Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Purposive Communication
Uploaded by
Marinel Vergara0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesReviwer for purposive communication, cultures and diverse understanding
Original Title
PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentReviwer for purposive communication, cultures and diverse understanding
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesPurposive Communication
Uploaded by
Marinel VergaraReviwer for purposive communication, cultures and diverse understanding
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION - Anything that conveys meaning
that carries a message from one
Classification of Communication
person to another.
Communication
Thayer (1968)
- a process in which people sends
- A mutual interchange of ideas by
messages or exchange ideas or
any effective means
thoughts weather through verbal
or non-verbal manner Forms of Communications
- a latin word “communicare” o Intrapersonal
means to share, unite, or to have
o Interpersonal
things in common
o Organizational
- “communis” means
o Inter-organizational
commonness
- a process dynamic, ongoing,
continuous A.)According to Mode
- 3 phases expressions, Verbal – Latin: vorbis,
interpretations, response most common, used words
CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS o a. oral
- In oral communication,
Leagans (1961)
Spoken words are used. It
includes face-to-face
- A process in which two or more conversations, speech,
people exchange ideas, facts, telephonic conversation,
feelings, or impressions in such video, radio, television, voice
over internet.
ways that each gains a common Communication is influence
understanding of the meaning by volume, speed and clarity
of speaking.
and use of messages.
o b. written
Rogers (1983) Non-Verbal – with-out
- The process by which the using words; body
message is being transmitted language, facial. Thriugh
from source to receiver. signs or symbols
expressions, hand gestures
Brooker (1949)
Visual – used images,
signs, and symbols, to
communicate; photo Personal 1-4 feet
drawing, maps, charts conversation
B.)According to Context Intimate 6-8 feet
Intrapersonal conversation
Interpersonal Social distance 4- 12 business
Organizational - Bussiness Public 12- 25 feet
environment
Extended/ Mediated - o Space and Physical;
technological tools arrangement – distance
Interculture – among between people and objects
people of diverse culture o Distance and Space –
o a.) intracultural – physical gap between
same racial / ethnic participance; between
group people and objects
o b.) Interethnic – o Proxemics and Distance –
different ethnic communication through
group space
o c.) Interracial from o Physical Arrangement and
different races Environment – physical
o d.) international – order or materials;
surroundings
representatives from
different nations Chronemics - Use of time
Mass Communication – Olfactory – smell
(public) large audiences Tactile – touching, hand shaking,
through different modes kissing
C.) According to Purpose and Style Artifacts – physical obejects as a
Formal – inform, argue, tool
persuade, and entertain Appearance – personal choice of
Informal – social interaction (to clothing, t]etc.
socialize); casual and ordinary Eye gaze – move eys to specific
locations
Non- Verbal Communications o Pupil dilation – pupil gets
Type of Description bigger
Proxemics
o Blinking close/ open eyes rate – how fast or slow a person
involuntarily speaks
o Eye movement – shift of pitch – highness or lowness of a
position in its orbit tone
volume – loudness of a voice
Structure of Organizational
communication Stress – syllable (primary and
secondary) and word (compact
Downward – superior to words) (content words and
subordinates function words)
Upward subordinate to superior
Non- Verbal Communications
Horizontal – among members of
the same level Paralinguistics – tone of voice,
loudness, inflection and pitch
Forms of Grapevine Communication
Haptics – using sense of touch
Single chain- one person to o Dimensions of touch:
another (single sequence) Instrument of touch
Probability Chain Spreads – body parts; with
randomly objects
Converts gossip/ fact to people Intensity – how soft/
Cluster chain – 2-3 people start a hard a touch is.
