Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11 English Keynotes Section C Grammar 2
Uploaded by
Lalit KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
11 English Keynotes Section C Grammar 2
Uploaded by
Lalit KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE
Class 11 English Core
Section C
Grammar Practice 2
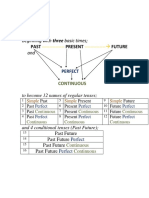
TENSES
Time Structures Uses Examples
VOICE
Active tenses and their passive equivalents
Tense Active Passive
S + V1 + O
Simple S + V2 + O O + to be + V3(pp)
S + shall/will + V1 + O
Continuous/progressive S + to be + V-ing + O O + to be + being + V3(pp)
Perfect S + to have + V3 O + to have + been + v3(pp)
Imperative V + O Let + O + be + V3
V1=base form of the verb V2=past tense of the verb
V3=past participle V-ing=present participle
Form of to be=am, is, are (present); was, were (past); will be/shall be(future)
Form of to have=have, has (present); had (past); will have/shall have (future)
Tense/verb form Active Voice Passive voice
Simple present Writes Is written
Present continuous Is writing Is being written
Simple past Wrote Was written
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 1 / 5
Past continuous was writing Was being written
Present perfect Has written Has been written
Past perfect Had written Had been written
Future Will write Will be written
Conditional Would write Would be written
Perfect conditional Would have written Would have been written
Present infinitive To write To be written
Perfect infinitive To have written To have been written
Present participle/gerund Writing Being written
Perfect participle Having written Having written Having been written
Modals
Meaning Modals Examples
i) Can John swim?
ii) My sister could swim when she was five. (past
ability)
iii) I couldn't’t find my mobile this morning. (past
can, could, be inability)
Ability able to, be iv) He could have run faster, but he didn't’t want to
capable of. overcome Sarang.
v) Rajat has not been able to attend school since the
illness.
vi) Jyoti was able to speak to Ann before she left.
vii) Will students be able to
work their assignments on line one day? (future
ability)
can, could, i) Can I come in?
Permission
may. ii) Students may take the books from library between
1.40 to 3.00. (written)
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 2 / 5
iii May I sit here ? (formal)
i) Can you pass me the salt? (most informal)
can, could, ii) Could you help me to find out the address? (formal)
Requests
will, would iii) Would you please count your change?
iv) Will you get me a glass of water, John?
i) All tourists must produce their I-cards whenever it is
required.
have (got) to, ii) The boss must get that report finished.
Obligation
must. iii) Do you have to write your date of birth on the
form?
iv) They had to come on the time.
i)I could have lend you the money, why didn't’t you
ask me ? (past ability)
could, can, ii) Raju may not be at home.
Possibility
may, might. iii) I may have/might have left my mobile in the office.
iv) You can ski on the hills.
v) He could be very unreasonable.
Teacher to pupil : (speaker’s authority) You must
ought to, practise at least two hours a day. Pupil to his friend:
Advice/Obligation should, have (external authority) I have to practise two hours a day.
to, must. His friend to pupil: (subject’s obligation or duty) You
ought to should practice for more than two hours.
i) You mustn't’t inform him anything.
ii) John can’t work until you’re better.
must not, may iii) Reference books may not be taken out of the
Prohibition
not, cannot. library. (written)
iv) Candidates must not begin writing until the bell
rings. (formal)
i) You don’t have to help me I can do my work.
Don’t have to, ii) They didn't’t have to sell their flat.
shouldn't have, iii) You shouldn't’t have bothered cooking. They would
No necessity
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 3 / 5
didn't need to, have bought a meal from hotel.
needn't have. iv) He didn't’t need to learn the poem by heart.
v) Passengers needn't’t have got down earlier.
• That must be Kamala She often comes on the time.
Assumptions & Will, should, • This book should be interesting.
deductions must, can’t • There must be a drawback in the planning.
• It will be an urgent call.
You can’t have finished already!
Offers & • Shall I do the typing?
Shall, will
suggestions • Shall we start now?
I’ll drop you at the station.
Rearranging the words for a meaningful sentence.
Following things will help you to from the meaningful sentence.
A sentence consists of a subject and a predicate.
A Sentence has some important elements – subject, verb, object, complement and adverbial.
Kinds of sentences & their structures
A. Based on meaning:
i. Assertive /statement:
I write a letter. S+v+o /c+.
ii. Interrogative /Question:
Do you complete your work?
Where have they been living for a decade?
(Helping verb +S+V+O+?)
