Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TRG P2 STPM 2023 (Skema)
Uploaded by
DylanEngOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TRG P2 STPM 2023 (Skema)
Uploaded by
DylanEngCopyright:
Available Formats
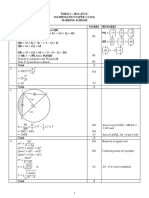
954/2/2019 CONFIDENTIAL*
JABATAN PENDIDIKAN NEGERI TERENGGANU
STPM 2023
PEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN
SEMESTER 2
MATHEMATICS T
954/2
SKEMA
DIBIAYAI OLEH KERAJAAN NEGERI TERENGGANU
Tidak dibenarkan menyunting atau mencetak mana-mana bahagian dalam modul ini
tanpa kebenaran Pengarah Pendidikan Negeri Terengganu
© Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Terengganu Page 1
STPM 954/2
954/2/2019 CONFIDENTIAL*
954/2 STPM
SCHEME MATHEMATICS T S2 2019
Total
No Working/Answer Partial marks
marks
1 1 1
(a) Evaluate lim − 1. [3]
h →0 h 1+ h
9−𝑥 2
,𝑥 ≠3
(b) Function f is defined by 𝑓(𝑥) = {|3−𝑥| 6
6, 𝑥=3
[3]
Determine whether f is continuous at x = 3.
1a
1 1 1 1 − √1 + ℎ 1 + √1 + ℎ
lim [ − 1] = lim [ ][ ] M1
ℎ→0 ℎ √1 + ℎ ℎ→0 ℎ √1 + ℎ 1 + √1 + ℎ
1 1 − (1 + ℎ) [3]
= lim [ ] M1
ℎ→0 ℎ √1 + ℎ(1 + √1 + ℎ)
1
=− A1
2
1b (3+𝑥)(3−𝑥)
lim 𝑓(𝑥) = lim− (3−𝑥)
= lim−(3 + 𝑥) = 6 M1
𝑥→3− 𝑥→3 𝑥→3
(3 + 𝑥)(3 − 𝑥)
lim+ 𝑓(𝑥) = lim+ = lim+ −(𝑥 + 3) = −6 M1
𝑥→3 𝑥→3 −(3 − 𝑥) 𝑥→3 [3]
lim 𝑓(𝑥) ≠ lim+ 𝑓(𝑥) ⇒ since limit is not exist and not equal
𝑥→3− 𝑥→3 A1
f(3) = 6, then f is not continuous at x = 3.
Total 6
© Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Terengganu Page 2
STPM 954/2
954/2/2019 CONFIDENTIAL*
Total
No Working/Answer Partial marks
marks
2 The curve whose parametric equation is given by
𝒙 = 𝟑 + 𝟓 𝒄𝒐𝒔 𝒕 , 𝒚 = 𝟒 − 𝟓 𝒔𝒊𝒏 𝒕 [6] [6]
Find the equation of the normal to the curve at the origin .
