Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory Report in Microbiology and Parasitology
Uploaded by
ynaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory Report in Microbiology and Parasitology
Uploaded by
ynaCopyright:
Available Formats
LABORATORY REPORT IN
MICROBIOLOGY AND PARASITOLOGY
Madam Jaraba, Khyla Exercise 2
BS Psychology 1A March 15, 2023
Associate Professor Carina C. Batol March 16, 2023
MAKING A WET MOUNT
I. Objectives
1. To make a wet mount of onion, tomato, cheek cell, and sperm cell.
2. To differentiate the cell of onion, tomato, and cheek cell in Low Power Objective and High-Power
Objective.
3. To draw and color the onion, tomato, and cheek cell.
4. To appreciate the variety of cell shape, size in tomato, onion, and cheek cell.
II. Materials Needed
1. Fresh Mount Slide
2. Cover Slip/Cover Glass
3. Compound Microscope
4. Beaker
5. Dropper
6. Water
7. Iodine
8. Tomato
9. Onion
10. Cheek Cell
11. Sperm Cell
III. Methodology
1. Prepare your specimen: Collect a thin slice of your sample and place it on a clean, dry slide.
2. Add a drop of liquid: Add a drop of water, saline solution, or any other liquid that will provide a suitable
medium for the specimen to remain visible.
3. Place a coverslip: Palace the cover slip at a 45-degree angle with one edge touching the water and let go.
The coverslip will fall over the sample and be held in place by surface tension.
4. Seal the edges: Use a piece of tissue paper or a lens wipe to remove excess liquid from the edges of the
coverslip.
5. Label and observe: Label the slide, and observe the specimen under the microscope. Adjust the focus and
illumination as necessary to obtain a clear image.
6. Disposal: once you are done with your observation, dispose of the slide and coverslip in a container
designated for the biological waste.
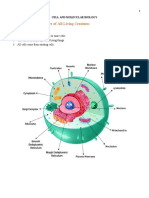
IV. Data and Results
PLANT CELL DESCRIPTION FUNCTION
1. Cell Membrane Made up of a matrix of pectin Provides tensile strength and protection
polysaccharides that is highly cross- against mechanical and osmotic stress
linked and contains a network of
cellulose microfibrils and cross-linking
glycans.
2. Lysosome A sac-like compartment inside a cell that The digestive system of the cell
has enzymes that can break down
cellular components that need to be
destroyed
3. Cytoplasm Helps keep organelles suspended, the Holding the components of the cell and
internal structure of the cell supported, protects them from damage.
and the plant cell's shape is maintained.
4. Nucleus A membrane bound organelle that Store DNA or hereditary information
contains the DNA of the cell required for cell division, metabolism
and growth
5. Nuclear A double layer that encloses the cell's Separate the chromosomes from the
Membrane nucleus, where the chromosomes reside cell's cytoplasm and other contents
6. Nucleolus Less organelle within the nucleus that Facilitating ribosome biogenesis
manufactures ribosomes, the cell's
protein-producing structures
7. Vacuole Providing structural support, as well as Maintaining cell acidity and turgor
serving functions such as storage, waste pressure, regulating the storage and
disposal, protection, and growth transport of substances, controlling the
transport and localization of key
proteins through the endocytic and
lysosomal-vacuolar transport pathways,
and responding to biotic and abiotic
stresses.
