Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 Planning
Uploaded by
sagarkota008Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 Planning
Uploaded by
sagarkota008Copyright:
Available Formats
Basic Civil Engineering A.
Y 2022-2023
PLANNING
All buildings should be properly planned, keeping in view the various
requirements of a good building. Except strength requirement, all
other requirements of a good building are taken care at the stage of
planning.
Strength requirement is taken care during structural design of
building components.
However in planning the building by-laws of the statutory authorities
should not be violated. Planning of the building is an art combined
with science.
Principles of planning of buildings may be grouped into:
1. Orientation
2. Energy efficiency
3. Utility
4. Other requirements of the building
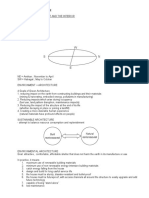
PLANNING SUITABLE ORIENTATION
Orientation means setting out the plan of the building with respect to north-
south and east-west directions to provide an opportunity to user to enjoy
sun-shine and breeze when required and to avoid the same whenever not
required. This is also known as planning the aspect of a building. Aspect
means arrangement of doors, windows in the external wall to make good use
of nature. This term has nothing to do with the architectural aspect of
outlook of building. Kitchen should have eastern aspect to enjoy morning
sunshine, means, kitchen should be located on the eastern side of the
building to make use of morning sun rays.
The following are the required aspects for various parts of the building in the
northern hemisphere of earth:
(a) Kitchen–eastern aspect.
(b) Dining room–southern aspect to enjoy winter sun.
(c) Drawing and living room–southern or south-eastern aspect to enjoy
winter sun.
(d) Bed rooms–western or south-western aspect to enjoy breez in summer.
(e) Reading room, class room, stairs, northern aspect to enjoy diffused light.
The following suggestions should be kept in mind in the orientation of a
building in India:
(a) Place long walls towards north-south and short walls in east-west
directions so as to reduce
the area exposed to direct sun rays.
(b) Provide verandah and balcony on east and west.
(c) Provide chejjas on doors and windows on southern side to protect them
from sun’s rays.
PLANNING FOR ENERGY EFFICIENCY
1 LAKIREDDY BALI REDDY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
Basic Civil Engineering A.Y 2022-2023
A building should be planned in such a manner that it gives maximum day
lighting, ventilation and heat insulation. If these requirements are fulfilled,
requirement of electric energy comes down.
(a) Light: Natural light provides hygenic atmosphere. Light should not be
glaring but it should be uniformly distributed. Providing windows and
ventilators of appropriate size at suitable positions contributes a lot
for natural lighting. For residential buildings window area to floor area
should not be less than 1/10th while for school buildings it should
not be less than 1/5th of floor area. For factory buildings north light
trusses should be provided to get maximum diffused light.
(b) Ventilation: Ventilation is the circulation of the air in the building.
Natural ventilation can be achieved by selecting and positioning of
doors, windows and ventilators at suitable places. Always cross
ventilations should be planned suitably. Provision of ventilators at roof
level helps in driving out hot airs. In case it is not possible to achieve
natural ventilation for any part of the building provide ordinary or
exhaust fans.
(c) Heat Insulation: Thicker exterior walls provide insulation against
heat. Proper ventilation also helps in achieving heat insulation. Sun
shades provided to doors, windows and ventilators help in achieving
heat insulation. In factories and assembly halls height should be more
to reduce temperature inside the building. The position of furnaces in
the factories should be located away from the other parts of the
factory. The openings should be provided at higher level in the wall to
remove hot air.
PLANNING FOR SUITABLE UTILITY
Principles of planning for suitable utility are:
1. Roominess
2. Furniture Requirements
3. Groupings
4. Circulation.
1. Roominess:
1. It refers to suitable proportioning of length, width and height of rooms
in the building to get maximum benefit from the minimum
dimensions. Length to width ratio should be 1.2 to 1.5.
2. If it is nearly square lot of area is wasted for movement, while, it is
more than 1.5, it gives the ‘tunnel’ effect.
3. Doors for rooms should be properly located so that utility and privacy
are maximum.
4. Cupboards and lofts should be provided to increase roominess. Proper
colours to wall and floor also give roominess effect.
5. Light colour gives effect of more space.
2. Furniture Requirements:
a) In planning residential, office, laboratory, hospital buildings positions
of required furniture should be drawn and then room dimensions,
positions of doors, windows, wardsities etc. planned.
