Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9.3 Transistor
9.3 Transistor
Uploaded by
Fajar Tri WibowoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9.3 Transistor
9.3 Transistor
Uploaded by
Fajar Tri WibowoCopyright:
Available Formats
SEK.
MEN SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
9.3
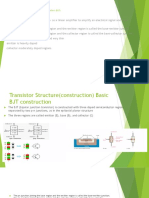
Describe a transistor in terms of its terminal A transistor has three leads connected to the emitter, base and collector. The emitter emits or sends charge carriers through the thin base layer to be collected by the collector. There is two-type of transistor: npn transistor and pnp transistor. In an npn transistor the emitter sends negative electrons to the collector. In an pnp transistor, the p-type emitter sends positive holes to the collector. In both cases, the arrow on the emitter shows the direction of current flow. The output current, of a transistor flows between the emitter and the collector. The current in the collector lead is called collector current, IC. The base current, IB is used to control the collector current through the transistor. The base current can be used to switch the collector current on or off. 1. Base current is too small compared to the collector current. The unit of base current is A while the unit for the collector current is mA. ( Ic >>>> IB ) Current = Collector current Amplication base current Emitter current, IE is equal the sum of base current and collector current IE = IB + IC Ie > Ic > IB
2.
Transistor as a current amplifier
3.
A small change in the base current, results in a big change in the collector current, Ic >>>>Ib
Transistor as an automatic switch
4.
If there is no current flow in the base circuit, then there is also no current flow in the collector circuit. IB = 0 then IC = 0 transistor is switch off IB flows then IC flows transistor is switch on
197
SEK. MEN SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
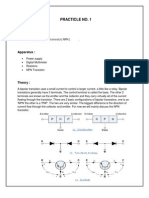
Activity 1: To find the relationship between the base current (IB) and collector current, (IC) in a transistor Hypothesis: _________________________________________________________________________ Manipulated variable : _________________________ Responding variable : ___________________ Controlled variable : ____________________________
Apparatus : transistor, resistors of 2.2 k, 3.9 k, 4.7 k, 6.8 k, 8.2 k and 10.0 k, connecting wires, dry cells, milliammeters with range 0 1 mA and 0 100 mA 1. Switch S1 is open and switch S2 is closed. The readings of the ammeters are recorded. 2. Both switches S1 and S2 are closed. The readings of the ammeters are recorded. Repeat the experiment by replacing the 10.0 k in the base circuit with 8.2 k, 6.8 k, 4.7 k, 3.9 k and 2.2 k.
R / k IB / mA Ic / mA
2.2 0.60 94.0
3.9 0.45 70.0
4.7 0.32 46.0
6.8 0.20 36.0
8.2 0.13 24.0
10.0 0.08 10.0
Plot graph of IC against IB. Calculate the gradient of the graph.
Discussion 1. Which milliammeters measure Base current: Collector current : 2. When S1 opened, S2 closed : IB = ______ IC = _____ 3. How would the readings of the milliammeter A1 and A2 compare?
4. What does the gradient of the graph represent?
198
SEK. MEN SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
Conclusion: A small increase in the ______ current results in a big increase in the ____________ current.
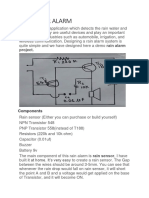
Describe how a transistor can be used as an automatic switch. Potential divider circuit Choose a suitable resistor R1 and a variable resistor R2. The voltage at base terminal can be adjusted to switch the transistor on or off. If the variable resistor = 0, base voltage = 0 and the transistor remains off. If the variable resistor is increased, the base voltage increases. When the base voltage reaches certain minimum value, the base current switches the transistor on. The large collector current flows through the transistor causing the bulb to light up.
If the variable resistor in the transistor is replaced by a device such as light dependent resistor (LDR), a thermistor or a microphone, the transistor can be used as an automatic switch controlled by light, heat or sound Activity 2: A light controlled switch 1. 2. The LDR has a very ___________ resistance in darkness and a _________ resistance in light. R is a fixed _____________ The LDR and R form a potential divider in the circuit. Circuit switches on the bulb at night and switches off the bulb at day time automatically Draw a circuit diagram
Circuit switches on the light at daytime and switches off the bulb at night automatically
In daylight, the LDR has a very _______ resistance as compared to R. Therefore the base voltage is ___________ enough to switch the transistor on and to light ________ the bulb. In darkness, the LDR has a very _________ resistance and therefore the base voltage is too ________ to switch the transistor ________. The bulb light _____
In daylight, the LDR has a very _______ resistance as compared to R. Therefore the base voltage is too ___________ to switch the transistor on In darkness, the LDR has a very _________ resistance and the base voltage is ________ to switch the transistor ________ to light ______ the bulb.
