Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.2 - L4 - More About Photosynthesis
1.2 - L4 - More About Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
فاطمه عيسى0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views20 pagesOriginal Title
1.2_L4_ More about Photosynthesis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views20 pages1.2 - L4 - More About Photosynthesis
1.2 - L4 - More About Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
فاطمه عيسىCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
1.
2 More about
Photosynthesis
1 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Learning Outcomes
Grades E–D: Grades C–B: Grades A–A*:
-Recall that -Suggest a hypothesis -Explain why
photosynthesis takes and plan an experiment photosynthesis takes
place in chloroplasts. to test it. place in chloroplasts.
-Carry out practical -Describe a test for the -Explain how the
work safely. presence of starch in structure of plant’s
plants. leaves support
photosynthesis.
-Explain why plants
need magnesium and
nitrate.
2 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Starter
• Where does photosynthesis take place?
Why?
3 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
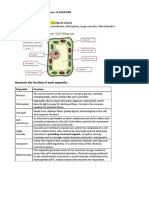
Chloroplasts and Chlorophyll
4 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
How is glucose used?
5 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Where does the excess amount of
Carbohydrates go?
Isn’t that similar to us
storing food? How?
6 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
How can you test for photosynthesis?
The presence of starch in a leaf can be used to show that
photosynthesis has taken place.
Iodine is used to test for starch.
It reacts with starch and changes
colour from brown to blue-black.
The starch test can be used to
prove that photosynthesis
needs light, carbon dioxide and
chlorophyll to take place.
How would you set up an experiment to test the conditions
needed for photosynthesis?
How would you make the experiment fair and reliable?
7 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Testing leaves for starch
8 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Testing Leaves for Starch
9 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Is chlorophyll needed for photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll cannot be removed from a plant without killing
the plant. Instead, variegated leaves can be used to show
chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis.
Variegated leaves have pale parts,
which do not contain chlorophyll.
The green parts of the leaf contain
chlorophyll and are the control.
Which areas will react with iodine?
Only the green areas of the leaf
react with the iodine and turn
blue-black. Without chlorophyll,
the pale areas have been unable
to produce starch and do not turn
blue-black.
10 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
How do leaves maximise photosynthesis?
Leaves are the most efficient
solar panels on Earth!
What does this mean?
Like solar panels, leaves
convert energy from the
Sun into usable chemical
energy.
Although leaves come in a
variety of shapes and sizes,
they share certain features
that enable the plant to
maximize photosynthesis.
11 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
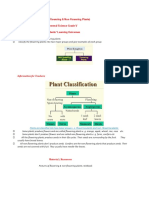
How are leaves adapted for photosynthesis?
To increase photosynthesis, leaves have certain key features:
thin – this allows gases to
reach cells easily
wide and flat – this create a
large surface area to absorb
as much light as possible
veins – these carry water to the
cells and carry glucose away
and also support leaves
stomata – these are pores on
the underside of leaves through
which gases move in and out.
12 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Structure of a leaf activity
13 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Take a look inside a leaf
14 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
How do gases enter and leave plants?
On the underside of leaves are small holes, or pores, called
stomata. A single hole is called a stoma. Each stoma is
surrounded by two guard cells.
When guard cells gain water,
they curve outwards. This
opens the stoma, allowing
gases in and out.
Losing water causes the guard
cells to come closer together,
closing the stoma. This stops
the movement of gases, but
also prevents water loss.
15 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Minerals and Plants Growth
16 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
1) Magnesium
• Magnesium is needed to make the green pigment,
chlorophyll.
• Less chlorophyll means less photosynthesis and
leaves will look yellow instead of green.
17 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
2) Nitrate
• Nitrate contains nitrogen atoms which are needed to
convert carbohydrates to protein and also to make
chlorophyll.
• Proteins are essential for making new cells so plants
can grow well
• Without enough nitrogen, leaves die and plants stay
small.
18 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Minerals
19 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
Plenary – Tweet Your Thoughts
• Post in three points, what did you learn
today?
