Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 1 Arithmetic Sequence
Uploaded by
Dave Sedigo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views4 pagesmath
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmath
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views4 pagesLesson 1 Arithmetic Sequence
Uploaded by
Dave Sedigomath
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
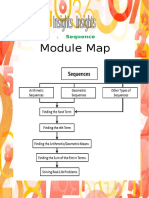
Lesson 1 Arithmetic Sequence
An arithmetic sequence is a sequence where every term after the first is obtained by adding a
constant called the common difference.
A sequence is a set of real numbers that is formed according to a certain logical order.
Lesson 2 Geometric and Other Sequence
A geometric sequence is a sequence where each term after the first is obtained by multiplying
the preceding term by a nonzero constant called the common ratio.
Arithmetic Means terms m 1, m2, ..., mk between two numbers a and b
such that a1, m1, m2, ..., mk , b is an arithmetic sequence.
Common Difference a constant added to each term of an arithmetic
sequence to obtain the next term of the sequence.
Common Ratio a constant multiplied to each term of a geometric sequence to obtain the next
term of the sequence.
Fibonacci Sequence a sequence where its first two terms are either both 1, or 0 and 1; and
each term, thereafter, is obtained by adding the two preceding terms.
Finite Sequence a function whose domain is the finite set {1, 2, 3, ..., n}
Geometric Means terms m 1, m2, ..., mk between two numbers a and b
such that a1, m1, m2, ..., mk , b is a geometric sequence.
Harmonic Sequence a sequence such that the reciprocals of the terms form an arithmetic
sequence.
Infinite Sequence a function whose domain is the infinite set {1, 2, 3, } Sequence (of real
numbers) a function whose domain is the finite set {1, 2, 3, , n} or the infinite set {1, 2, 3, }
Term - any number in a sequence
Degree of a Polynomial - the highest degree of a term in a polynomial
Factor Theorem - the polynomial P(x) has x r as a factor if and only if
P(r) = 0
Mathematical Model - a mathematical representation of some phenomena in real world.
Polynomial - an algebraic expression of the form anxn + a n 1 x n 1 + an 2x n 2 + + a1x + a0,
where an 0, and a0, a1, a2, , an are real numbers.
THEOREMS:
Rational Root Theorem - Let a n 1x n 1 + an 2x n 2 + + a1x + a0 = 0 be a polynomial equation of
degree n. If , in lowest terms, is a rational
root of the equation, then p is a factor of a0 and q is a factor of an.
Remainder Theorem - If the polynomial P(x) is divided by (x r), the
remainder R is a constant and is equal to P(r).
Synthetic Division - a short method of dividing polynomial expressions using only the
coefficient of the terms.
Lesson 1 Division of Polynomials
Lesson 2 The Remainder Theorem and Factor Theorem
Lesson 3 Polynomial Equations
You might also like
- An Introduction to Linear Algebra and TensorsFrom EverandAn Introduction to Linear Algebra and TensorsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- MATH 10 Q1 Summary ReviewerDocument3 pagesMATH 10 Q1 Summary Reviewerangge pagaNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic & Geometric SequenceDocument3 pagesArithmetic & Geometric SequenceprincessaltheacantosNo ratings yet
- MATH SEQUENCES AND POLYNOMIALSDocument2 pagesMATH SEQUENCES AND POLYNOMIALSshiimiineeNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS 10 First Quarter ReviewerDocument6 pagesMATHEMATICS 10 First Quarter ReviewerMaljur fraden Y. DizonNo ratings yet
- Finally: Partial FractionsDocument10 pagesFinally: Partial FractionsPrabodh GuptNo ratings yet
- Sequence and SeriesDocument4 pagesSequence and Seriesdiana jardinanNo ratings yet
- DS Lecture - Sequence and SumsDocument26 pagesDS Lecture - Sequence and SumsTanzeel KhanNo ratings yet
- Sequence and SeriesDocument17 pagesSequence and SeriesLuis DemandanteNo ratings yet
- Equations, Functions, Sequences, and Binomial Theorem ExplainedDocument2 pagesEquations, Functions, Sequences, and Binomial Theorem ExplainedLim Chun KuanNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series: (Barisan Dan Deret)Document3 pagesSequences and Series: (Barisan Dan Deret)Sharon RivaniNo ratings yet
- Math PDFDocument78 pagesMath PDFneil manalo50% (2)
- Math links summarizedDocument16 pagesMath links summarizedMarlo Lao BernasolNo ratings yet
