Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alegre Hagad Bsba 2a
Uploaded by
Carmela Alegre0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views22 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views22 pagesAlegre Hagad Bsba 2a
Uploaded by
Carmela AlegreCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
INTEG
n o lo g y
h
i en ce and tec
s c
MATH
ERS PRESENTED BY:
Alegre, Carmela C.
Hagad, Angelica C.
BSBA 2-A
Mr. Jerold Cabus
Report Content
What is Integers? Addition of Integers
Example of Integers Subtraction of Integers
Integers on a Number Multiplication of
Line Integers
Graphing Integers on a Division of Integers
Number Line Rules of Integers
Integer Operations
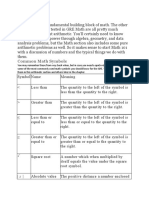
WHAT IS INTEGERS ?
• The term “integer” was adapted in Mathematics from
Latin. Integer means intact or whole. Integers are
very much like whole numbers, but they also include
negative numbers among them.
• An integer is a number with no decimal or fractional
part, from the set of negative and positive numbers,
including zero.
Example :
Examples of integers are: -5, 0, 1, 5, 8, 97, and 3,043.
A set of integers, which is represented as Z, includes:
Positive Integers: An integer is positive if it is greater than zero.
Example: 1, 2, 3 . . .
Negative Integers: An integer is negative if it is less than zero. Example:
-1, -2, -3 . . .
Zero is defined as neither negative nor positive integer. It is a whole
number.
cgdfyuyiudrywaejtweo
jtgweothhjwekhtweoi
5yw
INTEGERS ON A
NUMBER LINE
• A number line is a visual representation of numbers
on a straight line. This line is used for the
comparison of numbers that are placed at equal
intervals on an infinite line that extends on both
sides, horizontally.
• Just like other numbers, the set of integers can also
be represented on a number line.
Integer Operations
• The four basic arithmetic operations associated with integers are:
• Addition of Integers
• Subtraction of Integer
• Multiplication of Integers
• Division of Integers
• There are some rules for doing these operations.
• If there is no sign in front of a number, it means that the number is positive. For example,
5 means +5.
ADDITION OF INTEGERS
• While adding two integers, we come across the following cases:
• Both integers have the same signs: Add the absolute values of
integers, and give the same sign as that of the given integers
to the result.
• One integer is positive and the other is negative: Find the
difference of the absolute values of the numbers and then
give the original sign of the larger of these numbers to the
result.
*We can also solve the above problem
using a number line. The rules for the
addition of integers on the number line
are:
*always start from "0".
*move to the right side, if the number is
positive.
*move to the left side, if the number is
negative.
The next number in the given problem is -10 + 5, which is negative.
We move from)-10 units to the left side.
SUBTRACTION OF
INTEGERS
• To carry out the subtraction of two integers:
• Convert the operation into an addition problem by
changing the sign of the subtrahend.
• Apply the same rules of addition of integers and solve
the problem thus obtained in the above step.
Example :
Subtracting two integers: Calculate the value of 5-(2).
Now, the rules for this operation
will be the same as for the
addition of two integers.
MULTIPLICATION OF
• Multiplication INTEGERS
of integers is the process of
repetitive addition including positive and negative
numbers or we can simply say integers.
• Multiplying 2 positive numbers
• Multiplying 2 negative numbers
• Multiplying 1 positive and 1 negative number
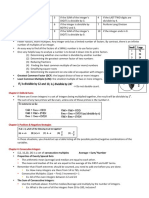
Multiplication of Integers Rules and
Steps
• Multiplication of Integers Rules
Types of Integers Result Example
Both Integers Positive Positive 2 × 5 = 10
Both Integers Negative Positive –2 × –3 = 6
1 Positive and 1 Negative Negative –2 × 5 = –10
Multiplication of Integers Rules and
Steps
• Steps for Multiplying Integers
Step 1. Determine the absolute value of the numbers.
Step 2. Find the product of the absolute values.
Step 3. Once the product is obtained, determine the sign of the number according to
the rules or conditions.
