Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structure Functions
Uploaded by
Gian Carlo Madriaga0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesOriginal Title
SPGBIO1.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesCell Structure Functions
Uploaded by
Gian Carlo MadriagaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
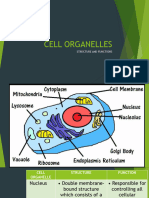
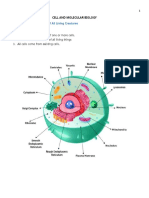
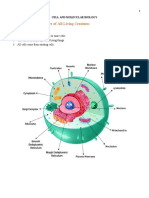
CELL STRUCTURE DESCRIPTION FUNCTION
GENETIC CONTROL OF CELL
• NUCLEUS A specialized structure occurring in Controls and regulates the activities of
• Nuclear pores most cells and separated from the rest the cell and carries the genes,
• Nuclear envelope of the cell by a double layer, the structures that contain the hereditary
• Nucleolus nuclear membrane. information.
• a minute opening or • regulate the movement of
passage way through the molecules from the
nuclear envelope. nucleus to the cytoplasm,
• a highly regulated and vice versa.
membrane barrier that • to allow separation of DNA
separates the nucleus from from cytoplasm machinery
the cytoplasm in eukaryotic and it is the regulation of
cells. contents that move in and
• a region found within the out of the nucleus through
cell nucleus that is small holes called nuclear
concerned with producing pores.
and assembling the cell's • facilitating ribosome
ribosomes. biogenesis.
• RIBOSOMES A particle that is present in large Decoding the message and the
numbers in all living cells and serves as formation of peptide bonds.
the site of protein synthesis.
Manufacture, distribution, and breakdown of molecules
• Endoplasmic Reticulum A network of membranes inside a cell To produce proteins for the rest of the
(ER) through which proteins and other cell to function.
• Smooth molecules move. • synthesizes lipids,
• Rough • meshwork of fine disklike phospholipids as in plasma
tubular membrane vesicles. membranes, and steroids.
• series of connected flattened • to produce proteins for the
sacs. rest of the cell to function.
• Golgi Apparatus A membrane-bound organelle found in Helps process and package proteins
eukaryotic cells that is made up of a and lipid molecules, especially proteins
series of flattened stacked pouches destined to be exported from the cell.
called cisternae.
• Lysosomes A membrane-bound cell organelle that functions as the digestive system of
contains digestive enzymes. the cell.
• Vacuoles A small cavity or space in the tissues of Help sequester waste products.
an organism containing air or fluid.
• Peroxisomes Are small, membrane-enclosed Contain digestive enzymes for breaking
organelles that contain enzymes down toxic materials in the cell and
involved in a variety of metabolic oxidative enzymes for metabolic
reactions, including several aspects of activity.
energy metabolism.
Energy Processing
• Mitochondria Are membrane-bound cell organelles Main job of mitochondria is to perform
that generate most of the chemical cellular respiration.
energy needed to power the cell's
biochemical reactions.
• Chloroplast An organelle within the cells of plants Convert light energy into relatively
and certain algae that is the site of stable chemical energy via the
photosynthesis. photosynthetic process.
Structural support, Movement, and Communication between Cells
• Cytoskeleton A structure that helps cells maintain Helps cells maintain their shape and
• Microtubule their shape and internal organization. internal organization and provides
• filamentous intracellular mechanical support that enables cells
structures that are to carry out essential functions like
responsible for various kinds division and movement.
of movements in all • they provide the rigid,
eukaryotic cells. organized components of the
cytoskeleton that give shape
to many cells.
• Plasma Membrane/Cell Is the membrane found in all cells that Provides protection for a cell.
Membrane separates the interior of the cell from
the outside environment.
• Plant Cell Wall A tough outer covering that lies right provides tensile strength and
outside the cell membrane. protection against mechanical and
osmotic stress.
