mangal100% (2)
- Electrical InstallationDocument3 pagesElectrical InstallationWalid KhelfaNo ratings yet
- 11.pneumatic Pressure Testing.Document7 pages11.pneumatic Pressure Testing.Mohammad Fazal KhanNo ratings yet
- (SWMS - 04) Carpentry Work Temporary & PermanentDocument6 pages(SWMS - 04) Carpentry Work Temporary & PermanentPRATEEK SINGHNo ratings yet
- Marine Gyro-Compasses and Automatic Pilots: A Handbook for Merchant Navy OfficersFrom EverandMarine Gyro-Compasses and Automatic Pilots: A Handbook for Merchant Navy OfficersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- What Is Apqp & PpapDocument5 pagesWhat Is Apqp & PpapprafakeNo ratings yet
- n800-ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMDocument190 pagesn800-ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMLucía jandigNo ratings yet
- Boleh Merevisi Kriteria Severity, Kecuali 9 Dan 10Document3 pagesBoleh Merevisi Kriteria Severity, Kecuali 9 Dan 10Reza WijayaNo ratings yet
- Master Builders SA - Safe Work Method Statement - Timber Roof Truss Installation CraneDocument6 pagesMaster Builders SA - Safe Work Method Statement - Timber Roof Truss Installation CraneDaniel JulianNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard Analysis Site InspectionDocument12 pagesJob Hazard Analysis Site InspectionNonsoufo eze100% (1)
- Job Safety AnalysisDocument3 pagesJob Safety AnalysisAndhy DhannyNo ratings yet
- Pfmea Ranking TableDocument3 pagesPfmea Ranking TableKrunal Pandya100% (3)
- 36 Midlum PDFDocument241 pages36 Midlum PDFVanni Daghe De-sblock CerneccaNo ratings yet
- Process Safety System (Relief and Blowdown System) : Psvs and Mechanical Systems Flare Gathering Network Flares and VentsDocument36 pagesProcess Safety System (Relief and Blowdown System) : Psvs and Mechanical Systems Flare Gathering Network Flares and Ventsandi dipayadnyaNo ratings yet
- #014 Working AloftDocument4 pages#014 Working AloftTolias EgwNo ratings yet
- EHSMS09 Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) Formand Safe Work Method Statement (SWMS)Document4 pagesEHSMS09 Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) Formand Safe Work Method Statement (SWMS)yanaNo ratings yet
- STADT Lean Propulsion - Commercial - E - 22R6DDocument22 pagesSTADT Lean Propulsion - Commercial - E - 22R6DVegard SømliøyNo ratings yet
- RPN RankingsDocument5 pagesRPN RankingsThế PhongNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Permit FormDocument3 pagesConfined Space Permit FormEbenezer OpuniNo ratings yet
- HAZOP ReportDocument4 pagesHAZOP ReportHtoo Akari KhinNo ratings yet
- Confied Space WorkDocument10 pagesConfied Space WorkTiroNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioner InstallationDocument3 pagesAir Conditioner InstallationWalid KhelfaNo ratings yet
- Packing Pumps New - FO-GL-HAL-HSE-0103FDocument4 pagesPacking Pumps New - FO-GL-HAL-HSE-0103FMohamed El-SawahNo ratings yet
- FMEA AnalysisDocument30 pagesFMEA AnalysisThivanka Nirushan Withanage100% (1)
- 425-445 Watt: Cheetah Plus HC 78MDocument2 pages425-445 Watt: Cheetah Plus HC 78MshafiqNo ratings yet
- Cheetah Plus JKM425-445M-78H-D1.2-EN-F35Document2 pagesCheetah Plus JKM425-445M-78H-D1.2-EN-F35Panchal SiddharthNo ratings yet
- qf771-37 Electrical BedDocument3 pagesqf771-37 Electrical BedmohammedNo ratings yet
- FMEA RankingDocument2 pagesFMEA RankingDaviNo ratings yet
