Professional Documents
Culture Documents
REVIEWER Phy Sci
REVIEWER Phy Sci
Uploaded by
Yvonne De Venecia MalicdemCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
REVIEWER Phy Sci
REVIEWER Phy Sci
Uploaded by
Yvonne De Venecia MalicdemCopyright:
Available Formats
REVIEWER (PHYSICAL SCIENCE)
Bigbang Theory- the leading explanation for how the universe began. Simply put, it says the universe as
we know it started with an infinitely hot and dense single point that inflated and stretched — first at
unimaginable speeds, and then at a more measurable rate — over the next 13.7 billion years to the still-
expanding cosmos that we know today.
Nuclear Fussion- formation of heavier elements during star formation
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star undergoes a sequence of radical changes during its
lifetime.
Low-mass star- Main sequence star> protostar> red giant> white dwarf
High-mass star- Main sequence star> red super giant> supernova> neutron star or black hole
Atomic number= No. of protons and electrons. It led to the synthesis of new elements
Synthesis of new elements is accomplished by bombarding target atoms of heavy elements with ions.
Hydrogen fused into helium, fusion stops, and the pressure in the core decreases.
How to determine polarity- Electronegativity or VESPRY Theory
Intermolecular forces- forces that hold molecules together in a substance
Different macromolecules/biomolecules:
Carbohydrates- for producing energy
Proteins- serve as biochemical catalysts, hormones, enzymes. Peptide bond exist in this macromolecule
Lipids- for storing energy, absorbing vitamins. Contains a glycerol molecule and three fatty acid chains.
Nucleic Acids- storage and expression of genomic information.
Elements may have same IMFA but different boiling points because of Electronegativity
F2 and Cl2 are gases, Br2 is a liquid, and I2 is a solid- They have different intermolecular forces present.
Solid- Strongest IMFA
Intermolecular forces - the forces that hold molecules together in a substance
The sequence of amino acids determines the protein's three-dimensional shape and therefore its function
Change in sequence of DNA- altering its structure and function.
New type of lipid molecule- It may alter the fluidity of the membrane, affecting the cell's ability to transport
molecules.
Lipids are hydrophobic, while carbohydrates are hydrophilic
Collision Theory- Colliding with one another
Concentration- amount of substance per unit volume
temperature increase= increasing the kinetic energy of molecules
Exothermic reaction- Energy absorbed is less than the energy released. Hence, heat of reaction is
negative
Catalyst- speeds up a chemical reaction.
Coal- Fossil fuel
Fossil fuels have a higher environmental impact than renewable sources of energy.
Hydropower- An energy from falling or fast-running water
Solar cells- directly converting the light energy of the sun into electrical energy.
Ammonia- active ingredient in most glass cleaners
alcohol kill microorganisms- By denaturing the proteins of microorganisms.
The additives enhance the product
Oil spill in tiles- best cleaning agent is detergent
Ph level below 7- acidic Ph level above 7- basic
the function of citric acid- To act as a disinfectant
use of bleach- Whitening agent
use of baking soda- To remove stains and odors
function of surfactants- To remove dirt and oil
You might also like
- Origin of ElementsDocument27 pagesOrigin of ElementsJoanna Ruth SeproNo ratings yet
- What's the Difference Between Fission and Fusion? | Children's Physics of EnergyFrom EverandWhat's the Difference Between Fission and Fusion? | Children's Physics of EnergyNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Perfect Answer Revision Guide CIE IGCSE Co Ordinated SciencesDocument96 pagesThe Perfect Answer Revision Guide CIE IGCSE Co Ordinated SciencesJun Woo Yang100% (1)
- Cambridge Secondary Checkpoint - Science (1113) April 2019 Paper 2 Mark SchemeDocument14 pagesCambridge Secondary Checkpoint - Science (1113) April 2019 Paper 2 Mark SchemeImmanuel Suman Shiju82% (11)
