Professional Documents
Culture Documents
W6las 4
W6las 4
Uploaded by
Cris AlcalaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
W6las 4
W6las 4
Uploaded by
Cris AlcalaCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: ___________________________________________Grade & Section: _________________
Subject: Mathematics 9 Teacher: _______________________________ Score: ______________
Lesson : Quarter 4 Week 6 LAS 4
Activity Title : SSA Case
Learning Target : Solving Oblique Triangles Involving Two Sides and an Angle Opposite One of
Them
Reference(s) : Module 2 – Triangle Trigonometry. Ease Module. Department of Education.
LAS Writer : Ronel S. Besonia, TII
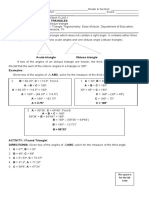
Another case of oblique triangle that can be solved using the law of sines involves two sides
and an angle opposite one of them.
Examples:
The given parts and the unknown parts are shown in the figures:
1. b = 15, a = 20, A = 80o25’ C
15 20
80o25’
A c B
To solve for B: To solve for C: To solve for c:
𝒂 𝒃 A + B + C = 180o 𝒂 𝒄
= =
sin 𝑨 sin 𝑩 sin 𝑨 sin 𝑪
80o25’ + 47o41’ + C = 180
𝒃 sin 𝑨 𝒂 sin 𝑪
sin 𝑩 = 𝒄=
𝒂 C = 180o – (80o25’ + 47o41’) sin 𝑨
15 sin 80°25′ C = 180o – 128o6’ 20 sin 51°54’
sin 𝑩 = 𝒄=
20 sin 80°25’
C = 51o54’ 20 (0.78694)
15 (0.98604)
sin 𝑩 = 𝒄=
20 (0.98604)
sin 𝑩 = 0.73953 𝒄 = 𝟏𝟓. 𝟗𝟔
𝑩 = 𝐴𝑟𝑐𝑠𝑖𝑛 (0.73953)
𝑩 = 𝟒𝟕°𝟒𝟏′𝟐𝟗′′
ACTIVITY: Lean On Triangle
DIRECTION/S: Solve triangle ABC described by the given parts.
1. a = 12, b = 18, B = 45o
2. b = 20, c = 32, B = 24o
3. a = 2.5, c = 5.2, C = 79o
4. a = 9, b = 14.4, B = 37.8o
5. b = 0.751, c = 1 B, C = 32o45’
This space is
for the QR
Code
You might also like
- TrigonometryDocument10 pagesTrigonometryviddusagarNo ratings yet
- Mastering PHP 7Document7 pagesMastering PHP 7timi_pek33% (3)
- Amc8 V5Document181 pagesAmc8 V5Shuai ChenNo ratings yet
- Mono Point Bendix - Renault 19Document98 pagesMono Point Bendix - Renault 19Ivan Alilovic100% (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Trigonometry PresentationDocument24 pagesTrigonometry Presentationitsankurz100% (2)
- Geometry Lesson 2 PolygonsDocument5 pagesGeometry Lesson 2 PolygonsNagy ElrahebNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Gianne Denise C. Dueñas IV-VanadiumDocument24 pagesSubmitted By: Gianne Denise C. Dueñas IV-VanadiumalyssajeanneNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Math Chapter 3 Understanding QuadrilateralsDocument44 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Math Chapter 3 Understanding QuadrilateralssdevanNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument30 pagesTrigonometrySour PlumNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Triangle Sum TheoremDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in Triangle Sum TheoremRashie Paño100% (1)
- W6las 3Document1 pageW6las 3Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- W6las 2Document1 pageW6las 2Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- This Space Is For The QR CodeDocument2 pagesThis Space Is For The QR CodeJessa Lou Liba CapapasNo ratings yet
- Algebra and Trigonometry 8th Edition Aufmann Solutions ManualDocument66 pagesAlgebra and Trigonometry 8th Edition Aufmann Solutions Manualrebeccagomezearndpsjkc100% (37)
- PolygonDocument46 pagesPolygonsheykrizzleNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - Angle Sum PropertyDocument20 pagesLESSON 2 - Angle Sum PropertyshamsmolNo ratings yet
- PolygonsDocument8 pagesPolygonsmuralleNo ratings yet
- Sine, Cosine, and Solving Oblique Triangles (More Examples)Document34 pagesSine, Cosine, and Solving Oblique Triangles (More Examples)BEVERLY DOMINGONo ratings yet
- Algebra and Trigonometry 8th Edition Aufmann Solutions Manual 1Document124 pagesAlgebra and Trigonometry 8th Edition Aufmann Solutions Manual 1ivelisse100% (37)
- Algebra and Trigonometry 8th Edition Aufmann Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesAlgebra and Trigonometry 8th Edition Aufmann Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmatthewjordankwnajrxems100% (11)
- Circular Measures PDFDocument11 pagesCircular Measures PDFpizamNo ratings yet
- Examples:: This Space Is For The QR CodeDocument1 pageExamples:: This Space Is For The QR CodeJessa Lou Liba CapapasNo ratings yet
