Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BSSPAR1: Chapter 4 Radio Resource Management: 1 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Uploaded by
Zoheir KacimiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BSSPAR1: Chapter 4 Radio Resource Management: 1 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Uploaded by
Zoheir KacimiCopyright:
Available Formats
BSSPAR1: Chapter 4
Radio Resource Management
1 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Legal Notice
Intellectual Property Rights
All copyrights and intellectual property rights for Nokia Siemens Networks training documentation, product
documentation and slide presentation material, all of which are forthwith known as Nokia Siemens Networks
training material, are the exclusive property of Nokia Siemens Networks . Nokia Siemens Networks owns the
rights to copying, modification, translation, adaptation or derivatives including any improvements or
developments. Nokia Siemens Networks has the sole right to copy, distribute, amend, modify, develop,
license, sublicense, sell, transfer and assign the Nokia Siemens Networks training material.
Individuals can use the Nokia Siemens Networks training material for their own personal self-development
only, those same individuals cannot subsequently pass on that same Intellectual Property to others without
the prior written agreement of Nokia Siemens Networks .
The Nokia Siemens Networks training material cannot be used outside of an agreed Nokia Siemens
Networks training session for development of groups without the prior written agreement of Nokia Siemens
Networks.
2 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Module Objectives
• Give an overview about the signalling to establish and release a call
• Discuss the standard and maximum acceptable interference level
algorithm used for TCH allocation
• Explain prioritised TCH allocation
• Give an overview about the parameter settings applied to queuing
• Explain how the queue is entered and left, and how these processes
interact with handover and especially directed retry
• Discuss the algorithms to verify call drop and re-establish a call
• Explain TCH allocation and queuing for Wireless Priority of Service
(WPS)
3 © Nokia Siemens Networks
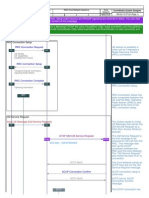
Signalling (Mobile Originating Call)
MS Channel request (RACH) NETWORK
Immediate assignment (AGCH) Immediate assignment
Service request (SDCCH)
Service request
Authentication request (SDCCH)
Authentication response (SDCCH) Authentication
Ciphering mode command (SDCCH)
Ciphering mode complete (SDCCH) Ciphering mode setting
Setup (SDCCH)
Call proceeding (SDCCH) Call initiation
Assignment command (SDCCH)
Assignment complete (FACCH) Assignment of traffic channel
Alert (FACCH)
Call confirmation
Connect (FACCH)
Connect acknowledged (FACCH) Call accepted
4 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Signalling (Mobile Terminating Call)
MS Page request (PCH) NETWORK
Channel request (RACH) Immediate assignment
Immediate assignment (AGCH)
Page response (SDCCH)
Service request
Authentication request (SDCCH)
Authentication response (SDCCH) Authentication
Ciphering mode command (SDCCH)
Ciphering mode complete (SDCCH) Ciphering mode setting
Setup (SDCCH)
Call confirmation (SDCCH) Call initiation
Assignment command (SDCCH)
Assignment complete (FACCH) Assignment of traffic channel
Alert (FACCH)
Call confirmation
Connect (FACCH)
Connect acknowledged (FACCH) Call accepted
