Professional Documents
Culture Documents
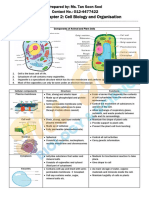
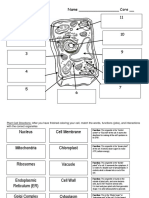
Cell Organelles
Uploaded by
api-4181768860 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
627 views36 pagesOriginal Title
cell organelles
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
627 views36 pagesCell Organelles
Uploaded by
api-418176886Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 36
Cell Organelles
Structure and Function
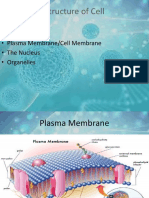
Plasma (Cell) Membrane
• Structure: • Function
• Phospholipid bilayer • Is semi-permeable
with embedded (allows some
proteins molecules in/out)
Plasma (Cell) Membrane
Membrane
Nucleus
• Structure: • Function:
• Double membrane • Contains DNA in the
(nuclear envelope) form of chromatin
• Pores in membrane (DNA + proteins)
• Directs the cell’s
activities
Nucleolus
• Structure: • Function:
• Prominent in nucleus • Site of ribosome
synthesis
Nucleus
Ribosomes
• Structure: • Function:
• Made of rRNA and • Site of protein
proteins synthesis
Ribosomes
Ribosomes
Smooth ER
• Structure: • Function:
• Network of flattened • Lipid synthesis
sacs of membrane
connected to the
nuclear envelope
• Has NO ribosomes
attached
Smooth ER
• Smooth ER
Rough ER
• Structure: • Function:
• Network of flattened • Modifies proteins;
sacs of membrane sends them to Golgi
connected to the in vesicles
nuclear envelope
• HAS ribosomes
attached
Rough ER
• Rough ER
Vesicles
• Structure: • Function:
• Membranous sac • Transports materials
Vesicle
• Vesicle
Golgi Apparatus
• Structure: • Function:
• Flattened sacs of • Stores materials
membrane stacked • Packages proteins for
on top of one another, shipment out of cell
but NOT connected
Golgi Apparatus
• Golgi
Lysosomes
• Structure: • Function:
• Contains digestive • Digestion of damaged
enzymes in a organelles and
membranous sac macromolecules
Lysosomes
• Lysosome
Contractile Vacuole
• Structure: • Function:
• Membranous sac • Collect and expel
• Looks like a wheel excess water
with spokes
• Found in some
protists
Contractile Vacuole
• Contractile vacuole in amoeba (left) and
paramecium (right).
Central Vacuole
• Structure: • Function:
• Membranous sac • Storage, absorbs
• Found in plant cells water
Central Vacuole
• Central vacuole
Cell Wall
• Structure: • Function:
• Cellulose-plants • Support and
• Chitin-fungi protection
• Not found in animals
Cell Wall
• Cell wall
Chloroplasts
• Structure: • Function:
• Double membrane • Photosynthesis
• Contains DNA and (converting solar
ribosomes energy to chemical
energy)
Chloroplast
• Chloroplasts
Mitochondria
• Structure: • Function:
• Double membrane • Cellular respiration
• Contains DNA and (breaks down
ribosomes sugar/food to form
ATP)
Mitochondria
• Mitochondria
Cytoskeleton
• Structure: • Function:
• Protein fibers: • Maintains cell shape;
• Microfilaments cell movement
• Intermediate filaments • Anchors organelles
• Microtubules • Cell support; tracks
for organelles to
move on
Cytoskeleton
• cytoskeleton
Centrioles
• Structure: • Function:
• Made of microtubules • Cell division (?)