- Antoinettes Math ProjectDocument11 pagesAntoinettes Math ProjectMc Ramil B. PraderoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-Numerical Methods for Solving EquationsDocument20 pagesUnit 3-Numerical Methods for Solving Equationsyeswanth3604No ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics 2Document390 pagesEngineering Mathematics 2narsinh badveNo ratings yet
- Math Reviewer 1Document14 pagesMath Reviewer 1Quintos, Juan Antonio A.No ratings yet
- Sequences of Real NumbersDocument55 pagesSequences of Real NumbersVijay ChhipaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentalsof Theoryof NumbersDocument76 pagesFundamentalsof Theoryof NumbersLaptop of AkashNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Math 10 (Peta 4)Document9 pagesPortfolio in Math 10 (Peta 4)Bryce Pandaan100% (2)
- MathematicsDocument78 pagesMathematicsJohneil Perea Asi100% (2)
- A Problem in Enumerating Extreme PointsDocument9 pagesA Problem in Enumerating Extreme PointsNasrin DorrehNo ratings yet
- Divide and Conquer AlgorithmsDocument11 pagesDivide and Conquer Algorithmsgashaw asmamawNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods c2/10Document3 pagesNumerical Methods c2/10Iustin CristianNo ratings yet
- CHP4 P2Document30 pagesCHP4 P2NUR SYAFIQAH BINTI BAIDROL AZMEE / UPMNo ratings yet
- Math LT#2 1stGP ReviewerDocument15 pagesMath LT#2 1stGP ReviewerCedrick Nicolas ValeraNo ratings yet
- Theory of EquationsDocument38 pagesTheory of EquationsVirat ViratNo ratings yet
- Geometric SequencesDocument8 pagesGeometric Sequenceszendikar21No ratings yet
- Vieta's Formulas and the Identity TheoremDocument5 pagesVieta's Formulas and the Identity TheoremIqbalScribd2014No ratings yet
- Polynomial InterpolationDocument10 pagesPolynomial InterpolationJuwandaNo ratings yet
- Geometric Sequences: ExampleDocument5 pagesGeometric Sequences: ExampleSelva KumarNo ratings yet
- Revision - Elements or Probability: Notation For EventsDocument20 pagesRevision - Elements or Probability: Notation For EventsAnthony Saracasmo GerdesNo ratings yet
- 0001 492-3-103378AnalyticalNumberTheory 21MAT23DB11Document126 pages0001 492-3-103378AnalyticalNumberTheory 21MAT23DB11Ruma MehlaNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations in Two Variables: Quick Reference, STD: X 1Document4 pagesLinear Equations in Two Variables: Quick Reference, STD: X 1Sarbu GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Sequence and SummationDocument35 pagesSequence and SummationHritika RaiNo ratings yet
- T&S BookDocument8 pagesT&S BookFun TimeNo ratings yet
- Algorithms for Recursion and FactorialsDocument15 pagesAlgorithms for Recursion and FactorialsAbdullah MalikNo ratings yet
- L-T-P Theory Marks Sessional Total Credit Test Assig/AttDocument73 pagesL-T-P Theory Marks Sessional Total Credit Test Assig/AttKanchanNo ratings yet
- BUSANA Basics PDFDocument21 pagesBUSANA Basics PDFWu YueyangNo ratings yet
- The Real Number SystemDocument2 pagesThe Real Number SystemMadhur SharmaNo ratings yet
- G of Terms: Vincent John FondalesDocument23 pagesG of Terms: Vincent John FondalesBea Doreen FaicolNo ratings yet
- Sección Europea: I.E.S. Izpisúa BelmonteDocument3 pagesSección Europea: I.E.S. Izpisúa BelmonteinmaillanNo ratings yet
- Factor TheoremDocument7 pagesFactor TheoremWijaya SteenNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Formulas For CE Board ExamDocument19 pagesMathematics Formulas For CE Board ExamAllan Bautista100% (4)
- Removal Grade 10Document18 pagesRemoval Grade 10ROSELYN SANTIAGONo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 ReviewerDocument2 pagesMathematics 10 ReviewerJoshua MartinezNo ratings yet
- grade-10-math-summaryfirst-to-fourth-quarter_compressDocument59 pagesgrade-10-math-summaryfirst-to-fourth-quarter_compressRenz NolloraNo ratings yet
- QM - Session #05 - Logarithm, Progressions, FunctionsDocument25 pagesQM - Session #05 - Logarithm, Progressions, Functionsapi-3741610No ratings yet
- Recursive Definitions and Solving Recurrence Relations (RDSRDocument6 pagesRecursive Definitions and Solving Recurrence Relations (RDSRraghavajayNo ratings yet
- Euclid Stage 3 Class 2 Notes Algebra 2 (Polynomials and FloorDocument7 pagesEuclid Stage 3 Class 2 Notes Algebra 2 (Polynomials and FloorHappy Dolphin100% (1)
- pr1 Soln PDFDocument6 pagespr1 Soln PDFRahulNo ratings yet
- Sequence: Mathematics (Sequence and Series)Document3 pagesSequence: Mathematics (Sequence and Series)SatishNo ratings yet
- 13 1 NotesDocument2 pages13 1 Notesapi-245995785No ratings yet
- Euclid Club 2022: Sequences, Series, Diophantine EquationsDocument7 pagesEuclid Club 2022: Sequences, Series, Diophantine EquationsMarco HappyFeet KurepaNo ratings yet