- A Mathematics Powerpoint by Eric ZhaoDocument24 pagesA Mathematics Powerpoint by Eric ZhaomousypusaNo ratings yet
- A Mathematics Powerpoint by Eric ZhaoDocument24 pagesA Mathematics Powerpoint by Eric ZhaoculesricNo ratings yet
- Triangle Trigonometry: What This Module Is AboutDocument25 pagesTriangle Trigonometry: What This Module Is AboutisayblankNo ratings yet
- g11 6 TrigonometryDocument73 pagesg11 6 Trigonometryapi-235269401No ratings yet
- Las Math9 Q4 W6Document7 pagesLas Math9 Q4 W6Maxene Angelie RabanalNo ratings yet
- Sol 0139Document20 pagesSol 0139ebrahimipour1360No ratings yet
- Ircham Badrus Rahmadani - Tugas 1Document8 pagesIrcham Badrus Rahmadani - Tugas 1Bahru RoziNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry ComparisonDocument7 pagesTrigonometry ComparisonDwi PPNo ratings yet
- This Tutorial Will Cover Everything You Need To Know About Geometry For The GMATDocument82 pagesThis Tutorial Will Cover Everything You Need To Know About Geometry For The GMATzubishuNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Solving Equations: The General SolutionDocument1 page4.4 Solving Equations: The General SolutionreacharunkNo ratings yet
- PolygonsDocument7 pagesPolygonsMuralee VeeramalaiNo ratings yet
- Solutions Class 7Document6 pagesSolutions Class 7virajNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Module No. 1: Week 1: 3rd Quarter: S0Lving Right TrianglesDocument4 pagesTrigonometry Module No. 1: Week 1: 3rd Quarter: S0Lving Right TrianglesCat PusaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 QuadrilateralsDocument4 pagesChapter 15 QuadrilateralsscihimaNo ratings yet
- Aturan Sin Dan CosDocument7 pagesAturan Sin Dan CosRico MartenstyaroNo ratings yet
- Geometria CompletoDocument15 pagesGeometria CompletoMiguel Angel Chavarria CaldasNo ratings yet
- PRE-cal 1Document46 pagesPRE-cal 1Pat G.No ratings yet
- The Law of Sines PDFDocument5 pagesThe Law of Sines PDFMobeen YaseenNo ratings yet
- (M) Trigonometric RatioDocument31 pages(M) Trigonometric RatioSocial Credits Positive Million AspirantNo ratings yet
- Trigo Module 5Document7 pagesTrigo Module 5Princess Loraine DuyagNo ratings yet
- INTROMATH moduleWEEk-67Document6 pagesINTROMATH moduleWEEk-67REIANA MITZI M. FernandezNo ratings yet
- 1 - Trigonometric Ratio (2012)Document32 pages1 - Trigonometric Ratio (2012)Anonymous FckLmgFyNo ratings yet
- SEMI DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN MATHEMATICS Law of CosineDocument7 pagesSEMI DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN MATHEMATICS Law of CosineDNiel Gonzales BautistaNo ratings yet
- GRADE-10 TrigonometryDocument14 pagesGRADE-10 TrigonometryjulianqophisoNo ratings yet
- 7th MathsDocument6 pages7th MathsAli SufianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Trigonometry - ExerciseDocument48 pagesChapter 9 - Trigonometry - ExercisePavithiran Yogarajah100% (1)
- EGAR - ME 66 Activity 1Document2 pagesEGAR - ME 66 Activity 1Narfred EgarNo ratings yet
- 042 Trigonometry ReviewDocument6 pages042 Trigonometry Reviewefua.dhrNo ratings yet
- Taller Velocidad Relativa Mateo Usuga UDocument16 pagesTaller Velocidad Relativa Mateo Usuga UMateo Usuga UsugaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 37 Angles and Triangles: EXERCISE 152 Page 412Document19 pagesChapter 37 Angles and Triangles: EXERCISE 152 Page 412TABAR TikalongNo ratings yet
- UEM Sol To Exerc Chap 037Document19 pagesUEM Sol To Exerc Chap 037TABAR TikalongNo ratings yet
- 8 Circular MeasuresDocument10 pages8 Circular MeasuresanisahanuarNo ratings yet
- TG 36º X 29,06 AB 41,92 X A : Solución X 40 Solución C 115,69 B 50 A 14,31 20 (17) 2 (0.2471)Document6 pagesTG 36º X 29,06 AB 41,92 X A : Solución X 40 Solución C 115,69 B 50 A 14,31 20 (17) 2 (0.2471)Juan Carlos Pérez PérezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationPromit SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: B 90º X Tan x1 XDocument2 pagesTrigonometry: B 90º X Tan x1 XHorror TalesNo ratings yet
- SQPMath10StandardCh 06trigonometryDocument2 pagesSQPMath10StandardCh 06trigonometryHorror TalesNo ratings yet
- Actividad 2.2Document5 pagesActividad 2.2Caroina Gonzalez OrtegaNo ratings yet