5 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Signalling (Call Release)
Network initiated
MS Disconnect NETWORK
Release Call clearing
Release complete
Channel release
Release
MS initiated
MS Disconnect NETWORK
Release Call clearing
Release complete
Channel release
Release
6 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Standard TCH Allocation (General Criteria)
MS capabilities
Channel rate : full, half, dual, multi rate
Speech codecs : normal FR, normal HR, EFR, AMR FR, AMR HR, doubleHR(OSC)
MSC demands
A interface circuit allocated for call
BTS demands
Speech codec capabilities
TCH configuration
Current resources
Homogeneous use of TRXs and radio time slots
Large free groups of radio time slots for high loaded HSCSD BTS
7 © Nokia Siemens Networks
TCH_HR_RADIO_CONGESTION_TIME (sec)
TCH_FR_RADIO_CONGESTION_TIME (sec)
TCH Allocation
2 TRX=16 channels
PEAK_PERMANENT_GPRS_CH
SDCCH
SDCCH_CONG_TIME(sec)
BCCH
PEAK_GPRS_CHANNELS
TCH_PEAK_BUSY_HALF
TCH_PEAK_BUSY_FULL
AVE_SDCCH (SDCCH/8)
AVE_GPRS_CHANNELS
PEAK_PERMANENT_GPRS_CH
AVE_AVAIL_FULL_TCH
AVE_TCH_BUSY_FULL
PEAK_BUSY_SDCCH
AVE_GPRS_CHANNELS
AVE_BUSY_SDCCH
AVE_TCH_BUSY_FULL
PEAK_BUSY_TCH
16.0
14.0
12.0
TIME
10.0
12:00:00 AM 32 5.0 18 6.3 4.0 9 9 0 0 8.48 0 4.7 8 2
RTSL
8.0
1:00:00 AM 32 3.1 13 6.8 3.4 9 9 0 0 1.41 0 4.2 9 2
6.0
2:00:00 AM 32 1.7 12 5.2 2.9 7 7 0 0 0 0 5.8 9 2
4.0 3:00:00 AM 32 1.5 12 6.2 1.4 7 7 0 0 0 0 4.8 9 2
4:00:00 AM 32 1.6 10 8.0 1.7 5 5 0 0 0 0 3.0 9 2
2.0
5:00:00 AM 32 8.8 32 5.7 0.8 6 6 0 559 0 0 5.3 9 2
0.0 6:00:00 AM 32 5.2 18 4.3 1.1 6 6 0 0 0 0 6.7 9 2
7:00:00 AM 32 6.5 23 8.5 2.6 8 8 0 0 0 0 2.5 6 2
2:00:00 AM
4:00:00 PM
12:00:00 AM
4:00:00 AM
6:00:00 AM
8:00:00 AM
12:00:00 PM
2:00:00 PM
6:00:00 PM
8:00:00 PM
10:00:00 PM
10:00:00 AM
8:00:00 AM 32 4.8 20 6.6 2.2 7 7 0 0 0 0 4.4 9 2
9:00:00 AM 32 4.3 20 6.8 2.4 8 8 0 0 0 0 4.3 9 2
10:00:00 AM 32 5.2 32 7.5 2.6 9 9 0 2 0.21 0 3.5 9 2
11:00:00 AM 32 5.9 18 6.3 2.9 9 9 0 0 8.98 0 4.7 9 2
12:00:00 PM 32 5.9 19 6.8 3.9 9 9 0 0 13.52 0 4.2 8 2
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1:00:00 PM 32 7.3 24 6.4 3.4 9 9 0 0 8.96 0 4.6 9 2
TRX1 BCCH SDCCH SDCCH V/D V/D V/D V/D V/D 2:00:00 PM 32 6.8 30 6.2 3.9 9 9 0 0 44.05 0 4.8 8 2
TRX2 SDCCH SDCCH V/D V/D V/D V/D D D 3:00:00 PM 32 7.1 21 6.7 4.7 9 9 0 0 64.18 0 4.3 9 2
4:00:00 PM 32 7.7 23 6.6 3.9 9 9 0 0 25.61 0 4.4 8 2
5:00:00 PM 32 8.5 23 6.7 3.9 9 9 0 0 34.51 0 4.3 9 2
How can be optimized? 6:00:00 PM
7:00:00 PM
32 10.7 27 8.3 5.9
32 11.1 28 8.4 5.6
9
9
9
9
0
0
0 320.58
0 217.77
0
0
2.7
2.6
7
9
2
2
8:00:00 PM 32 10.4 30 7.8 5.5 9 9 0 0 284.15 0 3.2 8 2
9:00:00 PM 32 9.3 26 7.5 5.3 9 9 0 0 217.65 0 3.5 8 2
10:00:00 PM 32 8.3 22 7.5 5.2 9 9 0 0 185.36 0 3.5 9 2
8 © Nokia Siemens Networks 11:00:00 PM 32 5.8 21 6.8 4.6 9 9 0 0 89.61 0 4.2 9 2
Standard TCH Allocation
(Interference Bands)
Measurement of uplink receive level on idle channels = uplink interference
Averaging over interferenceAveragingProcessAverPeriod (AP) = 1..32 SACCH
periods
Classification into interference bands based on interferenceAveragingProcess
(BO1..BO4) = -110..-47 dBm
BSC tries to allocate TCH from best interference band (can be requested by MSC)
If not available,
BSC tries to take TCH from next band
BO5 –47 (fixed)
rxLevUL = -75 dBm
BO4 -90
BO3 -95
BO2 -100
BO1 -105
BO0 –110 (fixed)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
9 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Measurement Coding
LEVEL QUALITY INTERFERENCE
RxLev Coding BER(%) Coding I Interf.