• In animal cells; NOT
in plant cells
Centrioles
• Centrioles
Cilia
• Structure: • Function:
• 9+2 arrangement of • Movement
microtubules • “Sweeping” of airway
• Short; hair-like in humans
Cilia
• Cilia in paramecium (left) and human
bronchi cells (right)
Flagella
• Structure: • Function:
• 9+2 arrangement of • Movement
microtubules
• Long, whip-like
Flagella
Flagella
You might also like
- Cells P PrintDocument5 pagesCells P PrintAnca CosticaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function: Roma Grace H. Dizon, MS BioDocument56 pagesCell Structure & Function: Roma Grace H. Dizon, MS BioDen Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- CEll Structures and Functions - SHSDocument42 pagesCEll Structures and Functions - SHSGABRIEL LOUIS GUANONo ratings yet
- The CellDocument25 pagesThe CellmaryshealshealNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellDocument38 pagesPlant and Animal CellteeahhhnaNo ratings yet
- Ultrastr of The CellDocument14 pagesUltrastr of The CellMuhammad Nor RifaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function: Basic Theor Y of LifeDocument34 pagesCell Structure & Function: Basic Theor Y of LifeJhea DoriaNo ratings yet
- 04.03 Cell Structure and Functions Guided Notes: ObjectivesDocument2 pages04.03 Cell Structure and Functions Guided Notes: ObjectivesAlyssa NewmenNo ratings yet
- Document9 PDFDocument2 pagesDocument9 PDFAlyssa NewmenNo ratings yet
- Document9 PDFDocument2 pagesDocument9 PDFAlyssa NewmenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cells Lesson 7Document18 pagesChapter 2 Cells Lesson 7May Khin NyeinNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Document7 pagesCell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Amrul Zlalu AdaNo ratings yet
- Biology Basic ConceptsDocument6 pagesBiology Basic ConceptsAhsni128No ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: Concepts of The Cell TheoryDocument2 pagesCells and Tissues: Concepts of The Cell TheoryMarie SamNo ratings yet
- Edit Structure and Functional CellDocument20 pagesEdit Structure and Functional CellArifiaNo ratings yet
- 5-Cell StructureDocument65 pages5-Cell StructureShydene SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures - RRDocument12 pagesCell Structures - RRRaphael JosephNo ratings yet
- Cells Continued!!!: Structures and FunctionsDocument29 pagesCells Continued!!!: Structures and Functionsldooley05100% (1)
- Cell UltrastructureDocument47 pagesCell UltrastructureEugenia Migranova100% (1)
- Integrated Principles of ZoologyDocument41 pagesIntegrated Principles of ZoologyEstherNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function 2022Document43 pagesCell Structure & Function 2022Kavita MahaseNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Biology MidtermsDocument6 pagesScience 6 Biology MidtermsSamantha Avril UmandapNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument53 pagesCell Structuremuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument53 pagesCell Structuremuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- 2 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument55 pages2 Cell Structure and FunctionRiz MarieNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument30 pagesCell Structure FunctionAngelo GabrielNo ratings yet
- Review of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument25 pagesReview of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cellsevil twinNo ratings yet
- BIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 4Document16 pagesBIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 4Noor JanahiNo ratings yet
- M. Rizano Priatmoko Alvin Julian R. Dhimas Andianto M. Farrell Hidayat Rainanda MuhammadDocument36 pagesM. Rizano Priatmoko Alvin Julian R. Dhimas Andianto M. Farrell Hidayat Rainanda MuhammadfrlolNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & OrganisationDocument62 pagesCell Structure & OrganisationSUNDARI SIVASANKARNo ratings yet
- 2 Biology 1-2-07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocument63 pages2 Biology 1-2-07 Pro Vs Eu CellsRakesh NeelakandanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument42 pagesCell Structure FunctionRoderick PorterNo ratings yet
- Cells & Physiology - Lecture (Week 3-4)Document59 pagesCells & Physiology - Lecture (Week 3-4)Trevannie EdwardsNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life-IIDocument14 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life-IIPankaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Week 4 5 - Cell Structure - Function (1) (Final)Document44 pagesWeek 4 5 - Cell Structure - Function (1) (Final)hhhhNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument94 pagesThe CellKorean DramaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Functions ReviewDocument54 pagesCell Parts and Functions ReviewKathryn Warner - Central Peel SS (2522)No ratings yet