(Wh word +h.V.+S+V+O+?)
iii. Exclamatory –
How wonderful it is!
What a great king Ashoka was!
(How + adj./adv. + S+V+!)
(What + det + adj/adv + S+V+!)
iv. Imperative -
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 4 / 5
Open the door
V+O/A
B. Based on the structure:
1. Simple = consists of only one predicate
I am living in New Delhi.
2. Complex = consists of one main clause and sub-ordinate clause/s.
e.g. If I come to you, I will give a book to you.
3. Compound = consist of two or more than two clauses of equal importance.
e.g. We came in first but we did not win the race.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 5 / 5
You might also like
- 11 English Core Impqsection C Grammar 02 NewDocument20 pages11 English Core Impqsection C Grammar 02 NewSaddy ButtNo ratings yet
- Teacher: Josué Fuentes Blanco: English Iii 2 Partial "What Abilities Do You Have?"Document30 pagesTeacher: Josué Fuentes Blanco: English Iii 2 Partial "What Abilities Do You Have?"jospatdarjosNo ratings yet
- Activity English II - Week 5Document5 pagesActivity English II - Week 5Lina Fernanda MesaNo ratings yet
- Week 4-The Noun ClauseDocument16 pagesWeek 4-The Noun ClauseNaufal Nur HilmyNo ratings yet
- Tenses: I. Present 1. Simple Present TenseDocument9 pagesTenses: I. Present 1. Simple Present Tensemichael100% (5)
- ENGLISH GRAMMAR 5 (Lengkap 15 11 15)Document65 pagesENGLISH GRAMMAR 5 (Lengkap 15 11 15)j chanNo ratings yet
- Tenses of EnglishDocument3 pagesTenses of Englishmuhammad mustanginNo ratings yet
- Course Guide Grammar Time of Work: Laura Valentina González Acosta 40 201812864 July 11ThDocument9 pagesCourse Guide Grammar Time of Work: Laura Valentina González Acosta 40 201812864 July 11ThLaura Gonzalez20No ratings yet
- Modals ÖzetDocument21 pagesModals ÖzetmehmetNo ratings yet
- I.Guia Didáctica 4° Año - Verb Tenses (Goal)Document5 pagesI.Guia Didáctica 4° Año - Verb Tenses (Goal)Manuel Alejandro Gutierrez NuñezNo ratings yet
- Tenses Review TDocument5 pagesTenses Review T2dcdm684pxNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Revision X ENGLISHDocument25 pagesLast Minute Revision X ENGLISHstalinbthomas20No ratings yet
- EnglishGrammar Class 8 PDFDocument148 pagesEnglishGrammar Class 8 PDFShinta Nurlaili100% (2)
- CBSE Class 10 English TensesDocument28 pagesCBSE Class 10 English TensesasNo ratings yet
- Guide Modal Verbs BORRADORDocument6 pagesGuide Modal Verbs BORRADORLINDA KATHERINE MENDEZ GARCESNo ratings yet
- Lampiran RPP TersusunDocument14 pagesLampiran RPP TersusunMasri Manas100% (2)
- Iworkasa I'm A in My Freetime, I Love My Hobby IsDocument40 pagesIworkasa I'm A in My Freetime, I Love My Hobby IsDuc NGOAnhNo ratings yet
- Verb (Kata Kerja) : 10 February 2021Document12 pagesVerb (Kata Kerja) : 10 February 2021salsabilla tamaraNo ratings yet
- General Review Interchange 2 Units 1 To 4Document18 pagesGeneral Review Interchange 2 Units 1 To 4anibal ariasNo ratings yet
- SpokenEnglish Sec2 Lesson19Document7 pagesSpokenEnglish Sec2 Lesson19Guindo AmadouNo ratings yet
- Grammar 2 (Forms of Verbs, Passive Voice)Document22 pagesGrammar 2 (Forms of Verbs, Passive Voice)M Dwi RafkyNo ratings yet
- Activity English II - Week 5Document6 pagesActivity English II - Week 5luisa acevedoNo ratings yet
- Are You Satisfied With The Way You Have Learnt English ? (Yes/No)Document5 pagesAre You Satisfied With The Way You Have Learnt English ? (Yes/No)RamprabhuNo ratings yet
- 272761Document26 pages272761dbznfgscb5No ratings yet
- Indirect ExcerciseDocument4 pagesIndirect ExcerciseMustika Ratna SabatiniNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Future Modality HandoutDocument4 pagesWeek 7 Future Modality HandouttomNo ratings yet
- English - VERBDocument15 pagesEnglish - VERBsmalldust96No ratings yet