𝑑𝑥
𝒙 = 𝟑 + 𝟓 𝒄𝒐𝒔 𝒕 ; = −5 sin 𝑡
𝑑𝑡 B1
𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑦
𝑑𝑦 (either 𝑜𝑟 )
𝑑𝑡 𝑑𝑡
𝒚 = 𝟒 − 𝟓 𝒔𝒊𝒏 𝒕 ; = −5 cos 𝑡
𝑑𝑡
𝑑𝑦 −5 cos 𝑡
= = cot 𝑡 A1
𝑑𝑥 −5 sin 𝑡
At the origin , 𝑥 = 0 , 𝑦 = 0
3 4 M1 6
cos 𝑡 = − 5 , sin 𝑡 = 5
(either cos 𝑡 𝑜𝑟 sin 𝑡)
𝑑𝑦 −5 cos 𝑡 3
𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒𝑛𝑡, 𝑑𝑥 = = cot 𝑡 = − 4 A1
−5 sin 𝑡
4
Gradient of nomal = B1
3
Equation of nomal to the curve at point (0,0),
4
𝑦−0= (𝑥 − 0)
3
4
𝑦= x A1
3
TOTAL 6
© Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Terengganu Page 3
STPM 954/2
954/2/2019 CONFIDENTIAL*
Total
No Working/Answer Partial marks
marks
3 By using the substitution 𝑎𝑥 = 2 sin 𝜃, , find the value of a if
2 [6] 6
𝜋
∫0𝑎 √4 − (𝑎𝑥)2 d𝑥 = 2
ax = 2 sin
2
𝑥= 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃
𝑎
2
𝑑𝑥 = 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃𝑑𝜃 B1
𝑎
2
𝑎 𝜋
∫ √4 − (𝑎𝑥)2 𝑑𝑥 =
0 2
𝜋
2 2 𝜋 M1 (Subs dx and ax
∫ √4 − 4𝑠𝑖𝑛2 𝜃 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃𝑑𝜃 =
0 𝑎 2 correctly)
B1 (Correct limit)
𝜋
2 2 𝜋
∫ 2𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃𝑑𝜃 = 6
0 𝑎 2
𝜋
2 2 𝜋
∫ (𝑐𝑜𝑠2𝜃 + 1) 𝑑𝜃 =
0 𝑎 2
𝜋
2 𝑠𝑖𝑛2𝜃 2 𝜋 M1
[ + 𝜃] =
𝑎 2 0 2 (Use double angle)
2 𝜋 𝜋
[ − 0] = A1
𝑎 2 2
2
=1
𝑎
𝑎=2 A1
TOTAL 6
© Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Terengganu Page 4
STPM 954/2
954/2/2019 CONFIDENTIAL*
Total
No Working/Answer Partial marks
marks
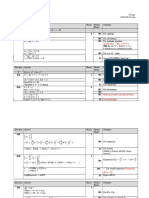
4 1 1
Using the substitution 𝑦 = + , show that the differential
𝑥 𝑧
𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑧 4𝑧
equation 𝑥 2 𝑑𝑥 = 1 − 2𝑥 𝑦 2 2
can be reduced to 𝑑𝑥
= 𝑥
+2 . [3]
9
Hence, find the general solution of the differential equation,
𝑑𝑦 [6]
𝑥 2 𝑑𝑥 = 1 − 2𝑥 2 𝑦 2
1 1 𝑑𝑦 1 1 𝑑𝑧 B1
𝑦=𝑥+𝑧 => 𝑑𝑥
= − 𝑥 2 − 𝑧2 𝑑𝑥
𝑑𝑦
𝑥 2 𝑑𝑥 = 1 − 2𝑥 2 𝑦 2
1 1 𝑑𝑧 1 1 2
M1
𝑥 2 (− 𝑥 2 − 𝑧2 𝑑𝑥) = 1 − 2𝑥 2 (𝑥 + 𝑧)
3
𝑑𝑦
(sub. ‘his’ 𝑑𝑥 to eliminate all 𝑦)
𝑥 2 𝑑𝑧 1 2 1
−1 − 𝑧2 𝑑𝑥 = 1 − 2𝑥 2 (𝑥 2 + 𝑥𝑧 + 𝑧2 )
𝑥 2 𝑑𝑧 4𝑥 2𝑥 2 𝑑𝑧 4𝑧 A1
− 𝑧2 𝑑𝑥 = − 𝑧
− 𝑧2
, 𝑑𝑥
= 𝑥
+2 (shown)
𝑑𝑧 4𝑧
𝑑𝑥
− 𝑥
=2
4
1
Integrating factor = 𝑒 − ∫𝑥𝑑𝑥 = M1
𝑥4
1 𝑑𝑧 4𝑧 2
. − =
𝑥 4 𝑑𝑥 𝑥5 𝑥4
𝑑 𝑧 2
( )
𝑑𝑥 𝑥 4
= 𝑥4 A1
(transform into integrable form)
𝑧 2 M1
∴ 𝑥4
= ∫ 𝑥 4 𝑑𝑥
2 M1
= − 3𝑥 3 + 𝑐 6
2
𝑧 = − 𝑥 + 𝑐𝑥 4
3
𝑥 2
= − 𝑥 + 𝑐𝑥 4
𝑥𝑦 − 1 3
3𝑐𝑥 4 −2𝑥
= 3
M1
3 (attempt to write 𝑦 in
𝑥𝑦 − 1 = 3 terms of 𝑥)
3𝑐𝑥 − 2
3
𝑥𝑦 = +1
3𝑐𝑥 3 − 2
1 3
𝑦= (1 + ) A1
𝑥 3𝑐𝑥 3 − 2
TOTAL 9
© Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Terengganu Page 5
STPM 954/2
954/2/2019 CONFIDENTIAL*
Total
No Working/Answer Partial marks
marks
5 𝟐
Given that 𝒚 = 𝟏+𝟒𝒙𝟐 .