- JRA 10-005 Insttalation of New Dodo GateDocument9 pagesJRA 10-005 Insttalation of New Dodo GateAijaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Asia Pacific Weekly Incident Summary 08-Jul-2014 (Indonesia)Document15 pagesAsia Pacific Weekly Incident Summary 08-Jul-2014 (Indonesia)Anonymous cKdbnUHNo ratings yet
- Safe - Work - Method - Statement - Roof - Truss - Installation V1.0Document8 pagesSafe - Work - Method - Statement - Roof - Truss - Installation V1.0hurairamughal666No ratings yet
- Cheetah Plus JKM430 445M 78H V D3C1 EN Vico Export Solar Energy PDFDocument2 pagesCheetah Plus JKM430 445M 78H V D3C1 EN Vico Export Solar Energy PDFThắng CòiNo ratings yet
- qf771-17 Traction Unit-2Document3 pagesqf771-17 Traction Unit-2mohammedNo ratings yet
- JRA No 11-193 Hydro Testing On 28 Bar Pressure For (WP) Water Produce Lines at FEC AreaDocument8 pagesJRA No 11-193 Hydro Testing On 28 Bar Pressure For (WP) Water Produce Lines at FEC AreaAijaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- FMEA StandardDocument4 pagesFMEA Standardjawahar ramNo ratings yet
- To Start & Run Fire Water Pump, Welding Machines and Air Compressors Including Topping Up of Diesel Fuel. PlatformDocument2 pagesTo Start & Run Fire Water Pump, Welding Machines and Air Compressors Including Topping Up of Diesel Fuel. PlatformMohamad Hakim Kamal ArifinNo ratings yet
- Decision Making MM5009: Nama: Hasbi Asidik NIM: 29120131Document15 pagesDecision Making MM5009: Nama: Hasbi Asidik NIM: 29120131Hasbi AsidikNo ratings yet
- Chop Saw PDFDocument3 pagesChop Saw PDFAnonymous YrCsoYgNo ratings yet
- 793CDF Brochure 2 PagesDocument4 pages793CDF Brochure 2 PagesAdriano SantanaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Positioning Conference October 13-14, 2015: Preventative Maintenance Methods For Heavy Duty Azimuth ThrustersDocument29 pagesDynamic Positioning Conference October 13-14, 2015: Preventative Maintenance Methods For Heavy Duty Azimuth ThrustersTou BouNo ratings yet
- Field Service Jsa: Prepare Yes / No / NADocument2 pagesField Service Jsa: Prepare Yes / No / NADeba RinaNo ratings yet
- FRP Bonding CHESS - JSADocument6 pagesFRP Bonding CHESS - JSADanial AfandiNo ratings yet
- Selecting Elbows For Pneumatic Conveying SystemsDocument5 pagesSelecting Elbows For Pneumatic Conveying SystemstylerstearnsNo ratings yet
- Robinson RH22 A-Check PresentationDocument16 pagesRobinson RH22 A-Check Presentationzero610No ratings yet
- TSA-013 - Night ShiftDocument2 pagesTSA-013 - Night ShiftMusadiq HussainNo ratings yet
- Pamplate PDFDocument2 pagesPamplate PDFVidyasenNo ratings yet
- Jsa Hot Work-Fabrication of Assembly BedDocument4 pagesJsa Hot Work-Fabrication of Assembly BedAbhi SandiNo ratings yet
- Series DDocument3 pagesSeries DHugo Martinez LopezNo ratings yet
- JSA Welding & GrindingDocument2 pagesJSA Welding & GrindingtaufikNo ratings yet
- TP1 TP2 TP3 Ranking Table PFMEA English 27-06-2019 2Document5 pagesTP1 TP2 TP3 Ranking Table PFMEA English 27-06-2019 2白子健No ratings yet
- 101.1 IntroductiontoALDocument29 pages101.1 IntroductiontoALBassemNo ratings yet
- Types of FiltrationDocument9 pagesTypes of FiltrationdangtkyenNo ratings yet
- Datasheet - Jinko Solar JKM330M 60H V - 2019 - ENGDocument2 pagesDatasheet - Jinko Solar JKM330M 60H V - 2019 - ENGCorina Elizabet García MejíaNo ratings yet
- Job Safety and Environmental Analysis / Work Method Statement WorksheetDocument7 pagesJob Safety and Environmental Analysis / Work Method Statement WorksheetMohammed AbdulNo ratings yet