- RQB Grade 6 PT1Document7 pagesRQB Grade 6 PT1Deepika's KitchenNo ratings yet
- KLS8 - Sem1 - PPT3 - Ability and WillingnessDocument42 pagesKLS8 - Sem1 - PPT3 - Ability and WillingnessNadia ListyantariNo ratings yet
- Grammar Fs I So Part 2Document9 pagesGrammar Fs I So Part 2Asija ŠahinovićNo ratings yet
- Dr. Fe M. Tangalin Dmmmsu-Sluc Agoo, La UnionDocument55 pagesDr. Fe M. Tangalin Dmmmsu-Sluc Agoo, La UnionJen Mamuyac-CastilloNo ratings yet
- The VerbDocument21 pagesThe VerbAbdus SamadNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: States of Verb, Verb To Be' and Its 12 Tenses: Infinitive Base Present Past Past ParticipleDocument6 pagesLesson 1: States of Verb, Verb To Be' and Its 12 Tenses: Infinitive Base Present Past Past ParticipleLaiba AarzooNo ratings yet
- Recursa Inglés IIIDocument12 pagesRecursa Inglés IIILalaNo ratings yet
- MODALS STD 10thDocument13 pagesMODALS STD 10th24 -Aditya Nair - 10 ANo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Verb PPT 1Document15 pagesBahasa Inggris Verb PPT 1Thariq ZataNo ratings yet
- Habitual Actions Now, Past Actions, Tomorrow Structure: Affirmative (Svo), Negative (Not), Interrogative (?)Document3 pagesHabitual Actions Now, Past Actions, Tomorrow Structure: Affirmative (Svo), Negative (Not), Interrogative (?)Fatiha JlilNo ratings yet
- Tense System 22.11Document8 pagesTense System 22.11Waff LeraNo ratings yet
- Passive by MeDocument8 pagesPassive by Mehaticeozkan5778No ratings yet
- The Passive VoiceDocument1 pageThe Passive VoiceLaliNo ratings yet
- Udgam School For Children Subject: English Topic: Auxiliary Verb Worksheet: 2 (ANSWER KEY) Name: - Class: VII Sec: - Roll No: - DateDocument14 pagesUdgam School For Children Subject: English Topic: Auxiliary Verb Worksheet: 2 (ANSWER KEY) Name: - Class: VII Sec: - Roll No: - DateYASHVI MODI0% (1)
- Set PresDocument18 pagesSet PresauroracamstraNo ratings yet
- Level1 English Online-1 PDFDocument13 pagesLevel1 English Online-1 PDFInas Nadaa0% (1)
- Adults II Tenses Review and ExercisesDocument3 pagesAdults II Tenses Review and ExercisesGer SanzNo ratings yet
- Udgam School For Children: Page 1 of 2 Class-VII / Subject - English / WorksheetDocument2 pagesUdgam School For Children: Page 1 of 2 Class-VII / Subject - English / WorksheetYASHVI MODINo ratings yet
- Questions: A. Yes/No QuestionDocument7 pagesQuestions: A. Yes/No Questiondanny ferdito gustiawanNo ratings yet
- Subject and VerbDocument13 pagesSubject and VerbNawan Tabah PangestuNo ratings yet
- Времена английского языкаDocument4 pagesВремена английского языкаI. N.No ratings yet
- WiderWorld2e 4 GrammarPresentation 8.2Document6 pagesWiderWorld2e 4 GrammarPresentation 8.2cooleugene64No ratings yet
- English GrammerDocument12 pagesEnglish GrammerSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Rumus TensesDocument5 pagesRumus TensesNonny Tentia MNo ratings yet
- Passive - Voice X 2024 Page 49Document9 pagesPassive - Voice X 2024 Page 49Felix LidanNo ratings yet
- Int Iv Unit Iii PDFDocument31 pagesInt Iv Unit Iii PDFMed Ali ElmailNo ratings yet
- Modern Chinese (BOOK 2) – Learn Chinese in a Simple and Successful Way – Series BOOK 1, 2, 3, 4From EverandModern Chinese (BOOK 2) – Learn Chinese in a Simple and Successful Way – Series BOOK 1, 2, 3, 4Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Tiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3From EverandTiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3No ratings yet
- Understanding the Concepts of English PrepositionsFrom EverandUnderstanding the Concepts of English PrepositionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How To Make A Detailed OutlineDocument8 pagesHow To Make A Detailed OutlineIvan Clark PalabaoNo ratings yet