𝒅𝒚
a) Show that 𝒅𝒙
= −𝟒𝒙𝒚𝟐 [2]
b) Use Maclaurin theorem, find the expansion of y up 10
to the terms in x3. [5]
Hence, find the Maclaurin series for tan– 1 2x. [3]
5a 2
𝑦 = 1+4𝑥2 = 2(1 + 4𝑥 2 )−1
𝑑𝑦 M1
𝑑𝑥
= −2(1 + 4 𝑥 2 )−2 [8𝑥]
Correct composite diff.
[2]
𝑑𝑦 −16𝑥 2 2
𝑑𝑥
= (1+4 𝑥 2 )2
= −4𝑥 (1+4𝑥2 )
𝑑𝑦 A1
∴ 𝑑𝑥
= −4𝑥𝑦 2
Check approach.
5b 𝑑2 𝑦 𝑑𝑦
M1
𝑑𝑥 2
= −4𝑥 [2𝑦 𝑑𝑥 ] − 4𝑦 2 𝑑2 𝑦
Find 𝑑𝑥 2
; must have the
= −8𝑥𝑦(−4𝑥𝑦 2 ) − 4𝑦 2 𝑑𝑦
= 32𝑥 2 𝑦 3 − 4𝑦 2 term −4𝑥 [2𝑦 𝑑𝑥 ]
M1
𝑑3 𝑦 𝑑𝑦 𝑑𝑦 𝑑3 𝑦
𝑑𝑥 3
= 32𝑥 (3𝑦 2 𝑑𝑥 ) + 32𝑦 3 (2𝑥) − (8𝑦 𝑑𝑥 )
2
Find ;
must have at
𝑑𝑥 3
2 2 (−4𝑥𝑦 2 ) 3 (2𝑥) 2
= 96𝑥 𝑦 + 32𝑦 − 8𝑦(−4𝑥𝑦 ) least 1 correct term in ‘his’
= −384𝑥 3 𝑦 4 + 96𝑥𝑦 3 product rule. [5]
Note: If 1st M0, then all zeros.
When x = 0, A1
𝑑𝑦 𝑑2𝑦 𝑑3 𝑦
y=2, = 0, = −16, =0 All correct
𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥 2 𝑑𝑥 3
M1
(−16)
𝑦 = 2+0+ 𝑥2 + 0 + … Sub. ‘his’ 4 coef. into
2!
Maclaurin expansion.
𝑦 = 2 − 8𝑥 2 + … A1
𝑑 2
tan−1 2𝑥 =
𝑑𝑥 1+4𝑥 2
2
tan−1 2𝑥 = ∫ 1+4𝑥 2 𝑑𝑥
tan−1 2𝑥 = ∫(2 − 8𝑥 2 + … ) 𝑑𝑥 [3]
M1
8𝑥 3
= 2𝑥 − +⋯+ 𝑐 Use integration process to
3
obtain 𝑡𝑎𝑛−1 2𝑥 with c
© Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Terengganu Page 6
STPM 954/2
954/2/2019 CONFIDENTIAL*
M1
When x = 0, 𝑐 = 0 Sub. x = 0 to find c.
8𝑥 3
𝑡𝑎𝑛−1 2𝑥 ≈ 2𝑥 − 3
+⋯ A1
Note : If without +… or ≈, then NWW-1
ALTERNATIVE 5b:
𝑑3 𝑦 𝑑𝑦 𝑑2 𝑦 𝑑𝑦 2 𝑑𝑦 M1
𝑑𝑥 3
= −8𝑦 𝑑𝑥 + (−8𝑥) [𝑦 𝑑𝑥 2 + (𝑑𝑥 ) ] − (−8𝑦 𝑑𝑥 ) 𝑑3 𝑦
Find 𝑑𝑥 3
;
must have at
least 1 correct term in
‘his’ product rule.
