Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L3 Tissues
L3 Tissues
Uploaded by
qyalmonicar8381valOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L3 Tissues
L3 Tissues
Uploaded by
qyalmonicar8381valCopyright:
Available Formats
TENSES OF VERBS
GE 105
Mr. Ranie Jaen| 1St Semester | BSBio– 1B
S.Y. 2023 – 2024
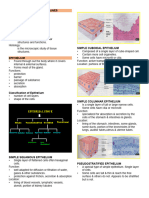
● Cells are arranged in tissues that provide specific function
for the body SIMPLE COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM
● Cells of different tissues are structured differently, which
● Made up of a row of elongated cells
leads to their differences in function.
o Nuclei – all located near the basement
● Tissues of the human body – has 4 major types membrane
o May be ciliated
4 MAJOR TISSUES ● FUNCTION: Protection, Secretion, Absorption
o Protects underlying tissues - Lines the uterus,
stomach, and intestines
o Absorb nutrients
- Intestine – these cells possess microvilli
- Increase the surface area available for
absorption
o Secretes digestive fluids - Mucus-secreting
goblet cells can be found among columnar cells
EPITHELIAL TISSUES
● Widespread throughout the body
o Covers organs, and lines body surfaces
● Anchored to a basement membrane
● Tightly packed cells containing little intercellular material STRATFIED EPITHELIUM
● Generally, lack blood vessels PSEUDOSTRATIFIED EPITHELIUM
o Avascular – “no blood”
● Appear layered; but not truly layered
● Replaced frequently
o Due to varying positions of their nuclei within the
row of cells
SIMPLE EPITHELIUM
● FUNCTION: Secretion and protection
SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM
● Cilia may be present, along with mucus-secreting goblet
● Made up of a single layer of thin, flattened cells cells
o Line and sweep debris from respiratory tubes
● Suited for diffusion
● FUNCTION: Exchange of gases, protection
o exchange of gases in the lungs
o Lines blood and lymph vessels as well as body
cavities
STRATFIED SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM
● Made up of layers of flattened cells
o Designed to protect underlying layers
SIMPLE CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM ● FUNCTION: Protect
● Single layer of cube-shaped cell ● Makes up the outer layer of the skin
o Nuclei – centrally located
● Lines the:
● FUNCTION: Secretion and absorption o Mouth
o Secretion & absorption - Kidneys o Throat
o Secretion – glands o Vagina
o Anal canal
● In the skin, outer layers of the cell undergo keratinization
o Does not occur where tissues remain moist
- Throat, vagina, anal canal
TRANSCRIBED BY: LOVE FRANCHESKA LEGASPI 1
LECTURE 3 | ANAPHY – TISSUES
● Made up of cells designed to produce and secrete
substances into ducts or into body fluids
● FUNCTION: Secretion of fluid (tissues)
o Exocrine – glands that secretes products into
ducts
o Endocrine – glands that secrete into body fluids
and blood
CLASSIFICATION OF GLANDS
STRATFIED CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM ● Classified by the ways they secrete their products
● Consists of three layers of cuboidal cells lining a lumen
of the:
o Mammary glands
o Sweat glands
o Salivary glands
o Pancreas
● FUNCTION: Protect
o Several layers of cells provide greater protection
than one single layer
Merocrin
● Release fluid by exocytosis
e
(pancreas)
● Grouped as serous
● Produce a watery fluid, or mucus
STRATFIED COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM which produce a thicker, protective
substance
● Consists of several layers of cells Apocrine
● Lose portions of their cell bodies
● Found in the vas deferens (male urethra) and parts of the during secretion (mammary glands)
pharynx ● Produces and removes
Holocrine
● Release entire cells (sebaceous
glands)
● Cells peel off from the tissue and
disintegrates to form tissue
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIUM
● Bind, support, protect, serve as framework, fill spaces,
● Designed to distend and return to its normal size store fat, produce blood cells, protect against infection,
o Lining of the urinary bladder and repair tissue damage
o Bile storage
● Have more abundant matrix (intercellular material)