- 4 Cell and TissuesDocument44 pages4 Cell and TissuesAmbreen RiazNo ratings yet
- K2-1.3 Sel FungsiDocument108 pagesK2-1.3 Sel Fungsikevin eaNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة 2023-12-28 في 4.37.00 مDocument35 pagesلقطة شاشة 2023-12-28 في 4.37.00 مaaggkk12332118No ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument10 pagesBio Noteschanhongyi16No ratings yet
- Cell - Structure - Function Chapter 2Document42 pagesCell - Structure - Function Chapter 2ErizaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument42 pagesCell Structure and Functioncelineable100% (1)
- Cell Structure & Function: Source: Http://koning - Ecsu.ctstateu - Edu/cell/cell - HTMLDocument100 pagesCell Structure & Function: Source: Http://koning - Ecsu.ctstateu - Edu/cell/cell - HTMLMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document100 pagesChapter 2AQEESHA NUWAIRA BINTI USMAN BN21110154No ratings yet
- Module 1Document40 pagesModule 1Kylene AlimNo ratings yet
- Cell: Parts and Their FunctionsDocument12 pagesCell: Parts and Their FunctionsAllex Leigh DominguezNo ratings yet
- 1.6 - Compare Animal Cells and Plant CellsDocument14 pages1.6 - Compare Animal Cells and Plant CellsKexinNo ratings yet
- CellDocument37 pagesCellgeezariana790No ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument39 pagesCell Structure & Functiondacspinlac100% (9)
- Fisiologi Sel Dan JaringanDocument39 pagesFisiologi Sel Dan JaringanPyrectic Williams100% (1)
- Cell Components: See This VideoDocument28 pagesCell Components: See This VideoDwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles PDFDocument23 pagesCell Organelles PDFEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Cells: General ZoologyDocument71 pagesCells: General ZoologyAzaleaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - CellDocument20 pagesChapter 4 - CellCrisha LimNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts 09-0Document20 pagesCell Parts 09-0Ali HarthNo ratings yet
- Components of CellDocument21 pagesComponents of CellAl Christian YaboNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and EukaryotcG7Document41 pagesProkaryotic and EukaryotcG7Nes ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Cell PartsDocument30 pagesCell PartsAnthony Gio L. AndayaNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument17 pagesWaterapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Humans and The EnvironmentDocument17 pagesHumans and The Environmentapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Population EcologyDocument18 pagesPopulation Ecologyapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Animal AdaptationsDocument10 pagesAnimal Adaptationsapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Plant AdaptationsDocument13 pagesPlant Adaptationsapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Ap Biology Basic Chemistry VocabDocument2 pagesAp Biology Basic Chemistry Vocabapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Why Organelles 1Document5 pagesWhy Organelles 1api-418176886No ratings yet
- Overview of The 6 KingdomsDocument23 pagesOverview of The 6 Kingdomsapi-418176886No ratings yet
- SpeciationDocument15 pagesSpeciationapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Evolutionary TheoryDocument14 pagesEvolutionary Theoryapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Early Earth and The Origin of LifeDocument22 pagesEarly Earth and The Origin of Lifeapi-418176886No ratings yet
- MicroevolutionDocument11 pagesMicroevolutionapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Classification Based On EvolutionDocument12 pagesClassification Based On Evolutionapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Biology 2004 EoctDocument20 pagesBiology 2004 Eoctapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Bacterial and Viral GeneticsDocument20 pagesBacterial and Viral Geneticsapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemsDocument27 pagesNervous Systemsapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Control Over The Cell CycleDocument11 pagesControl Over The Cell Cycleapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Signal Reception G Proteins KinasesDocument20 pagesSignal Reception G Proteins Kinasesapi-418176886No ratings yet
- TranslationDocument6 pagesTranslationapi-418176886No ratings yet