8. Golgi Body The site at which the complex Transporting, altering, and packing
polysaccharides of the cell wall are proteins and lipids to specific locations
synthesized. are the main duties of this cell organelle
9. Mitochondria Oblong shaped organelles found in the Produce energy through cellular
cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells respiration
10. Rough ER A cellular organelle composed of many To produce proteins for the rest of the
folds of tissues and channels cell to function
11. Smooth ER Tube-like structure located near the cell Make cellular products like hormones
periphery and lipids
12. Ribosome Small circular organelles found in the A micro-machine for making proteins
cell
13. Cell Wall Composed of a network of cellulose Provides tensile strength and protection
microfibrils and cross-linking glycans against mechanical and osmotic stress
embedded in a highly cross-linked
matrix of pectin polysaccharides
14. Chloroplast Convert light energy into relatively Accumulate the high levels of colourful
stable chemical energy via the pigments in plant tissues or organs
photosynthetic process
ANIMAL CELL DESCRIPTION FUNCTION
15. Cell Membrane Separates the interior of the cell from the To be a barrier keeping the constituents
outside environment of the cell in and unwanted substances
out
16. Lysosome A membrane-bound cell organelle that The digestive system of the cell
contains digestive enzymes.
17. Cytoplasm A gel-like material that fills the area Holding the components of the cell and
between the plasma membrane and the protects them from damage
nuclear membrane
18. Nucleus It is both the largest and stiffest Store the cell's DNA, maintain its
organelle and is easily identifiable by integrity, and facilitate its transcription
light microscopy and replication.
19. Nuclear A double layer that encloses the cell's Separate the chromosomes from the
Membrane nucleus, where the chromosomes reside cell's cytoplasm and other contents
20. Nucleolus The site of ribosome biogenesis Produce and assemble the cell's
ribosomes.
21. Golgi Body A cell organelle that helps process and A factory in which proteins received
package proteins and lipid molecules, from the ER are further processed and
especially proteins destined to be sorted for transport to their eventual
exported from the cell destinations: lysosomes, the plasma
membrane, or secretion
22. Mitochondria Membrane-bound cell organelles Generate most of the chemical energy
(mitochondrion, singular) that generate needed to power the cell's biochemical
most of the chemical energy needed to reactions
power the cell's biochemical reactions
23. Rough ER Involved in some protein production, To produce proteins that will become
protein folding, quality control and part of the endomembrane system, the
despatch plasma membrane or to be secreted.
24. Smooth ER Devoted almost exclusively to the To make cellular products like
manufacture of lipids and in some cases hormones and lipids
to the metabolism of them and
associated products
25. Ribosome An intercellular structure made of both The site of protein synthesis in the cell
RNA and protein, and it is the site of
protein synthesis in the cell
V. Drawing
VI. Answers to questions
1. What are the two general types of cells?
- Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are the two general types of cells.
2. Differentiate the two.
- Prokaryotic cells are always unicellular, but eukaryotic cells are frequently multicellular creatures.
Eukaryotic cells are also 100 to 10,000 times larger and far more complicated than prokaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic DNA is stored in the cytoplasm, whereas eukaryotic DNA is stored in the nucleus.
VII. Interpretation of data and result
The table depicts plant and animal cell differentiation. It also describes the parts, descriptions, and
functions of each cell.
VIII. Conclusion
As a result, I come to the conclusion that wet mounts are employed to see microorganisms. The
specimen is supported by the water's refractive index, which increases image quality even further. Water fills
the gap between the coverslip and the slide, securing the sample. Light can readily pass through the coverslip,
sample, and slide as a result. The wet mount method should be used to determine whether or not an organism
is motile.
