Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Isotopes 2018
Isotopes 2018
Uploaded by
Victoria Virgo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views18 pagesThis document discusses isotopes, which are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes have the same chemical properties but different physical properties. Examples of isotopes discussed include various forms of carbon, hydrogen, chlorine, and others. Some isotopes are radioactive and decay over time. Applications mentioned include using carbon-14 dating to determine the age of remains, using radioactive isotopes for radiotherapy and medical tracers, and using radioactive isotopes in pacemaker batteries.
Original Description:
Original Title
ISOTOPES 2018
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses isotopes, which are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes have the same chemical properties but different physical properties. Examples of isotopes discussed include various forms of carbon, hydrogen, chlorine, and others. Some isotopes are radioactive and decay over time. Applications mentioned include using carbon-14 dating to determine the age of remains, using radioactive isotopes for radiotherapy and medical tracers, and using radioactive isotopes in pacemaker batteries.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views18 pagesIsotopes 2018
Isotopes 2018
Uploaded by
Victoria VirgoThis document discusses isotopes, which are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes have the same chemical properties but different physical properties. Examples of isotopes discussed include various forms of carbon, hydrogen, chlorine, and others. Some isotopes are radioactive and decay over time. Applications mentioned include using carbon-14 dating to determine the age of remains, using radioactive isotopes for radiotherapy and medical tracers, and using radioactive isotopes in pacemaker batteries.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
ISOTOPES
3rd FORM CHEMISTRY
● Atomic number is unique to a particular element.
(Eg. All atoms of Mg have an atomic number of 12)
● The number of neutrons is NOT unique to a
particular element. There are some atoms of Mg that
have 12 neutrons, others which have 13 and others
which have 14.
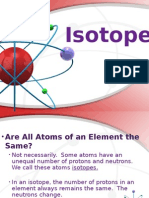
Atoms of the same element that
have the same number of protons
but different number of neutrons are
called ISOTOPES
(i.e. They have the same ATOMIC
NUMBER but different MASS
NUMBER)
ISOTOPES HAVE:
● The same chemical properties (Since they have the
same number and arrangement of electrons)
● Different physical properties (Because of the
different numbers of neutrons)
CARBON
Carbon-12 (C-12) Carbon-13 (C-13) Carbon 14 (C-14)
HYDROGEN
Protium Deuterium Tritium
NOTE: HYDROGEN IS THE ONLY ELEMENT THAT
HAS DIFFERENT NAMES FOR ITS ISOTOPES
CHLORINE
Chlorine-35 Chlorine-37
RADIOACTIVE
ISOTOPES
● Some isotopes have unstable nuclei
● In order to become stable they spontaneously eject
particles from the nucleus
● This is known as RADIOACTIVE DECAY
The time taken for half the nuclei
in a sample to undergo radioactive
decay is known as the HALF-
LIFE
CARBON-14
DATING
● Used to determine the age of plant and animal remains
● There is a specific amount of carbon-14 present in all living
organisms
● When an organism dies the carbon is no longer being
replenished
● The age of the specimen can be determined by the amount of
carbon-14 present in the sample
RADIOTHERAPY
● Utilizes radiation to control or cure cancer.
● Some of the particles and radiation emitted are able
to destroy cancer cells. This can be done both
externally and internally using various radioactive
isotopes as sources of radiation.
● Cobalt-60, Iodine-131 (Used for thyroid cancer),
Iridium-92 and Palladium-103
TRACERS
● Used to observe the functioning of organs and detect clots or
blockages
● Tracer is injected into the blood and a special device
used to detect the particles being emitted as it decays.