DIVISION OF
INTEGERS
• Division of integers involves the grouping of items.
It includes both positive numbers and negative
numbers
• Dividing 2 positive numbers
• Dividing 2 negative numbers
• Dividing 1 positive and 1 negative number
Division of Integers Rules and Steps
• Division of Integers Rules
Types of Integers Result Example
Both Integers Positive Positive 16 ÷ 8 = 2
Both Integers Negative Positive –16 ÷ –8 = 2
1 Positive and 1 Negative Negative –16 ÷ 8 = –2
Division of Integers Rules and Steps
To sum it all up and to make everything easy, the two most important
things to remember when you are multiplying integers or dividing
integers are:
• When the signs are different, the answer is always negative.
RULES OF
INTEGERS
Thank You for Listening
We hope you learn
Reference
• https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/integers/?fbclid=IwAR2eD01oO_9CUaSPi
CFktfo15SEn8t3dHXB0Visb_NuAFPOxOHqp0xH9uiI
• https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/multiplication-and-division-of-integers/
• https://images.app.goo.gl/PZoeEp2uWuihXzKd8
You might also like
- Math Cheat SheetDocument33 pagesMath Cheat SheetSanjeevG100% (6)
- MATH CHEAT SHEET Basic Math and Pre-Algebra Cheat - GRE - PDF DriveDocument37 pagesMATH CHEAT SHEET Basic Math and Pre-Algebra Cheat - GRE - PDF Drivemerlinsbeardeduncle100% (1)
- GRE - Quantitative Reasoning: QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandGRE - Quantitative Reasoning: QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Power Meditation: by Mahaswami MedhiranandaDocument7 pagesPower Meditation: by Mahaswami Medhiranandaanhadbalbir7347No ratings yet
- Sat PDFDocument95 pagesSat PDFZaruhi ZhamharyanNo ratings yet
- GMAT Full Key NotesDocument8 pagesGMAT Full Key NotesRebecca Kuang91% (11)
- Integers 110704144554 Phpapp01Document51 pagesIntegers 110704144554 Phpapp01Mark SantosNo ratings yet
- GMAT Club MathDocument95 pagesGMAT Club MathmdzaidsidNo ratings yet
- GMAT Quant Formulaes Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesGMAT Quant Formulaes Cheat SheetRanganathan Thiruventhipuram RamarajanNo ratings yet
- Stress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9From EverandStress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9No ratings yet
- Real Numbers PresentationDocument43 pagesReal Numbers PresentationitsankurzNo ratings yet
- ASQ Auto Webinar Core Tools Slides 101203Document83 pagesASQ Auto Webinar Core Tools Slides 101203David SigalinggingNo ratings yet
- Maths Detailed NotesDocument112 pagesMaths Detailed NotesHarris KamranNo ratings yet
- Integers & Absolute ValueDocument26 pagesIntegers & Absolute ValueMr. AulisioNo ratings yet
- Walter BenjaminDocument15 pagesWalter BenjaminAndrea LO100% (1)
- + - Integers - Addition & SubtractionDocument14 pages+ - Integers - Addition & Subtractionodylor100% (1)
- Absolute Value and The Fundamental Operations On IntegersDocument25 pagesAbsolute Value and The Fundamental Operations On IntegersHazel ColaNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Week 3 Q1Document15 pagesMath 7 Week 3 Q1Carl Joshua Francisco100% (1)
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Manual ViscosimetroDocument55 pagesManual ViscosimetroLUIS XV100% (1)
- Chap 1 Fraction PDFDocument43 pagesChap 1 Fraction PDFAmirah NatasyaNo ratings yet
- By: Prashant Kumar AryaDocument14 pagesBy: Prashant Kumar AryaYogender AryaNo ratings yet
- INTEGERS InterventionsDocument8 pagesINTEGERS InterventionsJessievel BernasNo ratings yet
- Week 14 - Whole Numbers - IntegersDocument14 pagesWeek 14 - Whole Numbers - IntegersDaisy CleonaNo ratings yet