20 of 48 © Boardworks Ltd 2007
You might also like
- PEMETAAN DSKP SN Tahun 1-3 DLPDocument8 pagesPEMETAAN DSKP SN Tahun 1-3 DLPLAU SING WAH Moe88% (8)
- Year 9 Science C3Document42 pagesYear 9 Science C3Ventus Tan100% (2)
- Pradip Krishen - Rao Jodha Desert Rock ParkDocument36 pagesPradip Krishen - Rao Jodha Desert Rock ParkSuneel SharmaNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesPhotosynthesisSultana KhanNo ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesDocument50 pagesAlwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Boardworks PhotosynthesisDocument48 pagesBoardworks Photosynthesiskian shahNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument43 pagesPlant NutritionSubaashNairNo ratings yet
- Leaf and MineralsDocument16 pagesLeaf and MineralsfarahNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Revision Notes Prd58wDocument5 pagesTopic 6 Revision Notes Prd58wSeve ReyesNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE Biology: 6.1 Photosynthesis & Leaf StructureDocument33 pagesCIE IGCSE Biology: 6.1 Photosynthesis & Leaf Structuremirharizwan2009No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Plant Responses#3Document29 pagesPhotosynthesis and Plant Responses#3BALQIS NURAZIZAHNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument59 pagesPhotosynthesisAima AzharNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION - PlantDocument8 pagesNUTRITION - PlantKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument28 pagesPlant NutritionEmanuel SafiNo ratings yet
- Class 13 - Photosynthesis ExperimentsDocument38 pagesClass 13 - Photosynthesis Experimentssheliza mohammedNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology CIE: 6. Plant NutritionDocument25 pagesIGCSE Biology CIE: 6. Plant NutritionMuhammad Hassan munirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2Hend HamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PhotosynthesisDocument99 pagesChapter 6 Photosynthesisjzdf2d9nnvNo ratings yet
- Structure of A LeafDocument82 pagesStructure of A Leaflevie agacerNo ratings yet
- Savemyexams Igcse Biology Photosynthesis and Leaf Structure WorksheetDocument34 pagesSavemyexams Igcse Biology Photosynthesis and Leaf Structure WorksheetkatisspeedNo ratings yet
- Bio PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesBio PhotosynthesisDoreth BridgemanNo ratings yet
- 2e Nutrition Flowering PlantsDocument36 pages2e Nutrition Flowering PlantsAghaanaa JaiganeshNo ratings yet
- Boardworks Transport in PlantsDocument40 pagesBoardworks Transport in PlantsJessica MagtagñobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants: Learning ObjectivesDocument14 pagesChapter 10 - Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plants: Learning Objectivesthanks btNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition Summary NotesDocument15 pagesPlant Nutrition Summary Notesazaanhasnat345No ratings yet
- Science 9 - Chapter 1 1.1 - 1.2Document12 pagesScience 9 - Chapter 1 1.1 - 1.2Hương Minh Phạm QuinnNo ratings yet
- CHP 1 PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesCHP 1 Photosynthesisjoyce heahNo ratings yet
- L6.3 Laef StructureDocument19 pagesL6.3 Laef StructureDima ArafatNo ratings yet
- Biology SQ3RDocument68 pagesBiology SQ3RJay JustNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisAyca UgurluNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition (Photosynthesis)Document45 pagesPlant Nutrition (Photosynthesis)Hamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument36 pagesPlant NutritionAbdul WarsiNo ratings yet
- Uses of Glucose in PlantsDocument12 pagesUses of Glucose in PlantsMr H BioNo ratings yet
- Sameeha Rida 20OSB1200 IGCSE VIII A Biologyworksheetonphotosynthesis 1Document6 pagesSameeha Rida 20OSB1200 IGCSE VIII A Biologyworksheetonphotosynthesis 1Sameeha RidaNo ratings yet
- 6.plant NutritionDocument31 pages6.plant NutritiontandmacgmNo ratings yet
- Describe & Draw The Plant Cell (Work Sheet) o Nucleus, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Chloroplast, Large Vacuole, MitochondriaDocument16 pagesDescribe & Draw The Plant Cell (Work Sheet) o Nucleus, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Chloroplast, Large Vacuole, MitochondriaStudy's AnayNo ratings yet
- Excerpt PDFDocument10 pagesExcerpt PDFerikNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION - PlantDocument8 pagesNUTRITION - Planttnkele73No ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument29 pagesPlant NutritionKenzy AlkoshiryNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cells v1.0Document39 pagesAnimal and Plant Cells v1.0Vincent Karani100% (1)
- IGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionDocument14 pagesIGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionsarNo ratings yet
- 植物的营养Document51 pages植物的营养2375606245No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Mastery BookletDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis Mastery Bookletapi-422428700No ratings yet
- UNIT 3 - Ch10 - Plants and Food - Students' NotesDocument24 pagesUNIT 3 - Ch10 - Plants and Food - Students' NotesMostafa A MansiNo ratings yet
- Term 3 - Transport in Plants (Handout)Document35 pagesTerm 3 - Transport in Plants (Handout)Ivan PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Plant NutritionDocument29 pagesPlant NutritionAyan Taimu raituNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument37 pagesPhotosynthesisibrahimgrewallNo ratings yet
- Leaves Bio Yr9Document12 pagesLeaves Bio Yr9Aliza ShahidNo ratings yet
- Experiments On PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesExperiments On PhotosynthesisMwesigwa JoshuaNo ratings yet