- The Genetic Basis of CancerDocument31 pagesThe Genetic Basis of Cancerapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Cell Communication OverviewDocument12 pagesCell Communication Overviewapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Control of Gene Expression in EukaryotesDocument16 pagesControl of Gene Expression in Eukaryotesapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Viruses Lytic and Lysogenic CyclesDocument19 pagesViruses Lytic and Lysogenic Cyclesapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis SimplifiedDocument5 pagesProtein Synthesis Simplifiedapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Biology in PicturesDocument61 pagesBiology in Picturesapi-418176886No ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument13 pagesMeiosisapi-418176886No ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument11 pagesTranscriptionapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Transcription SimplifiedDocument5 pagesTranscription Simplifiedapi-418176886No ratings yet
- MitosisDocument25 pagesMitosisapi-418176886No ratings yet
- MitosisDocument25 pagesMitosisapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Organelles FunctionsSeiji MingNo ratings yet
- PG TRB Zoology Revision Test Unit IV and VDocument13 pagesPG TRB Zoology Revision Test Unit IV and VRoopa Roopavathy100% (1)
- Cell-The Unit of Life - Shobhit NirwanDocument23 pagesCell-The Unit of Life - Shobhit NirwanVraj M Barot63% (8)
- Cell Comparison PowerpointDocument17 pagesCell Comparison Powerpointapi-269617713100% (1)
- Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function Chapters 6-7Document4 pagesUnit 2: Cell Structure and Function Chapters 6-7api-542216138No ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument10 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYShaira Kaye AlimariNo ratings yet
- Hhis Lec Prelims FinalsDocument101 pagesHhis Lec Prelims FinalsJOANNA MARIE SIGUANo ratings yet
- Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer. Absolutely No ErasuresDocument2 pagesEncircle The Letter of The Correct Answer. Absolutely No ErasuresARISNo ratings yet
- 04 Lecture AnimationDocument66 pages04 Lecture AnimationJoshua VidalNo ratings yet
- Krauses Essential HumanDocument315 pagesKrauses Essential HumanJames Mark Magsipoc OrtegaNo ratings yet
- What Is Life? Molecules of Life Cell As Fundamental Unit Cell Membranes and Organelles Cell Metabolism Cells Organized Into Tissues Types of TissuesDocument67 pagesWhat Is Life? Molecules of Life Cell As Fundamental Unit Cell Membranes and Organelles Cell Metabolism Cells Organized Into Tissues Types of TissuestesterNo ratings yet
- What Is BiochemistryDocument7 pagesWhat Is BiochemistryFatima gulzarNo ratings yet
- Micro Electro Functional Ultrastructure - An Atlas of Tissue Biology and Pathology - M. Pavelka, J. Roth (Springer, 2005) WW PDFDocument341 pagesMicro Electro Functional Ultrastructure - An Atlas of Tissue Biology and Pathology - M. Pavelka, J. Roth (Springer, 2005) WW PDFOlteanu Dragos-NicolaeNo ratings yet
- Sat Ntse 2020 Stage 2 SolutionsDocument42 pagesSat Ntse 2020 Stage 2 SolutionsArchana DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Lecture: Bachelor of Science in Medical Laboratory ScienceDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Its FunctionsDocument25 pagesCell Parts and Its FunctionsSen Armario100% (1)
- Biology HL Study MaterialDocument90 pagesBiology HL Study MaterialelenaNo ratings yet
- Name - Core - 1 11: Plant Cell FoldableDocument5 pagesName - Core - 1 11: Plant Cell FoldableNoralyn Ngislawan-GunnawaNo ratings yet
- (@akash - Test - Papers) CSS-03 - BASED ON CST 5&6Document15 pages(@akash - Test - Papers) CSS-03 - BASED ON CST 5&6Priyanka SomkuwarNo ratings yet
- Class 9 BiologyDocument32 pagesClass 9 BiologyAbinaya ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal CellsDocument16 pagesGrade 4 Unit 3 Lesson 1 Plant & Animal CellsSandWich TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionsDocument44 pagesPlant and Animal Organ System and Their FunctionsClara MaeNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Term ReviewerDocument19 pagesAnaPhy Term ReviewerJoher Mendez100% (1)
- Biology For Prelims (Sscstudy - Com)Document385 pagesBiology For Prelims (Sscstudy - Com)Abhisar KhokharNo ratings yet
- 06 Flp-1 1st Half Syllabus (Student Copy)Document15 pages06 Flp-1 1st Half Syllabus (Student Copy)Saad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Broad/Scope Scientific Discipline: Biochemistry Is Applied To Medicine, Dentistry, andDocument9 pagesBroad/Scope Scientific Discipline: Biochemistry Is Applied To Medicine, Dentistry, anddavenNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet - WK7Document6 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet - WK7wobbleshopeNo ratings yet
- Science Readings 2Document40 pagesScience Readings 2ErosCupidNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5: The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument78 pagesChapter - 5: The Fundamental Unit of LifeRoboNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Biology Foundation Bharati BhawanDocument175 pagesClass 9 Biology Foundation Bharati Bhawans86% (7)