2 LAKIREDDY BALI REDDY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
Basic Civil Engineering A.Y 2022-2023
b) In case of planning a hostel room for two students it may need
centrally placed
c) door while if it is for three students, it should be near the end of front
wall.
d) Positions of cots, study tables and cupboard should be drawn and
room planned. In designing a living room, positions of sofa, chairs,
T.V. show case etc. should be drawn and size of the room and
positions of doors fixed.
e) Availability of circulation area should be checked.
f) Thus the furniture requirement influences the planning of a building
to a great extent.
3. Grouping:
a) Grouping means disposition of various rooms in the building for the
convenience of users and their utility.
b) A dining room should be close to the kitchen, white sanitary block
should be away from kitchen, but convenient to bedrooms.
c) In case of offices, administrative department is located centrally. In
factories, various sections are located such that product moves in one
direction to get finally assembled after least movement.
d) In residential buildings grouping is to achieve comfort, privacy and
efficiency while in the case of other buildings it is to achieve
economical service.
4. Circulation:
A. Circulation means the space to be provided for movement from room
to room or floor to floor.
B. Passages, lobbies, halls provided serve horizontal circulation while
stairs and lifts serve vertical circulation.
C. Within a room also a portion of it serve for circulation while some
other portion serve for utility.
D. The following points should be considered in planning circulation:
(a) They should be straight.
(b) They should be sufficient.
(c) They should be sufficiently lighted and ventilated.
(d) Stairs should be easily accessible to all the users.
(e) Sanitary services should have access for every user through passage
lobby.
PLANNING FOR MEETING OTHER REQUIREMENTS
3 LAKIREDDY BALI REDDY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
Basic Civil Engineering A.Y 2022-2023
Principle of planning involves planning for meeting the following
requirements also:
1. Sanitary convenience
2. Prospects
3. Elegance
4. Flexibility
5. Privacy
6. Resistance to fire
7. Sound insulation
8. Protection from termite
9. Security against burglary
10. Economy
11. Provisions for future alterations.
1. Sanitary Convenience: Sanitary conveniences include provision of
bathrooms, lavatories, urinals etc. Provision of these are not only necessities
but statutory requirement also. These facilities should be located giving free
access to all users. In these blocks, suitable slopes should be given to the
floors to drain out water easily.
2. Prospects: It is about locating and selecting types of doors and windows
so as to reveal pleasant features and conceal undesirable features of the
buildings from a person viewing from outside.
3. Elegance: Elegance means general effect produced for a viewer from
outside. It depends upon proper positioning of doors, windows, ventilators,
chejjas, balconies etc. Elevations should be attractive. The width, height and
the projections in the building contribute a lot for the elegance. Taj Mahal is
an example famous for its elegance.
4. Flexibility: This aspect of planning means a room designed for a specific
purpose should be possible to use for other purposes, if necessary. A study
room may be planned for using as a guest room.
If partition is provided between living room and dining room, it is possible to
remove partition and use living room plus dining room for the family
functions. If independent access is given to backyard from kitchen,
backyard can be used for dinner functions. Thus in planning flexibility also
should be considered.
5. Privacy: Planning should take care of privacy of one room from other
room in a building as well as some parts of a building from neighbouring
buildings and from streets. It is ensured by proper grouping of rooms and by
suitably providing doors, windows and ventilators. Planning the entrance at
appropriate position also contributes a lot in providing privacy.
6. Resistance to Fire: It may be noted that concrete and masonry (stone or
brick) have better resistance to fire while steel and wood have lesser
resistance. Hence reduce use of steel and wood in kitchen and bathrooms
with electric heaters.
Kitchen should be so located that if fire is caught it is directed away from
the building by the wind rather than towards the building. In public
4 LAKIREDDY BALI REDDY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
Basic Civil Engineering A.Y 2022-2023
buildings and assembly halls stair cases should be easily accessible and
always more than one is provided.
7. Sound Insulation: Noise pollution can be reduced by suitable planning of
the building. Some of them are:
(a) Orienting the building suitably so that rooms are kept away from road
side.
(b) Using hollow blocks for the walls.
(c) Plugging door and window openings tightly.
(d) Using false ceilings.
(e) By fixing water closet cisterns on outer walls instead on wall common to
rooms.
(f) By fixing water closet pan on a thin pad.
(g) Holding pipes passing through walls and floors by insulated clips.