- Parent Leaflet Child Death Review v2Document24 pagesParent Leaflet Child Death Review v2InJailOutSoonNo ratings yet
- PNB V DalmacioDocument6 pagesPNB V DalmacioRuss TuazonNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PDFDocument5 pagesUnit 1 PDFaadhithiyan nsNo ratings yet
- Translation UasDocument5 pagesTranslation UasHendrik 023No ratings yet
- History Esssay LayoutDocument2 pagesHistory Esssay LayoutArturo Daniel Laborde CortezNo ratings yet
- Grand Boulevard Hotel Vs Genuine Labor OrganizationDocument2 pagesGrand Boulevard Hotel Vs Genuine Labor OrganizationCuddlyNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgment, Dedication, Curriculum Vitae - Lanie B. BatoyDocument3 pagesAcknowledgment, Dedication, Curriculum Vitae - Lanie B. BatoyLanie BatoyNo ratings yet
- House Tax Assessment Details PDFDocument1 pageHouse Tax Assessment Details PDFSatyaNo ratings yet
- Roselie Ann A. de Guzman Bsihm3A Centro Escolar University - (Makati)Document14 pagesRoselie Ann A. de Guzman Bsihm3A Centro Escolar University - (Makati)Cristopher Rico DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Final Technical Documentation: Customer: Belize Sugar Industries Limited BelizeDocument9 pagesFinal Technical Documentation: Customer: Belize Sugar Industries Limited BelizeBruno SamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basic-Concepts-Of-EconomicsDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Basic-Concepts-Of-EconomicsNAZMULNo ratings yet
- SIP Annex 5 - Planning WorksheetDocument2 pagesSIP Annex 5 - Planning WorksheetGem Lam SenNo ratings yet
- Ppg-Gdch-Nur-45 Crash Cart Maintenance and ChecksDocument5 pagesPpg-Gdch-Nur-45 Crash Cart Maintenance and ChecksKenny JosefNo ratings yet
- CLOUDDocument2 pagesCLOUDSawan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Starting Your BusinessDocument8 pagesModule 4 - Starting Your BusinessJHERICA SURELLNo ratings yet
- Statutory and Regulatory BodyDocument4 pagesStatutory and Regulatory BodyIzzah Nadhirah ZulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Returns To Scale in Beer and Wine: A P P L I C A T I O N 6 - 4Document1 pageReturns To Scale in Beer and Wine: A P P L I C A T I O N 6 - 4PaulaNo ratings yet
- My Portfolio: Marie Antonette S. NicdaoDocument10 pagesMy Portfolio: Marie Antonette S. NicdaoLexelyn Pagara RivaNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv - Lesson 1Document2 pagesUnit Iv - Lesson 1SHIERA MAE AGUSTINNo ratings yet
- Basic Fortigate Firewall Configuration: Content at A GlanceDocument17 pagesBasic Fortigate Firewall Configuration: Content at A GlanceDenisa PriftiNo ratings yet
- Bible Trivia Questions - Bible Challenges For KidsDocument4 pagesBible Trivia Questions - Bible Challenges For KidsVinessa Johnson100% (1)
- Test Bank: Corporate RestructuringDocument3 pagesTest Bank: Corporate RestructuringYoukayzeeNo ratings yet
- Data Warga RT 02 PDFDocument255 pagesData Warga RT 02 PDFeddy suhaediNo ratings yet
- Conflict Resolution in ChinaDocument26 pagesConflict Resolution in ChinaAurora Dekoninck-MilitaruNo ratings yet
- A Melody of Life: Espiritu Santo Parochial School of Manila, Inc. 1913 Rizal Avenue, Sta. Cruz, ManilaDocument4 pagesA Melody of Life: Espiritu Santo Parochial School of Manila, Inc. 1913 Rizal Avenue, Sta. Cruz, ManilaIrene Carmela Empress ParkNo ratings yet
- Document 2 - Wet LeasesDocument14 pagesDocument 2 - Wet LeasesDimakatsoNo ratings yet
- Swami VivekanandaDocument20 pagesSwami VivekanandaRitusharma75No ratings yet
- Edu 414-1Document30 pagesEdu 414-1ibrahim talhaNo ratings yet
- Modern Dispatch - Cyberpunk Adventure GeneratorDocument6 pagesModern Dispatch - Cyberpunk Adventure Generatorkarnoparno2No ratings yet