Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Organelles
Uploaded by
Andrie Yzabelle Ohcocya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesOriginal Title
CELL-ORGANELLES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesCell Organelles
Uploaded by
Andrie Yzabelle OhcocyaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
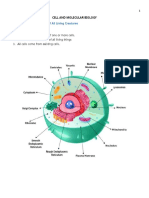
CELL ORGANELLES
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS
CELL STRUCTURE FUNCTION
ORGANELLE
Nucleus • Double membrane- • Responsible for
bound structure controlling all
which consists of a cellular
nuclear envelope, activities as well
chromatin, and as a center for
nucleolus genetic
materials, and
it’s transferring
CELL STRUCTURE FUNCTION
ORGANELLE
Cell • Consists of a phospholipid • Provides
Membrane bilayer along with two types of mechanical support
proteins viz. embedded proteins that facilities the
and peripheral proteins that shape of the cell
function in providing shape and while enclosing the
allowing the movement of cell and its
particles in and out of the cell components from
the external
environment
• Regulates what
can be allowed to
enter and exit the
cell through
channels, acting as
CELL STRUCTURE FUNCTION
ORGANELLE
Mitochondrion • Double membrane-bound • Responsible for the
cell organelles which contains supply and storage of
two membranes with the energy for the cell
outer layer being smooth
while the inner layer is
marked with folding and
finger-like structures called
cristae
CELL STRUCTURE FUNCTION
ORGANELLE
Smooth • Lacks ribosomes • Has a function
Endoplasmic during lipid
Reticulum synthesis
Rough • With ribosomes • Involved in
Endoplasmic attached on the protein synthesis
Reticulum cytosolic face of
Endoplasmic Reticulum
CELL STRUCTURE FUNCTION
ORGANELLE
Golgi Apparatus • Membrane-bound organelle • Has an essential
found in eukaryotic cells purpose of directing
(cells with clearly defined proteins and lipids to
nuclei) that is made up of a their destination and
series of flattened stacked thus, act as the “traffic
pouches called cisternae police” of the cell
CELL STRUCTURE FUNCTION
ORGANELLE
Lysosome • Membrane-bound • Responsible for
organelles that occur in the intracellular digestion
cytoplasm of animal cell; where the larger
granular or spherical macromolecules are
degraded into smaller
molecules with the
help of enzymes
present in them
CELL ORGANELLE STRUCTURE FUNCTION
Cytoplasm • Consists of a cytosol; a gel-like • Most of the vital
substance that contains other cellular and enzymatic
matter; cell organelles; smaller cell- reactions like cellular
like bodies bound by separate respiration and
membranes; and cytoplasmic translation of mRNA
inclusions; insoluble molecules that into proteins occur in
store energy and are not the cytoplasm
surrounded by any layer. • The process called
cytoplasmic streaming
helps in the distribution
of various nutrients and
facilitates the
movement of cell
organelles within the
cell
CELL STRUCTURE FUNCTION
ORGANELLE
Chloroplast • Membrane-bound • Cite of
organelles that occur in the photosynthesis.
cytoplasm of plant cell. Produces the food that
the plants need.
CELL STRUCTURE FUNCTION
ORGANELLE
Centriole and •made up of 9 microtubules • Helps or aids animal
Spindle fibers cell during cell division
through producing
spindle fibers that are
attaching to the
chromosomes during
metaphase
CELL STRUCTURE FUNCTION
ORGANELLE
Ribosome A ribosome is a complex complex molecular
of RNA and protein and machine found
is, therefore, known as a inside the living
ribonucleoprotein. It is cells that produce
composed of two proteins from
subunits – smaller and amino acids during
larger. a process called
protein synthesis
or translation. The
process of protein
synthesis is a
primary function,
which is performed
by all living cells.
CELL STRUCTURE FUNCTION
ORGANELLE
Cell Wall Varies its composition maintenance of the cell
structure and shape. The wall
depending on the type of is rigid, so it protects the cell
organism. and its contents.
ASSIGNMENT
Differentiate plant and animal
cell.
What are the organelles present
and not present in each cell type?
Thank youuu!