● Provides distensibility and keeps urine from diffusing back
● Have good blood supplies (except cartilage)
into the internal cavity
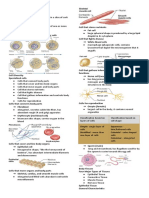
3 MAJOR CELL TYPES
● Most common cell type
Fibroblast
● Fixed star shape
● Secretes fibers and is large in size
● Produces fiber
● Scavenger cells
Macrophages
● Defend against infection
’
● Immune system – engulfs bacteria
and destroys it inside
● Located near blood vessels (large)
GLANDULAR EPITHELIUM Mast cells
where they release
o Heparin (anticoagulant)
TRANSCRIBED BY: LOVE FRANCHESKA LEGASPI 2
LECTURE 3 | ANAPHY – TISSUES
o Histamine (inflammation) ● Cartilage cells (chondrocytes) – lie within lacunae in the
CONNECTIVE TISSUE FIBERS gel-like fluid matrix
● Enclosed within a connective tissue – Perichondrium
● White fibers ● Most common:
Collagenous
● Made of protein collagen o Hyaline – ends of the bone
o Elastic – external ears
● Add strength for holding body parts o Fibro – shock absorber (lamina -spinal)
together (connects) ● Osteocytes – bone cells
● Yellow fibers o Lie within lacunae
Elastic
o Arranged in circles (osteons) around osteonic
● Made of protein elastin canals interconnected by canaliculi
● Stretchy and add flexibility to certain ● Has a good blood supply – enabling rapid recovery after
types of connective tissues (contracts an injury
and relapse)
● Thin collagenous fibers
Reticular
● Form supportive networks in a variety
of tissues
LOOSE CONNECTIVE (AREOLAR) TISSUE
● Forms delicate and thin membranes throughout the body
● FUNCTION: Bind body parts together – skin & underlying BLOOD
organs ● Compose of cells (red and white)
● Majority of the cells are fibroblasts that are separated by o Suspended in a liquid matrix called plasma
a gel-like ground substance that contains collagenous ● FUNCTIONS: transport substances throughout the body
and elastic fibers
ADIPOSE TISSUE 4 TYPES OF BONE
● Loose connective tissue
Osteogenic Cells – bone repair & growth
● FUNCTION: store fat
Osteocytes Maintain cells (primary cells)
● Found beneath the skin, around joints padding the Osteoblast Form bones
Osteoclast Bone destruction
kidneys, and other internal organs, and in certain
abdominal membranes ● White blood cells – increase in WBC = infection
● Red blood cells – Plasma (liquid matrix)
● Platelets (thrombocytes) – stop bleeding
MUSCLE TISSUE
● Muscle cells, or fibers can contract
DENSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE
● Consists of densely packed collagenous fibers
o Very strong; but lacks good blood supply
SKELETAL MUSCLE TISSUE
● Attached to bone
o Can be controlled by conscious effort (voluntary)
● Cells (muscle fibers) – long and cylindrical, striated, have
● Part of tendons and ligaments
many nuclei, and contract from nervous impulse.
CARTILAGE SMOOTH MUSCLE TISSUE
● Rigid connective tissue ● Lacks striations;l Uni-nucleate
● FUNCTION: framework (support) for various structures ● Consists of spindle-shaped cells
● Lacks vascular system – heals slowly
TRANSCRIBED BY: LOVE FRANCHESKA LEGASPI 3
LECTURE 3 | ANAPHY – TISSUES
● Involuntary muscle ● FUNCTION: Protection and production of mucus
● Found in the walls of the internal organs, and in the
SYNOVIAL
digestive tract, blood vessels, and urinary bladder
● Line the joint cavities
● Consist of only connective tissues
● FUNCTION: Secrete lubricating synovial fluid
CUTANEOUS
CARDIAC MUSCLE TISSUE
● Consists of the skin (integument)
● Found only in the heart
● Consists of branching fibers that are connected to each
other with intercalated disks
● Involuntary muscle
o Single nucleus in each cell; but appears
striated
NERVOUS TISSUE
● Found in the brain, spinal cord, and the nerves
● Neurons – nerve cells that conduct nervous impulses
● Neuroglia – helper cells that support and nourish neurons
EPITHELIAL MEMBRANES
● Composed of a layer of epithelial tissue and a layer of
connective tissue
● Cover body surfaces and line body cavities
● Four main types: serous, mucous, synovial, and
cutaneous
● Considered to be organs because these membranes are
composed of more than one type of tissue
TYPES OF MEMBRANES
SEROUS
● line body cavities that lack openings to the outside.