TOTAL 10
Total
No Working/Answer Partial marks
marks
7
6 A function is defined by 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 3 − 𝑥 + 2, 𝑥 > 0.
(a) Show that 𝑓(𝑥) = 0 has a root between 1.4 and 1.5. [2]
8
(b) Using the Newton-Raphson method with 𝑥0 = 1.45 as a first
approximation, find the root, giving your answer correct to 3
decimal places. [6]
7
6a 𝑓(1.4) = (1.4)3 - (1.4) + 2 = −0.256 < 0
7
𝑓(1.5) = (1.5)3 - + 2 = 0.7083 > 0 M1
(1.5) 2
Since 𝑓(1.4) 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑓(1.5) have different signs and f is a A1
continuous function for 𝑥 > 0, therefore 𝑓(𝑥) = 0 has a root
between 1.4 and 1.5.
7 7
6b 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑥 3 − 𝑥 + 2 , 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = 3𝑥 2 + 𝑥 2 B1
for diff.
Given 𝑥0 = 1.45,
𝑓(1.45) M1A1
𝑥1 = 1.45 − = 1.4271 𝑜𝑟 1.42706
𝑓 ′ (1.45)
6
𝑓(1.4271)
𝑥2 = 1.4271 − = 1.4270 𝑜𝑟 1.42695
𝑓 ′ (1.4271)
M1
𝑥3 = 1.4270 𝑜𝑟 1.42695 M1
∴ 𝑥 = 1.427 (3 𝑑. 𝑝) A1
TOTAL 8
© Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Terengganu Page 7
STPM 954/2
954/2/2019 CONFIDENTIAL*
PART B
Total
No Working/Answer Partial marks
marks
7 𝑥2
The equation of the curve is 𝑦 = 𝑥 2 −4 .
(a) Find the asymptotes [2]
(b) Find the coordinates of the stationary point, and
determine its nature [5]
15
(c) Determine the intervals where the function is increasing
and decreasing [2]
(d) Determine the intervals where y is concave upwards or
concave downwards [3]
𝑥2
Hence, sketch the graph of 𝑦 = [3]
𝑥 2 −4
7a The vertical asymptotes , 𝑥 = 2 , 𝑥 = −2 A1 both
2
The horizontal asymptotes , 𝑦 = 1 A1
7b 𝑥2
𝑦=
𝑥2 − 4
𝑑𝑦 (𝑥 − 4)(2𝑥) − (2𝑥)𝑥 2
2
= M1
𝑑𝑥 (𝑥 2 − 4)2 correct diff.
−8𝑥
= 2
(𝑥2 − 4)
−8𝑥
=0
(𝑥 − 4)2
2
𝑥=0 A1 5
stationary point is at (0,0) A1 (CAO)
Interval (−∞, 0) (0, −∞) M1
𝑑𝑦 Try to show correct
>0 < 0 method
𝑑𝑥
∴ (0,0)𝑖𝑠 𝑎 𝑚𝑎𝑥𝑖𝑚𝑢𝑚 𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 A1
7c 𝑑𝑦
> 0 𝑜𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙 (−∞, 0), 𝑥 ≠ −2 B1
𝑑𝑥
∴ 𝑦 𝑖𝑠 𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑜𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙 (−∞, −2) ∪ (−2,0)
2
𝑑𝑦
< 0 𝑜𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙 (0, ∞), 𝑥 ≠ 2
𝑑𝑥 B1
∴ 𝑦 𝑖𝑠 𝑑𝑒𝑐𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑜𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙 (0,2) ∪ (2, ∞)
© Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Terengganu Page 8
STPM 954/2
954/2/2019 CONFIDENTIAL*
7e 𝑑2 𝑦 8(3𝑥 2 + 4) M1
= 3
≠0
𝑑𝑥 2 (𝑥2 − 4) Correct second diff.