You might also like
- From Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.From EverandFrom Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.No ratings yet
- A Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneDocument4 pagesA Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- NatSci2 Chapter 3Document33 pagesNatSci2 Chapter 3kayNo ratings yet
- Divyasparshi: Healer Suresh NagarsekarDocument21 pagesDivyasparshi: Healer Suresh Nagarsekarprashant borgeNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 FullDocument130 pagesChap 5 Fullgaelle tannous100% (1)
- Cell Molecular Composition of CellDocument72 pagesCell Molecular Composition of Celljomel rondinaNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument24 pagesThe CellTyra Joyce Revadavia100% (1)
- Cell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Document7 pagesCell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Amrul Zlalu AdaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and EukaryotcG7Document41 pagesProkaryotic and EukaryotcG7Nes ConstanteNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument27 pagesIntroductionBaiawwal AmpatuanpendongNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument35 pagesBioenergeticsJaine LuzNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and Its StucturesDocument7 pagesCell Organelles and Its StucturesHailey Eisleen LazaroNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & OrganisationDocument62 pagesCell Structure & OrganisationSUNDARI SIVASANKARNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument94 pagesThe CellKorean DramaNo ratings yet
- Cells/Organ Elles Structures Functions: NucleusDocument8 pagesCells/Organ Elles Structures Functions: NucleusHazimah MohiddinNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsDocument16 pagesCarbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsTsu Wei Chua100% (5)
- CellDocument27 pagesCellTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Cell 2Document24 pagesCell 2DCRUZNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument41 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationKaesaav SelvamanikamNo ratings yet
- Organelle Present/Absent Description FunctionDocument5 pagesOrganelle Present/Absent Description FunctionTania BacsinNo ratings yet
- CellDocument24 pagesCellVenomNo ratings yet
- Transes, Cells + TissuesDocument7 pagesTranses, Cells + TissuesCristine Dominique E. DonaireNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument16 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationanippoNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton - GROUP 2Document19 pagesCytoskeleton - GROUP 2n42fjjy8g7No ratings yet
- Quiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)Document12 pagesQuiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)deaNo ratings yet
- STRUCTUREDocument2 pagesSTRUCTUREDanilo JR. BuaquiñaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Notes Week 1-3Document15 pagesGenetics Notes Week 1-3SOFHIA CLAIRE SUMBAQUILNo ratings yet
- Body Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesBody Cells and TissuesAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDocument54 pagesCell Structure AND Cell OrganisationAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Cell & Binomial NomenclatureDocument6 pagesCell & Binomial NomenclatureVenice De los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument16 pagesReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Cell Structure Functionss.y.2022 2023Document40 pagesLesson 2 Cell Structure Functionss.y.2022 2023Trisha Anthony CortazNo ratings yet
- L 2 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument25 pagesL 2 Cell Structure and Functionkaukab azimNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle CardsDocument6 pagesCell Organelle CardsVienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: CELL - : How Were Cells Discovered?Document5 pagesCHAPTER 1: CELL - : How Were Cells Discovered?Joy Mazo FaderagaoNo ratings yet
- CellDocument2 pagesCellTamarah RomeroNo ratings yet
- 3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument12 pages3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsPrince TeodocioNo ratings yet
- 2 Organisation of The Organism NotesDocument5 pages2 Organisation of The Organism Notesarayana sharmaNo ratings yet
- BIO 345 S13 Continuity S14 (Chapter 5) S15 S16 S17 S18Document153 pagesBIO 345 S13 Continuity S14 (Chapter 5) S15 S16 S17 S18gaelle tannous100% (1)
- Module 1 Unit 1 Cells As Basic Unit of LifeDocument30 pagesModule 1 Unit 1 Cells As Basic Unit of LifeMonique scheepersNo ratings yet
- Membrane Bound Organelles and Non Membrane Bound OrganellesDocument25 pagesMembrane Bound Organelles and Non Membrane Bound OrganellesAshlee Venice CebuNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument17 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (3)
- Parts of The Cell Worksheet - BiochemistryDocument3 pagesParts of The Cell Worksheet - BiochemistryAnonymous giver100% (1)
- Cell ReviewerDocument7 pagesCell ReviewerMar LagmayNo ratings yet