trens followed by others Location – The place
Speech Suprasegmentals where a person is
touched
Juncture – relationship between
Frequency – the
one sound and the sounds that
number of touches
immedie=ately precedes and
that occur
follow it
o Categories of touch:
Intonation – rise or fall of a
Social – polite;
speakers’ voice
communicate to a
o a. Non- Final – speakers
limited form of
emotion or personality interpersonal
rising – yes/ no involvement
falling – WH’s Professional –
functional;
communication to
subordinates
Friendship – warmth;
to let them know we
care for, value and
have interests in
them. This is the
most difficult o
interpret
Love – intimacy;
gestre that signal a
particularly close and
involve association
between individuals
Sexual – arousal;
equated with
intimate touch; most
sensitive form and
most communicative
Kinesics – study at hand, arm,
body. Face movements (general)
body language
Proxemics – perceive and use
space (space distancing)
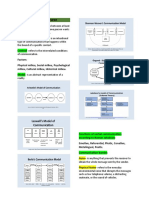
COMMUNICATION MODELS
You might also like
- Nature of CommunicationDocument3 pagesNature of CommunicationAicilaNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication FeedbackDocument3 pagesOral Communication FeedbackPortia IgnacioNo ratings yet
- PCOMDocument9 pagesPCOMXhiana ParkNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument21 pagesPurposive Communicationmarilyn wallaceNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesPurposive Communicationreen leighNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONDocument2 pagesCOMMUNICATIONwannabeeurzNo ratings yet
- PRELIMDocument3 pagesPRELIMTemptations MnlNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument26 pagesPurposive Communication Reviewerfernandeztrisha624No ratings yet
- Purcom Midterm Exam NotesDocument18 pagesPurcom Midterm Exam NotesShaina TelenNo ratings yet
- Communication ReviewerDocument3 pagesCommunication ReviewerJESTON AMBUNANNo ratings yet
- Hand Out For Midterm Exam in Oral CommDocument4 pagesHand Out For Midterm Exam in Oral CommRoland John MarzanNo ratings yet
- Oral Comms NotesDocument22 pagesOral Comms NotesJerico G. DespeNo ratings yet
- PRELIMDocument3 pagesPRELIMTemptations MnlNo ratings yet
- Purcom ReviewerDocument15 pagesPurcom ReviewerJhae Zharie Delasan PanosoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer of Purposive Com. (PRELIM)Document7 pagesReviewer of Purposive Com. (PRELIM)fabarracoso24No ratings yet
- T N E C Communication: HE Ature AND Lements OF OmmunicationDocument21 pagesT N E C Communication: HE Ature AND Lements OF OmmunicationMakai CunananNo ratings yet
- Oral ComDocument5 pagesOral ComVenise RevillaNo ratings yet
- Stem 11 - Oral CommunicationDocument5 pagesStem 11 - Oral CommunicationLance CastroNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument3 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerDaennise Louiseanna SebastianNo ratings yet
- Behavior and CommunicationDocument18 pagesBehavior and Communicationabinashheishnam72751No ratings yet
- Purposive Communcation ReviewerDocument7 pagesPurposive Communcation ReviewerGirlie VillamerNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument6 pagesPurposive CommunicationLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Kinesics Derived From The Greek Term "Kinesis"Document5 pagesKinesics Derived From The Greek Term "Kinesis"Mics RamosNo ratings yet
- Oral Comms Reviewer (3RD Quarter - Second Semester)Document2 pagesOral Comms Reviewer (3RD Quarter - Second Semester)Kaye LumodNo ratings yet
- Oral Com ReviewerDocument5 pagesOral Com ReviewerEricka Magadia100% (1)
- Reviewer CommunicationDocument2 pagesReviewer CommunicationJaimNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication PrelimDocument2 pagesOral Communication PrelimAngelika ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationsDocument2 pagesPurposive Communicationsviannametharam30No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document5 pagesUnit 1100497318No ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Lesson 1 - Communication, Importance and ProcessDocument5 pagesChapter 1. Lesson 1 - Communication, Importance and ProcessHazel HediaNo ratings yet