● They line the thorax and abdomen and cover the organs
within these cavities.
● made up of epithelium and loose connective tissue and
secrete serous fluid that acts as a lubricant.
MUCOUS
● line the cavities and openings that lead to the outside
of the body, including the oral and nasal cavities, and
openings of the digestive, reproductive, respiratory, and
urinary systems.
● They consist of epithelium and connective tissue with
specialized cells that secrete mucus.
TRANSCRIBED BY: LOVE FRANCHESKA LEGASPI 4
You might also like
- By-Products Handlers License - Co. Application FormDocument2 pagesBy-Products Handlers License - Co. Application FormAllen100% (2)
- 10 Thailand-CuisineDocument46 pages10 Thailand-CuisineYan Yang75% (4)
- Activity 4 - Epithelial TissueDocument4 pagesActivity 4 - Epithelial TissueMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument2 pagesAnimal TissuesMami AmihanNo ratings yet
- Transes Anaphy LEC (Activity 5 HISTOLOGY)Document6 pagesTranses Anaphy LEC (Activity 5 HISTOLOGY)Reign Saplaco100% (1)
- Module # Epitheleal TransDocument5 pagesModule # Epitheleal TransLara VanessNo ratings yet
- 02 HistologyDocument9 pages02 HistologyJinnwen MandocdocNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesEpithelial TissueJoan PaulineNo ratings yet
- The Tissues: The Four Primary Tissue TypesDocument10 pagesThe Tissues: The Four Primary Tissue TypesgilissaNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands, and Membranes 4 Basic Types of Tissue: Epithelial Connective Muscle NervousDocument6 pagesTissues, Glands, and Membranes 4 Basic Types of Tissue: Epithelial Connective Muscle NervousFheonna De La PeñaNo ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument10 pagesBody TissuesAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument10 pagesBody TissuesAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Tissues of The Human Body: Group 2Document34 pagesTissues of The Human Body: Group 2Jhana DanoNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues Group 2Document39 pagesAnimal Tissues Group 2Danielle Kate MadridNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue & Organ System: SMA Pradita DirgantaraDocument30 pagesAnimal Tissue & Organ System: SMA Pradita Dirgantarahafiz amriNo ratings yet
- Module 2.3 Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument12 pagesModule 2.3 Tissue Level of OrganizationchellesuguitanNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument13 pagesHistologyangelo davidNo ratings yet
- T I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueDocument6 pagesT I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueMarla TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Accessory Glands of The GITDocument3 pagesAccessory Glands of The GITDanielle CapangpanganNo ratings yet
- Module 2 TissuesDocument3 pagesModule 2 TissuesRaphael SevillaNo ratings yet
- 1 Animal OrganisationDocument29 pages1 Animal OrganisationPERTUNIA KORABINo ratings yet
- Animal CellsDocument52 pagesAnimal CellsCally ChanNo ratings yet
- E1.3 Body TissuesDocument5 pagesE1.3 Body TissueshzntrpNo ratings yet
- Entire Tissues UnitDocument32 pagesEntire Tissues Unitnao_gataNo ratings yet
- 07 Animal TissuesDocument12 pages07 Animal TissuesKeisha Clarice AdaroNo ratings yet
- Histology & Integumentary SystemDocument12 pagesHistology & Integumentary Systemopingaangelamae.opingaNo ratings yet
- Lec-2-Fundamental TissuesDocument11 pagesLec-2-Fundamental TissuesGenesis kiokNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ANAPHY NOTESDocument13 pagesChapter 4 ANAPHY NOTESShannelle SinciocoNo ratings yet
- Tissue FinalDocument6 pagesTissue FinalPongman92No ratings yet