- Hair & Hair Care ProductsDocument32 pagesHair & Hair Care ProductsAG STXLEZNo ratings yet
- Analytic Rubric For Grading Role Play of Earthquake DrillDocument2 pagesAnalytic Rubric For Grading Role Play of Earthquake DrillYvonne De Venecia Malicdem100% (1)
- BiochemistryDocument22 pagesBiochemistryChia JoseNo ratings yet
- Nu Cleo SynthesisDocument22 pagesNu Cleo SynthesisRaden Dave BaliquidNo ratings yet
- Hacking The Universe: Deepak Soman. Dinoop P.Malayil, Achu BDocument14 pagesHacking The Universe: Deepak Soman. Dinoop P.Malayil, Achu BDeepak Soman100% (1)
- Acp Module 5Document32 pagesAcp Module 5Mechel Cabaltera87% (15)
- Science 113 - Laboratory Course Guide in BiochemistryDocument3 pagesScience 113 - Laboratory Course Guide in BiochemistryYvonne De Venecia Malicdem100% (1)
- Science Week 1 - Origin of The Elements: 2 SemesterDocument8 pagesScience Week 1 - Origin of The Elements: 2 SemesterBOBBY AND KATESNo ratings yet
- Daniel, Reyden R. Abm 11 Sy Reviewer in Physical ScienceDocument23 pagesDaniel, Reyden R. Abm 11 Sy Reviewer in Physical ScienceREYNIEL ANGELIE DANIELNo ratings yet
- Phy ScqiDocument7 pagesPhy ScqifaminialjadenNo ratings yet
- Science Project Lesson 1 3Document12 pagesScience Project Lesson 1 3Mhie RecioNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Gen Science)Document3 pagesReviewer (Gen Science)Sophia LantinNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (PHYSICAL SCIENCE)Document9 pagesReviewer (PHYSICAL SCIENCE)Alexis Joy P. DangoNo ratings yet
- PS ReviewerDocument3 pagesPS ReviewerIt’s yanaNo ratings yet
- The Importance of The Formation of Light ElementsDocument2 pagesThe Importance of The Formation of Light ElementsAnnie BlanquezaNo ratings yet
- NUCLEAR FUSION 1-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesNUCLEAR FUSION 1-WPS OfficeHarshit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Physical ScienceDocument6 pagesReviewer in Physical SciencemkfolaesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document7 pagesChemistry 2Marie Angelie KilarioNo ratings yet
- AP Bio CHDocument3 pagesAP Bio CHlinuspauling101No ratings yet
- Physical ScienceeeeDocument8 pagesPhysical ScienceeeeHanna Rea UrpianaNo ratings yet
- Dayrit, Geoffrey C. Abm 11-B - Activity 1Document2 pagesDayrit, Geoffrey C. Abm 11-B - Activity 1Accounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 2021 2022 G8 Module 1 Q3 2023 2024Document3 pagesGRADE 8 2021 2022 G8 Module 1 Q3 2023 2024chartreusevermilionNo ratings yet
- Science 8 5Document9 pagesScience 8 5Hannah Leigh CoronelNo ratings yet
- P EcoDocument17 pagesP EcoCllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- 3 Bio ChemistryDocument7 pages3 Bio ChemistryartichokeyNo ratings yet
- q1 Reviewer in Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesq1 Reviewer in Physical ScienceDiane CabasogNo ratings yet
- Physical SciencepspsDocument8 pagesPhysical SciencepspsRose Adelweiz TauthoNo ratings yet
- Ma. Eloisa R. Jurilla: Humss X1 - ADocument44 pagesMa. Eloisa R. Jurilla: Humss X1 - AcatrinaNo ratings yet
- Energy Transformations Science Review: When Studying For This Portion of The Test, Be Sure To Review The FollowingDocument4 pagesEnergy Transformations Science Review: When Studying For This Portion of The Test, Be Sure To Review The FollowingsherryjasminNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument111 pagesEnergyDevi Prasad MNo ratings yet
- Physci ReviewerDocument7 pagesPhysci ReviewerYnah EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- SCI02-Prelims The Big Bang Theory & NucleosynthesisDocument12 pagesSCI02-Prelims The Big Bang Theory & NucleosynthesisMORAN DianaNo ratings yet
- Rebyuwer Sa Asignaturang AghamDocument5 pagesRebyuwer Sa Asignaturang AghamjoshuaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 2Document2 pagesReviewer 2Claudine RuckaberleNo ratings yet
- ENERGY CHANGES AND RATES OF REACTIONS FimalDocument11 pagesENERGY CHANGES AND RATES OF REACTIONS FimalIsaacNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 2Document6 pagesModule 1 Lesson 2MARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 1Document4 pagesChemistry Unit 1kicsirekaNo ratings yet