- Ge-Pc Midterm NotesDocument7 pagesGe-Pc Midterm NotesJamaica JaneNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 06 Aug 2021Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 06 Aug 2021John BahadarNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument4 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerMarmoleño SamanthaNo ratings yet
- Communication: Verbal and Non VerbalDocument23 pagesCommunication: Verbal and Non VerbalMonique MosesNo ratings yet
- EL 109 Module 1Document6 pagesEL 109 Module 1laylavaldez18No ratings yet
- 04 27 2021 Notes On Communication Process Universal Components Noise Context CluesDocument3 pages04 27 2021 Notes On Communication Process Universal Components Noise Context Cluesgwen calluengNo ratings yet
- Basic Purposive CommunicationDocument38 pagesBasic Purposive CommunicationDimple EstacioNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer For PCDocument17 pagesMidterm Reviewer For PCMark Ace SibiNo ratings yet
- Language Its NatureDocument22 pagesLanguage Its NatureKwenzie FortalezaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PlateaDocument31 pagesUnit 1 PlatealuismianchuelaNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesPurposive CommunicationPearl NoconNo ratings yet
- Communication Processes, Principles and Ethics. (FIRST SEMESTER EXAMDocument4 pagesCommunication Processes, Principles and Ethics. (FIRST SEMESTER EXAMyaoi yuriNo ratings yet
- Communication SkillsDocument15 pagesCommunication SkillsSandra VNo ratings yet
- Communication The Value of CommunicationDocument4 pagesCommunication The Value of CommunicationJared PaulateNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument10 pagesCommunicationJade BalatonNo ratings yet
- Communication Processes Principles and EthicsDocument41 pagesCommunication Processes Principles and EthicsJohn Flores100% (1)
- Social Relation, Concept of Time, Concept of Space, GesturesDocument1 pageSocial Relation, Concept of Time, Concept of Space, GesturesVincent EmilioNo ratings yet
- Jerilyn Rafols Activity 2Document5 pagesJerilyn Rafols Activity 2Danica RafolsNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument7 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerElvira MirajulNo ratings yet
- Speaker Speech Audience: Which Channel To, Whom and With WhatDocument2 pagesSpeaker Speech Audience: Which Channel To, Whom and With WhatLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- GEC 5 Chapter 1 Lesson 1Document12 pagesGEC 5 Chapter 1 Lesson 1Matet Recabo MataquelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document1 pageLecture 1shirleymcoronaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication NotesDocument5 pagesPurposive Communication NotesMary Hyazinth MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Mock Examination Reviewer PURCOMDocument32 pagesMock Examination Reviewer PURCOMCAJES NOLINo ratings yet
- Munication in The Digital AgeDocument37 pagesMunication in The Digital AgeRechiel A. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PURC111Document10 pagesReviewer PURC111priya garciaNo ratings yet
- PCM ReviewerDocument19 pagesPCM ReviewerAlexa Mae Villasis MajeranoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Language & CommunicationDocument23 pagesModule 1 Language & CommunicationDarwin Charles IgnacioNo ratings yet
- J. Paul LeaganDocument15 pagesJ. Paul LeaganAries C. GavinoNo ratings yet
- Buset FinanceDocument6 pagesBuset FinanceMarinel VergaraNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Reviewer All LessonsDocument7 pagesPhilosophy Reviewer All LessonsMarinel VergaraNo ratings yet
- Review of Financial Statement PreparationDocument5 pagesReview of Financial Statement PreparationMarinel VergaraNo ratings yet
