Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4 2 RG
Uploaded by
api-252900678Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 2 RG
Uploaded by
api-252900678Copyright:
Available Formats
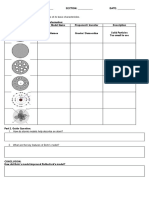
4 The Structure of Matter
Date:
Name:
4.2 Ionic and Covalent Bonding
Important Terms
Ionic bond
Metallic bond
Covalent bond
What Holds Bonded Atoms together?
1. How many different kinds of bonds describe the way atoms bond in most substances?
_______________________
2. Atoms bond when their _____________________ _____________________ interact.
3. Why are atoms with full outermost energy levels less reactive than atoms with only partly
filled outermost energy levels?
4. Explain what happens when two hydrogen atoms bond, as described on page 115-116.
5. Bonds are often represented as sticks or bars, but behave more like what?
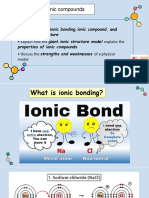
Ionic Bonds
6. Atoms of __________________________ elements form _____________________ charged ions.
Atoms of _______________________ elements form _____________________ charged ions.
7. Some atoms do not share electrons to fill their outermost energy level. Instead, they
_____________________ electrons.
8. In your own words, briefly explain what happens to Na + (sodium) and Cl (Chlorine) ions to
form table salt.
Metallic Bonds
9. In your own words, briefly describe why electrons can move freely between atoms in
metals.
Covalent Bonds
10.Covalent bonds are often formed between _____________________ atoms.
11.In covalent bonds, atoms do not transfer electrons to one another, but instead
_____________________ one electron with the other atoms.
12.What is drawn between the two atoms to indicate that the atoms share electrons?
13.
The bond between two nitrogen atoms is stronger than the bond between two
oxygen atoms. Why is this?
4 The Structure of Matter
Date:
Name:
Section Review, p. 122
#1
a.
c.
b.
d.
#2
#4
#8 [Hint: use the image on the top of p. 120 to help you.]
You might also like
- Ionic Covalent Bonding Web QuestDocument5 pagesIonic Covalent Bonding Web QuestFiona IsbellNo ratings yet
- Intramolecular BondsDocument18 pagesIntramolecular BondsEudes SantosNo ratings yet
- 780 Chemistry Atoms and Molecules 0Document4 pages780 Chemistry Atoms and Molecules 0Anonymous rWJCoarANo ratings yet
- 6-1 Concept ReviewDocument2 pages6-1 Concept ReviewEmilyNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument3 pagesTypes of Chemical BondssalimNo ratings yet
- Bonding PacketDocument24 pagesBonding PacketIra Munirah100% (2)
- Answer of Textbook Exercise (Fill in The Blank)Document3 pagesAnswer of Textbook Exercise (Fill in The Blank)Hui ShuenNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q2 Mod2Document16 pagesScience 9 q2 Mod2Prince U KennardNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument41 pagesChemical BondingaswaniNo ratings yet
- Why To Study - Material Technology & Heat TreatmentDocument22 pagesWhy To Study - Material Technology & Heat TreatmentdNo ratings yet
- L1 Chemistry Review - WELCHDocument5 pagesL1 Chemistry Review - WELCHkamrynwelch1No ratings yet
- Covalent BondsDocument59 pagesCovalent BondstornomarialynNo ratings yet
- LBC Alchemy SE Lesson26Document5 pagesLBC Alchemy SE Lesson26Sean MartinsonNo ratings yet
- C2 SYLLABUS CONTENT Bonding Structure and Properties of Matter CHEMISTRYDocument7 pagesC2 SYLLABUS CONTENT Bonding Structure and Properties of Matter CHEMISTRYNancyNo ratings yet
- Different Substances WorksheetDocument1 pageDifferent Substances WorksheetJohnNo ratings yet
- C07 Chemical BondingDocument42 pagesC07 Chemical BondingKevonSingh1100% (1)
- Study Guide Bonding Ionic CovalentDocument4 pagesStudy Guide Bonding Ionic Covalentapi-267858901No ratings yet
- CHEMICAL BONDING-workbokDocument9 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING-workbokJenny Rose BatalonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision BookletDocument9 pagesChemistry Revision BookletNour MakaremNo ratings yet
- Physical Basis & Classification of Welding Processes 2020Document42 pagesPhysical Basis & Classification of Welding Processes 2020jaikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFDocument6 pagesLesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFMia ChanNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChemical BondingdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Bonding - Ionic + Covalent BondsDocument9 pagesStructure and Bonding - Ionic + Covalent BondsKimaya RichardsNo ratings yet
- MC ch06Document129 pagesMC ch06SarahNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter and Its Chemical StructureDocument27 pagesProperties of Matter and Its Chemical Structureanalingling alcasidNo ratings yet
- Bonding NotesDocument2 pagesBonding NotesdodoNo ratings yet
- 06 Properties & Structure SummaryDocument1 page06 Properties & Structure SummaryJean AlmiraNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Properties of Solids StudentDocument7 pages3.2 Properties of Solids StudentZachary Daniel UyNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument6 pagesTypes of Chemical BondsjoeldpenosNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding IMP-2Document2 pagesChemical Bonding IMP-2Sujith KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.2 GsDocument19 pagesChapter 6.2 Gszain nNo ratings yet
- Learning: Formation of Elements in The Universe and Properties of MatterDocument7 pagesLearning: Formation of Elements in The Universe and Properties of Matterrhiantics_kram11No ratings yet