- 2.4 (A) Main Organ For PhotosynthesisDocument22 pages2.4 (A) Main Organ For PhotosynthesisVERNESS CHIA XIN THONG MoeNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and Photosynthesis - EditedDocument17 pagesPlant Structure and Photosynthesis - Editedchloe.phamNo ratings yet
- C6 - Plant NutritionDocument5 pagesC6 - Plant NutritionThet Htar ZawNo ratings yet
- Year 10 PhotosynthesisDocument50 pagesYear 10 PhotosynthesisShentong Penny WangNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Research Paper PDFDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis Research Paper PDFpjrozhiig100% (1)
- Plant Nutrition NotesDocument18 pagesPlant Nutrition NotesDavid ReeseNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition Part 2Document16 pagesPlant Nutrition Part 2Nicolas SchroppNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument23 pagesPhotosynthesisBLESSING UHUONo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesisElizabeth ThomasNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS Grade 10Document76 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS Grade 10Mecheal ThomasNo ratings yet
- Smackslidecom Exchanging Mate 5fca76fcdc9b2Document23 pagesSmackslidecom Exchanging Mate 5fca76fcdc9b2Aref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Hydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeFrom EverandHydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeNo ratings yet
- 1.1-L3-Lab ExperimentDocument10 pages1.1-L3-Lab Experimentفاطمه عيسى100% (1)
- 1.3 TheCarbonCycleDocument14 pages1.3 TheCarbonCycleفاطمه عيسىNo ratings yet
- Spot The Mistake The Carbon Cycle Powerpoint English Ver 2Document7 pagesSpot The Mistake The Carbon Cycle Powerpoint English Ver 2فاطمه عيسىNo ratings yet
- Book PDFDocument184 pagesBook PDFفاطمه عيسىNo ratings yet
- Identifying The Hazards Caused by Geological Processes: Geologic Event Hazards They Cause EarthquakeDocument7 pagesIdentifying The Hazards Caused by Geological Processes: Geologic Event Hazards They Cause Earthquakejzeaska damianNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1Document14 pagesPhotosynthesis 1Kithmini100% (1)
- Chapter 23 Assessment - BiologyDocument3 pagesChapter 23 Assessment - BiologyBushra IshratNo ratings yet
- Sijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia EditDocument75 pagesSijil Tinggi Persekolahan Malaysia EditDiana Ana0% (2)
- Study of Phytochemical Composition On Kaempferia Parviflora Wall Ex BakerDocument9 pagesStudy of Phytochemical Composition On Kaempferia Parviflora Wall Ex BakerKumaresh PalNo ratings yet
- Louvre DamperTandem DamperengfinDocument16 pagesLouvre DamperTandem DamperengfinDan PascaruNo ratings yet
- Macmillan Science Level 3 Pupil S Book Topic 1 PP 8 11Document4 pagesMacmillan Science Level 3 Pupil S Book Topic 1 PP 8 11reema2050reemaNo ratings yet
- 2122 Ye S4 Biology MSDocument4 pages2122 Ye S4 Biology MSOlivia LinNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan of Plants (Flowering & Non-Flowering Plants) General Science Grade V Students' Learning OutcomesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan of Plants (Flowering & Non-Flowering Plants) General Science Grade V Students' Learning OutcomesMariel AronNo ratings yet
- Banana Bunchy Top DiseaseDocument2 pagesBanana Bunchy Top DiseaseAlimohammad YavariNo ratings yet
- Wjec Biology SpectificaionDocument93 pagesWjec Biology SpectificaionLucy EvrettNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm Is The Most Successful Plant in The Exploitation of Many Terrestrial HabitatsDocument8 pagesAngiosperm Is The Most Successful Plant in The Exploitation of Many Terrestrial Habitatsaesha89100% (5)
- Mango LeavesDocument5 pagesMango LeavesMuthuswamy JayaramNo ratings yet
- Biology 2: Fundamentals of Biology 2 Fourth Quarter: SY 2018-2019 Laboratory Activity #3: Demonstrating Transpiration IDocument3 pagesBiology 2: Fundamentals of Biology 2 Fourth Quarter: SY 2018-2019 Laboratory Activity #3: Demonstrating Transpiration IMelancholiaNo ratings yet
- Classification: O Level IGCSE 2022-2023Document8 pagesClassification: O Level IGCSE 2022-2023Abdulrahman Mohammed100% (1)
- DePauw Nature Park Field Guide To Spring WildflowersDocument14 pagesDePauw Nature Park Field Guide To Spring WildflowersaaguilardNo ratings yet
- 1 - Characteristics and Classification of Living ThingsDocument3 pages1 - Characteristics and Classification of Living ThingsAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Bio 611Document14 pagesLab 3 Bio 611Zureen SofeaNo ratings yet
- Leaf ShapesDocument7 pagesLeaf Shapesbhaavan22No ratings yet
- 12 Biology Projects PDFDocument30 pages12 Biology Projects PDFAnurag PMNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 2quiz 1Document1 pageGENERAL BIOLOGY 2quiz 1Jewo CanterasNo ratings yet
- Aspen LeavesDocument3 pagesAspen LeavessheejasamNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Different Fertilizers On Plant GrowthDocument2 pagesThe Effect of Different Fertilizers On Plant GrowthVeerath தமிழன்0% (2)
- +potato Haifa.Document38 pages+potato Haifa.Creative EnglishNo ratings yet
- Buletin Kebun Raya (Irawati, 2017)Document16 pagesBuletin Kebun Raya (Irawati, 2017)Yusuf RachmandhikaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Source-Sink Restriction and Plant Density Changes On The Role of Assimilate Remobilization in Corn Grain YieldDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Source-Sink Restriction and Plant Density Changes On The Role of Assimilate Remobilization in Corn Grain Yieldshah khalidNo ratings yet
- Bandit-Seaslugs-12879-Article and QuizDocument5 pagesBandit-Seaslugs-12879-Article and Quizapi-327227161No ratings yet