199
SEK. MEN SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
Activity 3: Design a temperature operated switch The resistance of a thermistor varies with temperature. When the temperature increases, the resistance of the thermistor will _________
Thermistor
Figure shows a transistor-based circuit that function as a heat controlled switch. At room temperature, the thermistor has a . resistance compared to R. Therefore, the base voltage of the transistor is too low to switch on the transistor.
Diode RB high
Relay
Alarm
When the thermistor is heated, its . drops considerablely compared to R. Therefore, the ., VB is high enough to switch . the transistor. When the transistor is switch on, the relay switch is activated and the relay is switched . The circuit can also be used in a fire alarm system.
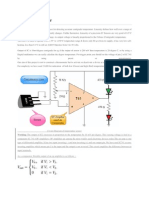
Transistor as a Current Amplifier A transistor functions as a current amplifier by allowing a small current to control a larger current. The magnitude of the ., IC is primarily determined by the .., IB. A .. change in the base current, IB will cause a .. change in the collector current, IC. The current amplification can be calculated as follows: A
mA
R2 R1 R IB IE
IC
Current Amplification
I C I B
Transistor circuit II (need one cell) Rx and RY : Voltage divider VRx = VRY = Rx ( Rx + Ry) x V
Ry xV ( Rx + Ry)
200
SEK. MEN SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
TUTORIAL 9.3
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS 1. Diagram 1 shows a symbol for npn transistor. Electrodes P, Q and R refer to
4. What are the electrical components that must be placed at P and Q in the circuit as shown in Diagram 2
Diagram 1 P Base Base Collector Emitter Q Emitter Collector Base Base R Collector Emitter Emitter Collector
Diagram 2 P Bulb Battery Resistor Bulb Q Bulb Bulb Battery resistor
A B C D
A B C D
2. The diagram shows the symbol for a transistor.
5. An npn transistor is connected to a dc power supply as shown in Diagram 3.
Which of the following shows the correct name of the electrode P and the type of the transistor? (2003) Electrode P Type of transistor Emitter pnp Collector pnp Emitter npn Collector npn
Diagram 3 Which of the following is correct? A Ie > Ic >Ib B Ie > Ib >Ic C Ic > Ie >Ib D Ic > Ib >Ie 6. In which circuit does the bulb light up? (2004)
A B C D
3. Which symbol represents the pnp transistor?
201
SEK. MEN SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
7. The function of transistor in the circuit shown in Diagram 5 is ___
11. In which circuit will the light-emitting diode (LED) light up when the switch is on? (2005)
A. B. C. D.
Diagram 5 Rectifier Amplifier Automatic switch Voltage divider
8. The function of the transistor in the circuit shown in Diagram 6 is 12. Which of the following circuits can function? (2006)
A. B. C. D.
Diagram 6 Receiver A switch Transmitter Heater 13. Diagram shows an automatic switch circuit to light up a bulb at night.
10. Which of the following shows the correct circuit to light up the bulb during daylight but light off the bulb at night.
What changes should be done to light up the bulb during the day time? (2007) A. Reverse the therminals of the battery B. Interchange R1 and R2 C. Replace the npn transistor with a pnp transistor D. Replace resistor R3 with a resistor of lower resistance
202
SEK. MEN SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
STRUCTURE QUESTIONS 1. Diagram 7 shows a light dependent resistor (LDR), resistors R and S, a light emmiting diode (LED), a transistor and a battery that will be connected to form a circuit. The LED emits lights when it is in a bright surroundings.
(i) State one electronic component which needs to be replaced. Give a reason for your answer. _____________________________ _____________________________ [2] (ii) Name two electronic components that are needed to replace the unsuitable components. _____________________________ _____________________________ [2] E. In the space below, draw a circuit diagram to show the new circuit. [2]
Diagram 7 (a) (i) State one function of a transistor. ________________________________ [1] (ii) Complete the circuit in Figure 25.1 so that the LED emits light in a bright surroundings. [1] (iii) Give one reason why LED emits light in a bright surroundings. _________________________________ [1] (b) What modification is required to the circuit so that the LED will emits light when the surroundings become dark? ________________________________ [1] (c) An alarm is needed which emits sound when there is a fire. Two modifications have to be made to the circuit in (a)(ii) by replacing electronic components. 2. Diagram 7 shows a circuit that acts as a switch to light up bulb M when the surrounding at P is dark. P is a light dependent resistor LDR.
