Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Combinational Circuit
Uploaded by
Muhd Darwish Mohd Zailani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views28 pagesThe document discusses encoders, decoders, multiplexers, and programmable logic devices like PROMs. It explains that encoders are the inverse of decoders and convert binary codes to n-bit codes. Multiplexers select one of several input lines based on the select lines and transmit the selected input to the output. PROMs allow Boolean functions to be executed by programming the OR array to output 1s for minterms of the function based on the address inputs.
Original Description:
Original Title
Combinational Circuit (3).ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses encoders, decoders, multiplexers, and programmable logic devices like PROMs. It explains that encoders are the inverse of decoders and convert binary codes to n-bit codes. Multiplexers select one of several input lines based on the select lines and transmit the selected input to the output. PROMs allow Boolean functions to be executed by programming the OR array to output 1s for minterms of the function based on the address inputs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views28 pagesCombinational Circuit
Uploaded by
Muhd Darwish Mohd ZailaniThe document discusses encoders, decoders, multiplexers, and programmable logic devices like PROMs. It explains that encoders are the inverse of decoders and convert binary codes to n-bit codes. Multiplexers select one of several input lines based on the select lines and transmit the selected input to the output. PROMs allow Boolean functions to be executed by programming the OR array to output 1s for minterms of the function based on the address inputs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 28
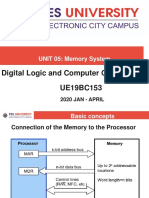
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
ENCODER
• Encoder is the inversion of decoder.
• Several sets of input line, select one, it produce
similar code for selected line
• Consist of 2n (or less) input line and n output line
• Created from OR gate
• Example:
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 1
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
Truth table
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 2
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
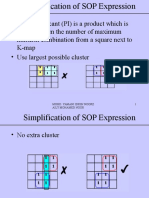
ENCODER
• With the aid of K-map (don’t care situation), we can get
D0 = F1 +F3
D1 = F2 +F3
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 3
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
ENCODER (Octal to Binary)
• At one time, only one input line has a value of 1
• Most of the time needs priority encoder
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 4
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
ENCODER (Octal to Binary)
• Can you get 2n to n encoder without using Karnaugh map
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 5
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
DEMULTIPLEXER
• Given input line & sets of selection line, demultiplexer
will send data directly from input to selected output line
• Example: 1 to 4 Demultiplexer
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 6
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
DEMULTIPLEXER
• Demultiplexer is similar to decoder with enable as
follows:
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 7
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
MULTIPLEXER
• multiplexer is a device which consist of
– Several input line
– Several select line
– One output line
• It transmit one from 2n input line to one output
line using n select line. It is also known as data
selector
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 8
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
MULTIPLEXER
• Truth table for 4-1 multiplexer
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 9
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
MULTIPLEXER
• Output for multiplexer is Sum of the (product of
data lines and selection lines)
• Example: Output for 4-1 multiplexer is
• 2n-to-1 line multiplexer or 2n:1 MUX is made
from n:2n decoder with 2n input line added, for
each AND gate.