- Name - Mandeep Class - 1xa Roll No - 17 Topic - Polynomials Given To-Ms - SatinderDocument15 pagesName - Mandeep Class - 1xa Roll No - 17 Topic - Polynomials Given To-Ms - SatinderMandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Exploring Progressions Problems CollectionDocument61 pagesExploring Progressions Problems Collectionwill bNo ratings yet
- Ps1 Solution (VERY IMP)Document6 pagesPs1 Solution (VERY IMP)Omega ManNo ratings yet
- Theory of Equations ExplainedDocument7 pagesTheory of Equations Explained20CESB002 ANANTHA KRISHNAN ANo ratings yet
- End Term Exam: Sukrit Chatterjee - E19ECE039Document6 pagesEnd Term Exam: Sukrit Chatterjee - E19ECE039Sukrit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Sequences (Part 1)Document51 pagesSequences (Part 1)sukanto bagchiNo ratings yet
- Assigned TaskDocument4 pagesAssigned TaskDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Ap Q1 LLSDocument1 pageAp Q1 LLSDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Word Processing Exercise 2Document2 pagesWord Processing Exercise 2Dave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Photoshop IntroDocument37 pagesPhotoshop IntroSara KhanNo ratings yet
- Medecine SchedDocument1 pageMedecine SchedDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Q1, Wk7 (Autosaved)Document30 pagesQ1, Wk7 (Autosaved)Dave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Iñakie Tmled Bstapon Ots Unknown Swangi Dark Balmond Barsiga TmdaddyDocument1 pageIñakie Tmled Bstapon Ots Unknown Swangi Dark Balmond Barsiga TmdaddyDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Report JoyDocument9 pagesReport JoyDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- MEASUREMENTS and CONVERSIONSDocument1 pageMEASUREMENTS and CONVERSIONSDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Parental Consent FormDocument1 pageParental Consent FormDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent Learners Learning Principles 2Document7 pagesChild and Adolescent Learners Learning Principles 2Dave SedigoNo ratings yet
- OBE FrameworkDocument16 pagesOBE FrameworkDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- SW Abcd: Driving A DisplayDocument5 pagesSW Abcd: Driving A DisplayDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- TEAM H PPT Chapter 1 2 3Document8 pagesTEAM H PPT Chapter 1 2 3Dave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science WHLP Week 3 N 4Document2 pagesPhysical Science WHLP Week 3 N 4Dave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Household Record of Inhabitants (Brgy Copy)Document1 pageHousehold Record of Inhabitants (Brgy Copy)Dave SedigoNo ratings yet
- CS Form No. 212 Revised Personal Data Sheet 2Document13 pagesCS Form No. 212 Revised Personal Data Sheet 2ferosiacNo ratings yet
- q1, Wk1, Day 1 - Intro To PhiloDocument17 pagesq1, Wk1, Day 1 - Intro To PhiloDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- ITS 130 Module CompleteDocument67 pagesITS 130 Module CompleteDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- University Calendar For School Year 2020-2021: M T W TH F SDocument2 pagesUniversity Calendar For School Year 2020-2021: M T W TH F SDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Day& Time Learning Areas Physical Science Learning Competency Learning TaskDocument2 pagesDay& Time Learning Areas Physical Science Learning Competency Learning TaskDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Beloved: Kirby LlabanDocument32 pagesBeloved: Kirby LlabanDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Units CalclulationDocument4 pagesUnits CalclulationDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Create in MeDocument30 pagesCreate in MeDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Education Dept Teacher Program SY 2022-2023Document2 pagesPhilippine Education Dept Teacher Program SY 2022-2023Dave SedigoNo ratings yet
- q1, Wk1, Day 4 - Intro To PhiloDocument3 pagesq1, Wk1, Day 4 - Intro To PhiloDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Factoring Difference of Two SquaresDocument15 pagesFactoring Difference of Two SquaresDave Sedigo100% (1)
- More of You: Jay LaquianDocument45 pagesMore of You: Jay LaquianDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Have Your Way: Dexter SubanDocument48 pagesHave Your Way: Dexter SubanDave SedigoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 - P.E PPT (Week 1)Document30 pagesGrade 8 - P.E PPT (Week 1)Dave Sedigo100% (1)