Interval (−∞, −2) (−2,2) (2, ∞)
𝑑2 𝑦
>0 < 0 >0
𝑑𝑥 2
𝑑2 𝑦 3
> 0, 𝑜𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑠 (−∞, −2)𝑎𝑛𝑑 (2, ∞)
𝑑𝑥 2 B1
∴ 𝑖𝑠 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑐𝑎𝑣𝑒 𝑢𝑝𝑤𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑜𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑠
(−∞, −2)𝑎𝑛𝑑 (2, ∞)
𝑑2 𝑦
< 0, 𝑜𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑠 (−2,2) B1
𝑑𝑥 2
∴ 𝑖𝑠 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑐𝑎𝑣𝑒 𝑑𝑜𝑤𝑛𝑤𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑜𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑠 (−2,2)
D1
( correct shape
Q1 and Q2)
D1
( correct shape
Q3 and Q4) 3
D1
All correct
with asymptotes and
labelling
TOTAL 15
© Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Terengganu Page 9
STPM 954/2
954/2/2019 CONFIDENTIAL*
Total
No Working/Answer Partial marks
marks
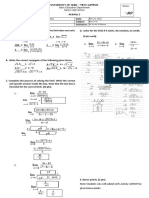
8 The region R in the first quadrant, is bounded by the line 𝑥 + 𝑦 =
2
2 and the curve 𝑦 = 1+𝑥 between their point of intersection.
Find the coordinates of these points of intersection and draw a
sketch showing the region R clearly. [6]
1
Show that the area of R is ( 3 − 4 ln 2 ) [5]
2
Find the volume of solid formed when R is rotated 3600 about
[4]
the x-axis
𝑦 = 2 − 𝑥 − − − (1)
2
𝑦 = 1+𝑥 ------------(2)
(1)=(2):
2 M1-try to solve
2−𝑥 =
1+𝑥
( 2 − 𝑥)(1 + 𝑥) = 2
𝑥 − 𝑥2 = 0
𝑥(𝑥 − 1) = 0
𝑥 = 0 𝑜𝑟 𝑥 = 1
𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑥 = 0 , 𝑦 = 2 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑥 = 1, 𝑦 = 1 M1
6
∴ 𝑇ℎ𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑝𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝑎𝑟𝑒 ( 0,2)𝑎𝑛𝑑 (1,1) A1
D1
correct shape
- Q1 and Q3
D1
straight line and
labelling
D1-all correct
1
1 2 𝑥2
Area = ∫0 (2 − 𝑥 − )dx= [2𝑥 − − 2 ln(1 + 𝑥)] M1
1+𝑥 2 0
(1)2 (0)2
=[2(1) − 2
− 2 ln(1 + 1)] − [2(0) − 2
− 2 ln(1 + 0)] M1
5
3
= − 2 ln 2 M1A1
2
1
= ( 3 − 4 ln 2 )𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡 2 (shown ) A1
2
© Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Terengganu Page 10
STPM 954/2
954/2/2019 CONFIDENTIAL*
1 2 2
Volume = 𝜋 ∫0 [(2 − 𝑥)2 − ( ) ] 𝑑𝑥 M1
1+𝑥
(2−𝑥)3 1
4
= 𝜋 [− + 1+𝑥] M1
3 0
(2−1)3 4 (2−0)3 4
4
= 𝜋 [(− + 1+1) − (− + 1+0)] M1
3 3
7
= 𝜋 (3 − 2)
1
= 3 𝜋 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡 3 A1
TOTAL 15
© Jabatan Pelajaran Negeri Terengganu Page 11
STPM 954/2
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- D1.1 Given Points M (-1,2,1), N (3,-3,0) and P (-2,-3,-4), Find (A) R (B) R + R (C) - R - (D) A (E) - 2 - 3 - SolutionDocument40 pagesD1.1 Given Points M (-1,2,1), N (3,-3,0) and P (-2,-3,-4), Find (A) R (B) R + R (C) - R - (D) A (E) - 2 - 3 - Solutionhiruma aizen67% (3)
- Prob 3Document10 pagesProb 3Jawad Ul Hassan ShahNo ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument31 pagesParabolaHanz GadongNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 101/3/2016: Mathematics III (Engineering)Document47 pagesTutorial Letter 101/3/2016: Mathematics III (Engineering)Shivesh Sohawan100% (2)
- DK & JC's Maths P2 PamphletDocument85 pagesDK & JC's Maths P2 PamphletBernard Chisangano83% (30)
- (Comprehensive Course in Analysis) Barry Simon-Advanced Complex Analysis - A Comprehensive Course in Analysis, Part 2B-American Mathematical Society (2015)Document370 pages(Comprehensive Course in Analysis) Barry Simon-Advanced Complex Analysis - A Comprehensive Course in Analysis, Part 2B-American Mathematical Society (2015)Cecilio Sánchez Fernández100% (1)