IX. References
https://elementalscience.com/blogs/science-activities/how-to-make-a-microscope-slide
You might also like
- A Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneDocument3 pagesA Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell 1. NucleusDocument2 pagesParts of A Cell 1. NucleusVon Lester SanchezNo ratings yet
- Central Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellDocument6 pagesCentral Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellNEIL MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- List All The Structures of Both Cell Types and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesList All The Structures of Both Cell Types and Their FunctionsAira Shane MargesNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 FullDocument130 pagesChap 5 Fullgaelle tannous100% (1)
- Module 2 LectureDocument13 pagesModule 2 LectureJeal NochefrancaNo ratings yet
- 2f7a3f9c-cb36-469b-96f4-72c9e24a82c0Document12 pages2f7a3f9c-cb36-469b-96f4-72c9e24a82c0Kalina KichukovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document11 pagesChapter 5EDLE FAITH ANDREA CATABIANNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Compare Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument4 pagesCompare Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsJung Somin100% (1)
- Module 2 CytogeneticsDocument17 pagesModule 2 CytogeneticsFrances Riane SimoyNo ratings yet
- NOTES Unit 3 - The CellDocument7 pagesNOTES Unit 3 - The CellCarina LattoNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 3: Structure of A Cell and MitosisDocument9 pagesActivity No. 3: Structure of A Cell and MitosisEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Cells: Structure and Organization: 7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi 1Document23 pagesCells: Structure and Organization: 7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi 1fabia afaniNo ratings yet
- Group 5-4Document84 pagesGroup 5-4googlegirl18No ratings yet
- Cañete, Rea May (Cell Bio - Parts and Function of The Cell) - FLTamayao - Nov 14 2 PDFDocument6 pagesCañete, Rea May (Cell Bio - Parts and Function of The Cell) - FLTamayao - Nov 14 2 PDFRheaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument6 pagesCellsaryam aliNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Function and PropertiesDocument10 pagesCell Structure Function and PropertiesWanda JohnNo ratings yet
- Worksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleDocument3 pagesWorksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleLaureen BarbsNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Structure & FunctionDocument4 pagesCell Organelles Structure & FunctionDaniel ChinNo ratings yet
- Biochem-Lec MergedDocument28 pagesBiochem-Lec MergedNel joy PaurilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Organelles and FunctionsMia NavarroNo ratings yet
- CELL: It's A: CommunityDocument67 pagesCELL: It's A: Communitybae joohyunNo ratings yet
- Bio 49 Activity 1Document6 pagesBio 49 Activity 1Theresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- Bio Assignment 1Document6 pagesBio Assignment 1ditucalan.ha2003No ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument5 pagesMICROBIOLOGYCia RraNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument21 pagesCellsEXTRA ACCOUNTNo ratings yet
- Basic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismDocument2 pagesBasic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismkikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structure and TaxonomyEarl Nikko ChingNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument4 pagesBiochemistryAaliyah Ashley CerboNo ratings yet
- L 2 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument25 pagesL 2 Cell Structure and Functionkaukab azimNo ratings yet
- Ana CellsDocument4 pagesAna CellsDCRUZNo ratings yet
- 复习笔记IBDP Biology SL complete notesDocument5 pages复习笔记IBDP Biology SL complete notescynwuyxNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 Cell StructureDocument31 pagesCh.4 Cell StructureEmma WisemanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The Cell 1Document6 pagesExercise 1 The Cell 1MJMadlangbayan100% (1)
- LESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypesDocument6 pagesLESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypessandraNo ratings yet