● Eg. Technetium-99, Iodine-131
PACEMAKERS
● Medical devices used to regulate the beating of the heart by
delivering a small electric charge to the cardiac muscle
● Pacemakers incorporate batteries containing radioactive
isotopes which produce energy to power the device as
they decay. (eg. Plutonium-238)
● These batteries last far longer than chemically powered
ones due to the long half-life
PACEMAKERS
You might also like
- What Is An IsotopeDocument8 pagesWhat Is An IsotopeifeanyichukwuNo ratings yet
- 1 6-IsotopesDocument22 pages1 6-IsotopesRemuel BelciñaNo ratings yet
- Notes On AtomDocument7 pagesNotes On Atomprincefresh853No ratings yet
- AN ATOM NEW For StudentsDocument10 pagesAN ATOM NEW For StudentsfaithiverogheneNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem ReviewerDocument4 pagesGen Chem ReviewerVeronica Hycinth SabidoNo ratings yet
- Isotopes & Their UsesDocument3 pagesIsotopes & Their Useshetanshvasoya.tgesNo ratings yet
- NOTES - 4.3 - Atomic - Mass - Isotopes - 2017 - SlideshowDocument16 pagesNOTES - 4.3 - Atomic - Mass - Isotopes - 2017 - SlideshowJoseph MusabukaNo ratings yet
- Atomic IsotopesDocument16 pagesAtomic Isotopesbrenda.mboghoNo ratings yet
- NOTES - 4.3 Atomic Mass Isotopes 2017 SlideshowDocument16 pagesNOTES - 4.3 Atomic Mass Isotopes 2017 SlideshowFatma MohamedNo ratings yet
- General-Chemistry1 Week 2 IsotopesDocument20 pagesGeneral-Chemistry1 Week 2 IsotopesSir Miguel MalvarNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 - Common Isotopes and Their UsesDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 - Common Isotopes and Their UsesMarcus MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- ISOTOPESDocument16 pagesISOTOPESJireh PasiliaoNo ratings yet
- IsotopesDocument15 pagesIsotopesapi-276003030No ratings yet
- SSC Mts Ex: Studymaterialfor GenralawarenessDocument8 pagesSSC Mts Ex: Studymaterialfor GenralawarenessAmrit SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction About Health Physics: DefinitionDocument24 pagesIntroduction About Health Physics: DefinitionRyan PazonNo ratings yet
- Structure PropertiesoforganicmoleculesDocument31 pagesStructure Propertiesoforganicmoleculeslan phương diệp thịNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure ChemistryDocument71 pagesAtomic Structure ChemistryNoor Syaqirah Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Elements and Compounds ElementsDocument6 pagesElements and Compounds ElementsAmna GhafoorNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Elements Notes by ThinkerDocument3 pagesAtoms and Elements Notes by ThinkerIshmael TynoeNo ratings yet
- Isotopes - PPT 10 3 20220Document29 pagesIsotopes - PPT 10 3 20220CJNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsDocument28 pagesAtoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument5 pagesAtomic StructureMustafa OmerNo ratings yet
- 1C Atomic StructureDocument24 pages1C Atomic Structurejustme.azma.meNo ratings yet
- Radioactive IsotopeDocument1 pageRadioactive IsotopeAvon Glorane MirandaNo ratings yet
- Bio-Physique Lesson1Document2 pagesBio-Physique Lesson1sreypichNo ratings yet
- Isotopes and IsobarsDocument14 pagesIsotopes and Isobarsssuryadharshan2009No ratings yet
- Gen Chem The Structure of An AtomDocument22 pagesGen Chem The Structure of An AtomKC KayeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Separatin Atomic StructureDocument28 pagesChemistry Separatin Atomic StructureShakay WrightNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Physics First UnitDocument18 pagesCambridge Physics First Unitmusic LenzoNo ratings yet
- NUCLEUS of An ATOM Describe The Composition of The NucleusDocument6 pagesNUCLEUS of An ATOM Describe The Composition of The Nucleusmiss lolipopNo ratings yet
- Sim For MunicipalDocument21 pagesSim For MunicipalJenelyn SarbodaNo ratings yet
