Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Cell 1
Plant Cell 1
Uploaded by
Reina JaneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Cell 1
Plant Cell 1
Uploaded by
Reina JaneCopyright:
Available Formats
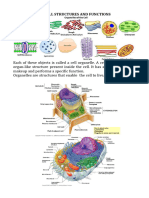
PLANT CELL
Plant cells are rectangular shaped, eukaryotic, or nucleus-containing, Nucleus:
contains DNA, the genetic
cells with a rigid cell wall. Within the plant cell structures called organelles, blueprint of a living organism.
perform functions necessary to cell and plant survival. On average, plant
cells are between 10 and 100 micrometers long, around the same size as
Cytosol:
the diameter of a human hair. Unlike animal cells, plant cells make their fluid within the cell that
own food through photosynthesis. This process, powered by surrounds the organelles.
energy from sunlight, involves producing oxygen and
glucose from water and carbon dioxide.
Endoplasmic reticulum:
Vacuole: network of membranes that
a fluid-filled organelle that helps synthesize proteins
stores food and nutrients and lipids.
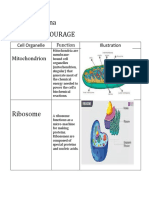
Ribosome:
small organelle often attached
to the endoplasm reticulum
Chloroplast:
that help create proteins.
the site of photosynthesis,
organelle containing
chlorophyll, molecules that
absorb sunlight and give
Golgi apparatus:
plants their green color
membrane-bound sacs
responsible for storing, and
transporting proteins and
lipids.
Lysosome:
an organelle that contains Mitochondrion:
digestive enzymes and breaks a bean-shaped organelle
down biological molecules responsible for converting raw
materials into usable energy.
Cell membrane:
Cell wall: two layers of lipid, or fat, molecules
encloses the cell membrane that enclose the cell and regulate
and gives plant cells their which molecules can go inside and
shape and rigid structure. outside of the cell.
You might also like
- Karst Hydrology and Physical Speleology - Fred Bogli PDFDocument298 pagesKarst Hydrology and Physical Speleology - Fred Bogli PDFJorge Grandas S100% (1)
- Cell VocabularyDocument3 pagesCell Vocabularyapi-537617514No ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsDocument16 pagesCarbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsTsu Wei Chua100% (5)
- Global Roaming Tutorial For LTE Only Operators White Paper V1.0Document41 pagesGlobal Roaming Tutorial For LTE Only Operators White Paper V1.0Azmir MNo ratings yet
- Draughts PersonDocument44 pagesDraughts PersonAmila Rangana Karunarathne100% (3)
- Week 2 - Introduction To BiochemistryDocument34 pagesWeek 2 - Introduction To BiochemistryPaula LouiseNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Structure & FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Organelles Structure & FunctionDaniel ChinNo ratings yet
- Int-UpperInt Placement Test PDFDocument3 pagesInt-UpperInt Placement Test PDFh1238709mNo ratings yet
- 14 - SCRsystemInstallationGuideLineDNOx2 - V7.3Document103 pages14 - SCRsystemInstallationGuideLineDNOx2 - V7.3George Huarcaya Diaz100% (1)
- Basic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismDocument2 pagesBasic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismkikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Adobe Photoshop CC 2020 Crack Serial Key PDFDocument3 pagesAdobe Photoshop CC 2020 Crack Serial Key PDFDemarcusNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Biology NotesDocument36 pagesPreliminary Biology NotesSaad KashifNo ratings yet
- CellFunctions PlantCellDocument1 pageCellFunctions PlantCellHENNESA JOYCE ALABANo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument1 pageAnimal CellBenju Arios TamayoNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 FullDocument130 pagesChap 5 Fullgaelle tannous100% (1)
- 04 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument23 pages04 Cell Structure and Functionธนเสฐฐ์ กิตติวรรธโนทัยNo ratings yet
- M3 - Exercise 4. Plant and Animal CellDocument10 pagesM3 - Exercise 4. Plant and Animal CellVanessa RafaelNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2Document12 pagesGen Bio 2Ma.Dulce ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell StructureDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cells: Chapter 7-2: Cell Structurejmunozbio@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 - Differences Between Eukaryotes and ProkaryotesDocument4 pages1.3.1 - Differences Between Eukaryotes and ProkaryotescarlNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument16 pagesReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- F4 C2 NotesDocument15 pagesF4 C2 Notesmarisyayasmin050907No ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument8 pagesCell TheoryTrisha Lee DuranteNo ratings yet
- Assignment in General Biology 1Document3 pagesAssignment in General Biology 1neil aldwin garciaNo ratings yet
- What Are Cell OrganellesDocument19 pagesWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 LectureDocument13 pagesModule 2 LectureJeal NochefrancaNo ratings yet
- Asa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaDocument1 pageAsa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaMary Pauline G. CamposNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles FunctionsDocument1 pageCell Organelles FunctionsFedomessi10 Is a geniusNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- Cells To TissuesDocument4 pagesCells To TissuesJanelle Grace OrdanizaNo ratings yet
- PRPM110L Module 3 & 4Document10 pagesPRPM110L Module 3 & 4CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Cell ReviewerDocument7 pagesCell ReviewerMar LagmayNo ratings yet
- STRUCTUREDocument2 pagesSTRUCTUREDanilo JR. BuaquiñaNo ratings yet
- Salud - Lab Activity 3 - The Cell - Biochem - BSN 1-Coc A. PDFDocument5 pagesSalud - Lab Activity 3 - The Cell - Biochem - BSN 1-Coc A. PDFFaye SaludNo ratings yet