Diagram 7
(a) What is the characteristic of LDR? ___________________________________
203
SEK. MEN SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
(b)(i) Name component Q. __________________________________ (ii) What is the function of component Q? _________________________________ (c) What is the function of resistor R? ___________________________________ (d) (i) What is the change to the voltage Vp when the surrounding P is dark? __________________________________ (ii) How does the change of the voltage light up the bulb M? __________________________________ (e) Explain why the bulb must not be connected directly to the circuit switch. ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ SPM 2006 Section A # 7(c) 3. (c) The door of a lift is fitted with a light transmitter and a detector which is a light dependent resistor. If the light dependent resistor detects light, the relay switch is activated and the lift door will close. Diagram 8 shows an electronic circuit for the control system of the lift door. (iii) Explain how the circuit functions. _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ [3 m] (i) State the relationship between the resistance and the intensity of light received by the light dependent resistor. ________________________________ ________________________________ (ii) Complete the circuit in Diagram 8 by drawing the resistor and the light dependent resistor using the symbols given below.
Diagram 8
204
SEK. MEN SAINS MUZAFFAR SYAH
SPM 2007 Section B 10(d) 4. Diagram 9 shows a circuit with a transistor that acts as an automatic switch.
Diagram 9 The transistor in the circuit causes the light diode (LED) to light up when it is dark. A technician wants a fan labeled 240 V, 100 W in a room to be automatically switched on when the room is hot. Suggest modifications that can be made to the circuit in Diagram 4 so that the fan can be automatically switched on when the room is hot. State and explain the modifications based on the following aspects: - the electrical components that are needed to replace the LED and the light dependent resistor (LDR) in the circuit. - The positions of the electrical components in the circuit. [10 m]
205
You might also like
- Asme B18.8.2 2000Document39 pagesAsme B18.8.2 2000Jesse ChenNo ratings yet
- Creative Major Scale Exercises For Clarinet & SaxophoneDocument70 pagesCreative Major Scale Exercises For Clarinet & SaxophoneMuzika100% (2)
- IEC 60076-2 Ed. 3.0 PDFDocument12 pagesIEC 60076-2 Ed. 3.0 PDFPrasetiyo Hananto0% (3)
- Datasheet - 2 Antena Gps Gpsglonass 36 N GaDocument4 pagesDatasheet - 2 Antena Gps Gpsglonass 36 N GaJohn olivNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab 14Document14 pagesElectronics Lab 14Aruna KumarasiriNo ratings yet
- Design of Audio Amplifier Using BJT Transistors - Analog AssignmentDocument20 pagesDesign of Audio Amplifier Using BJT Transistors - Analog AssignmentSheragin Tavassoli100% (3)
- CentrifugalCompressor5 (1) SelectionDocument5 pagesCentrifugalCompressor5 (1) SelectionbsssnivasNo ratings yet
- Nota TransistorDocument13 pagesNota TransistorLokman HakimNo ratings yet
- 4 3transistor 100805015532 Phpapp02Document12 pages4 3transistor 100805015532 Phpapp02Hafeeza YusofNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Physics Sir Mas FaizDocument23 pagesForm 5 Physics Sir Mas FaizNur Aina SofrinaNo ratings yet
- Rain AlarmDocument15 pagesRain AlarmTARIT DAS100% (4)
- PRACTICLE NO 1 CTDocument3 pagesPRACTICLE NO 1 CTAnb BajwaNo ratings yet
- How Does A Transistor Circuit WorksDocument30 pagesHow Does A Transistor Circuit WorksJacob BrackettNo ratings yet
- Lecture Week 03Document54 pagesLecture Week 03عبدالله قيس محمود الحيدريNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 COE0047Document16 pagesHomework 1 COE0047ADRIAN MINANo ratings yet
- Chap 3Document48 pagesChap 3belacheweshetu222No ratings yet
- Chap 3Document40 pagesChap 3sm7526359No ratings yet
- ConversationDocument2 pagesConversationKusi HemanthNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Understanding TransistorsDocument19 pagesLesson 3 - Understanding TransistorsThiyaku MaruthaNo ratings yet
- Transistores Como InterruptoresDocument18 pagesTransistores Como InterruptoresSayuri CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument60 pagesChapter 5: Power Semiconductor DevicesDipti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Transistors Question and Answers Doc by PranghiDocument15 pagesTransistors Question and Answers Doc by PranghiPRANGHI80% (10)