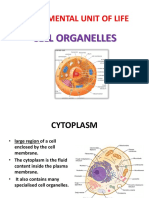
• Cytoplasm A thick solution that fills each cell and Responsible for holding the
is enclosed by the cell membrane. components of the cell and protects
them from damage.
• Vesicles A self-contained structure consisting of Help transport materials that an
fluid or gas surrounded and enclosed organism needs to survive and recycle
by an outer membrane called the lipid waste materials.
bilayer.
For Cell Division
• Centriole Are paired barrel-shaped organelles Organizing microtubules that serve as
located in the cytoplasm of animal cells the cell's skeletal system and they help
near the nuclear envelope. determine the locations of the nucleus
and other organelles within the cell.
CELL STRUCTURE PROKARYOTE EUKARYOTE BOTH FUNCTION
Cell Wall • Provides tensile
strength and
protection against
mechanical and
osmotic stress.
Plasma • Provides protection
Membrane for a cell.
Nucleus • Controls and regulates
the activities of the
cell (e.g., growth and
metabolism) and
carries the genes,
structures that
contain the hereditary
information.
Rough ER • To produce proteins
for the rest of the cell
to function.
Golgi Body • Helps process and
package proteins and
lipid molecules,
especially proteins
destined to be
exported from the
cell.
Smooth ER • It synthesizes lipids,
phospholipids as in
plasma membranes,
and steroids.
Mitochondrion • Generate most of the
chemical energy
needed to power the
cell's biochemical
reactions
Ribosomes • Decoding the message
and the formation of
peptide bonds.
Flagella • Flagella have an active
role in aiding cell feeding
and eukaryotic
reproduction. In
prokaryotes flagella
serve as propulsion
mechanisms, they're the
chief way for bacteria to
swim through fluids.
Cilia • to move water relative
to the cell in a regular
movement of the cilia.
You might also like
- Oil & Gas Amine Sweetening Unit ManualDocument56 pagesOil & Gas Amine Sweetening Unit ManualAariz Khan100% (2)
- Chapter 1 - Quiz 2 Form A: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. P. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8Document2 pagesChapter 1 - Quiz 2 Form A: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. P. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8Olalekan Oyekunle0% (1)
- Solutions of Mini Case Bruce HoniballDocument5 pagesSolutions of Mini Case Bruce HoniballShivshankar Yadav100% (1)
- CellDocument27 pagesCellTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument10 pagesBio Noteschanhongyi16No ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument15 pagesCell OrganellesAndrie Yzabelle OhcocyaNo ratings yet
- A Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneDocument3 pagesA Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Functions: Also Called Plasma Membrane, Support and ProtectionDocument4 pagesCell Structures and Functions: Also Called Plasma Membrane, Support and Protectionrimel usmanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Cell FunctionsDocument24 pagesModule 1 Cell FunctionsLady MeowNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology BasicsDocument17 pagesCell Biology BasicsHizzei Caballero100% (3)
- Plant Cell Structure Lec NotesDocument26 pagesPlant Cell Structure Lec NotesFranchez Cassandra EscanderNo ratings yet
- Group 2. Presentation - Cell 1Document57 pagesGroup 2. Presentation - Cell 1Thông LêNo ratings yet
- M3 Lesson 1Document2 pagesM3 Lesson 1kristinemehNo ratings yet
- CellDocument34 pagesCellSadaf JavedNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure: A Guide to the Organelles and Components of the CellDocument24 pagesCellular Structure: A Guide to the Organelles and Components of the CellTyra Joyce Revadavia100% (1)
- CHAPTER 1: CELL - : How Were Cells Discovered?Document5 pagesCHAPTER 1: CELL - : How Were Cells Discovered?Joy Mazo FaderagaoNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Organelles and Their FunctionsVienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document22 pagesLecture 3raja11160No ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument18 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (1)
- Cell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Document7 pagesCell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Amrul Zlalu AdaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument32 pagesCell Structure and Functionnaveedalikhoso365100% (1)