8. Protection from Termite: Building should be protected from termite
attack by (a) Treating the foundation with chemicals at the time of
construction.
(b) Using well seasoned and well treated wood in the building.
9. Security against Burglary: By providing thicker walls, using stronger
doors and windows in outer walls, security against burgling is improved.
Providing grills to windows and additional shutters to doors are some of the
methods of improving security. Alarms fitted in walls, roofs also improve
security of the buildings.
10. Economy: Economy without sacrificing comfort, conveniences and
durability is another basic principle of planning a building. For this
circulation area should be minimised. Materials should be so selected that
maintenance cost is minimized.
11. Provision for Future Expansion: Building should be planned making
suitable provision for future expansion. Some of the steps required for it are:
(a) Improving elevations without dismantling any part during future
expansion.
(b) Extending building horizontally or vertically without damaging the
existing building.
(c) Improving the flooring.
5 LAKIREDDY BALI REDDY COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
You might also like
- Building PlanningDocument5 pagesBuilding PlanningRavi MalikNo ratings yet
- Part A - Conceptual DesignDocument11 pagesPart A - Conceptual DesignRohan ShreshthiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23Document7 pagesChapter 23Govind Shriram ChhawsariaNo ratings yet
- Principles of PlanningDocument26 pagesPrinciples of PlanningNitin RaoNo ratings yet
- BPD Module IDocument70 pagesBPD Module ISyed Fahad AliNo ratings yet
- Structural Planning and Design of ThreeDocument92 pagesStructural Planning and Design of ThreefrancisNo ratings yet
- Structural Planning and Design of Three Storey Building: November 2012Document93 pagesStructural Planning and Design of Three Storey Building: November 2012Brian Masogoyi NNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Functional Planning of BuildingsDocument17 pagesChapter-2 Functional Planning of BuildingsSileshi AzagewNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Functional Planning of BuildingsDocument17 pagesChapter-2 Functional Planning of BuildingsAbel MulugetaNo ratings yet
- Orientation of BuildingsDocument6 pagesOrientation of BuildingsStudio AsBm100% (1)
- Green BuildingsDocument15 pagesGreen BuildingsprashmceNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 - Space Planning Part 1..Document29 pagesMODULE 6 - Space Planning Part 1..Rod VincentNo ratings yet
- CivilMinorProject New PDFDocument93 pagesCivilMinorProject New PDFRuellynne Barberan BonifacioNo ratings yet
- C - E - D by AssignmentDocument12 pagesC - E - D by AssignmentAbhyudayaPrakashNo ratings yet
- Unit1.Plng& AC070814Document103 pagesUnit1.Plng& AC070814Ajay Kumar koreNo ratings yet
- Unit V Building Planning NotesDocument10 pagesUnit V Building Planning NotesCh VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Cad Report 123Document6 pagesCad Report 123Hitesh HiremathNo ratings yet
- Basic Elements of Planning: StructureDocument24 pagesBasic Elements of Planning: StructuregoodprangyaNo ratings yet
- Planning and Functional Design - Lect1Document28 pagesPlanning and Functional Design - Lect1Vanessa FernandesNo ratings yet
- Principles of Building PlanningDocument44 pagesPrinciples of Building PlanningSantosh Kumar MNo ratings yet
- Inroduction 11Document21 pagesInroduction 11Hidayah NathangcopNo ratings yet
- Building Maintenance and RepairDocument5 pagesBuilding Maintenance and RepairFariba Samia OmiNo ratings yet
- Paper On False Ceiling-LibreDocument16 pagesPaper On False Ceiling-LibreIrumbu StalinNo ratings yet
- Special Purpose Spaces and Public InteriorsDocument38 pagesSpecial Purpose Spaces and Public InteriorsTrip BuilderNo ratings yet
- INRODUCTIONDocument22 pagesINRODUCTIONHidayah NathangcopNo ratings yet
- BPCAD Unit 4 NotesDocument28 pagesBPCAD Unit 4 NotesMeneme Marege AyechalemeNo ratings yet