- Prelim - ProbSet 1Document2 pagesPrelim - ProbSet 1Alixandra Isobel De VeraNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Chapter OverviewDocument6 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structure: Chapter OverviewJeriz Marie GamboaNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument18 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (1)
- Cell Membrane Transport LectureDocument9 pagesCell Membrane Transport LectureJanine LimjucoNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 2Document13 pages02 Handout 2Janna AngelesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document22 pagesLecture 3raja11160No ratings yet
- In Genetics and CytogeneticsDocument11 pagesIn Genetics and CytogeneticsMaithiliNo ratings yet
- Biology q1 Week 2Document32 pagesBiology q1 Week 2Lorraine Jumaquio RonquilloNo ratings yet
- NUDES Lab Activity 2Document5 pagesNUDES Lab Activity 2Ella RetizaNo ratings yet
- Cells: Nucleus (Eukaryotes) or Nucleoid (Bacteria)Document33 pagesCells: Nucleus (Eukaryotes) or Nucleoid (Bacteria)Leandro GalzeranoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Major and Subcellular OrganellesDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of Major and Subcellular OrganellesMEDRANO, Hana Jhiemyka O.No ratings yet
- Light Microscopy and Staining TechniquesDocument17 pagesLight Microscopy and Staining TechniquesEANo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles FunctionsDocument1 pageCell Organelles FunctionsFedomessi10 Is a geniusNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsjhabNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Reviewer - Key ConceptsDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Reviewer - Key ConceptsynaNo ratings yet
- Biokim 4 - Bu Asih - sEL 2019Document74 pagesBiokim 4 - Bu Asih - sEL 2019Rizky NNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureDocument31 pagesDokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureJairra Jae LunaNo ratings yet
- Diagramas Celulas Eucarionte, ProcarionteDocument4 pagesDiagramas Celulas Eucarionte, ProcarionteAdriana Santiago RoaNo ratings yet
- Ommonly Used Microbes in Biotechnology and FermentationDocument26 pagesOmmonly Used Microbes in Biotechnology and FermentationLeigh JilianNo ratings yet
- Cells Memorization SheatDocument2 pagesCells Memorization SheatNiomi ButtermilkNo ratings yet
- Material For Genbio Week 1Document6 pagesMaterial For Genbio Week 1John Ferri PatunganNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - CellsDocument55 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Cellsemmanuelchilengwe5No ratings yet
- ENTREPDocument1 pageENTREPynaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Disaster PDFDocument6 pagesReviewer Disaster PDFynaNo ratings yet
- BG of The StudyDocument1 pageBG of The StudyynaNo ratings yet
- BerzabalRainierJohn Activity1 OdtDocument1 pageBerzabalRainierJohn Activity1 OdtynaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Disaster PDFDocument6 pagesReviewer Disaster PDFynaNo ratings yet
- BerzabalRainierJohn Activity1 OdtDocument1 pageBerzabalRainierJohn Activity1 OdtynaNo ratings yet
- Onion Cell Membrane Osmosis Lab ReportDocument2 pagesOnion Cell Membrane Osmosis Lab ReportynaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab Report on OsmosisDocument2 pagesMicrobiology Lab Report on OsmosisynaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Open Waste Burning on Air QualityDocument1 pageEffects of Open Waste Burning on Air QualityynaNo ratings yet
- LABREP4Document2 pagesLABREP4ynaNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Cell Membrane Microbiology Lab ReportDocument2 pagesOsmosis and Cell Membrane Microbiology Lab ReportynaNo ratings yet
- 2TSY2223 - GED0001 - TW04-23: Specialized English Program 1Document1 page2TSY2223 - GED0001 - TW04-23: Specialized English Program 1ynaNo ratings yet
- Learning by Association: Classical Conditioning: (CR), Which Is The Acquired Response To TheDocument4 pagesLearning by Association: Classical Conditioning: (CR), Which Is The Acquired Response To TheynaNo ratings yet
- Specialized English Program 1Document2 pagesSpecialized English Program 1ynaNo ratings yet
- Importance of MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesImportance of MicrobiologyynaNo ratings yet
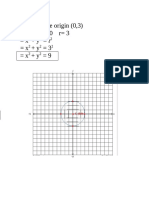
- Find the equation of a circle centered at (0,3Document2 pagesFind the equation of a circle centered at (0,3ynaNo ratings yet