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 10
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
MULTIPLEXER
Input
Lines
Added
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 11
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
MULTIPLEXER
• Usage:
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 12
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
LARGE MULTIPLEXER
• Large multiplexer can be built from smaller
multiplexer
• 8:1 multiplexer can be built from smaller
multiplexer like this
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 13
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
LARGE MULTIPLEXER
• Other example the building of 8:1 multiplexer
from smaller multiplexer
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 14
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
LARGE MULTIPLEXER
• 16:1 multiplexer can be
built using five 4:1
multiplexer
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 15
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
MULTIPLEXER (Function Execution)
• Boolean Function can be executed using multiplexer
• 2n:1 multiplexer can execute Boolean function with n input
variable as the following
– Expression in SOM
Example:
– Combine n variable to n selection line
– Put 1 at data line if it is a minterm for that function, else 0
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 16
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit – MSI Circuit
MULTIPLEXER (Function Execution)
• This method succeed because
• Put 1 at I1,I2, I3, and 0 at the remaining
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 17
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit (Programmable Logic Device)
Read-Only-Memory (ROM)
• Semiconductor memory is a device where data can be
stored and fetched
• Logically, this memory device can be said as memory
cells table (data)
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 18
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit (Programmable Logic Device)
Read-Only-Memory (ROM)
• ROM is a memory device where data can only be read but
cannot be written
• Writing is done by special programming device
(programmable ROM)
• Any Boolean function can be executed by using ROM. The
steps: Get TT, take its input as address and output as data
• Advantage: Boolean function is executed directly
• Disadvantage: Didn't use the “don’t care” and variable input
numbers is limited (e.g. 10 input – 1K, 16 input – 64K, 20
input – 1M)
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 19
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit (Programmable Logic Device)
Read-Only-Memory (ROM)
• Ready-made ROM Device Type
– ROM: Read Only Memory
Data is written to memory by “mask programming” when
manufacturing process. High cost to start and very cost effective
if produced in large quantity
– PROM: Programmable ROM
Semi-custom chip. Fuse can be burnt with “special hardware
programming unit”. High cost for small quantity and it cannot
be erased after programmed.
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 20
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit (Programmable Logic Device)
Read-Only-Memory (ROM)
• Ready-made ROM Device Type
– EPROM: Erasable PROM
Similar with PROM only that data can be erased by exposing it
to ultra violet light
– EEPROM: Electrically EPROM
PROM where data to be erased can be selected by “hardware
programmer unit” other than ultra violet light. Very useful for
isolated device where it can be reprogrammed from far
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 21
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit (Programmable Logic Device)
Programmable Read-Only-Memory (PROM)
• Device with hardwired AND array (i.e. decoder) and
programmable OR array
• AND array (decoder) execute 2n minterm product
combination for n input (known as n:2n decoder)
• n line input and m line output
• Input bit variable combination – address
• Input bit combination for output line – word (each word
contain m bit)
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 22
MOHAMED NOOR
Programmable Read-Only-Memory (PROM)
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 23
MOHAMED NOOR
Programmable Read-Only-Memory (PROM)
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 24
MOHAMED NOOR
Programmable Read-Only-Memory (PROM)
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 25
MOHAMED NOOR
Combinational Circuit (Programmable Logic
Device)