- #107 Manual Handling - Deck DeptDocument6 pages#107 Manual Handling - Deck DeptTolias EgwNo ratings yet
- Wiac - Info PDF Jsa For Using Jack Hammer PRDocument3 pagesWiac - Info PDF Jsa For Using Jack Hammer PRmaiman.mzakiNo ratings yet
- RA Emergency Generator Batteries RenewalDocument15 pagesRA Emergency Generator Batteries RenewalAndRuhaNo ratings yet
- Grs 642Document46 pagesGrs 642mrafi18No ratings yet
- BB5Document4 pagesBB5Foued DridiNo ratings yet
- 290BPSWING Gear Box DisassDocument2 pages290BPSWING Gear Box DisassKo ZayNo ratings yet
- Quicksilver Activ 855 Cruiser IVDocument2 pagesQuicksilver Activ 855 Cruiser IVEva AbellaNo ratings yet
- 40LM040 120 - 72125 - R72125 - (31 12 2020) - From - SimonDocument5 pages40LM040 120 - 72125 - R72125 - (31 12 2020) - From - SimonJohn Mark DolorNo ratings yet
- Corsa B s14sz FusesDocument3 pagesCorsa B s14sz FusesMshiboniumNo ratings yet
- Tire Size Chart ENG 151106Document1 pageTire Size Chart ENG 151106Johan CahyantoNo ratings yet
- Turn Signal - Stop - Hazard Lamps Ford Fiesta 1.6Document5 pagesTurn Signal - Stop - Hazard Lamps Ford Fiesta 1.6Ismael LopezNo ratings yet
- 07 Kawasaki MotorHMB-M-200109 14Document80 pages07 Kawasaki MotorHMB-M-200109 14Yanis Anis HabetNo ratings yet
- BPS 100-200Document2 pagesBPS 100-200Long CaoNo ratings yet
- DJ Alagendran Automobiles Private LimitedDocument2 pagesDJ Alagendran Automobiles Private LimitedDJ Automobiles MarketingNo ratings yet
- 204-00 Suspension SystemDocument3 pages204-00 Suspension SystemFerhan SerdarogluNo ratings yet
- Irca Part 4Document6 pagesIrca Part 4Vikash100% (2)
- 9321 18 ING 01 DOC 06 - B - B 4 - TowerMillDocument79 pages9321 18 ING 01 DOC 06 - B - B 4 - TowerMillDyajaira Huarcaya HilarionNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Design and The Physics of Traffic SafetyDocument7 pagesVehicle Design and The Physics of Traffic SafetyDzenita Hamzic HalilagicNo ratings yet
- Titanium 0607Document100 pagesTitanium 0607yongjun xiaNo ratings yet
- Initial Quick Test LogDocument7 pagesInitial Quick Test LogDedi RahmatNo ratings yet
- Training Final Drives - 7 (A)Document46 pagesTraining Final Drives - 7 (A)DraganNo ratings yet
- V110e F1-Z CarburetorDocument1 pageV110e F1-Z CarburetorGalla GarageNo ratings yet
- Mac Culloch Titan 57Document5 pagesMac Culloch Titan 57robertNo ratings yet
- Dynapac Cc7200 Spare Parts CatalogueDocument10 pagesDynapac Cc7200 Spare Parts Cataloguemartha100% (31)
- Operation and Maintenance Manual: Series 92/93 Pneumatic ActuatorDocument14 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual: Series 92/93 Pneumatic ActuatorInstrumentistas de Turno ARCO MezclasNo ratings yet
- Danfoss 103 Easy User GuideDocument2 pagesDanfoss 103 Easy User GuidePaul JonesNo ratings yet
- Furniture AnnexDocument6 pagesFurniture AnnexAlaa HusseinNo ratings yet
- Raw Water Pump SW9051-01Document3 pagesRaw Water Pump SW9051-01Aleks BaggiNo ratings yet
- Parts Bulletin: 4000 Series Long Block-Gas Engine BOM UpdateDocument3 pagesParts Bulletin: 4000 Series Long Block-Gas Engine BOM UpdatebaljeetjatNo ratings yet
- Pump Checklist - Pre-CommissioningDocument2 pagesPump Checklist - Pre-CommissioningKalpeshkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- VHD9301 Insurance Quotation (Axa)Document2 pagesVHD9301 Insurance Quotation (Axa)Carson NgNo ratings yet