- 10 Rakesh KumbhareDocument5 pages10 Rakesh Kumbharevenkatesh gidijalaNo ratings yet
- Gibberd2 2009Document7 pagesGibberd2 2009sriramabgNo ratings yet
- BQS 207 POWER POINT - Week 1,2,3,4 Introduction, Windows, DoorsDocument18 pagesBQS 207 POWER POINT - Week 1,2,3,4 Introduction, Windows, DoorsZechariah OburuNo ratings yet
- SR SIR Building Planning PDFDocument6 pagesSR SIR Building Planning PDFSIDDHARTHA MAITYNo ratings yet
- 1 - Orientation of BuildingDocument31 pages1 - Orientation of BuildingM Bilal Zahid100% (1)
- Energy Efficient Design Strategies in Hot-Dry AreaDocument22 pagesEnergy Efficient Design Strategies in Hot-Dry AreaKapil AroraNo ratings yet
- False CeilingDocument9 pagesFalse CeilingNilesh ThanviNo ratings yet
- Basic Requirements of A BuildingDocument1 pageBasic Requirements of A BuildingsheffyNo ratings yet
- Planning of BuildingDocument11 pagesPlanning of BuildingVasant DhawaleNo ratings yet
- Building Planning and EstimatesDocument32 pagesBuilding Planning and EstimatesMary Hope QuimpanNo ratings yet
- CE013 - Plate 2 - Floor PlanDocument3 pagesCE013 - Plate 2 - Floor PlanKaty Perry100% (1)
- Eco-Friendly Green Modular HomeDocument4 pagesEco-Friendly Green Modular HomeKarenlee LeeNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 3Document38 pagesActivity No. 3marcusluismacusiNo ratings yet
- Ct111l - Topic 3 - Learning-ModuleDocument9 pagesCt111l - Topic 3 - Learning-ModuleSimon Rei EstacioNo ratings yet
- Elevation DesignDocument132 pagesElevation DesignpvamshiNo ratings yet
- Design ToolsDocument7 pagesDesign ToolsKevin Acosta100% (1)
- E3 ShelterDocument17 pagesE3 ShelterChhotuNo ratings yet
- For Architectural Dissertation Project On: SynopsisDocument7 pagesFor Architectural Dissertation Project On: SynopsisPratik PatidarNo ratings yet
- Building Construction: Ayub A. Mirza MSC in Civil and Environmental EngineeringDocument31 pagesBuilding Construction: Ayub A. Mirza MSC in Civil and Environmental EngineeringAmmar MedeniNo ratings yet
- LD44 - 2502009684 - Kadek Ayu Mustika DewiDocument7 pagesLD44 - 2502009684 - Kadek Ayu Mustika DewiMstka DwNo ratings yet
- A PROJECT On G 5 Buildings EngineeringcivilDocument37 pagesA PROJECT On G 5 Buildings Engineeringcivilpankaj sahuNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil Mod2Document29 pagesBasic Civil Mod2veenau 1No ratings yet
- Ad124 Planning ConsiderationDocument24 pagesAd124 Planning ConsiderationSheil RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Drawing2-Unit-3-Module First YearDocument22 pagesDrawing2-Unit-3-Module First YearJN AnoreNo ratings yet
- Cost Effective Building Techniques ArchitectureDocument13 pagesCost Effective Building Techniques Architecturekit sparkNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Dimension of HousingDocument25 pagesLecture 2 - Dimension of HousingLuv SinghNo ratings yet
- M.Arch. GREEN BUILDING STRATEGIES CHECKLISTDocument166 pagesM.Arch. GREEN BUILDING STRATEGIES CHECKLISTRuqayya AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document17 pagesLecture 8qtyzyvx7znNo ratings yet
- A PROJECT ON g+5 BuildingsDocument36 pagesA PROJECT ON g+5 BuildingsVishakha PatelNo ratings yet
- Theory 2Document5 pagesTheory 2Camille CiokonNo ratings yet
- Aakriti ShantiniketanDocument31 pagesAakriti ShantiniketanDeepika Darkhorse ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Renovation: Strategies for Commercial Building Systems and EnvelopeFrom EverandSustainable Renovation: Strategies for Commercial Building Systems and EnvelopeNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Natural Ventilation Design: A Component in Creating Leed ApplicationFrom EverandA Guide to Natural Ventilation Design: A Component in Creating Leed ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Vacation Homes and Log CabinsFrom EverandVacation Homes and Log CabinsRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Kansai Structur PDFDocument29 pagesKansai Structur PDFsantoso100% (1)