Execute logical function with PROM
• Example (8X3 ROM) –
• First, convert each function to SOP
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 26
MOHAMED NOOR
Execute logical function with PROM
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 27
MOHAMED NOOR
Execute logical function with PROM
MOHD. YAMANI IDRIS/ NOORZAILY 28
MOHAMED NOOR
You might also like
- 8086 Hardware 2 MEMORY and IO IntefaceDocument46 pages8086 Hardware 2 MEMORY and IO IntefaceНемања БорићNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Memory and Programmable LogicDocument43 pagesChapter 7 Memory and Programmable LogicShoaib SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Digital MemoriesDocument59 pagesDigital MemoriesAnkit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Fluent Tips and TricksDocument137 pagesFluent Tips and TricksalmohammadiNo ratings yet
- ESD 03 ARM ArchitectureDocument37 pagesESD 03 ARM ArchitectureAkshay Gattu100% (1)
- Ram RomDocument24 pagesRam RomYatin Kshirsagar87% (15)
- Chapter 1: Introduction To HCS12/MC9S12 The HCS12 Microcontroller Han-Way Huang Minnesota State University, Mankato September 2009Document31 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To HCS12/MC9S12 The HCS12 Microcontroller Han-Way Huang Minnesota State University, Mankato September 2009Omar LopezNo ratings yet
- Logic GatesDocument21 pagesLogic GatesMuhd Darwish Mohd ZailaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Single-Chip Microcomputer (Microcontroller)Document17 pagesIntroduction To Single-Chip Microcomputer (Microcontroller)Mohammed Dyhia Ali100% (1)
- LogicGates IntroDocument10 pagesLogicGates IntroMuhd Darwish Mohd ZailaniNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic and Storage DevicesDocument63 pagesProgrammable Logic and Storage DevicesHectorLopezNo ratings yet
- 10 Memory InterfaceDocument49 pages10 Memory Interfacemarah qadiNo ratings yet
- Lec 13-16Document44 pagesLec 13-16Ebrahim SiddikNo ratings yet
- Memory and Programmable Logic: CSA051 - Digital Systems 數位系統導論Document33 pagesMemory and Programmable Logic: CSA051 - Digital Systems 數位系統導論J RaviNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 - Memory SystemDocument42 pagesUNIT 5 - Memory SystemAnamika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cam Module 5 RomDocument28 pagesCam Module 5 Romnamitha rNo ratings yet
- 1 History of MicroprocessorDocument80 pages1 History of MicroprocessorRaghav GuptaNo ratings yet
- DERTS Lec4Document32 pagesDERTS Lec4quNo ratings yet
- Embedded System Design (BEE-446) : MemoryDocument41 pagesEmbedded System Design (BEE-446) : MemoryRéussi ÉlevéNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Hosni Al-SaeedDocument10 pagesAhmed Hosni Al-Saeedfaris daboolNo ratings yet
- 3.chap3 Automatisme Et Infirmatique IndustrielleDocument37 pages3.chap3 Automatisme Et Infirmatique IndustrielleHkbv GjvcNo ratings yet
- War Field Spying Robot With Night Vision Wireless Camera by Android ApplicationsDocument32 pagesWar Field Spying Robot With Night Vision Wireless Camera by Android ApplicationsharshithaNo ratings yet
- COE 202: Digital Logic Design Memory and Programmable Logic DevicesDocument25 pagesCOE 202: Digital Logic Design Memory and Programmable Logic DevicesSai RaghuNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Design: A Unified Hardware/Software IntroductionDocument39 pagesEmbedded Systems Design: A Unified Hardware/Software IntroductionAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Spying Robot For Army PurposeDocument31 pagesSpying Robot For Army Purposeankit25393No ratings yet
- ARM ArchitectureDocument24 pagesARM ArchitectureLeena VsNo ratings yet
- Memory and Programmable LogicDocument47 pagesMemory and Programmable Logicdewantosatrio50% (2)
- Programmable Logic: - FactsDocument18 pagesProgrammable Logic: - FactsGiuseppe TipaldiNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and Embedded SystemsDocument32 pagesMicroprocessors and Embedded SystemsEmmanuel MupingaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document71 pagesUnit 5Dr.G.Nirmala PriyaNo ratings yet
- Benm 2123 Microprocessor Technology: Chapter 1: Introduction To MicroprocessorDocument24 pagesBenm 2123 Microprocessor Technology: Chapter 1: Introduction To MicroprocessorDeva RaguNo ratings yet
- Computing & Informatics: Short Notes: Microprocessors Intel 8085Document38 pagesComputing & Informatics: Short Notes: Microprocessors Intel 8085Sayak BoseNo ratings yet