- MLS - HISTOLOGY Lec - M2-UNIT1 (Epithelia and Glands)Document22 pagesMLS - HISTOLOGY Lec - M2-UNIT1 (Epithelia and Glands)ataraNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Histology) : Joash Nathaniel S. Tan, PTRPDocument41 pagesTissues (Histology) : Joash Nathaniel S. Tan, PTRPLleana Tan100% (1)
- Histology Lec 1 & 2Document22 pagesHistology Lec 1 & 2Asma Ghazy100% (1)
- Zoo Lab UwUDocument38 pagesZoo Lab UwUHannah Danniella NapolesNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals - Mind Maps - Yakeen 3.0 2024Document3 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals - Mind Maps - Yakeen 3.0 2024thakur.shrish.singhNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument23 pagesAnimal TissueMadhav KhanalNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Type Function Characteristics Structure LocationDocument4 pagesAnimal Tissues: Type Function Characteristics Structure LocationHannah Danniella NapolesNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Cell ConnectionsDocument3 pagesTissues: Cell ConnectionsRalph AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 4Document9 pagesAnaphy Chapter 4Rober Rhyne OmamalinNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Transes PDFDocument11 pagesEpithelial Tissue Transes PDFFAUL MANGAYANo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue or Epithelium: FunctionsDocument10 pagesEpithelial Tissue or Epithelium: FunctionsJOAN KLAIRE I. LIBOTNo ratings yet
- Epithelium Tissues: CellularityDocument6 pagesEpithelium Tissues: CellularityErika VerastigueNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument7 pagesTissuesShahina ShayneNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Mia Rev3Document5 pagesAnaphy Mia Rev3antonettevegamia3No ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesCells and Tissuesgrafei pennaNo ratings yet
- Human Body TissuesDocument5 pagesHuman Body TissueschellesuguitanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 TissuesDocument6 pagesLesson 2 TissuesRodefe AmitNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy & PhysiologyTyrNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document9 pagesCH 7Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956100% (1)
- HistologyDocument16 pagesHistologyJeong song parkNo ratings yet
- Tissues in AnaphyDocument8 pagesTissues in AnaphyAngela EstorninosNo ratings yet
- A-P Chapter 4 TissueDocument21 pagesA-P Chapter 4 TissueMONIQUE VELASCONo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 22Document8 pagesAnimal Tissues 22Arleen ColacionNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physio HandoutsDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physio HandoutsKoj LozadaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: - Are Widespread Throughout The BodyDocument9 pagesEpithelial Tissue: - Are Widespread Throughout The BodyElyka AbellaNo ratings yet
- (BMED66) HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY WITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Laboratory Lecture Body Tissue Lesson 4Document16 pages(BMED66) HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY WITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Laboratory Lecture Body Tissue Lesson 4Cerisse MaeNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument11 pagesUntitled Documenthazzell solisNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument11 pagesUntitled Documenthazzell solisNo ratings yet
- ANIMAL-CELL Group 2Document35 pagesANIMAL-CELL Group 2mjecbjNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesKenken MijaresNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - Chapter 4Document16 pagesAnaphy - Chapter 4Deanne Joyce AdelantarNo ratings yet