- Gse Explanation 7 To 10Document15 pagesGse Explanation 7 To 10Nayan PaulNo ratings yet
- APES Units 1 & 2: Abiotic and Biotic Parts of EcosystemsDocument115 pagesAPES Units 1 & 2: Abiotic and Biotic Parts of EcosystemsJulisa HenryNo ratings yet
- Scientific Definitions For Malaysia Form 3 Science Syllabus: ShortDocument5 pagesScientific Definitions For Malaysia Form 3 Science Syllabus: ShortNg Juen ShengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Structure of The Atom: Prepared by MHS 2009Document10 pagesChapter 2: The Structure of The Atom: Prepared by MHS 2009AceNo ratings yet
- PHYSCIDocument8 pagesPHYSCIMharc PerezNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Inorganic ChemistryDocument5 pagesReviewer in Inorganic ChemistryPrincess Aleia SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Fission vs. Fusion - What's The Difference?Document10 pagesFission vs. Fusion - What's The Difference?WaJaHaT ALINo ratings yet
- Chemistry Component NotesDocument24 pagesChemistry Component NotescptilaonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument28 pagesUntitledDana MikaelaNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument36 pagesScience NotesYippiyippi Lala100% (1)
- Written ReportDocument6 pagesWritten ReportDiane NabolNo ratings yet
- Es Module 2Document4 pagesEs Module 2Chelsie ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument27 pagesChemistry NotesBbg FeeruwuNo ratings yet
- By MUHAMMAD ILYAS Teacher Gorikote LRS & Javed Iqbal PDT Aku-Ied, PDCN For Edip Project of Aus-AidDocument14 pagesBy MUHAMMAD ILYAS Teacher Gorikote LRS & Javed Iqbal PDT Aku-Ied, PDCN For Edip Project of Aus-AidDijith JhansiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2ahmedbarre14300No ratings yet
- Nuclear FusionDocument6 pagesNuclear FusionmokshNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Eportfolio Name: Oleta, Cristinejoy Section: AccentureDocument33 pagesPhysical Science: Eportfolio Name: Oleta, Cristinejoy Section: AccentureCristinejoy OletaNo ratings yet
- The-Formation-of-Heavier-Elements-during-Star-Formation (New)Document90 pagesThe-Formation-of-Heavier-Elements-during-Star-Formation (New)gerymeaquino37No ratings yet
- Form 4 Add Science (NOTES)Document18 pagesForm 4 Add Science (NOTES)SherilynTeohNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument6 pagesScienceYomna OmerNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - Merged - MergedDocument71 pagesMODULE 1 - Merged - MergedSean Darrell TungcolNo ratings yet
- Geochemical Reactions: Eochemistry and Water QualityDocument50 pagesGeochemical Reactions: Eochemistry and Water QualityRyan BolingNo ratings yet
- 3rdQ Physical Science ReviewerDocument4 pages3rdQ Physical Science ReviewerDesiree Tenorio VillezaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 1Document25 pagesPhysical Science 1EJ RamosNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotesAlaiza PandaNo ratings yet
- TOS-PHYSICAL SCIENCE-3rd-QUARTERDocument3 pagesTOS-PHYSICAL SCIENCE-3rd-QUARTERYvonne De Venecia MalicdemNo ratings yet
- ProfEd107 - Activity 1-Malicdem YZDocument1 pageProfEd107 - Activity 1-Malicdem YZYvonne De Venecia MalicdemNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Content To Learning Outcomes Name: Yvonne Zarah DV. Malicdem Schedule: 3:00-4:00 PM Program: BSED ScienceDocument1 pageActivity 1: Content To Learning Outcomes Name: Yvonne Zarah DV. Malicdem Schedule: 3:00-4:00 PM Program: BSED ScienceYvonne De Venecia MalicdemNo ratings yet
- ProfEd107 - Activity 1-Malicdem YZDocument1 pageProfEd107 - Activity 1-Malicdem YZYvonne De Venecia MalicdemNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Content To Learning Outcomes Name: Yvonne Zarah DV. Malicdem Schedule: 3:00-4:00 PM Program: BSED ScienceDocument1 pageActivity 1: Content To Learning Outcomes Name: Yvonne Zarah DV. Malicdem Schedule: 3:00-4:00 PM Program: BSED ScienceYvonne De Venecia MalicdemNo ratings yet