(dBm) Band
-110dBm 0 < 0.2 0
-109 1 0.2-0.4 1 -110 to -105 0
-108 2 0.4-0.8 2 -104 to -100 1
. . 0.8-1.6 3 -99 to -95 2
. . -94 to -90 3
1.6-3.2 4
- 49 61
3.2-6.4 5 -89 to -47 4
- 48 62
- 47dBm 63 6.4-12.8 6
> 12.8 7
10 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Maximum Interference Level
(Call Set Up + Intra Cell Handover)
Standard algorithm
Does not avoid allocation of strongly interfered channels
-> dropped calls
-> channels allocated again with same consequence
Maximum interference level algorithm
BSC tries to allocate TCH from interference band, into which MAX_INTF_LEV falls
-> TCH usually from better band than according the standard algorithm
MAX_INTF_LEV = RXLEV_UL - cNThreshold + (msTxPwrMax - MS_TXPWR)
Parameters
RXLEV_UL current uplink receive level
cNThreshold (CNT)0..63 dB desired C/N ratio
MS_TXPWR current MS output power
msTxPwrMax maximum allowed MS output power in serving cell
11 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Maximum Interference Level
(Inter Cell Handover)
MAX_INTF_LEV = RXLEV_DL - rxLevBalance - cNThreshold
• RXLEV_UL is current uplink receive level
• BSC tries to allocate TCH in target cell from interference band, into which MAX_INTF_LEV falls
MO Abbreviated Range And Step Description Default BSC - MML
Class Name value Name
BSC rxLevBalance 0...20 dB, step 1 Balance between the DL signal level and 5 dB RXBAL
dB the UL signal level within the BSC
coverage area. DL is considered RXBAL
dB stronger than UL.
BTS cnThreshold 0...63, step 1 The minimum acceptable C/N 0 CNT
(carrier/noise) ratio when selecting a time
slot to be allocated for a call or handover.
12 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Prioritized TCH Allocation
Whole band , 50 channels 1 ch=200kHz
Case1 BCCH, 30 channels TCH, 20 channels
Case2 All 50 channels for BCCH and TCH
Priority for TCH from BCCH TRX
BCCH transmitted permanently -> no additional interference in network
Planned to be least interfered channels
Priority for TCH from other TRX
BCCH TRX does not hop in case of RF hopping -> hopping gain only for other TRX
Parameter
trxPriorityInTCHAlloc (TRP) 0 = no priority
1 = priority for BCCH TRX
2 = priority for other TRX
3 = priority for BCCH TRX for non-AMR users,
priority for other TRX for AMR users
13 © Nokia Siemens Networks
RX level based TCH Allocation
Enables to differentiate Rx level requirement for:
• MS camping to the network /RxLev Access Min
• MS accessing to TCH /RX level based TCH access
RX level based TCH allocation method
• RX Level measured by the MS is used to determine whether the BTS is
acceptable for TCH allocation
• TCH allocation for emergency calls is not restricted due to low RX level
Provides better drop call meters and better performance of MSs
• MSs having too low Rx levels are not allowed to camp the network
By separating camping and TCH access thresholds the operator will be able to
provide the maximum camping footprint
Note! RG20 feature – Energy optimized TCH allocation
14 © Nokia Siemens Networks
RX level based TCH Allocation
Allows to define minimum C/N ratios separately for each call type (AMR FR, AMR HR, EFR/FR, HR
and 14.4 data)
Parameter values ‘RX level based TCH access’:
0: RX level based TCH access is not used (C/N definitions not in use)
1: RX level based TCH access is used in call setup
2: RX level based TCH access is used in call setup and in handovers
Soft blocking C/N FR: 0…63dB/ def: 12dB
Soft blocking C/N FR: 0…63dB/ def: 12dB
Soft Blocking C/N HR: 0…63dB/ def: 14dB
Soft Blocking C/N HR: 0…63dB/ def: 14dB
Soft blocking C/N AMR FR: 0…63dB/ def: 7dB
Soft blocking C/N AMR FR: 0…63dB/ def: 7dB
Soft blocking C/N AMR HR: 0…63dB/ def: 12dB
Soft blocking C/N AMR HR: 0…63dB/ def: 12dB
Downlink RX Level Soft blocking C/N 14.4 : 0…63dB/ def: 14dB
Soft blocking C/N 14.4 : 0…63dB/ def: 14dB
-> TCH Access
15 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Queuing (Parameters)
Priorities
No TCH available for call set up / handover -> request put into queue
Different kinds of requests can have different priorities
queuePriorityUsed (QPU) Y/N enables use of priorities
queueingPriorityCall (QPC) 1..14 priority for call set up request
queuePriorityNonUrgentHo (QPN) 1..14 priority for non urgent handover (power
budget,
umbrella, slow moving MS, traffic reason)
request
queueingPriorityHandover (QPH) 1..14 priority for urgent handover (all other) request
Queue length and time
maxQueueLength (MQL) 0..100% percentage of number of TCHs handled by
BTS timeLimitCall (TLC) 0..15 s time a call set up request is kept in the queue
0 = queuing is disabled
timeLimitHandover (TLH) 0..10 s time a handover request is kept in the queue
0 = queuing is disabled