- 07 Structural Organism in Animal Ncert MasterDocument12 pages07 Structural Organism in Animal Ncert MasterexercisestartNo ratings yet
- ConfirmationDocument2 pagesConfirmationTechnical A-Star Testing & Inspection MalaysiaNo ratings yet
- PVP2000-PVP5200 Data Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesPVP2000-PVP5200 Data Sheet PDFRES SupplyNo ratings yet
- Breaking Bad NewsDocument1 pageBreaking Bad NewsUZNAPMNo ratings yet
- FSW-Tech Handbook For Specialists and Engineers - enDocument172 pagesFSW-Tech Handbook For Specialists and Engineers - enkamal touilebNo ratings yet
- Business Class M2 Maintenance ManualDocument153 pagesBusiness Class M2 Maintenance ManualEdwin Alfonso Hernandez Montes100% (2)
- Energy AuditDocument20 pagesEnergy AuditSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Sangfor IAM V12.0.17 Associate 2019 01 IntroductionDocument22 pagesSangfor IAM V12.0.17 Associate 2019 01 IntroductionGilangNo ratings yet
- Coetzer (2003) The - Development - of - A - Holistic - Community - Based - NeurDocument6 pagesCoetzer (2003) The - Development - of - A - Holistic - Community - Based - Neurhoranvera10No ratings yet
- UW 2021 Notes - Lungs UsmleDocument422 pagesUW 2021 Notes - Lungs Usmlekathi raja sekhar100% (1)
- 4 Quick Meals To Cook On A Weber BBQDocument3 pages4 Quick Meals To Cook On A Weber BBQHome FiresNo ratings yet
- Slowcooker RVKB LR 02122009Document10 pagesSlowcooker RVKB LR 02122009Alexandre_Pill_2054No ratings yet
- Catalog BB Type HDocument2 pagesCatalog BB Type HdioalfanandaNo ratings yet
- Quartz GroupDocument10 pagesQuartz GroupJICA DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Professional Work RecordDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Professional Work Recordmy09No ratings yet
- Acasestudyfrom Mahan Coal Block Singrauli MPDocument5 pagesAcasestudyfrom Mahan Coal Block Singrauli MPSarah DanielNo ratings yet
- All Contents MergedDocument154 pagesAll Contents MergedBAHAAHAHANo ratings yet
- Potentiality of Coir Coconut Husk and Sodium Bicarbonate Baking Soda As Compost Catalyst To Reduce Waste Among Filipino HouseholdsDocument38 pagesPotentiality of Coir Coconut Husk and Sodium Bicarbonate Baking Soda As Compost Catalyst To Reduce Waste Among Filipino HouseholdsHANNAH MARIE VINOYANo ratings yet
- Antonette Garcia ThesisDocument28 pagesAntonette Garcia ThesisRovhie Gutierrez BuanNo ratings yet
- HTML ExamplesDocument80 pagesHTML ExamplesZaraNo ratings yet
- Millennial Parents On Campus:: Reflecting On How To Discover Confluence With This ConstituencyDocument26 pagesMillennial Parents On Campus:: Reflecting On How To Discover Confluence With This ConstituencyLeon GuintoNo ratings yet
- Buckeye Power Light CompanyDocument0 pagesBuckeye Power Light CompanybalamaestroNo ratings yet
- Generation III Sonic Feeder Control System Manual 20576Document32 pagesGeneration III Sonic Feeder Control System Manual 20576julianmataNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke Maria Grace Ang-De Guzman, MDDocument9 pagesIschemic Stroke Maria Grace Ang-De Guzman, MDJohn Benedict Bondoc100% (3)
- Malaika Synopsis PresentationDocument23 pagesMalaika Synopsis PresentationSundas SaikhuNo ratings yet
- Alloy Selection For Service in Chlorine, Hydrogen Chloride and Hydrochloric AcidDocument12 pagesAlloy Selection For Service in Chlorine, Hydrogen Chloride and Hydrochloric Acideugenio.gutenbertNo ratings yet
- Improving The Metal Casting Quality Using High-Permeability Sand Aggregates - Part 03Document2 pagesImproving The Metal Casting Quality Using High-Permeability Sand Aggregates - Part 03Oscar SotomayorNo ratings yet
- Mpac1000 SpecDocument6 pagesMpac1000 SpecalstomNo ratings yet
- External Beam Planning RGDocument870 pagesExternal Beam Planning RGrubenNo ratings yet