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument16 pagesReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument35 pagesBioenergeticsJaine LuzNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 FullDocument130 pagesChap 5 Fullgaelle tannous100% (1)
- 1Q Gen Bio ReviewerDocument8 pages1Q Gen Bio ReviewerNonoy VictimNo ratings yet
- 2 Organisation of The Organism NotesDocument5 pages2 Organisation of The Organism Notesarayana sharmaNo ratings yet
- Cell Molecular Composition of CellDocument72 pagesCell Molecular Composition of Celljomel rondinaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellDocument11 pagesEukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellAvyanna MillerNo ratings yet
- D. Cell OrganellesDocument64 pagesD. Cell OrganellesHannz Raven Maligo DelicaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules & Cells Biol10002 Lectures 1-9 Cell Biology Geoff Mcfadden, RM 211 Biosciences 2 (Old Botany)Document41 pagesBiomolecules & Cells Biol10002 Lectures 1-9 Cell Biology Geoff Mcfadden, RM 211 Biosciences 2 (Old Botany)waimoeNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellsAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument94 pagesThe CellKorean DramaNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Biology MidtermsDocument6 pagesScience 6 Biology MidtermsSamantha Avril UmandapNo ratings yet
- Review of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument25 pagesReview of Cell Biology Concepts: Differences Between Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cellsevil twinNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJes NapiñasNo ratings yet
- 2nd Q CEellDocument30 pages2nd Q CEellDeserie ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: A Guide to the OrganellesDocument11 pagesCell Structure: A Guide to the OrganellesAli MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesFundamental Unit of LifeRishabh SinghNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument27 pagesIntroductionBaiawwal AmpatuanpendongNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & OrganisationDocument62 pagesCell Structure & OrganisationSUNDARI SIVASANKARNo ratings yet
- OrganellesDocument3 pagesOrganellesJeanelle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument56 pages2.1 Cell Structure and Functionazrixone54No ratings yet
- Cells in Our BodyDocument6 pagesCells in Our BodyKareysha ManceraNo ratings yet
- Unit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupDocument56 pagesUnit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupYahya RhamadanNo ratings yet
- Biology Quick Notes by Disha PublicationDocument27 pagesBiology Quick Notes by Disha PublicationMunish Mechie100% (1)
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument9 pagesBIOLOGYARNEL TRES REYESNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton - GROUP 2Document19 pagesCytoskeleton - GROUP 2n42fjjy8g7No ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document40 pagesLecture 3Hà Nguyễn Thị ViệtNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Second Trimester ScienceDocument36 pagesStudy Guide Second Trimester ScienceuzielcgcursoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell Division: Learning Outcomes Laboratory SuppliesDocument6 pagesCell Structure and Cell Division: Learning Outcomes Laboratory SuppliespedroNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureDocument31 pagesDokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureJairra Jae LunaNo ratings yet
- Class - Ix - Cell OrganellesDocument22 pagesClass - Ix - Cell OrganellesshamshadNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and EukaryotcG7Document41 pagesProkaryotic and EukaryotcG7Nes ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Quiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)Document12 pagesQuiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)deaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 & 3 - ZoologyDocument4 pagesChapter 2 & 3 - ZoologyAngel MerilloNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument30 pagesCell Structuremazura100% (1)
- Cells PowerpointDocument4 pagesCells Powerpointlu.justina100% (2)