- Lecture1 6Document21 pagesLecture1 6MjdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 2.1Document85 pagesChapter 3 2.1vipar snikeNo ratings yet
- BJT TouhidDocument38 pagesBJT TouhidA.K.M.TOUHIDUR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorsDocument43 pagesSemiconductorsTariku MantafoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Understanding Transistors: Transistor CircuitDocument9 pagesLesson 3 - Understanding Transistors: Transistor CircuitSiti Arbaiyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document7 pagesLab Report 1Katherine Ann YutocNo ratings yet
- Best Unit-Ii: Civil Engineering (Vi Sem)Document54 pagesBest Unit-Ii: Civil Engineering (Vi Sem)KumarNo ratings yet
- Topic 4: Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument188 pagesTopic 4: Bipolar Junction TransistorsbhargaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ElectronicsDocument78 pagesChapter 1 ElectronicsBenjaminNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.1 TransistorsDocument23 pagesChapter 4.1 TransistorsNabinNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document30 pagesUnit 3[C3B] Aqilah HusnaNo ratings yet
- E-Note 12138 Content Document 20231030103638AMDocument23 pagesE-Note 12138 Content Document 20231030103638AMArun ANo ratings yet
- Transistor. s2r PDFDocument60 pagesTransistor. s2r PDFdiya shajiNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument30 pagesBasic ElectronicsMd. Mahamudul Hasan100% (1)
- BJT S: Over Temperature and Also From One Transistor ToDocument1 pageBJT S: Over Temperature and Also From One Transistor ToKrisha Joanne VillarNo ratings yet
- Transistors: John Bardeen William Shockley Bell Lab ReplacedDocument18 pagesTransistors: John Bardeen William Shockley Bell Lab ReplacedRadha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Transistors and Their WorkingDocument22 pagesDifferent Types of Transistors and Their WorkingVenki EdeNo ratings yet
- BJT Written Report Group 8Document11 pagesBJT Written Report Group 8Jayvee GusenalemNo ratings yet
- Unit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document9 pagesUnit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Gunjan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument16 pagesChapter Three Bipolar Junction TransistorsGizachew BalchaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document32 pagesChapter 3AdsbymeNo ratings yet
- To Design The Automatc Night Lamp Using Logic CircuitDocument38 pagesTo Design The Automatc Night Lamp Using Logic CircuitSouvik PalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document46 pagesUnit 2Manan JainNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 3. Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument31 pagesUnit-3 3. Bipolar Junction TransistorshivaniNo ratings yet
- Assessment 6 - ROBILLOSDocument2 pagesAssessment 6 - ROBILLOSRobillos, Alessandra Benedict S.No ratings yet
- Temperature SensorDocument5 pagesTemperature SensorAbhinav Madheshiya100% (1)
- Pertemuan 12 (OSILATOR1)Document23 pagesPertemuan 12 (OSILATOR1)nozamaNo ratings yet
- Monday, September 15, 2014 2:45 PM: Electronics Page 1Document4 pagesMonday, September 15, 2014 2:45 PM: Electronics Page 1papachanjoNo ratings yet
- ECE319 (CS) Unit3 & Unit 4Document97 pagesECE319 (CS) Unit3 & Unit 4panmeena17No ratings yet
- BE 3 UnitDocument19 pagesBE 3 Unit08sunnyjaganNo ratings yet
- Constructional Details of A Transistor: Why Do We Need Transistors?Document18 pagesConstructional Details of A Transistor: Why Do We Need Transistors?sreenadh reddyNo ratings yet
- Lab.5 Power ElectronicsDocument7 pagesLab.5 Power Electronicsbaig79No ratings yet
- Tesla Coil NPN TransistorDocument16 pagesTesla Coil NPN TransistorRaj TokasNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Transistor Tutorial, The BJT TransistorDocument8 pagesBipolar Transistor Tutorial, The BJT TransistorAjay Kumar MattupalliNo ratings yet
- Analogue Electronic Design Module E EEE2039 / EEE2026 / EEE2042Document36 pagesAnalogue Electronic Design Module E EEE2039 / EEE2026 / EEE2042Arvish RamseebaluckNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Electronic: 9.3 TransistorDocument25 pagesChapter 9: Electronic: 9.3 TransistorSathya SeelanNo ratings yet