- Common Isotopes and Their UsesDocument49 pagesCommon Isotopes and Their UsesNicole Joyce Catabay FloresNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and BondingDocument30 pagesAtomic Structure and BondingVenusCrazy 550No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument27 pagesAtomic Structure and The Periodic TableDavies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: 3.1 - Atoms and ElementsDocument4 pagesUnit 3: 3.1 - Atoms and ElementsRaffaella LaxaldeNo ratings yet
- Isotopes Radioactive IsotopesDocument16 pagesIsotopes Radioactive Isotopesapi-272083070No ratings yet
- General Chemistry I Handout 2Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry I Handout 2Roxan Oxima ClabriaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Chemistry Textbook - Section 1.1 The AtomDocument3 pagesSummary of Chemistry Textbook - Section 1.1 The AtomRachel JeffresonNo ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 2 StudentDocument18 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 2 StudentJhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Atoms and ElementsDocument31 pagesChapter 3 Atoms and Elementschitminthu560345No ratings yet
- 2.1 Molecules To MetabolismDocument7 pages2.1 Molecules To MetabolismDayoun SongNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Kimia Farmasi Dasar 090919Document58 pagesKuliah Kimia Farmasi Dasar 090919Mey NurtikaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Topic 2 The Chemistry of LifeDocument45 pagesAnaphy Topic 2 The Chemistry of LifejhasmineabonNo ratings yet
- Chem Exam NotesDocument10 pagesChem Exam NotesVinisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- ChemLec NotesDocument19 pagesChemLec NotesScyrah Allana RiegoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Number Atomic Nucleus IsotopesDocument1 pageAtomic Number Atomic Nucleus IsotopesHadiNo ratings yet
- IsotopesDocument12 pagesIsotopesCamylle NicdaoNo ratings yet
- CIE Chemistry Chapter 2 - Atoms, Elements and CompoundsDocument38 pagesCIE Chemistry Chapter 2 - Atoms, Elements and CompoundsIt's futfutiNo ratings yet
- Isotopes and Relative Atomic MassDocument2 pagesIsotopes and Relative Atomic MassMaxNo ratings yet
- Elements and CompoundsDocument6 pagesElements and CompoundsGhh TyuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document49 pagesLecture 1bkrmnbxbjtNo ratings yet
- ChemistrymidtermDocument4 pagesChemistrymidtermapi-311220298No ratings yet
- Chemistry RevisionDocument34 pagesChemistry RevisionYinmon ThantNo ratings yet
- FUNCHEM.2 2021 Slides 2021 2Document27 pagesFUNCHEM.2 2021 Slides 2021 2shabanaNo ratings yet
- Atoms & Isotopes: Mrs. Page Chemistry10Document24 pagesAtoms & Isotopes: Mrs. Page Chemistry10RENE N. RAMILONo ratings yet
- Isotopes, The Siblings of AtomsDocument3 pagesIsotopes, The Siblings of AtomsFatafut ShoppingNo ratings yet
- Everything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandEverything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- How Is Mercury Used Today? Chemistry Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandHow Is Mercury Used Today? Chemistry Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1From EverandConcepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1No ratings yet
- PolymersDocument36 pagesPolymersVictoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- Recording Depreciation in The Accounting BooksDocument1 pageRecording Depreciation in The Accounting BooksVictoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure 3Document41 pagesElectronic Structure 3Victoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- Response and Stimulus UpdatedDocument54 pagesResponse and Stimulus UpdatedVictoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- Translocation in The Phloem and Storage OrgansDocument11 pagesTranslocation in The Phloem and Storage OrgansVictoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- Uptake of Water in PlantsDocument12 pagesUptake of Water in PlantsVictoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- KS4 What Is BloodDocument40 pagesKS4 What Is BloodVictoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- Separation Techniques NotesDocument4 pagesSeparation Techniques NotesVictoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- 2018osmosis - DiffusionDocument11 pages2018osmosis - DiffusionVictoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument15 pagesMatterVictoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument18 pagesPaper ChromatographyVictoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- Radioactive PollutionDocument24 pagesRadioactive PollutionPuja SolankiNo ratings yet