- W7las 3Document1 pageW7las 3Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- W6las 2Document1 pageW6las 2Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- M7-Q4-W5 - Las-2Document1 pageM7-Q4-W5 - Las-2Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- M7-Q4-W5 - Las 4Document1 pageM7-Q4-W5 - Las 4Cris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ReadingDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in ReadingCris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Teaching - Guide - Peace EducationDocument2 pagesTeaching - Guide - Peace EducationCris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Catch-Up Fridays Teaching GuideDocument3 pagesCatch-Up Fridays Teaching GuideCris AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Review Paper On Catalytic Converter For Automotive Exhaust EmissionDocument6 pagesReview Paper On Catalytic Converter For Automotive Exhaust Emissionpamela garciaNo ratings yet
- The Relational ModelDocument34 pagesThe Relational Modellouarianedlr17No ratings yet
- Resistance Training Vs Static Stretching Effects.22Document8 pagesResistance Training Vs Static Stretching Effects.22Domenic MicheliNo ratings yet
- Print Hello World #Include #Include Void Main (Printf (" Hello World") Getch )Document30 pagesPrint Hello World #Include #Include Void Main (Printf (" Hello World") Getch )AstitvaTyagiNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: TFT LCD Monitor Model: L500BDocument37 pagesService Manual: TFT LCD Monitor Model: L500BVlade NaumovskiNo ratings yet
- Idle Perf Factor 1706793308Document6 pagesIdle Perf Factor 1706793308marroco13100% (1)
- Secury Module XPSAC5121Document4 pagesSecury Module XPSAC5121juan ochoaNo ratings yet
- LCSI Media Converter ST CMC-U011FST-MM 2kmDocument1 pageLCSI Media Converter ST CMC-U011FST-MM 2kmramyheshmatNo ratings yet
- GCSE Structures and Bonding Summary SheetDocument2 pagesGCSE Structures and Bonding Summary SheetBabalola TomisinNo ratings yet
- UNIT-II - Structuring The Data, Computations and ProgramDocument105 pagesUNIT-II - Structuring The Data, Computations and Programrenu.dandgeNo ratings yet
- OSIsoft Differentiation 20200406Document2 pagesOSIsoft Differentiation 20200406Venkatesh RamanNo ratings yet
- مُثَلَّث: Maslas Meaning in EnglishDocument1 pageمُثَلَّث: Maslas Meaning in EnglishMr Asraf AllyNo ratings yet
- 202005121235123360asheesh-NEWTON RINGDocument4 pages202005121235123360asheesh-NEWTON RINGRakNo ratings yet
- IRFP240: 20A, 200V, 0.180 Ohm, N-Channel Power Mosfet FeaturesDocument7 pagesIRFP240: 20A, 200V, 0.180 Ohm, N-Channel Power Mosfet FeaturesAdah BumboneNo ratings yet
- VTU Final Year Seminar Report FRONT PAGESDocument6 pagesVTU Final Year Seminar Report FRONT PAGESangryprashNo ratings yet
- Swart 2016Document7 pagesSwart 2016TommysNo ratings yet
- Table of IonsDocument2 pagesTable of IonsLucia Jimenez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Note CHP 3 Material Science 281 Uitm Em110Document40 pagesNote CHP 3 Material Science 281 Uitm Em110bino_ryeNo ratings yet
- Dlink Dir-803 RouterDocument6 pagesDlink Dir-803 RouterNajmul Puda PappadamNo ratings yet
- Sine and Cosine Rule: Formul Ae For Right-Angled Triangl EsDocument7 pagesSine and Cosine Rule: Formul Ae For Right-Angled Triangl EsJennifer ElliottNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual DBT 210 PDFDocument19 pagesLab Manual DBT 210 PDFBELAL ALSUBARINo ratings yet
- Sediment Mixtures and Bed Stratigraphy - Jagers - 2012Document33 pagesSediment Mixtures and Bed Stratigraphy - Jagers - 2012javierNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics and Animation Journal 1Document51 pagesComputer Graphics and Animation Journal 1templategamingffNo ratings yet
- Crane Systems: Greer Company Greer Company Greer Company Greer CompanyDocument14 pagesCrane Systems: Greer Company Greer Company Greer Company Greer Companyduongpndng100% (1)
- To Develop Sample Webservice Application Using XfireDocument11 pagesTo Develop Sample Webservice Application Using XfirekaarthikhaNo ratings yet
- Development of Electroless Ni P Coatings On Sisal FiberDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Electroless Ni P Coatings On Sisal FiberHemachandranNo ratings yet
- 12th Round MTech WeblistDocument4 pages12th Round MTech Weblistsm69xdNo ratings yet
- Separador Electromagnetico 2400 EriezDocument4 pagesSeparador Electromagnetico 2400 EriezVictor MoralesNo ratings yet