- Whole NumbersDocument40 pagesWhole NumbersHarshit YadavNo ratings yet
- A Slide Show by Mr. Mark MartinDocument9 pagesA Slide Show by Mr. Mark MartinjamespelorianaNo ratings yet
- 6H Kelompok 1 Modul Number and OperationsDocument36 pages6H Kelompok 1 Modul Number and OperationsMuhammad Ribhi MurobbiNo ratings yet
- Project WorkDocument47 pagesProject WorkVaibhav bhandariNo ratings yet
- Operationswithintegers PDFDocument4 pagesOperationswithintegers PDFGian Carlo AngonNo ratings yet
- EBA 1093 Mathematics For Accountants & EBE 1133 Business MathematicsDocument72 pagesEBA 1093 Mathematics For Accountants & EBE 1133 Business MathematicsNur AinNo ratings yet
- Math Reviewer1Document26 pagesMath Reviewer1baluyot.xandrakamilNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic: Common Math SymbolsDocument38 pagesArithmetic: Common Math SymbolsDivya GersappaNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions and InequalitiesDocument34 pagesAlgebraic Expressions and Inequalitiesapi-241390860No ratings yet
- Contemporary Mathematics ReportDocument31 pagesContemporary Mathematics ReportAngelene Mae MolinaNo ratings yet
- ArithmeticDocument7 pagesArithmeticLaraib IjazNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Whole NumbersDocument1 pageChapter - 2 Whole NumberspreethaNo ratings yet
- The Number Properties Review PDFDocument7 pagesThe Number Properties Review PDFMehak Mann DhillonNo ratings yet
- Math Report 1Document34 pagesMath Report 1balquinbesmonteNo ratings yet
- Formulae Class 7-1Document14 pagesFormulae Class 7-1PoojaNo ratings yet
- Integers & Pythagoras' TheoremDocument12 pagesIntegers & Pythagoras' TheoremMasdianahNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study Guide: Math: Topic: Number Systems Essential Question: What Are The Different Types of Number Systems?Document4 pagesMidterm Study Guide: Math: Topic: Number Systems Essential Question: What Are The Different Types of Number Systems?api-281100019No ratings yet
- 03: The Real Number System: Elementary Algebra - Core Concept Cheat SheetDocument1 page03: The Real Number System: Elementary Algebra - Core Concept Cheat SheetCharmaine Atienza NapaNo ratings yet
- Number SystemDocument68 pagesNumber Systemmitparikh1046No ratings yet
- Number SystemDocument23 pagesNumber Systemmark porralNo ratings yet
- NTS 1Document132 pagesNTS 1jakhro_2008No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Divisibility & PrimesDocument25 pagesChapter 1: Divisibility & PrimesYue HUNo ratings yet
- Math Cheat SheetDocument37 pagesMath Cheat SheetBuzz OldwretchNo ratings yet
- Integers in Computer-Final GargarDocument10 pagesIntegers in Computer-Final GargarChris GumisadNo ratings yet
- Integers: Comparing and OrderingDocument19 pagesIntegers: Comparing and OrderingNino-prexy AcdalNo ratings yet
- Math 6 Q3 W8Document43 pagesMath 6 Q3 W8Patricia SarahNo ratings yet
- Maths Form 2Document2 pagesMaths Form 2sohu1234No ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Week 1 & 2 Mathematics 7: Lesson 3: Absolute Value of A NumberDocument10 pagesQuarter 1 Week 1 & 2 Mathematics 7: Lesson 3: Absolute Value of A NumberDevie Anne BiscarraNo ratings yet
- Gec Math Wk2Document51 pagesGec Math Wk2The Negative ThinkerNo ratings yet
- Math Revision Sheet 6 TH GradeDocument2 pagesMath Revision Sheet 6 TH GradeBala SathiamoorthyNo ratings yet
- MTC7 0203 Q1 FPFDocument19 pagesMTC7 0203 Q1 FPFDomingo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Math English IntegersDocument11 pagesMath English Integersvirtual.dikmat2021No ratings yet
- Mathematical InductionDocument153 pagesMathematical InductionRicky SinghNo ratings yet