- B M Subramanya Swamy CIE Co Ordinator & Examination Officer Kanaan Global School Jakarta Indonesia Swamy@kanaanglobal - Sch.idDocument42 pagesB M Subramanya Swamy CIE Co Ordinator & Examination Officer Kanaan Global School Jakarta Indonesia Swamy@kanaanglobal - Sch.idB M Subramanya SwamyNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Organelles - Structure and FunctionKaryl Marie Rodas JaminNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureDocument31 pagesDokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureJairra Jae LunaNo ratings yet
- ELS Cell PresentationDocument16 pagesELS Cell Presentationmatthew09163651700No ratings yet
- Group 2. Presentation - Cell 1Document57 pagesGroup 2. Presentation - Cell 1Thông LêNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDocument48 pagesCell Structure AND Cell OrganisationBabasChongNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument24 pagesCell StructureDave BoocNo ratings yet
- Organelle Biochemical Process ImportanceDocument5 pagesOrganelle Biochemical Process Importanceaira roperezNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions (Flores)Document4 pagesEukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions (Flores)Dharyl FloresNo ratings yet
- Cells & Physiology - Lecture (Week 3-4)Document59 pagesCells & Physiology - Lecture (Week 3-4)Trevannie EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Act 2CDocument3 pagesAct 2CCHARLIENE FAYE ASPRERNo ratings yet
- Review of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument25 pagesReview of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cellsevil twinNo ratings yet
- Cyto Lesson 3Document5 pagesCyto Lesson 3Sittie Psyche A. AdtizNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell and Plant CellDocument1 pageAnimal Cell and Plant CellFabian PhilipNo ratings yet
- Lesso N 2: Organe LlesDocument19 pagesLesso N 2: Organe LlesMicha E.No ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument10 pagesBio Noteschanhongyi16No ratings yet
- Biotic Community ConceptDocument2 pagesBiotic Community Conceptmichaeluriel100% (2)
- The Physical SelfDocument14 pagesThe Physical SelfDaniel John ArboledaNo ratings yet
- LET GenEd 2019Document6 pagesLET GenEd 2019Yaj CruzadaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 Molecular Basis of HeredityDocument6 pagesExercise 5 Molecular Basis of HeredityHiroshi MatsushimaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 ProteinsDocument9 pagesWorksheet 2 ProteinsSahar GhanemNo ratings yet
- Science 8: 4 QUARTER Module 4Document10 pagesScience 8: 4 QUARTER Module 4katt100% (1)
- Spier, Raymond E. Eds. Encyclopedia of Cell Technology, Volumes 1-2 PDFDocument1,422 pagesSpier, Raymond E. Eds. Encyclopedia of Cell Technology, Volumes 1-2 PDFDimitar MinkovNo ratings yet
- Science7 q2 Mod6of8 Asexual Sexualrep v2Document26 pagesScience7 q2 Mod6of8 Asexual Sexualrep v2Ishi OcheaNo ratings yet
- BCH4125 2022 - Lecture4 5 Jan20 25Document61 pagesBCH4125 2022 - Lecture4 5 Jan20 25Fatima AkbariNo ratings yet
- Cells Unit TestDocument9 pagesCells Unit TestDanna SchererNo ratings yet
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and The Case For Intelligent Design by Stephen C. Meyer (Excerpt)Document20 pagesDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and The Case For Intelligent Design by Stephen C. Meyer (Excerpt)HarperOne (an imprint of HarperCollins)100% (12)
- Xii Biology Pre Board PDFDocument16 pagesXii Biology Pre Board PDFnbmbNo ratings yet
- Brassica OleraceaDocument115 pagesBrassica Oleracea24 ChannelNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 NotesDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 NotesHenry SathyanNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 DLLDocument13 pagesGrade 9 DLLJennifer AlindoganNo ratings yet
- Genetics II QuizDocument8 pagesGenetics II QuizSchool Others0% (2)
- Type of Cell FunctionDocument3 pagesType of Cell FunctionDerek Pagsolingan0% (1)
- Biosafty and Bioethics 3rd Year Biology Dep'tDocument17 pagesBiosafty and Bioethics 3rd Year Biology Dep'telsaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Taxonomy: Classification and Naming of Living ThingsDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Taxonomy: Classification and Naming of Living ThingsChique Ann MaalaNo ratings yet
- 15 Gene Expression Translation SDocument6 pages15 Gene Expression Translation SHelp Me Study TutoringNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and ArchaeaDocument17 pagesProkaryotes and ArchaeaAngela CanlasNo ratings yet
- 4Q - Biotechnology - Activity SheetsDocument10 pages4Q - Biotechnology - Activity Sheetsjessica ignacioNo ratings yet
- BIO102 Practice ExamDocument10 pagesBIO102 Practice ExamKathy YuNo ratings yet
- Meiosis LabDocument2 pagesMeiosis Labapi-197683383No ratings yet
- P ART Ii. Phonetics (0.5 PT)Document8 pagesP ART Ii. Phonetics (0.5 PT)Ngân Nguyễn TháiNo ratings yet
- RiboswitchesDocument30 pagesRiboswitchesYaseswini NeelamrajuNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Gene ExpressionDocument34 pagesRegulation of Gene ExpressionJay Fickle100% (1)
- Papaya: Biology, Cultivation, Production and UsesDocument74 pagesPapaya: Biology, Cultivation, Production and UsesBisham SangroulaNo ratings yet
- Forensic DNA Fingerprinting Using Restriction EnzymesDocument33 pagesForensic DNA Fingerprinting Using Restriction Enzymesbharad wajNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument7 pagesTranslationFathimaNo ratings yet