- MATH8-Relations and Functions Worksheet AnswersDocument15 pagesMATH8-Relations and Functions Worksheet AnswersRhealyn Joy Narciso100% (2)
- Pembahasan Simulasi SBMPTN Nasional (140418) - Saintek PDFDocument24 pagesPembahasan Simulasi SBMPTN Nasional (140418) - Saintek PDFRara KasimNo ratings yet
- O Level 4048-01 MS PDFDocument10 pagesO Level 4048-01 MS PDFjackhelmanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics f4 p2 MsDocument13 pagesMathematics f4 p2 Msfredmbuvi1No ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS Form 4 Term 2 Joint Exam PP1 Marking Scheme - Docx-1Document9 pagesMATHEMATICS Form 4 Term 2 Joint Exam PP1 Marking Scheme - Docx-1otienolorenzo462No ratings yet
- Answer Scheme 2018-2 Kulai Term 2 STPM Trial Exam 2018: y X y X e y Dy D D X X X X Ydx DX DXDocument4 pagesAnswer Scheme 2018-2 Kulai Term 2 STPM Trial Exam 2018: y X y X e y Dy D D X X X X Ydx DX DXMichelles JimNo ratings yet
- 9FM0-01 June 22 Mark SchemeDocument21 pages9FM0-01 June 22 Mark SchemescribdNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Higher TierDocument8 pagesMathematics: Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Higher Tiershiven.solankiNo ratings yet
- 4E Add Math Prelim Paper 1 2021 - Marking SchemeDocument10 pages4E Add Math Prelim Paper 1 2021 - Marking SchemetiffanyNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Functions Modeling Change A Preparation For Calculus 5th Edition Connally Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Functions Modeling Change A Preparation For Calculus 5th Edition Connally Solutions Manual PDFjosephdcugward100% (10)
- Functions Modeling Change A Preparation For Calculus 5th Edition Connally Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFunctions Modeling Change A Preparation For Calculus 5th Edition Connally Solutions Manualloanmaiyu28p7100% (24)
- Algebraic Expressions Notes Day-2Document4 pagesAlgebraic Expressions Notes Day-2SatanatomicNo ratings yet
- MAT00A1 Test 1 - 2019Document12 pagesMAT00A1 Test 1 - 2019blessedatlehangNo ratings yet
- Name: .................................... Class: .................................... Date: ...................................Document3 pagesName: .................................... Class: .................................... Date: ...................................Euis NurdianaNo ratings yet
- Mat 5 PP2 MSDocument10 pagesMat 5 PP2 MSbradley omariNo ratings yet
- D 16) 1 (1 ) 4) 1 - (Arsinh: January 2006 6675 Pure Mathematics P5/FP2 Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesD 16) 1 (1 ) 4) 1 - (Arsinh: January 2006 6675 Pure Mathematics P5/FP2 Mark SchemeykkamNo ratings yet
- 11maths V2 Slow Learner EMDocument13 pages11maths V2 Slow Learner EMbavanprasath3No ratings yet
- Further Mathematics Sample MS FINALDocument14 pagesFurther Mathematics Sample MS FINALbello marvellousNo ratings yet
- June 2008 - Mechanics M2Document7 pagesJune 2008 - Mechanics M2x30nNo ratings yet
- Inv Trigo Function IntegrationDocument4 pagesInv Trigo Function IntegrationMatthew JordanNo ratings yet
- Repeated QuesDocument8 pagesRepeated QuesMohamed TahmeedNo ratings yet
- 2016 P1 Pahang State ADocument8 pages2016 P1 Pahang State AZuraini Arshad100% (1)