- Simple Math Rules: Mastering the Foundations of ArithmeticFrom EverandSimple Math Rules: Mastering the Foundations of ArithmeticNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Higher Direct ProportionDocument1 pageLesson Plan Higher Direct ProportionJonathan RobinsonNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Method Is An Organized Way of Figuring Something OutDocument1 pageThe Scientific Method Is An Organized Way of Figuring Something OutRick A Middleton JrNo ratings yet
- SyllogismDocument6 pagesSyllogismjj3problembearNo ratings yet
- AndragogyDocument7 pagesAndragogyRenee Gods-Creation BurgeNo ratings yet
- DfgtyhDocument4 pagesDfgtyhAditya MakkarNo ratings yet
- 12.22.08 Dr. King Quotes BookletDocument16 pages12.22.08 Dr. King Quotes BookletlamchunyienNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform Infrared Quantitative Analysis of Sugars and Lignin in Pretreated Softwood Solid ResiduesDocument12 pagesFourier Transform Infrared Quantitative Analysis of Sugars and Lignin in Pretreated Softwood Solid ResiduesDaisyOctavianiNo ratings yet
- T50 - SVPM - 2014 - 13 - Risk Assessment in Ship Hull Structure Production Using FMEADocument13 pagesT50 - SVPM - 2014 - 13 - Risk Assessment in Ship Hull Structure Production Using FMEACiutacu AndreiNo ratings yet
- 7.IITD 2012 Theory of VibrationDocument9 pages7.IITD 2012 Theory of Vibrationlaith adnanNo ratings yet
- Essay Plan and StructureDocument3 pagesEssay Plan and StructureNinaNCNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Molas PratoDocument176 pagesCatalogo Molas Pratocassio_tecdrawNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seventeen: Managing Conflict, Politics, and NegotiationDocument32 pagesChapter Seventeen: Managing Conflict, Politics, and NegotiationFajar PranandaNo ratings yet
- (SQP2) Sample Question Paper 2Document2 pages(SQP2) Sample Question Paper 2Vraj M BarotNo ratings yet
- Activity Based Costing No.1Document3 pagesActivity Based Costing No.1joint accountNo ratings yet
- CIVL4903 2014 Semester 2 StudentDocument3 pagesCIVL4903 2014 Semester 2 StudentSuman SahaNo ratings yet
- Build A Cubic Meter LessonDocument3 pagesBuild A Cubic Meter Lessonapi-253637444No ratings yet
- Hostel Survey Analysis ReportDocument10 pagesHostel Survey Analysis ReportMoosa NaseerNo ratings yet
- The Entrepreneurial Spirit From Schumpeter To Steve Jobs - by Joseph BelbrunoDocument6 pagesThe Entrepreneurial Spirit From Schumpeter To Steve Jobs - by Joseph Belbrunoschopniewit100% (1)
- Doppler Weather RadarDocument35 pagesDoppler Weather RadarjosefalguerasNo ratings yet
- Effects of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) Education On Childhood Intestinal Parasitic Infections in Rural Dembiya, Northwest Ethiopia An Uncontrolled (2019) Zemi PDFDocument8 pagesEffects of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) Education On Childhood Intestinal Parasitic Infections in Rural Dembiya, Northwest Ethiopia An Uncontrolled (2019) Zemi PDFKim NichiNo ratings yet
- Spectrofotometru SpectroDirect (De La Lovibond)Document360 pagesSpectrofotometru SpectroDirect (De La Lovibond)FlaviusNo ratings yet
- Second Form Mathematics Module 5Document48 pagesSecond Form Mathematics Module 5Chet AckNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Writing Baby First TermDocument12 pagesScheme of Work Writing Baby First TermEmmy Senior Lucky100% (1)
- Five TemperamentDocument5 pagesFive TemperamentDhaivatPatelNo ratings yet
- STC 2010 CatDocument68 pagesSTC 2010 Catjnovitski1027No ratings yet
- Microelectronic CircuitsDocument22 pagesMicroelectronic CircuitsarunnellurNo ratings yet