- Mystery of Thailand's Young King's DeathDocument1 pageMystery of Thailand's Young King's DeathynaNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument2 pagesNarrative ReportynaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Reviewer - Key ConceptsDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Reviewer - Key ConceptsynaNo ratings yet
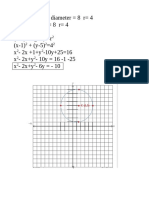
- Solving a quadratic equation: Circle with center (0, -4) and radius 7Document1 pageSolving a quadratic equation: Circle with center (0, -4) and radius 7ynaNo ratings yet
- Circle Act No.2Document1 pageCircle Act No.2ynaNo ratings yet
- States of Consciousness, Sleep and DreamsDocument41 pagesStates of Consciousness, Sleep and DreamsynaNo ratings yet
- Circle Act No.1Document2 pagesCircle Act No.1ynaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemynaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Urinary SystemDocument50 pagesChapter 12 - Urinary SystemynaNo ratings yet
- GenmathDocument18 pagesGenmathynaNo ratings yet
- BPSU Endocrine AssignmentDocument6 pagesBPSU Endocrine AssignmentynaNo ratings yet
- Activity 02 The Cell CityDocument4 pagesActivity 02 The Cell Citybernard0% (1)
- Histologic TechniquesDocument12 pagesHistologic TechniquesCatherine Merilleno100% (1)
- Chapter 9 - Multicellular OrganizationDocument43 pagesChapter 9 - Multicellular OrganizationLeah Hope CedroNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument109 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemGeorge MunyendoNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureDocument3 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell StructurejnfidnjNo ratings yet
- Classification of Neutrophilic Granulocytes 2000Document1 pageClassification of Neutrophilic Granulocytes 2000Gregorio De Las Casas100% (1)
- Performance Task 1.2 - 3D-Cell ModelDocument2 pagesPerformance Task 1.2 - 3D-Cell ModelRy Choco100% (1)
- Biology Note Grade 8 Chapter: CellsDocument7 pagesBiology Note Grade 8 Chapter: CellsAfrida AnnanNo ratings yet
- Cell 1Document2 pagesCell 1Trilochan TripathyNo ratings yet
- Example Preparation-HaCat CellsDocument5 pagesExample Preparation-HaCat Cellshorace35No ratings yet
- FCPS Part 1 SyllabusDocument37 pagesFCPS Part 1 SyllabusMd Hasan Imam100% (2)
- DPP XI Chapter - 8 Cell The Unit of Life 17Document17 pagesDPP XI Chapter - 8 Cell The Unit of Life 17Riya MondalNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 3: Structure of A Cell and MitosisDocument9 pagesActivity No. 3: Structure of A Cell and MitosisEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam - PEC 1 Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesPrelim Exam - PEC 1 Human Anatomy and PhysiologyColeen BentoyNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Is The ProtectiveDocument1 pageCell Wall Is The ProtectiveNicole AriasNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Midyear Exam Biology Form 4 2010Document18 pagesPaper 1 Midyear Exam Biology Form 4 2010FidaNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesThe Muscular SystemMazon, Dinah Melisse P.No ratings yet
- Reinforcement: 1. The Organization of The Human BodyDocument10 pagesReinforcement: 1. The Organization of The Human BodyAlba CubilloNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM 1 Cell Biomolecules PDFDocument3 pagesBIOCHEM 1 Cell Biomolecules PDFHarold James AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- ArtExaminingInterpreting HystologyDocument104 pagesArtExaminingInterpreting HystologyalmutazimNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 Fixation StudentDocument7 pagesExercise 3 Fixation StudentErika Nicole SiasonNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals - Animal Tissues 22-05-2020Document8 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals - Animal Tissues 22-05-2020BLR PUNEETBHAVAN COLLEGENo ratings yet
- MISCELLANEOUS BLOOD GROUP ANTIGENSDocument4 pagesMISCELLANEOUS BLOOD GROUP ANTIGENSIan Leo SantosNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal TissuesDocument10 pagesPlant and Animal TissuesSanjay AdakNo ratings yet
- Cartilage GraftsDocument30 pagesCartilage GraftsDr.Zahida AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Integrated Principles of ZoologyDocument41 pagesIntegrated Principles of ZoologyEstherNo ratings yet
- Module 1 BiochemDocument40 pagesModule 1 BiochemAlyssa PachecoNo ratings yet
- Bio 100 NotesDocument2 pagesBio 100 Notesapi-269828776No ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab ReviewerDocument7 pagesAnaphy Lab ReviewerJoice Bundang Maningo100% (1)