- Answer Cover Page: Orchid Park Secondary School Mid-Year Examination 2021Document11 pagesAnswer Cover Page: Orchid Park Secondary School Mid-Year Examination 2021Cass A.SNo ratings yet
- PMT Mock MSDocument25 pagesPMT Mock MSsaNo ratings yet
- Latihan UTS T. Kimia T. MetalurgiDocument3 pagesLatihan UTS T. Kimia T. MetalurgiSheva Intania Meilan PutriNo ratings yet
- As Level Further Maths Unit 1 Mark Scheme Jan19Document13 pagesAs Level Further Maths Unit 1 Mark Scheme Jan19huangdeshiouNo ratings yet
- Adma G.C.E P2 2021 SolutionsDocument12 pagesAdma G.C.E P2 2021 SolutionsChikuta ShingaliliNo ratings yet
- Gce June 2019 Paper I Maths MechanicsDocument10 pagesGce June 2019 Paper I Maths MechanicsblessingyakumNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Definite IntegralsDocument8 pagesLecture Notes - Definite IntegralslanzNo ratings yet
- 1920 SM015 - 2 SolutionDocument19 pages1920 SM015 - 2 SolutionMuhammad IzzuanNo ratings yet
- 2015 N5 Maths WS FDocument30 pages2015 N5 Maths WS FKumkum BharadwajNo ratings yet
- QA Basic Calculus Quarter 3 Week 3 FinalDocument15 pagesQA Basic Calculus Quarter 3 Week 3 Finalelyzaventura8No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies Module 1 - Answer Key: Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument4 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies Module 1 - Answer Key: Civil Engineering DepartmentCARL JAMESNo ratings yet
- Review of Algebra and Trigonometry: Pamantasan NG CabuyaoDocument16 pagesReview of Algebra and Trigonometry: Pamantasan NG CabuyaoJhon Mark SantoniaNo ratings yet
- Preview Unit 2 Test 1 2016Document2 pagesPreview Unit 2 Test 1 2016Eq BrownNo ratings yet
- INTEGRATIONDocument5 pagesINTEGRATIONannmoraa689No ratings yet
- Calculus (Test 1 Question) (Answers)Document7 pagesCalculus (Test 1 Question) (Answers)Bala GanabathyNo ratings yet
- 9709 w15 Ms 12 PDFDocument7 pages9709 w15 Ms 12 PDFyuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- فتح محاضرات رياضيات اول فصل ثاني 2Document71 pagesفتح محاضرات رياضيات اول فصل ثاني 2t86qpd68z6No ratings yet
- 2013 ACSBR MYE Sec 3 AM-answersDocument5 pages2013 ACSBR MYE Sec 3 AM-answerstoh tim lamNo ratings yet
- 1516 QS015 - 1 SolutionDocument25 pages1516 QS015 - 1 SolutionVeshal RameshNo ratings yet
- MSI Calculus MemosDocument34 pagesMSI Calculus Memoslulamangwenya67No ratings yet
- Lecture Trigo DerivativesDocument12 pagesLecture Trigo DerivativesMarlNo ratings yet
- Lim Lim: 11-Courage Basic Cal Stem Sir Lester CalderonDocument2 pagesLim Lim: 11-Courage Basic Cal Stem Sir Lester CalderonFranz Julian Arenasa PiscosNo ratings yet
- 9709 w15 Ms 11Document8 pages9709 w15 Ms 11yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Sup 2aDocument3 pagesSup 2aSamNo ratings yet
- Learning Tasks in CalculusDocument8 pagesLearning Tasks in CalculusGUEN BALDOMARNo ratings yet
- Determinar Función de Fuerzas Internas y Realizar Sus DiagramasDocument10 pagesDeterminar Función de Fuerzas Internas y Realizar Sus DiagramasAlejandro Copa YucraNo ratings yet
- MAT040 Lesson 2: The Indefinite Integral 2B: Integration by SubstitutionDocument12 pagesMAT040 Lesson 2: The Indefinite Integral 2B: Integration by SubstitutionGezem GigantoNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) : Summer 2018Document14 pagesMark Scheme (Results) : Summer 2018Daniel BoenfieNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Mathematics (Specification 6360) Mpc4Document16 pagesMark Scheme: Mathematics (Specification 6360) Mpc4Hwi Jun AnNo ratings yet