- Bonding Poster ProjectDocument1 pageBonding Poster Projectapi-303120399No ratings yet
- Class 12 Ionic BondDocument1 pageClass 12 Ionic BondIshraq KhanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Introduction To BondingDocument4 pagesModule 2 Introduction To BondingKimberly AllejosNo ratings yet
- 1-Sample Lesson PlanDocument7 pages1-Sample Lesson Planapi-301619700100% (4)
- Lesson 3 - INORGANIC CompoundsDocument15 pagesLesson 3 - INORGANIC CompoundsKym DacudaoNo ratings yet
- CH 01 Learning Objectives Klein 4e FA22Document1 pageCH 01 Learning Objectives Klein 4e FA22ajamufamNo ratings yet
- Materials Engineering ReviewerDocument2 pagesMaterials Engineering ReviewerLee Robin DianaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Activity SheetDocument17 pages2nd Quarter Activity SheetMarilyn OngkikoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemical BondingHarshal BandkarNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesMetallic BondingJohanna LipioNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument9 pagesMetallic BondingTosis MajidNo ratings yet
- Notes Chemistry - ch4 - 11Document17 pagesNotes Chemistry - ch4 - 11VikramNo ratings yet
- 10.4 Inside Ionic Compounds: ObjectivesDocument26 pages10.4 Inside Ionic Compounds: Objectivesmohamedbadr465No ratings yet
- Covalent & Metallic Bonds: Chapter 13 Section 3Document20 pagesCovalent & Metallic Bonds: Chapter 13 Section 3thegedusNo ratings yet
- G9 Q2 W2 Ionic or Covalent CompoundsDocument17 pagesG9 Q2 W2 Ionic or Covalent CompoundsCherrilyn Enverzo33% (3)
- LONGTEST Science 9 (AutoRecovered)Document2 pagesLONGTEST Science 9 (AutoRecovered)jerome CarpioNo ratings yet
- U18.1 Covalent Compounds and The Formation of Covalent BondsDocument18 pagesU18.1 Covalent Compounds and The Formation of Covalent BondsMaria Luisa BernalNo ratings yet
- Assignment #1Document1 pageAssignment #1rynrynNo ratings yet
- Phet Contribution 3431 5785Document5 pagesPhet Contribution 3431 5785aramki10% (1)
- BondingDocument18 pagesBondingesotericgraphicapparelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument33 pagesChemistry NotesmadisonNo ratings yet
- Ar Nature of MatterDocument1 pageAr Nature of Matterapi-264668182No ratings yet
- CH 6 Chemical BondingDocument14 pagesCH 6 Chemical Bondingapi-240972605No ratings yet
- Lesson 10.2 The Solid StateDocument14 pagesLesson 10.2 The Solid StatefitriNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonds GizmosDocument6 pagesIonic and Covalent Bonds GizmosCharley Ray TaylorNo ratings yet
- Imf SWDocument1 pageImf SWJoana Daisee N. EscobidoNo ratings yet
- C2 - Key Recall QuestionsDocument18 pagesC2 - Key Recall QuestionsYashkur Al-ShahwaniNo ratings yet
- Email BarbDocument3 pagesEmail Barbapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Power Lab CallieDocument4 pagesPower Lab Callieapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Student Owned HomeworkDocument4 pagesStudent Owned Homeworkapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Power LabDocument4 pagesPower Labapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Aea CertsDocument4 pagesAea Certsapi-252900678No ratings yet
- First and Second-Year Learning Projects and Program: ExcellenceDocument66 pagesFirst and Second-Year Learning Projects and Program: Excellenceapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Email BobDocument1 pageEmail Bobapi-252900678No ratings yet
- 16 1 RGDocument3 pages16 1 RGapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Obervation Nov 21Document3 pagesObervation Nov 21api-252900678No ratings yet
- Block PlanDocument1 pageBlock Planapi-252900678No ratings yet
- SeptemeberDocument2 pagesSeptemeberapi-252900678No ratings yet
- 2 19 Lesson PlanDocument2 pages2 19 Lesson Planapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Observation Nov 25Document3 pagesObservation Nov 25api-252900678No ratings yet
- 2 10 Formal ObservationDocument6 pages2 10 Formal Observationapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 9 19Document1 pageLesson Plan 9 19api-252900678No ratings yet
- Beginning SurveyDocument1 pageBeginning Surveyapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Lesson PlanDocument1 pageIonic and Covalent Lesson Planapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Hunting The Elements PacketDocument6 pagesHunting The Elements Packetapi-252900678No ratings yet
- 14-15 SyllabusDocument4 pages14-15 Syllabusapi-252900678No ratings yet
- No More Nuclear!Document11 pagesNo More Nuclear!api-252900678No ratings yet
- Beginning SurveyDocument1 pageBeginning Surveyapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Debate Project PacketDocument6 pagesNuclear Power Debate Project Packetapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ResourcesDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Resourcesapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Nuclear Decay CheckDocument2 pagesNuclear Decay Checkapi-252900678No ratings yet
- 14-15 SyllabusDocument4 pages14-15 Syllabusapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Demo Sheet Kinetic TheoryDocument2 pagesDemo Sheet Kinetic Theoryapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Science Lab Report Copy MadiDocument2 pagesScience Lab Report Copy Madiapi-252900678No ratings yet
- Nuclear Decay WsDocument3 pagesNuclear Decay Wsapi-252900678No ratings yet