- Unit Lecture 3Document41 pagesUnit Lecture 3Mohak KumarNo ratings yet
- Rim 2000Document6 pagesRim 2000Senki AlphonsNo ratings yet
- 3.transistors FinalDocument43 pages3.transistors FinalSanjana HaqueNo ratings yet
- Rain AlarmDocument3 pagesRain AlarmSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Transistor Tutorial, The BJT TransistorDocument14 pagesBipolar Transistor Tutorial, The BJT TransistoraleyhaiderNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Interence of WavesDocument64 pages6.5 Interence of Wavessuemozac100% (1)
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 WavesDocument28 pagesNota Padat Fizik F5 Wavesslokkro98% (102)
- 6.3 Refraction of WavesDocument52 pages6.3 Refraction of Wavessuemozac100% (2)
- Wave Motion How Do Waves Transfer Energy? Longitudinal & Transverse WavesDocument30 pagesWave Motion How Do Waves Transfer Energy? Longitudinal & Transverse Wavessuemozac100% (3)
- Energy Oscillating Vibrating: Smsains Muzaffar SyahDocument11 pagesEnergy Oscillating Vibrating: Smsains Muzaffar Syahhasl arbNo ratings yet
- 9 4 Logic GatesDocument12 pages9 4 Logic Gatessuemozac100% (3)
- 9 1 Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDocument14 pages9 1 Cathode Ray Oscilloscopesuemozac100% (6)
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Physics AnswersDocument14 pagesSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Physics AnswersChinWynn.com80% (5)
- SO20681 Parts Catalogue: 6CTAA8.3-GDocument87 pagesSO20681 Parts Catalogue: 6CTAA8.3-GTOPASONo ratings yet
- Ch. 10 Skin, Hair and Nails - Bickley and BatesDocument2 pagesCh. 10 Skin, Hair and Nails - Bickley and BatesfufuNo ratings yet
- Lab 6: Inject Android Malware Into A Benign AppDocument11 pagesLab 6: Inject Android Malware Into A Benign AppcilapibNo ratings yet
- IZhO 2024 Exp - EngDocument4 pagesIZhO 2024 Exp - EngINFINITYNo ratings yet
- Law of FlotationDocument8 pagesLaw of FlotationAmran DanialNo ratings yet
- Steven Fady Fayez Mehany: Youssef Ahmed Abdelmohsen YoussefDocument8 pagesSteven Fady Fayez Mehany: Youssef Ahmed Abdelmohsen YoussefAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Gtu PaperDocument20 pagesGtu PaperDaksh DalalNo ratings yet
- 20 Lilavati I (MSS)Document39 pages20 Lilavati I (MSS)Srinivas VamsiNo ratings yet
- DATS3TD2T23BRENDocument11 pagesDATS3TD2T23BRENroa elastal100% (1)
- Social Studies Sa1 Revision WS Class 5Document13 pagesSocial Studies Sa1 Revision WS Class 5faisal kingNo ratings yet
- Green Analytical Chemistry: Opportunities For Pharmaceutical Quality ControlDocument12 pagesGreen Analytical Chemistry: Opportunities For Pharmaceutical Quality Controlprajeet khedekarNo ratings yet
- Field Density (Sand Cone Method) Test (ASTM D 1556, AASHTO T - 191)Document5 pagesField Density (Sand Cone Method) Test (ASTM D 1556, AASHTO T - 191)m8877223No ratings yet
- High-Precision Fiber Optical GyroscopeDocument1 pageHigh-Precision Fiber Optical Gyroscopemichael_graciasNo ratings yet
- Errors in Chemical AnalysisDocument19 pagesErrors in Chemical AnalysisWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Learning CurvesDocument15 pagesLearning CurvesInnocent Won AberNo ratings yet
- Study On Friction Stir Welding On Shipbuilding Steel: by Varun Mohandas S7 Me B VAS15ME114Document24 pagesStudy On Friction Stir Welding On Shipbuilding Steel: by Varun Mohandas S7 Me B VAS15ME114Varun MohandasNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Positioning-Basic Student HandoutDocument158 pagesDynamic Positioning-Basic Student HandoutMartin Zagar100% (1)
- 8 2 Angle Bisectors of TrianglesDocument8 pages8 2 Angle Bisectors of Trianglesapi-332361871No ratings yet
- Antenna Design: Zero To HeroDocument17 pagesAntenna Design: Zero To HeroJesus AltamiranoNo ratings yet
- Printing Sudoku GridsDocument2 pagesPrinting Sudoku Gridskalam715265No ratings yet
- Bajaj Home ComfortDocument30 pagesBajaj Home ComfortShabbir WahabNo ratings yet
- What Is Meant by Airworthiness?Document2 pagesWhat Is Meant by Airworthiness?NobleSharmaNo ratings yet
- Ful Meterman CatalogueDocument20 pagesFul Meterman CatalogueIvana Vlade RadovanovicNo ratings yet
- Canet, 2015 AcoculcoDocument7 pagesCanet, 2015 AcoculcoNina HagenNo ratings yet
- Java StudyDocument61 pagesJava StudykrushnakanNo ratings yet