16 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Queuing (Entering the Queue)
Conditions
Timers set to values > 0
User of priorities enabled
Queue not full with requests of equal or higher priority than the current one
Queuing of call set up requests
Reservation of SDCCH resources
-> SDCCH easily overbooked
-> blocking of services like SMS or location update
17 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Queuing (Handover)
Handover request queued by target BTS
Handover timers hoPeriodPBGT and hoPeriodUmbrella stopped
Measurement processing and averaging continues as usual
Intra BSC handover Inter BSC handover
Queuing possibility checked for all Target BTS given by MSC by
possible target cells Order handover request message
according conventional ranking
18 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Queuing (Leaving the Queue)
With TCH allocation
Release of busy TCH
Check of queue from top to bottom for best matching request
If TCH allocation possible, request removed from queue
Without TCH allocation
Queuing timer expires
Request of higher priority enters full queue
19 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Queuing (Together with Directed Retry)
Directed Retry Timer maxTimeLimitDirectedRetry expires
call cleared, even if still in queue
Queuing timer expires
target cell evaluation continues, if directed retry timer is still running
20 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Dropped Call Control
Radio Link Timeout
BTS does not receive measurement report on
SACCH for running call for the first time
Counter initialised with value of radioLinkTimeout
(4,8,..64 SACCH periods)
SACCH not received again SACCH received again
Counter decremented by 1 Counter incremented by 2
(but not beyond initial value)
Counter has value 0 Example: short tunnel
Call release due to radio link
time out
21 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Dropped Call Control
Radio Link Timeout
• RLT is based on SACCH deletion but SACCH is though not using a
dynamic codec like voice in AMR, which means:
• Using the EFR RLT value an AMR customer can have the call dropped
because RLT = 0 when still the FER is good
• RLT is not anymore reliable with the same value in AMR than in EFR
• Due to the fact that the FER performance is different when comparing AMR
calls to EFR calls, the Radio Link Timeout need to be defined separately for
AMR
• The Radio Link Timeout parameters for AMR are ARLT and AHRLT. The
principle of these is the same than in the RLT but it is used only for the
AMR capable mobile stations. ARLT & AHRLT are not supported in Talk
Family base stations.
22 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Dropped Call Control
Call Reestablishment
Radio link timeout occurs
callReestablishmentAllowed (RE) set to Y
Receive level of BCCH measured for serving and adjacent cell
Averaged over 5 s
Strongest cell considered Example: long tunnel
BCCH decoded
C1 cell selection criterion fulfilled
Cell not barred
Cell belongs to selected PLMN
Attempt to re-establish call
Successful within 20s * Not successful within 20s *
call released
call re-established
23 © Nokia Siemens Networks
* MAX WAIT TIME OF RE-ESTAB REQ is a modifiable timer in MSC
Wireless Priority Service
• Wireless Priority Service is intended for National Security and
Emergency Preparedness (NS/EP) leaders and key personnel(ANSI
Markets)
• WPS calls are given priority access to the next available radio traffic
channel in congestion situation
• Reasonable amount of radio capacity must be available also for
public users
24 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Wireless Priority Service
Principle
Overload situation authorized personnel still should have access to network
access for commercial users must be denied
MS access class
Indicated by BCCH system information message
MS belongs to indicated access class access allowed
Otherwise access not allowed
WPS user
Has basic access class and one of access classes 12-14
25 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Wireless Priority Service
Resource management principle
Radio interface resource
WPS priority WPS preferred Public Service capacity %
capacity % capacity %
• Priority to WPS • Allowed to • Certain amount of public
users if the allocate to WPS calls must be served
share of WPS users without before resource to WPS
users is less restrictions when user can be allocated
than defined share of WPS when share of WPS users
WPS priority users exceeds exceeds WPS priority
capacity from WPS priority capacity and total cell
total cell load capacity but total load is exceeds WPS
• If cell is cell load is less priority capacity plus
congested WPS than WPS priority WPS preferred capacity
user is put on capacity plus WPS share.