- Emerging Memory Technology FinalDocument40 pagesEmerging Memory Technology FinalAISHA 20682No ratings yet
- Memory InterfacingDocument55 pagesMemory Interfacinganand787No ratings yet
- DR Somashekhar: Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai - 600 036Document16 pagesDR Somashekhar: Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai - 600 036Gunjan MudgalNo ratings yet
- Ram RomDocument42 pagesRam Rommohit mishraNo ratings yet
- CH-6 Basics of MicroprocessorsDocument38 pagesCH-6 Basics of MicroprocessorsbelaynehNo ratings yet
- RAM 2522 DKDocument40 pagesRAM 2522 DKDon Nipuna PandithasundaraNo ratings yet
- Boolean Algebra (4) K-MAP 2Document23 pagesBoolean Algebra (4) K-MAP 2Fir DausNo ratings yet
- Memory Devices: Prepared by Rajesh Paul - (Electronics) ADC-AMPDocument17 pagesMemory Devices: Prepared by Rajesh Paul - (Electronics) ADC-AMPSubrahmanyam GuduruNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic DevicesDocument38 pagesProgrammable Logic DevicesgayathriNo ratings yet
- MC Unit 1 NON CAMPUSDocument18 pagesMC Unit 1 NON CAMPUSSangamesh V AngadiNo ratings yet
- 18-A6 Report On Primary Memory.12Document23 pages18-A6 Report On Primary Memory.12rehana mohammedNo ratings yet
- Department of Ece Subject Code: Ec1203 Digital Electronics (For Third Semester Ece) Two Mark Questions-AnswersDocument12 pagesDepartment of Ece Subject Code: Ec1203 Digital Electronics (For Third Semester Ece) Two Mark Questions-AnswersSurendar PNo ratings yet
- Memory Devices, Circuits, and Subsystem Design: The 8088 and 8086 Microprocessors, Triebel and Singh 1Document55 pagesMemory Devices, Circuits, and Subsystem Design: The 8088 and 8086 Microprocessors, Triebel and Singh 1Ivan-Jeff AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Selection of Platform On ITDocument23 pagesSelection of Platform On ITAravind BabuNo ratings yet
- ES - Lecture 4 - Aug 4Document25 pagesES - Lecture 4 - Aug 4Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- مسيطرات كاملDocument101 pagesمسيطرات كاملahmed aliraqiNo ratings yet
- VBNVCBNBVNDocument16 pagesVBNVCBNBVNGunjan MudgalNo ratings yet
- VLSI Array SubsystemsDocument17 pagesVLSI Array SubsystemsSireesha Tekuru80% (5)
- Implementation of Combinational Logic by Standard Ics and Programmable Rom MemoriesDocument5 pagesImplementation of Combinational Logic by Standard Ics and Programmable Rom MemoriesJohn KirubaNo ratings yet
- T.Y. E.I. /2 / 1 Memories N.KapoorDocument5 pagesT.Y. E.I. /2 / 1 Memories N.KapoorNeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- Mcu - Pic - 2019 PDFDocument60 pagesMcu - Pic - 2019 PDFThành TâmNo ratings yet
- Euler Path: Traverses Each Branch of The Graph Exactly Once!Document53 pagesEuler Path: Traverses Each Branch of The Graph Exactly Once!mark peroseNo ratings yet
- K.Lalmuankima: Microcontroller Based System Design Unit - 3 & 4Document18 pagesK.Lalmuankima: Microcontroller Based System Design Unit - 3 & 4Lalmuankima KhawlhringNo ratings yet
- Reviewing The Basics Chapter 7Document3 pagesReviewing The Basics Chapter 7Gillaire Gleed100% (1)
- CPE102L Comp Funda Unit 3 The Computer Hardware ModuleDocument11 pagesCPE102L Comp Funda Unit 3 The Computer Hardware ModuleLei StarosaNo ratings yet
- 8086 InterfaceDocument26 pages8086 InterfacelucaslandonNo ratings yet
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- LECTURE 1.2 Phasor, Lead and LagJottedDocument28 pagesLECTURE 1.2 Phasor, Lead and LagJottedMuhd Darwish Mohd ZailaniNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2.2 Resistance Reactance and Impedance JottedDocument15 pagesLECTURE 2.2 Resistance Reactance and Impedance JottedMuhd Darwish Mohd ZailaniNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2.1 Electrical Components Across AC Jotted PDFDocument20 pagesLECTURE 2.1 Electrical Components Across AC Jotted PDFMuhd Darwish Mohd ZailaniNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3.1 RC Circuit JottedDocument23 pagesLECTURE 3.1 RC Circuit JottedMuhd Darwish Mohd ZailaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2 RL CIRCUIT JottedDocument20 pagesLecture 3.2 RL CIRCUIT JottedMuhd Darwish Mohd ZailaniNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 4.1 RLC Circuit JottedDocument32 pagesLECTURE 4.1 RLC Circuit JottedMuhd Darwish Mohd ZailaniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 Chemistry Muhammad Darwish Bin Mohd Zailani FK1Document16 pagesTutorial 5 Chemistry Muhammad Darwish Bin Mohd Zailani FK1Muhd Darwish Mohd ZailaniNo ratings yet