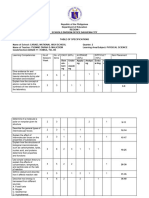
- Activity 5: Test of Specifications (Tos) Name: Schedule: ProgramDocument2 pagesActivity 5: Test of Specifications (Tos) Name: Schedule: ProgramYvonne De Venecia MalicdemNo ratings yet
- 107 - Activity 1 YzmDocument1 page107 - Activity 1 YzmYvonne De Venecia MalicdemNo ratings yet
- DBL 5818Document48 pagesDBL 5818Marko SamardžićNo ratings yet
- Lec 6C Alkyne Structure and ReactivityDocument37 pagesLec 6C Alkyne Structure and Reactivityseanroi.villas.lawNo ratings yet
- A Study On Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Fiber RDocument8 pagesA Study On Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Fiber RRachapalli AnjaliNo ratings yet
- 5FINAL Institutional Assessment Instruments 2Document8 pages5FINAL Institutional Assessment Instruments 2MAE ANN MAGDADARONo ratings yet
- Creative Free PowerPoint Template by PowerPoint SchoolDocument4 pagesCreative Free PowerPoint Template by PowerPoint SchoolLuke Gichimi CalatonNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document2 pagesProblem Set 1googley71No ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument20 pagesRedox ReactionsChavi PundirNo ratings yet
- Practical Research - TitlesDocument18 pagesPractical Research - TitlesBridget Anne BenitezNo ratings yet
- 3 Lec Notes Sterilization and DisinfectionDocument4 pages3 Lec Notes Sterilization and DisinfectionMacky IbayNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 - Polymers AnswersDocument4 pagesTutorial 2 - Polymers AnswersJoserineNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Acid Number According To ASTM D664, and IP 177 and The Base Number According To ISO 3771 in Fresh Motor OilDocument2 pagesDetermination of The Acid Number According To ASTM D664, and IP 177 and The Base Number According To ISO 3771 in Fresh Motor OilArath Leon ReyNo ratings yet
- GPML PresentationDocument18 pagesGPML PresentationHarindu VyasNo ratings yet
- ResAP (89) 1E Uso de Colorantes Metales y MetaloidesDocument6 pagesResAP (89) 1E Uso de Colorantes Metales y MetaloidesarceppNo ratings yet
- (Welding) ANSI-AWS Standard A5.5-96 Specification For Low-Alloy Steel Electrodes For Shielded Metal Arc Welding (Ebook, 55 Pages)Document55 pages(Welding) ANSI-AWS Standard A5.5-96 Specification For Low-Alloy Steel Electrodes For Shielded Metal Arc Welding (Ebook, 55 Pages)hammadNo ratings yet
- Krystaline Add (English)Document3 pagesKrystaline Add (English)José Luis CampelloNo ratings yet
- Matter How Are Materials Classified?: WMSU-ISMP-GU-001.00 Effective Date: 7-DEC-2016Document6 pagesMatter How Are Materials Classified?: WMSU-ISMP-GU-001.00 Effective Date: 7-DEC-2016Joycee DhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Directions: Choose The Letter That Corresponds To The CorrectDocument20 pagesChemistry: Directions: Choose The Letter That Corresponds To The CorrectJiwul Skie BalcitaNo ratings yet
- Reflections AcrylicDocument49 pagesReflections AcrylicananthNo ratings yet
- Field Operator ViralDocument5 pagesField Operator ViralGodwin GodwinNo ratings yet
- Application of Non-Conventional Extraction Methods: Toward A Sustainable and Green Production of Valuable Compounds From MushroomsDocument21 pagesApplication of Non-Conventional Extraction Methods: Toward A Sustainable and Green Production of Valuable Compounds From MushroomsNELSON ANDRES PINEDA CUBURUCONo ratings yet
- Team 6 Current Developments in Binder JettingDocument14 pagesTeam 6 Current Developments in Binder JettingShahzaib ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Research 1-5Document23 pagesGroup 5 Research 1-5Lone KnightNo ratings yet
- Nadca White Paper On Chemical Applications in Hvac Systems 0Document11 pagesNadca White Paper On Chemical Applications in Hvac Systems 0Luis RodasNo ratings yet
- Slaters RuleDocument2 pagesSlaters RulelubaajamesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Pharmacology Dr. Noor Al HasaniDocument10 pagesLecture 14 Pharmacology Dr. Noor Al Hasaniعلي الاسديNo ratings yet