queue preferred capacity • If cell is congested WPS
user is put on queue
26 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Wireless Priority Service
Cell Load Thresholds
Parameter
wpsPriCapa (WPIC) 0..100% percentage of cell load, for which WPS users have
higher priority
wpsPrefCapa (WPEC) 0..100% percentage of remaining cell load, which can be
occupied without restricting access for WPS users
PublicServCount (PSC) 0..10 number of public user that must be served prior to
serving the next WPS call in the round robin allocation
Example
8 TCHs
wpsPriCapa = 50% (8 * 0.5) = 4 TCHs
wpsPrefCapa = 75% (8 – 4) * 0.75 = 3 TCHs
round robin allocation is invoked when at least four WPS users occupy the cell and a total of seven or
more traffic channels (TCH) are occupied
27 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Wireless Priority Service
Cell Load Calculation
Cell load = occupied resources / working resources
Rules to estimate number of occupied and working resources
Channel Number of Number of
occupied resources working resources
Free FR timeslot 0 1
Reserved FR timeslot 1 1
Free DR timeslot 0 3
Half reserved DR timeslot 2 3
Fully reserved DR timeslot 3 3
Free HR timeslot 0 2
Half reserved HR timeslot 1 2
Fully reserved HR timeslot 2 2
Default (E)GRPS timeslot taken into account for load calculation
Dedicated (E)GPRS timeslot not taken into account for load calculation
28 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Wireless Priority Service
Round Robin Algorithm
At least wpsPriCapa capacity occupied by WPS users AND at
least wpsPrefCapa further capacity occupied by any users
Radio capacity assurance for public algorithm
Repeat steps until cell Serve publicServCount consecutive users
load falls below one of
the thresholds
Serve WPS user
29 © Nokia Siemens Networks
Wireless Priority Service
Queuing
One queue for WPS users and one for all other ones
Same priority parameters
msPriorityUsedInQueueing Y/N must be set to Y to replace WPS calls of low
MS priority level with such ones of high priority
level in a full queue
But individual timers for WPS queue
timeLimitWPS (TLW) 0..30 s analogue to timeLimitCall
timeLimitWPSHO (TLWH) 0..30 s analogue to timeLimitHandover
Queuing and directed retry
Queuing continues, if timer maxTimeLimitDirectedRetry expires earlier than queuing timer
Queuing instead of directed retry, if load of target cell exceeds upper threshold wpsPrefCapa
Inter BSC directed retry not possible for WPS user
30 © Nokia Siemens Networks
You might also like
- Satellite Communications: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandSatellite Communications: Principles and ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- BSSPAR - Chapter 03 - Radio - Resource - Management - MODocument26 pagesBSSPAR - Chapter 03 - Radio - Resource - Management - MOSamir Mezouar100% (1)
- CCSI_2G RNO BASIC TRAININGDocument83 pagesCCSI_2G RNO BASIC TRAININGRasyidi UsmanNo ratings yet
- Digital Audio Broadcasting: Principles and Applications of Digital RadioFrom EverandDigital Audio Broadcasting: Principles and Applications of Digital RadioWolfgang HoegNo ratings yet
- OMF000405 Case - Ysis-Congestion ISSUE1.4Document79 pagesOMF000405 Case - Ysis-Congestion ISSUE1.4tahir issaNo ratings yet
- Ericsson Accessibility KPI Opitimization - 2GDocument16 pagesEricsson Accessibility KPI Opitimization - 2GMohamed Amine BenabbesNo ratings yet
- OMF000405 Case Study - Congestion: ISSUE1.4Document79 pagesOMF000405 Case Study - Congestion: ISSUE1.4Mahamadou Ousseini BarkiréNo ratings yet
- 2G KPI and Troubleshooting AnalysisDocument72 pages2G KPI and Troubleshooting AnalysisNasreen AzadNo ratings yet
- Multi-Carrier and Spread Spectrum Systems: From OFDM and MC-CDMA to LTE and WiMAXFrom EverandMulti-Carrier and Spread Spectrum Systems: From OFDM and MC-CDMA to LTE and WiMAXNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Planning PrinciplesDocument120 pagesGSM Network Planning PrinciplesQuốc Minh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Getting Started with NSX-T: Logical Routing and Switching: The Basic Principles of Building Software-Defined Network Architectures with VMware NSX-TFrom EverandGetting Started with NSX-T: Logical Routing and Switching: The Basic Principles of Building Software-Defined Network Architectures with VMware NSX-TNo ratings yet