- Organelle With Solution 2022-23Document1 pageOrganelle With Solution 2022-23LuLaMejorNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsjhabNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsRaeson Amir ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaDocument6 pagesPamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaJosett RomanoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument5 pagesBiochemistry Reviewer202370092No ratings yet
- Act 2CDocument3 pagesAct 2CCHARLIENE FAYE ASPRERNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument14 pagesGeneral BiologyMason DeidriNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell Structure and FunctionsDanilo JR. BuaquiñaNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Paolo L Pena POGIIIIIIDocument4 pagesPaolo L Pena POGIIIIIIPatricia PeñaNo ratings yet
- Organelle Present/Absent Description FunctionDocument5 pagesOrganelle Present/Absent Description FunctionTania BacsinNo ratings yet
- The Biology of Agricultural Crops: Nature and Composition of PlantsDocument18 pagesThe Biology of Agricultural Crops: Nature and Composition of PlantsDanica DayananNo ratings yet
- Biochem-Lec MergedDocument28 pagesBiochem-Lec MergedNel joy PaurilloNo ratings yet
- A Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingDocument4 pagesA Cell Is The Smallest Unit of A Living ThingJONAVIE DEMALATANo ratings yet
- Benjamin Watson - Summer PiXL Gateway Biology - Cells TRANSITIONDocument15 pagesBenjamin Watson - Summer PiXL Gateway Biology - Cells TRANSITIONboobooNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report in Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument3 pagesLaboratory Report in Microbiology and ParasitologyynaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Second Trimester ScienceDocument36 pagesStudy Guide Second Trimester ScienceuzielcgcursoNo ratings yet
- Chem 104D MidtermsDocument27 pagesChem 104D MidtermsCASTAÑEDA, Jameela AnneNo ratings yet
- Cell Vocabulary: NameDocument3 pagesCell Vocabulary: NameStephanie BannickNo ratings yet
- Cells VIS ChartDocument1 pageCells VIS Chartdidua08No ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellElmer Tunggolh, Jr.No ratings yet
- Bio-024-Lab-Activity-3 Navarro, Mia Grace G.Document6 pagesBio-024-Lab-Activity-3 Navarro, Mia Grace G.Mia NavarroNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument9 pagesCellsjasmineNo ratings yet
- BioNOTES Midterm Study GuideDocument14 pagesBioNOTES Midterm Study Guidebro jo lolNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesCell OrganellesMotie KassabNo ratings yet
- Act 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesAct 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportRicky SalazarNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- Introductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02Document34 pagesIntroductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02DR KARSHAN NANDANIYANo ratings yet
- GRP WRKDocument5 pagesGRP WRKrheaNo ratings yet
- Wheeze in Children: Asthma Clinical Pathway: Departments of Emergency Medicine and PaediatricsDocument4 pagesWheeze in Children: Asthma Clinical Pathway: Departments of Emergency Medicine and Paediatricsscanutd100% (1)
- Yr 6 - English MA3 RevisionDocument36 pagesYr 6 - English MA3 RevisionSamiNo ratings yet
- Ais Fraud-Case StudyDocument3 pagesAis Fraud-Case StudyErica AlimpolosNo ratings yet
- Kissing FishDocument11 pagesKissing FishkohlerfernandaNo ratings yet
- Razr Iron Scorpions MC Series Book 1 Motorcycle Club Mafia Romance Crossover Universe Book 3 Harley Diamond All ChapterDocument66 pagesRazr Iron Scorpions MC Series Book 1 Motorcycle Club Mafia Romance Crossover Universe Book 3 Harley Diamond All Chapterphillip.mesias887100% (4)
- Uploading 8 23Document12 pagesUploading 8 23Shannara21No ratings yet
- Pioneer VSX 417Document52 pagesPioneer VSX 417cristakeNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Criteria Policy Anaysis of Circular Debt in PakistanDocument7 pagesMultiple-Criteria Policy Anaysis of Circular Debt in PakistanumairNo ratings yet
- Amateur PDFDocument218 pagesAmateur PDFAnonymous ToJLwXNo ratings yet
- MATH1240 Prelab0Document9 pagesMATH1240 Prelab0remodsouza832No ratings yet
- Principles of ArtsDocument19 pagesPrinciples of ArtsMiles SerranoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Medical Licensing ExaminationDocument3 pagesSyllabus of Medical Licensing Examinationapi-370059967% (3)
- Potterton Performa System HE User GuideDocument12 pagesPotterton Performa System HE User GuideReUp2009No ratings yet
- Guide Touchstone I Unit 2Document4 pagesGuide Touchstone I Unit 2Luz Maria Batista MendozaNo ratings yet
- Natres CasesDocument357 pagesNatres CasesqwertyuiopNo ratings yet
- Explained - How Fertiliser Subsidy Works - Explained News, The Indian ExpressDocument15 pagesExplained - How Fertiliser Subsidy Works - Explained News, The Indian ExpressmitheleshpurohitNo ratings yet
- Weld Overlay Cladding1Document3 pagesWeld Overlay Cladding1Yetkin ErdoğanNo ratings yet
- SorghumDocument12 pagesSorghumQudsia SyedNo ratings yet
- New Customer Emails For Muhammad AliDocument17 pagesNew Customer Emails For Muhammad Aliknotship.comNo ratings yet
- PDF IRH GuidebookDocument121 pagesPDF IRH GuidebookReems LordNo ratings yet
- Emesrt Section2 StandardsDocument4 pagesEmesrt Section2 StandardsNilson Alves de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Module 9 (2 WEEKS) QUESTIONDocument7 pagesForm 4 Module 9 (2 WEEKS) QUESTIONSYARIFAH SYARINA BT SHEIKH KAMARUZAMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- There Are Few Pros and Cons Associated With It Which Are Discussed BelowDocument1 pageThere Are Few Pros and Cons Associated With It Which Are Discussed BelowHarshit AgrawalNo ratings yet