- Proliferation of Nuclear WeaponsDocument7 pagesProliferation of Nuclear WeaponsVanshika KunduNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Radiation Protection in MedicineDocument287 pagesAn Introduction To Radiation Protection in MedicineYoussef MhamdiNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 12: Relative and Absolute DatingDocument24 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 12: Relative and Absolute DatingBok Mocorro275% (4)
- No More War PDF - Pauling, Linus, 1901Document260 pagesNo More War PDF - Pauling, Linus, 1901pdf ebook free downloadNo ratings yet
- Radiation Processing Industry - The Early YearDocument50 pagesRadiation Processing Industry - The Early YearNurul Fatia JannahNo ratings yet
- Radiation BiologyDocument155 pagesRadiation BiologyAliHasanCanoğluNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics IgcseDocument9 pagesNuclear Physics IgcseMuhammad asifNo ratings yet
- Numerical AtomsDocument6 pagesNumerical Atomsvishal_kalraNo ratings yet
- AP Physics II - Week of 4.20 - 4.24 ActivitiesDocument10 pagesAP Physics II - Week of 4.20 - 4.24 ActivitiesNephtali Pinos-anNo ratings yet
- Basic 1st Vol1Document254 pagesBasic 1st Vol1Ahmed shabanNo ratings yet
- Form Tech-4 - ARCDocument82 pagesForm Tech-4 - ARCAnkit Kumar ShahNo ratings yet
- Proton NMRDocument66 pagesProton NMRHaseeb ستيف ShaykhNo ratings yet
- Medical Physics Questions FOR Membership ExaminationDocument27 pagesMedical Physics Questions FOR Membership ExaminationMalen MohamadNo ratings yet
- Peaceful Uses of Nuclear TechnologyDocument11 pagesPeaceful Uses of Nuclear TechnologyStavros PagonidisNo ratings yet
- Victor Ninov's 'Discovery' of Element 118: A Case of Alleged Data Fabrication Mark Yashar U.C. Davis, Physics 280 6/1/07Document35 pagesVictor Ninov's 'Discovery' of Element 118: A Case of Alleged Data Fabrication Mark Yashar U.C. Davis, Physics 280 6/1/07Klass AlbánNo ratings yet
- NMR SpectrosDocument185 pagesNMR SpectrosBathir JafarNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity and Nuclear TransformaionDocument4 pagesRadioactivity and Nuclear TransformaionAthira I PNo ratings yet
- Conceptualized Transmutation Reactor To Mass-Produce Helium-3 and Precious MetalsDocument28 pagesConceptualized Transmutation Reactor To Mass-Produce Helium-3 and Precious MetalsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Materi 5 - Metode RadioaktifDocument23 pagesMateri 5 - Metode RadioaktifSius MacoNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAQA Physics Topic 4 Atomic Structure Knowledge OrganiserGabriel HoNo ratings yet
- Interactive - Textbook63-Absolute DatingDocument5 pagesInteractive - Textbook63-Absolute DatingAnalyn EnsanoNo ratings yet
- Interactive Textbook 2 PDF 4 2 AtomsDocument9 pagesInteractive Textbook 2 PDF 4 2 Atomsapi-240094705100% (1)
- Carbon 14 Dating ReadingDocument3 pagesCarbon 14 Dating ReadinghfhagerNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics P7 Radioactivity Past Paper QuestionsDocument23 pagesAQA Physics P7 Radioactivity Past Paper Questionsis7112No ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Oera Linda BookDocument135 pagesDokumen - Tips Oera Linda BookKevin ZidaneNo ratings yet
- Phys - Exam - May 2014-ZagazigDocument8 pagesPhys - Exam - May 2014-ZagazigWael ElsawyNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument5 pagesCase Studymarkmejia_025No ratings yet
- Fisiune Vs Fuziune NuclearaDocument3 pagesFisiune Vs Fuziune NuclearaVladPopoviciNo ratings yet