- BSSPAR1: Chapter 2 Radio Resource Administration: 1 © Nokia Siemens NetworksDocument34 pagesBSSPAR1: Chapter 2 Radio Resource Administration: 1 © Nokia Siemens NetworksJunaidNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- OMF000502 Network Planning Principle ISSUE1.3Document126 pagesOMF000502 Network Planning Principle ISSUE1.3Andrew MukisaNo ratings yet
- Digital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemFrom EverandDigital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Drop Call 2g GSM SystemDocument19 pagesDrop Call 2g GSM SystemAhmadArwani88No ratings yet
- GSM Optimization - Specific Real DealDocument83 pagesGSM Optimization - Specific Real DealoluwachintaNo ratings yet
- Radio Resource Administration: 1 © Nokia Siemens Networks RN20081EN12GLN0Document36 pagesRadio Resource Administration: 1 © Nokia Siemens Networks RN20081EN12GLN0Areej AhMadNo ratings yet
- WC02-Celluar Concept and Analysis (Part 3, 3G)Document55 pagesWC02-Celluar Concept and Analysis (Part 3, 3G)Nguyễn Thái NguyênNo ratings yet
- GSM Basic 3Document89 pagesGSM Basic 3sudib1986No ratings yet
- BY Sambit Kumar Panda: 2020hs11532 Shubham Kumar: 2020hs11502Document7 pagesBY Sambit Kumar Panda: 2020hs11532 Shubham Kumar: 2020hs11502sambitsoftNo ratings yet
- GSM Fund. New TempDocument40 pagesGSM Fund. New TempMahmoud EL-BannaNo ratings yet
- GSM Radio Network PlanningDocument148 pagesGSM Radio Network PlanningAhmed Gamal100% (1)
- GSM Mobile Terminate Call ProcedureDocument2 pagesGSM Mobile Terminate Call ProcedureMallesh C. BalamattiNo ratings yet
- Digital CommunicationDocument2 pagesDigital CommunicationHarshal SonarNo ratings yet
- 1.WCDMA Basic Principle IntroductionDocument74 pages1.WCDMA Basic Principle IntroductionANUPAM_HOLLOWNo ratings yet
- GSM Fundamentals: A Guide to GSM System Architecture and Key Wireless TechnologiesDocument77 pagesGSM Fundamentals: A Guide to GSM System Architecture and Key Wireless TechnologiesKhaled GamalNo ratings yet
- SRVCC With LTE ARIMASDocument2 pagesSRVCC With LTE ARIMASchooty80No ratings yet
- ZAIN Questions NPMDocument4 pagesZAIN Questions NPMAnonymus_01No ratings yet
- GSM, UMTS & LTE Signaling FlowsDocument12 pagesGSM, UMTS & LTE Signaling FlowsDong TejeroNo ratings yet
- Fig. 1 Radio Frequency Channels RFC On Um (MN1789EU10MN - 0002 Channel Configuration, 5)Document19 pagesFig. 1 Radio Frequency Channels RFC On Um (MN1789EU10MN - 0002 Channel Configuration, 5)Anonymous g8YR8b9No ratings yet
- RNP Case Analysis Congestion: Huawei Wireless Training DepartmentDocument95 pagesRNP Case Analysis Congestion: Huawei Wireless Training DepartmentSatwikaNarindraDhipaNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To UMTS OptimizationDocument92 pages01 Introduction To UMTS OptimizationKondapalli Phani TejaNo ratings yet
- PDF Umts Performance Trouble Shooting and Optimization Guidelines Ericsson AccessibilityDocument53 pagesPDF Umts Performance Trouble Shooting and Optimization Guidelines Ericsson AccessibilitydebasishNo ratings yet
- 2G-3G Fundamental Material TrainingDocument55 pages2G-3G Fundamental Material TrainingafcgemolongNo ratings yet
- IR Nterface: By: W EDocument35 pagesIR Nterface: By: W EAmine InpticNo ratings yet
- UMTS RAN Performance Troubleshooting GuidelinesDocument52 pagesUMTS RAN Performance Troubleshooting Guidelinesjunaid_ali_10100% (1)
- GSM OSS Optimization LectureDocument69 pagesGSM OSS Optimization LectureWahyu KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of MC DS CDMA For Various Techniques Using CadenceDocument5 pagesPerformance Analysis of MC DS CDMA For Various Techniques Using CadenceSakthidasan SankaranNo ratings yet
- The Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Document32 pagesThe Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)devajeet_nerist2840No ratings yet
- GSM BSS Network KPI CSSR Optimization ManualDocument64 pagesGSM BSS Network KPI CSSR Optimization ManualkenedyNo ratings yet
- optimization technical introductionDocument73 pagesoptimization technical introductionMohammed AbdullahNo ratings yet
- GSM Air Interface ExplainedDocument19 pagesGSM Air Interface ExplainedabdallahNo ratings yet
- GSM OSS Optimization LectureDocument69 pagesGSM OSS Optimization LectureEL Arellano MarasiganNo ratings yet