- Module1.1 - AntiDifferentiation Concepts - FormulasDocument3 pagesModule1.1 - AntiDifferentiation Concepts - FormulasJ KimNo ratings yet
- As Level Further Maths Unit 2 Mark Scheme Jan19Document15 pagesAs Level Further Maths Unit 2 Mark Scheme Jan19huangdeshiouNo ratings yet
- VizeDocument4 pagesVizeMehmet KayhanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mathematical Structures For ComputingDocument13 pagesAdvanced Mathematical Structures For ComputingugwakNo ratings yet
- M7 L1 Math Notebook - Cornell NotesDocument9 pagesM7 L1 Math Notebook - Cornell NotesMia AnguianoNo ratings yet
- T Veerarajan - Engineering Mathematics II-McGraw-Hill Education (2018)Document442 pagesT Veerarajan - Engineering Mathematics II-McGraw-Hill Education (2018)gauravNo ratings yet
- CALCULUS 2 FUNCTION and LIMIT PDFDocument74 pagesCALCULUS 2 FUNCTION and LIMIT PDFZikraWahyudiNazirNo ratings yet
- Pages From College Mathematic by ApollosDocument75 pagesPages From College Mathematic by ApollosSonal MulaniNo ratings yet
- Linear Observers Design and Implementation: Verica Radisavljevic-Gajic, Member, IEEEDocument6 pagesLinear Observers Design and Implementation: Verica Radisavljevic-Gajic, Member, IEEEgedeus8072No ratings yet
- Free Modules 55 PDFDocument13 pagesFree Modules 55 PDFLara ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Polyhedral Mesh Handling in Openfoam: Hrvoje JasakDocument13 pagesPolyhedral Mesh Handling in Openfoam: Hrvoje JasakZen KyoNo ratings yet
- Study Guide and Intervention: The Law of Sines and Law of CosinesDocument2 pagesStudy Guide and Intervention: The Law of Sines and Law of Cosinesessam aliNo ratings yet
- Algebraic ExpressionsDocument10 pagesAlgebraic ExpressionsSha MercsNo ratings yet
- Lecture6 0Document130 pagesLecture6 0hanoi6No ratings yet
- Sec Klee Minty Cube HandoutDocument4 pagesSec Klee Minty Cube HandoutPhuoc ThinhNo ratings yet
- EDA Lecture Module 4Document20 pagesEDA Lecture Module 4WINORLOSENo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Part V Duality and Sensitivity AnalysisDocument75 pagesChapter Two Part V Duality and Sensitivity AnalysisGetahun GebruNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationDocument8 pagesDifferential EquationVenkat GowdaNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming PDFDocument101 pagesLinear Programming PDFElijah SorianoNo ratings yet
- Aqa MFP3 W QP Jun06Document8 pagesAqa MFP3 W QP Jun06Vũ LêNo ratings yet
- Boolean Algebra (3) - K-MAPDocument28 pagesBoolean Algebra (3) - K-MAPFir DausNo ratings yet
- Solutions To HW11Document9 pagesSolutions To HW11Babasrinivas GuduruNo ratings yet
- GEN MATH MODULE Final PDFDocument103 pagesGEN MATH MODULE Final PDFDaniel Sigalat LoberizNo ratings yet
- 103 ExercisesDocument70 pages103 Exerciseshungbkpro90No ratings yet
- Exponential and Logarithmic SeriesDocument3 pagesExponential and Logarithmic Seriesdevli falduNo ratings yet
- Herstein: Topics in Algebra - Homomorphisms: by Bret Sherfinski June 21, 2015Document2 pagesHerstein: Topics in Algebra - Homomorphisms: by Bret Sherfinski June 21, 2015Lakshmi NarayanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument35 pagesQuadratic EquationKeerthivasan MohanNo ratings yet