- CELL & BINOMIAL NOMENCLATUREDocument6 pagesCELL & BINOMIAL NOMENCLATUREVenice De los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function in a NutshellDocument31 pagesCell Structure & Function in a NutshellHerzl Loraine PrioNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)Document46 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)MeryemNo ratings yet
- From Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.From EverandFrom Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.No ratings yet
- The PandemicDocument2 pagesThe PandemicGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- The PandemicDocument2 pagesThe PandemicGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- The PandemicDocument2 pagesThe PandemicGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Eto Ung SolutionnnnnnnnnDocument1 pageEto Ung SolutionnnnnnnnnGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- SPGBIO! MicroscopeDocument6 pagesSPGBIO! MicroscopeGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Sequence and Series With Mathematical InductionDocument17 pagesSequence and Series With Mathematical InductionGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Written Task 4 and Scaffold 4Document1 pageWritten Task 4 and Scaffold 4Gian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- SPGBIO! MicroscopeDocument6 pagesSPGBIO! MicroscopeGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document1 pageUntitled 1Gian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell Structure FunctionsGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Untitled 1Document1 pageUntitled 1Gian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- The Task of 5-Axis Milling PDFDocument4 pagesThe Task of 5-Axis Milling PDFManikanda PrabhucNo ratings yet
- Dialysis PrescriptionDocument23 pagesDialysis PrescriptionMercy Juliana Jacqualine100% (1)
- Integral CalculusDocument48 pagesIntegral CalculusVincent CortezNo ratings yet
- Slide No. 04 - Pert - Cpm1Document27 pagesSlide No. 04 - Pert - Cpm1NUSRAT RITUNo ratings yet
- Aisladores Polimericos vs. Aisladores Ceramicos Unmsm PDFDocument22 pagesAisladores Polimericos vs. Aisladores Ceramicos Unmsm PDFvgcasasNo ratings yet
- Sunningdale School Notes Summer 2022Document12 pagesSunningdale School Notes Summer 2022sunningdaleschoolNo ratings yet
- Small Cells 2013 BrochuresDocument22 pagesSmall Cells 2013 BrochuresChungwa ChanjiNo ratings yet
- VTBS 20-3DDocument1 pageVTBS 20-3Dwong keen faivNo ratings yet
- 3204-9-Resource Use and SustainabilityDocument25 pages3204-9-Resource Use and SustainabilityKezia NatashaNo ratings yet
- L1 Finding Nemo Teacher Notes American EnglishDocument9 pagesL1 Finding Nemo Teacher Notes American Englishcris_simescuNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 - Pengantar Remote SensingDocument60 pagesModul 1 - Pengantar Remote SensingNgurah Ade KalyanaNo ratings yet
- Farha WCM Project-1Document110 pagesFarha WCM Project-1a NaniNo ratings yet
- Kant ParadigmDocument265 pagesKant ParadigmkairospandemosNo ratings yet
- Watkins Göbekli Tepe Jerf El Ahmar PDFDocument10 pagesWatkins Göbekli Tepe Jerf El Ahmar PDFHans Martz de la VegaNo ratings yet
- Feed Water Heater ModellingDocument64 pagesFeed Water Heater ModellingSIVA KAVYANo ratings yet
- Model AnswerDocument27 pagesModel AnswerdishaNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB 4.1A Worksheet Key ConceptsDocument44 pagesAP Calculus AB 4.1A Worksheet Key ConceptsDavid Joseph100% (1)
- AmadiDocument18 pagesAmadijawad bello aNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Textile Finishing - 2020 PDFDocument11 pagesTopic 1 - Textile Finishing - 2020 PDFSadaf SweetNo ratings yet
- 2 Phantom Forces Gui Scripts in OneDocument11 pages2 Phantom Forces Gui Scripts in OneAthallah Rafif JNo ratings yet
- Des 415 Research 01Document29 pagesDes 415 Research 01Just scribble me For funNo ratings yet
- Pol Science ProjectDocument18 pagesPol Science ProjectAnshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Carte Blanche: The New James Bond Novel by Jeffery DeaverDocument12 pagesCarte Blanche: The New James Bond Novel by Jeffery DeaverSimon and Schuster0% (1)
- Mushroom Umami Taste EvaluationDocument10 pagesMushroom Umami Taste EvaluationMaryam HanifNo ratings yet
- Store Visit ChecklistDocument5 pagesStore Visit ChecklisthayeslnlNo ratings yet
- Hurqalya - HavarqalyaDocument64 pagesHurqalya - HavarqalyaBVILLARNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Mds-Ja20EsDocument84 pagesService Manual: Mds-Ja20Esfoxmulder6161695No ratings yet