- CDMA Wireless Transmission System OverviewDocument4 pagesCDMA Wireless Transmission System OverviewKrishnaRebelzNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - GSM Air Interface & Network PlanningDocument42 pagesModule 5 - GSM Air Interface & Network PlanningkarthiveeraNo ratings yet
- Basics of Drive Test in TEMSDocument45 pagesBasics of Drive Test in TEMSSatyenderKumarNo ratings yet
- GSM BSS Network KPI CSSR Optimization ManualDocument64 pagesGSM BSS Network KPI CSSR Optimization ManualAhmadArwani88100% (1)
- Signalling Flow Examples - v1Document11 pagesSignalling Flow Examples - v1Riyas MohamedNo ratings yet
- 3g Umts Originating CallDocument6 pages3g Umts Originating Callk.naveedNo ratings yet
- 1 WCDMA Principle.Document40 pages1 WCDMA Principle.biju_teleNo ratings yet
- Directional CSM ADocument6 pagesDirectional CSM ATina mariaNo ratings yet
- DHCP Protocol ExplainedDocument7 pagesDHCP Protocol Explained4119 RAHUL SNo ratings yet
- 3G Interview Questions in BriefDocument51 pages3G Interview Questions in Briefatungorai423483% (6)
- OptimizationDocument84 pagesOptimizationRamandeep Singh100% (1)
- Mobile Network Design: Mobile Comunication Division CPO/MND/RAD2aTRA - ppt/03-05-97/ 1Document101 pagesMobile Network Design: Mobile Comunication Division CPO/MND/RAD2aTRA - ppt/03-05-97/ 1Zoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Capacity Planning: TrunkingDocument41 pagesGSM Network Capacity Planning: TrunkingZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- 7-Different Radio SolutionsDocument6 pages7-Different Radio SolutionsZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- 8-Radio DESIGN ProcessDocument9 pages8-Radio DESIGN ProcessZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- 8-Radio DESIGN ProcessDocument9 pages8-Radio DESIGN ProcessZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- TRIPLE BAND ANTENNA SPECSDocument3 pagesTRIPLE BAND ANTENNA SPECSZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- RFS 10Document1 pageRFS 10Zoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- The Speed of Light Calculation in QuranDocument15 pagesThe Speed of Light Calculation in QuranAmirRaza100% (12)
- Radio Engineering and Cellular System PrinciplesDocument16 pagesRadio Engineering and Cellular System PrinciplesZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- LTE-Reuse Code Optimization (RCO)Document38 pagesLTE-Reuse Code Optimization (RCO)Zoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Whatyoudeserve 1Document8 pagesWhatyoudeserve 1Zoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument2 pagesPDFJosé Ignacio Espigares CuestaNo ratings yet
- CNNPX310R-6P: General SpecificationsDocument5 pagesCNNPX310R-6P: General SpecificationsZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- The Speed of Light Calculation in QuranDocument15 pagesThe Speed of Light Calculation in QuranAmirRaza100% (12)
- Alg 1Document4 pagesAlg 1Zoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Parameter values for LTE cellsDocument77 pagesParameter values for LTE cellsZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Indoor Omnidirectional Mimo Antenna 698-2700 MHZ: Product Data Sheet I-Ato2-698/2700MDocument2 pagesIndoor Omnidirectional Mimo Antenna 698-2700 MHZ: Product Data Sheet I-Ato2-698/2700MZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Panel Antennas: Electrical SpecificationsDocument1 pagePanel Antennas: Electrical SpecificationsZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Dual-beam Antenna with Integrated RET SpecsDocument2 pagesDual-beam Antenna with Integrated RET SpecsZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Jbeam 5160111Document1 pageJbeam 5160111Zoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Imap Isstar Client - Pack200lstDocument1 pageImap Isstar Client - Pack200lstZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Adjustable Gain Antenna for 1710-2200 MHz BandsDocument2 pagesAdjustable Gain Antenna for 1710-2200 MHz BandsMohammad KamruzzamanNo ratings yet
- Narrow-Beam Antennas 900MDocument3 pagesNarrow-Beam Antennas 900MZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Multi-band antenna specificationDocument2 pagesMulti-band antenna specificationZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- A19452101 - Narrow High GainDocument1 pageA19452101 - Narrow High GainZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- 4516 PDFDocument2 pages4516 PDFslymnNo ratings yet