- Science Technology and SocietyDocument5 pagesScience Technology and SocietyMarinel VergaraNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument12 pagesArt AppreciationMarinel VergaraNo ratings yet
- SMP - The Principles of Writing and Writing ProcessDocument1 pageSMP - The Principles of Writing and Writing ProcessMarinel VergaraNo ratings yet
- UTS 101 Reviewer FinalsDocument9 pagesUTS 101 Reviewer FinalsMarinel VergaraNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics and Social ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesBusiness Ethics and Social ResponsibilitiesMarinel VergaraNo ratings yet
- Ethics: Gilbert A. ApasDocument9 pagesEthics: Gilbert A. ApasHiedelynLlanoNo ratings yet
- How To Train A Dog at HomeDocument4 pagesHow To Train A Dog at HomepriyAnshu jakhwalNo ratings yet
- What Is Character FormationDocument12 pagesWhat Is Character FormationRey BongcasNo ratings yet
- Edup 3143 Task 2 - BrochureDocument7 pagesEdup 3143 Task 2 - BrochureTESL3062221 Siti Nur Elyanie Binti AyobNo ratings yet
- Elements of Positive CultureDocument3 pagesElements of Positive CultureDaniMNo ratings yet
- Toxic RelationshipDocument1 pageToxic RelationshipwidyasNo ratings yet
- Self Motivation Tips For SuccessDocument2 pagesSelf Motivation Tips For SuccessGary RolleNo ratings yet
- EDMA 401 Management AppraisalDocument25 pagesEDMA 401 Management AppraisalMary Joy CorpuzNo ratings yet
- 01 Session 05 Anxiety and FearDocument62 pages01 Session 05 Anxiety and FearMalakatete Mwaipojele-fNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For The Psychology of Prejudice and Discrimination 2nd EditionDocument14 pagesSolution Manual For The Psychology of Prejudice and Discrimination 2nd EditionChristopherHughesknmo100% (36)
- A Study of Theoretical Concepts of Job SatisfactionDocument6 pagesA Study of Theoretical Concepts of Job SatisfactionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 1 Understanding ConflictDocument68 pages1 Understanding ConflictSylvia Ufuoma EjenakeNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Topic 7-9Document7 pagesPersonal Development Topic 7-9selwyn duroNo ratings yet
- Attitudes and Practices Related To Sexuality and Sexual BehaviorDocument35 pagesAttitudes and Practices Related To Sexuality and Sexual BehaviorGalvin LalusinNo ratings yet
- Acctivity Design - Action ResearchDocument11 pagesAcctivity Design - Action ResearchElaine ElentorioNo ratings yet
- Types of Communication StrategyDocument3 pagesTypes of Communication StrategyJoshua Lander Soquita CadayonaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledAiven BarroaNo ratings yet
- Annie Wei AttachmentDocument19 pagesAnnie Wei AttachmentAnnie Wei0% (1)
- Edited English 101 Teacher's Guide Week 1-2Document15 pagesEdited English 101 Teacher's Guide Week 1-2Judy Ann NeriNo ratings yet
- 08 Chapter1Document20 pages08 Chapter1bijesh babuNo ratings yet
- Giving and Receiving Positive FeedbackDocument5 pagesGiving and Receiving Positive Feedbacksmansapadangp5No ratings yet
- QUIZ: Graded: Q.1. Explain Customer Perceived Value (CPV) - Q2.How Is Net Promoter Score' Calculated?Document39 pagesQUIZ: Graded: Q.1. Explain Customer Perceived Value (CPV) - Q2.How Is Net Promoter Score' Calculated?Hiba KhanNo ratings yet
- 5224 16989 1 PBDocument13 pages5224 16989 1 PBAdia RizkiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document8 pagesUnit 2PAING PARAMINo ratings yet
- Leadership Experience 6th Edition Daft Solutions ManualDocument38 pagesLeadership Experience 6th Edition Daft Solutions Manualakaterovelio6100% (12)
- ABCs of A Positive CultureDocument1 pageABCs of A Positive CultureJulia HeinemannNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 6Document14 pagesActivity 5 6camilo reyesNo ratings yet
- Free SalvatoDocument6 pagesFree SalvatoNebil MohammedNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 9 - Quarter 4 (5E)Document15 pagesMAPEH 9 - Quarter 4 (5E)Elaissa MaglanqueNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Chapter 5 Annotated SampleDocument20 pagesDissertation Chapter 5 Annotated SamplelavetterwilliamsNo ratings yet