- Unit-Ii: Timber: Building Construction - VDocument71 pagesUnit-Ii: Timber: Building Construction - VKittur AkshayNo ratings yet
- Tools at HeightDocument32 pagesTools at Heightkwakwa4No ratings yet
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Activity 2.0 - V2Document2 pagesWork Breakdown Structure (WBS) Activity 2.0 - V2Engr Benalito A Catap IIINo ratings yet
- Irrigation Well EstimateDocument7 pagesIrrigation Well Estimatesantosh.manojNo ratings yet
- Method Statement & Risk Assesment For Flooring WorksDocument6 pagesMethod Statement & Risk Assesment For Flooring Workschandanprakash3033% (3)
- Operator's Manual LATHE LeblondDocument97 pagesOperator's Manual LATHE LeblondS280RILEY75% (4)
- Bujes y Manguitos BrowningDocument8 pagesBujes y Manguitos BrowningFranco Sanchez QuirogaNo ratings yet
- Project Challenges at T2 - Mumbai International Airport Part 1 of 2Document5 pagesProject Challenges at T2 - Mumbai International Airport Part 1 of 2Mohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Catalogue BONDORDocument28 pagesCatalogue BONDORbrot tamaNo ratings yet
- Aslan 100 - GFRP - Rebar - FlyerDocument4 pagesAslan 100 - GFRP - Rebar - FlyerBogdanBNo ratings yet
- Lifting Equipment Thorough Examination Register: Almansoori Inspection ServicesDocument2 pagesLifting Equipment Thorough Examination Register: Almansoori Inspection ServicesMohamed YasirNo ratings yet
- Direction: Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer: Summative Test in Tle 8 (Eim Exploratory)Document2 pagesDirection: Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer: Summative Test in Tle 8 (Eim Exploratory)Detablan MariaNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument10 pagesProject ProposalPrincessNo ratings yet
- Shard Place: Exterior ExteriorDocument1 pageShard Place: Exterior ExteriorfereetNo ratings yet
- China Civil Engineering Construction Corperation: Repair Welding Procedure Qualification-Manual Metal ArcDocument1 pageChina Civil Engineering Construction Corperation: Repair Welding Procedure Qualification-Manual Metal ArcMakamu Max Las MokgaoganyiNo ratings yet
- Simplified Reinforced Concrete Design 2010 NSCPDocument207 pagesSimplified Reinforced Concrete Design 2010 NSCPjay-ar barangayNo ratings yet
- 9869 0014 01b Unigrout Flex S and Flex M Technical Specification EnglishDocument5 pages9869 0014 01b Unigrout Flex S and Flex M Technical Specification Englishignacio.garcia11No ratings yet
- 5th Sem Civil Engineering SyllabusDocument87 pages5th Sem Civil Engineering SyllabusPradyum ChavhanNo ratings yet
- Instruction Handbook: Sealing 16KA and 26KA For Pumps Type 1610, 1611, 2610, 2611Document10 pagesInstruction Handbook: Sealing 16KA and 26KA For Pumps Type 1610, 1611, 2610, 2611Dolores FuertesNo ratings yet
- ASTM C1202 12: Standard Test Method For Electrical Indication of Concrete's Ability To Resist Chloride Ion PenetrationDocument5 pagesASTM C1202 12: Standard Test Method For Electrical Indication of Concrete's Ability To Resist Chloride Ion Penetrationmunir ali azmiNo ratings yet
- Part 4.4 - CivilDocument334 pagesPart 4.4 - Civilanjas_tsNo ratings yet
- Never Going Back Again Tab TempoDocument3 pagesNever Going Back Again Tab TempoMarzia Panaccione100% (1)
- Experiment 2 KnittingDocument2 pagesExperiment 2 KnittingAvanish YadavNo ratings yet
- 02 01 Byg ClassicDocument204 pages02 01 Byg ClassicEscuela EntrenamientoNo ratings yet
- SPLE303 - Reinforced Concrete Design 5Document1 pageSPLE303 - Reinforced Concrete Design 5John BernalteNo ratings yet
- Geology and Civil Engineering RelationshipDocument2 pagesGeology and Civil Engineering RelationshipCHAEYOUNG-AH MARR MENo ratings yet
- 4651 4 PDFDocument10 pages4651 4 PDFdeshpande KingNo ratings yet
- BQ - SewerageDocument3 pagesBQ - SewerageZak HeroNo ratings yet
- Studies On Recycled Aggregates-Based Concrete: Major Rakshvir Sudhirkumar V. BaraiDocument9 pagesStudies On Recycled Aggregates-Based Concrete: Major Rakshvir Sudhirkumar V. BaraijuigaykeNo ratings yet