- 4516 PDFDocument2 pages4516 PDFslymnNo ratings yet
- Indoor Omnidirectional Mimo Antenna 698-2700 MHZ: Product Data Sheet I-Ato2-698/2700MDocument2 pagesIndoor Omnidirectional Mimo Antenna 698-2700 MHZ: Product Data Sheet I-Ato2-698/2700MZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Low-Loss Power Splitters - Multi-Band 800 - 2500 MHZ 860 10017, 860 10018, 860 10019Document1 pageLow-Loss Power Splitters - Multi-Band 800 - 2500 MHZ 860 10017, 860 10018, 860 10019Zoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- WCL - 3G Les AlhgDocument5 pagesWCL - 3G Les AlhgZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide To Download and Install Canon Printer Driver From Canon - ComijsetupDocument2 pagesQuick Guide To Download and Install Canon Printer Driver From Canon - ComijsetupComIJSetupNo ratings yet
- Eastman Kodak Case QuestionsDocument2 pagesEastman Kodak Case QuestionsPravet Singh KanwarNo ratings yet
- BHELVISIONDocument48 pagesBHELVISIONExecutive EngineerNo ratings yet
- Oil in WaterDocument2 pagesOil in WateriyyaniNo ratings yet
- Modern Work Plan Comparison EnterpriseDocument10 pagesModern Work Plan Comparison EnterpriseRicardo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Container Migration Methodology: November 2020Document24 pagesContainer Migration Methodology: November 2020aalejoNo ratings yet
- T2397489 RR - 139231029Document3 pagesT2397489 RR - 139231029Ikhtiander IkhtianderNo ratings yet
- Mobile TrackingDocument13 pagesMobile TrackingmohanngpNo ratings yet
- Airbus Group New Learning Catalogue Architecture Domains and Sub Domains For 2014 MYRDocument20 pagesAirbus Group New Learning Catalogue Architecture Domains and Sub Domains For 2014 MYRMatias Damian CastroNo ratings yet
- Moog641 661Document2 pagesMoog641 661Cameron JonesNo ratings yet
- SlimDAS Data Sheet NGISDocument4 pagesSlimDAS Data Sheet NGISbarthel996No ratings yet
- FPGA Architecture SulochanaDocument38 pagesFPGA Architecture SulochanaGagandeep Singh DhingraNo ratings yet
- GokulakrishnanDocument3 pagesGokulakrishnanBhuvanesh M.PNo ratings yet
- Technical Trading Co. LLC Fire Projects Division Fm-200 SystemDocument7 pagesTechnical Trading Co. LLC Fire Projects Division Fm-200 SystemmuthuvelaaNo ratings yet
- Laser Driver 06DLD203A ManualDocument44 pagesLaser Driver 06DLD203A Manualgoat100% (1)
- 1 - ADITYA Project ReportDocument42 pages1 - ADITYA Project ReportMonty SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biometric Fingerprint Based ATM Transaction SystemDocument46 pagesBiometric Fingerprint Based ATM Transaction SystemJawad Asif50% (2)
- Value Stream Mapping PDFDocument294 pagesValue Stream Mapping PDFAngie C. Joya100% (2)
- Process Control and InstrumentationDocument22 pagesProcess Control and InstrumentationJyoti Swaroop50% (2)
- 200watt Active Load UnitDocument14 pages200watt Active Load Unitagmnm1962No ratings yet
- Control PlaneDocument42 pagesControl PlanemakislaskosNo ratings yet
- Error CheckdisskDocument36 pagesError CheckdisskNguyễn HạnhNo ratings yet
- Senior Digital Marketing Director in Denver CO Resume Clark RappDocument6 pagesSenior Digital Marketing Director in Denver CO Resume Clark RappClarkRappNo ratings yet
- He - Full - Update - 11 99 99.00 RG U520 STD Hel 04Document4 pagesHe - Full - Update - 11 99 99.00 RG U520 STD Hel 04glennmeselNo ratings yet
- Title Block Editor Catia Eng v5Document49 pagesTitle Block Editor Catia Eng v5Nicole Gould100% (2)
- SMB-R Melt Blender Installation ManualDocument12 pagesSMB-R Melt Blender Installation ManualNestor Mario NesralaNo ratings yet
- Massey Ferguson 263 TRACTORS (GB) Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 819774)Document14 pagesMassey Ferguson 263 TRACTORS (GB) Service Parts Catalogue Manual (Part Number 819774)zhuangfuqian31No ratings yet
- Logcat 1702664817732Document13 pagesLogcat 1702664817732fabiandejesuscentenoNo ratings yet
- Indiegogo Crowdfunding Calendars Checklists ALL PDFDocument8 pagesIndiegogo Crowdfunding Calendars Checklists ALL PDFshiriishNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Skills and LiteracyDocument6 pagesBasic Computer Skills and LiteracyKrisyl Joy B. GalleronNo ratings yet